Water Ecology Test
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
What are the main parts of the “ice year”?
Freeze up, Main Winter, and Ice Break-Up
What are the main types of river ice?
Frazil ice and Anchor Ice (Dynamic) & Border Ice and Sorface Ice (Static)
What are the main physical effects of river ice on habitat conditions?
Velocity decrease makes middle faster (Ice friction), habitat alteration Light reduction, Dissolved oxygen dynamics, sediment transport and scour.
What ecological effects does river ice have?
Invertebrates: some bugs have cold hardiness and purposely freeze to avoid predators, species specific responses, increased drift during dynamic ice events
Fish: (EGG INCUBATION ice scour and freezing can damage eggs, anchor ice over eggs can reduce oxygen for eggs and they have to get it from ground instead) & (DISTRIBUTION small fish hide in substrates, large fish go to deeper pools, some use ice for cover) (VEGETATION ice scouring and sediment movement change aquatic and riparian plant communities)
What is the concept of stream orders and zonation?
Stream Orders: A hierarchical classification of streams (1st order = headwater streams, Higher orders = formed when lowers order streams merge) as order increases, channel size, discharge, and sediment load increase and gradient generally decreases.
Zonation: Different zones in a drainage basin (Erosion, Transportation, Deposition)
Name some important Canadian rivers, and where does their water flow?
Mackenzie River - Arctic Ocean
St. Lawrence River - Atlantic Ocean
Fraser River - Pacific Ocean
What is the water cycle, and what parts does it have?
the continuous movement of water between the atmosphere, land, and oceans.
Evaporation and Transpiration - water from land water into atmosphere
Condensation - water vapor forms clouds
Precipitation - rain or snow returns to surface
Infiltration and Percolation - water into the ground
Runoff - water flows into rivers and lakes, completing the cycle
What is a river, catchment vs. watershed, and basin?
River - naturally flowing body of water with a current from source to mouth through a gradient
Catchment: The land area where all precipitation drains to a common outlet.
Watershed: Often used interchangeably with catchment; the boundary dividing different catchments.
Basin: A larger-scale area encompassing one or more watersheds that drain into a common outlet (e.g., Hudson Bay Basin). Open area where water collects
What are the 3 dimensions of a river channel?
Lateral – River’s connection with its floodplain and banks
Longitudinal – Flow direction from headwaters to mouth.
Vertical (hyporheic) – Interaction between surface water and groundwater.
Understand the concept of habitat and different scales of habitat
Habitat - The place where a species lives, defined by physical and biological characteristics
Macrohabitat – Large-scale, e.g., entire catchment
Mesohabitat – Visually distinct features like pools, riffles, runs; link species to habitat type.
Microhabitat – Small-scale site measurements (e.g., juvenile fish habitat preferences).
What is a hydrograph and what factors affect it?
Hydrograph - A graph showing river discharge (flow) over time (instantaneous, annual, or multi-year).
Factors
Local climate and season (snowmelt, rainfall).
Catchment topography and geology.
Land use (urbanization, deforestation).
Lakes or wetlands (flow storage or delay).
Human impacts (water withdrawal, dams, regulation).
What is hydropeaking?
Hydropeaking refers to rapid, artificial fluctuations in river discharge caused by hydropower generation, where turbines are turned on/off to meet electricity demand. changing it can mess with the species used to a specific discharge for that time of year
What is the concept of environmental flows?
Environmental flows - “How much water does a river need” describe the quantity, timing, and quality of water flows required to sustain ecosystems and human needs that depend on them. (Summer is the zone of highest risk)
What is substrate, benthos, and biofilm/periphyton?
Be able to explain the difference between the three
Substrate - Underlying layer of organic material, minerals/stone that is on the bottom of a water body.
Benthos - community of organisms that live on or near the bottom of a body of water
Biofilm/Periphyton - community of fungi, bacteria, and algae that reside in a polysaccharide matrix on substrate and act as a food source to many organisms
What are benthic macroinvertebrates (BMIs)?
