anatomy final
1/571
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
572 Terms
brachial plexus acronym
real teataps drink cold beer
synarthrosis joints
no movement within the joint
sutures
synarthrosis. joints found only in skull. bones interlocked through sutural ligaments
synchonodrosis
synarthrosis. cartilaginous joint connecting two bones via hyaline cartilage
amphiarthrosis
slight movement within the joint
syndesmosis
amphiarthroses. ligaments that connect two bones but limit their motion. ex: interosseous membrane between ulan and radius
diarthroses
synovial joint. freely moving
characteristics of synovial joints
joint capsule, articular cartilages, synovial fluid, synovial membrane, accessory structures (cartilage, ligaments, tendons, bursa), sensory nerves and blood vessels
humero-ulnar joint
trochlea and trochlear notch
humeroradial joint
articulation between the humerus and the radius. capitulum and radial head
ulnar collateral ligament
connects the medial epicondyle of the humerus to the ulna
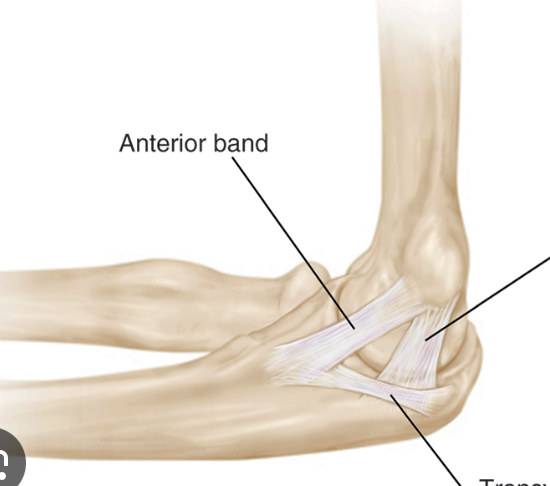
radial collateral ligament
connects the lateral epicondyle of the humerus to the radius
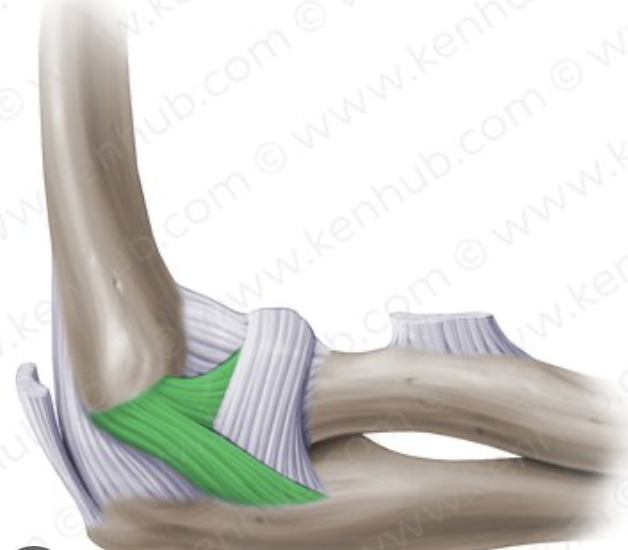