Be able to name common BMI groups in freshwater
small, aquatic animals and the aquatic larval stages of insects.
Some common groups - sponges, molluscs, worms, shrimp, and insects
What are EPTs?
For these, you must be able to name the scientific name of each Order (E, P, T), and the common name of their order
Ephemeroptera - Mayflies
Plecoptera - Stoneflies
Trichoptera - Caddisflies
What common adaptations do BMI have to life in moving water
flattening/streamlining of the body
hooks and grapples
filtering structures

Which of the EPT is this?
Ephemeroptera - Mayflies

which of the EPT is this?
Plecoptera - Stoneflies
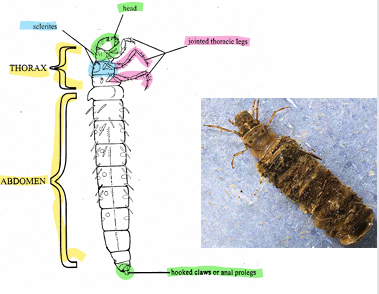
Which of the EPT is this?
Trichoptera - Caddisflies
What habitats might you find BMI?
swift currents
hyporheic zones
slow moving habitat
water surfaces
What is drift, different categories, and what causes drifting?
Drift is the downstream transport of organisms in the water column via active or passive entry.
Categories
Constant drift: Accidental dislodgement of organisms
Catastrophic drift: Caused by environmental disturbances such as floods, droughts, or pollutants.
Behavioural drift: Intentional movement of animals into the water column
Causes
proximal triggers like light (movement at night)
reduced food availability
high density could promote drift (excess production upstream)
Why are BMI’s important?
Indicators of stream/river processes (functional feeding processes)
Indicators of water quality (pollution tolerance, integrate short and long term conditions, relative sedentary)
Important food source for fish
Tracer of historic conditions (they have narrow temperature regimes, so their presence in the sediment can tell you something)
What are functional feeding groups?
Classification of how the BMI feeds (doesn’t mean they are the same type of BMI among said feeding groups)
shredders - feed on course organic matter (leaves) (ex. stonefly)
collectors - Feed on fine organic matter through filtration or gathering (ex. blackfies)
scrapers - Feed of the periphyton (algae) (ex. caddisfly)
predators - carnivores that feed on other invertebrates (ex. dragonflies)
What and how can BMI’s tell about the environment?
Water quality - BMI have different tolerances for water quality, so presence of a certain type could either be a good or bad indicators (you want lots of EPT’s)
Stream/River processes - particularly through feeding types can show nutrient cycling and energy flow in streams
Long term and Short term changes - you can infer environmental conditions due to the BMI’s relative sedentary nature.
What is CABIN, and why is that approach useful?
CABIN (Canadian Aquatic Biomonitoring Network) is a national standard program for assessing aquatic ecosystem health. It uses BMI samples and uses the Reference Condition Approach (RCA) to determine whether a site is “normal” or “impaired.” (EVERYTHING IS COLLECTED THE SAME)
Useful because…
lots of sites
consistent methods
cost efficient
normal vs. impaired assessment
What is a fish?
All are craniates
Most…
live in water
have paired fins
are vertebrates
ectotherms
have gills and jaws
Why study fish?
Indicator of environment
Human nutrition
Economy
Medical research
Tox tests (ex. LD 50)
General importance in ecosystems
Understand diversity of fish and their habitats and basic life history strategies in fish
~35,000 species of fish, if there is water and oxygen, fish will likely be there (11km below sea level or kms above sea level in mountains etc)
Life history strategies :
fast vs. slow water strategies
schooling vs. hierarchical vs. solitary
diurnal vs. nocturnal
migratory vs. resident
site fidelity
Describe what is diadromy (anadromy / catadromy) and give examples of species on both categories, including their life-history stages? (ON TEST FOR SURE)
Diadromy is when a fish spends part of its life in saltwater and part in fresh water
Anadromous fish - born in freshwater, reach adulthood at sea
Catadromous fish - born in ocean, reach adulthood in freshwater
Name examples of common fishes, their characteristics, habitats, population status in temperate parts of North America?
Salmonoids - Anadromous life history, adipose fin, important culturally (Atlantic salmon)
Brook trout - prefers cool water w/ o2, slower water, anadromy
Minnows - 12 NB species, warmwater, small bodied, variety of habitats and habits
Sticklebacks - littoral species (area close to shore in pond or lakes where light reaches the bottom), small bodied, 5 species in NB, abundant/common
Name common invasive fish species in NB
Rainbow trout
Small and Large mouth bass
Chain pickerel
What is the potential issue with invasions
They could displace the native fish by competition, they are almost impossible to remove, social acceptance/rejection (“come back” of predators)
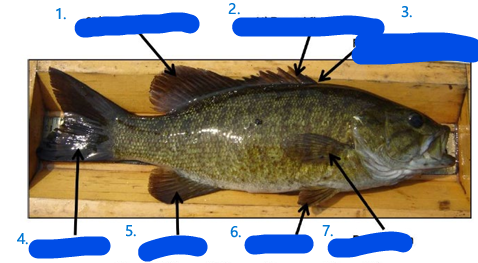
Label
2nd dorsal fin
1st dorsal fin (spiky)
fin insertion or origin
caudal fin
anal fin
pelvic fin
pectoral fin

Label
caudal fin
adipose fin
dorsal fin
anal fin
pelvic fin
pectoral fin
What is the role and sources of carbon in rivers?
Provides energy to lotic ecosystems
Sources : Autochtonous inputs (Algae) and Allochtonous inputs (Woody debris/leaves)
What is autochtonous production?
Organic matter produced in the stream
ex. Algae (Perifyton Slimy stuffwith algae, bacteria, fungi etc.. in saccharide matrix*), Macrophytes (Mosses) *Rivers, and Phytoplankton *Lakes and Large Rivers
What is allochtonous production?
Organic Matter produced outside of the stream
ex. Forests, fruits, animal carcasses, sewage and agricultural inputs
Describe forms of organic matter?
(DOM, FPOM, CPOM)
DOM - Fragments so small it is dissolved in to the water (<0.5µm)
FPOM - fragments are very fine, but are actual particles/clumps (<1mm and >5 µm)
CPOM - fragments are just larger that the FPOM (>1mm)
What does autotrophy and heterotrophy mean?
autotrophy - more independent because there is high carbon production, and slower moving dependance of the organic material
ex. Larger Rivers
heterotrophy - dependance on the organic material
ex. Small Headwater
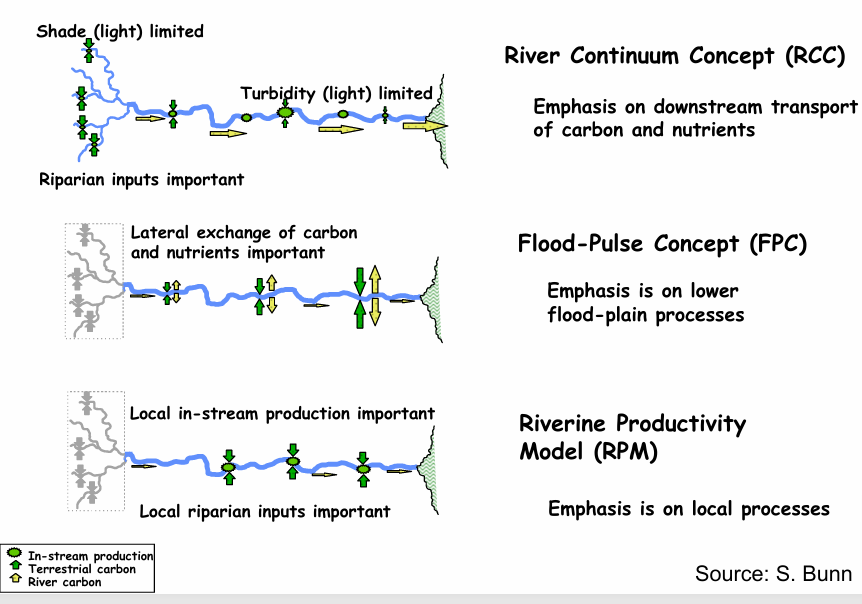
What is River Continuum Concept (RCC)?
A key concept on “how rivers work” by using a predictable continuum (Applicable to the temperate system)
Key Ideas
Physical Envm. - Solar input, temperature, and discharge varies
Biological Envm - Allochtonous inputs dominate upstream, Autochtonous inputs dominate downstream, functional feeding group vary
CRITICISMS - TEMPERATE STREAM BIAS, APPLICABLE TO PRISTINE STREAMS ONLY, PATTERN OF TEMPERATURE CHANGE
Name and describe other river ecosystem productivity models? How do they differ form RCC
Riverine Productivity Model (RPM) - Emphasis on the local processes (Higher P/R ratio on the banks where the light penetration is higher) *Localized little bathtub rings
Flood-Pulse Concept (FPC) - Emphasis on lower flood-plain processes (Pulses are natural predictable disturbances to which biota are adapted, and not having this hydrologic regimen is the real disturbance) *Latitudinal connectivity
Is the ecosystem efficiency in headwater streams high or low?
Generally Low, most ends up sent to the ocean unprocessed. (its like tossing 50% of your cash away)
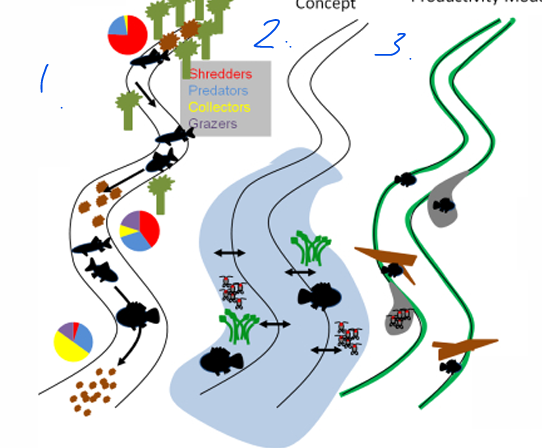
River continuum concept
Flood pulse concept
Riverine productivity Model
What are Marine Derived Nutrients?
nutrients and organic materials brought from the ocean into freshwater ecosystems by anadromous fish
• Lakes (potamodromous fish; e.g. whitefish)
• Oceans (anadromous fish; e.g. salmon, river herring)
What benefits to different ecosystem components (biofilm, animals, forests) MDN’s have?
MDN’s can provide a boost to N supply for those plants that need it
They provide nitrogen boosts to the forests
Biofilm enrichment boosts grazing insect populations (BMI)
higher biofilm abundance and different community composition
Many species (trout, char, sculpins, insects) consume salmon eggs.
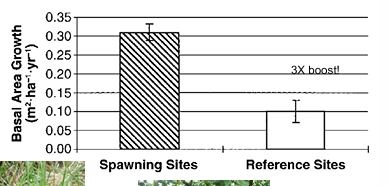
Evidence of MDN’s in West Coast?
Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis) – 24% of foliar N from salmon (Grew marginally better in spawning areas.
Alders dont really care to use the salmon N because they can fix their own nitrogen
Evidence of MDN’s in East Coast?
East Coast fish are mostly iteroparous, so nutrient inputs are smaller but still measurable.
Biofilm data shows more algae (and other components) downstream of barriers when anadromous fish are present.
Stable isotope patterns in the food web show clear incorporation of marine nitrogen.
How do MDN’s affect river ecosystem in East Coast?
MDNs boost productivity in nutrient-poor streams.
Downstream ecosystems near spawning sites have:
More biofilm
Higher nitrogen signatures in consumers
Higher trophic enrichment through the food web
MDN-supported fish (like brook trout) grow larger and maintain stronger populations.
Loss of anadromous fish reduces productivity and ecosystem health.
What is the riparian zone?
The riparian zone is the three-dimensional zone of direct interaction between terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems located along river and stream banks.
It mediates the transfer of energy and materials between land and water and is a biodiversity hotspot
Explain 5 ways streams and forests are interlinked.
1. Energy flows, CPOM, FPOM - Headwater streams are heterotrophic, and up to 98% of the OM in some streams comes from the forest
2. Effects on microclimate - light availability affects algal primary production, stream temperature is effects (influencing metabolism, o2 and growth)
3. Effects of forests on channel morphology - Bank Stability such as Roots provide stability and erosion resistance, While LWD Can provide habitat, and causes changes in flow and changes in vertical and lateral channel shape,
4. Filtering of sediments & nutrients at riparian zone - traps sediment from land overflow, slows water velocity to allow for nutrient assimilation, nitrogen removed through plant uptake
5. Provision of food and cover - provides cover from predators and shelter from flow, supplies terrestrial invertebrates to the fish (can make up 44% of their annual energy budget), important in the the summer especially
Is riparian zone and buffer zone the same?
No they are not
What is different between the two concepts?
Riparian Zone - Varies in time and space
Buffer Zone - typically a fixed width (Definition for fun: relatively intact riparian vegetation in otherwise altered watershed and often a legal requirement in many jurisdictions)
What are buffer zone rules in New Brunswick?
If you want to do forestry activity within 30 meters of a watercourse, you need a WaWA permit
VV Stuff that’s allowed VV
Selective harvest
only 30% of merchantable species
manual harvest within 15m of zone
some may even use the machine to reach into the 15 meter zone
cutting of non marketable vegetation
nothing more than 6m long
pre-commercial thinning
Why are fixed-width buffers so common?
Because until 50’s/60’s when buffers weren’t used negative effects were being seen (ex. fish population drop) so this was a easy way to provide some sort of protection
fixed buffers became standard because buffer width projects surrounding fixed buffers achieve some environmental objectives
What are common factors being considered when determining buffers?
Waterbody type
Slope
Waterbody Size
Fishbearing
Drinking water/aesthetics
Is there a better way of thinking about buffers zones than same fixed width everywhere?
How are hydrological response areas and hydrological units related to this discussion?
New thinking suggests that buffers should be based on hydrological response areas (HRA’s and hydrological units (HU’s). Some are sensitive and need a large buffer while some are resilient do not require a large buffer
they help determine how water moves in a landscape. and understanding them allows managers to design zones and harvest areas specific to them.
replaces the “one fixed width everywhere” to tailored and evidence based buffer sizes. (More complicated guidlines and more “Catchment planning” of riparian areas)
List some potential main effects that forestry activities impose on stream ecosystems?
Loss of stream connectivity
changes to sediment dynamics
degraded water quality
changes in water temperature
How can connectivity of aquatic ecosystems be affected by forestry, and how can it be mitigated?
Logging roads require stream crossings and improperly installed culverts.
Mitigation: Bridges or open bottom culverts when installed properly. Keep beavers away from culverts too!
How can sedimentation of aquatic ecosystems be affected by forestry, and how can it be mitigated?
Logging roads (Major sediment deposit)
Soil disturbance via machinery and rutting
MITIGATION - Using coarse gravel when making roads, and stabilizing the road edges (straw), and use silt fences to trap sediment
Name some direct and indirect effects if sedimentation?
DIRECT - Disruption of fish spawning, interference with visual cues/selection of mates, smothering of eggs and fish, turbidity messes with migration
INDIRECT - loss of habitat, reduced EPT, loss of cover
What are pesticides and why are they used in forestry? (herbicide & insecticide) effects
Herbicide - Controls unwanted plant life
Insecticide - Controls unwanted insects
Why? so that we can control species that are damaging resources/other species.
What is glyphosate, and why is it used?
A widely used herbicide, used to reduce competition from shrubs and undesired hardwoods via a EPSPS enzyme that prevent amino acid synthesis in plants.