annular ligament
wraps around the radius to secure in place with the ulna
glenohumeral ligament
connects the glenoid cavity and the humerus
coracoclavicular ligament
connects the coracoid process to the clavicle
coraco-acromial ligament
connects the coracoid and acromion processes
subacromial bursa
located below the acromion. provides cushion for joint
sub deltoid bursa
located below the deltoid muscle. provides cushioning
carpometacarpal joint
intercarpal joint
connects one carpal bone to another
radoiocarpal joint
connects radius to proximal carpals
anterior and posterior retinaculum
wraps around the tendons
ulnar collateral ligament (wrist)
radial collateral ligament (wrist)
pivot
rotational motion, monomial, ex: proximal radio-ulnar joint
hinge
angular motion, monomial, ex: elbow
saddle
angular motion, biaxial, ex: first carpometacarpal joint
condylar
angular motion, biaxial, ex: metacarpophalangeal joints 2-5
plane/sliding
slight linear motion, monomial, ex: sternoclavicular joint
ball and socket
angular motion/circumduction/rotation, triaxial, ex: shoulder joint
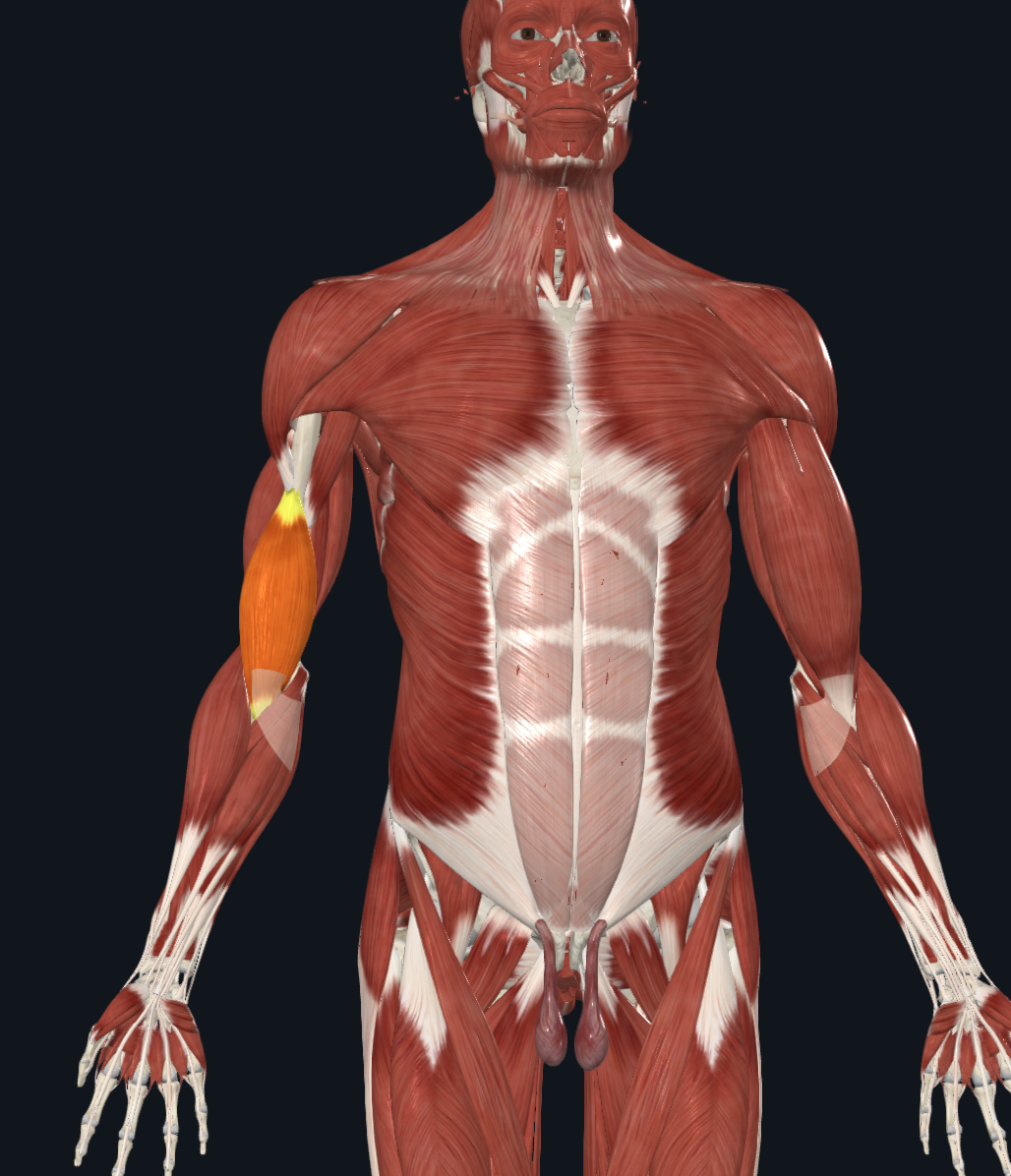
brachialis
extensor carpi radialis longus
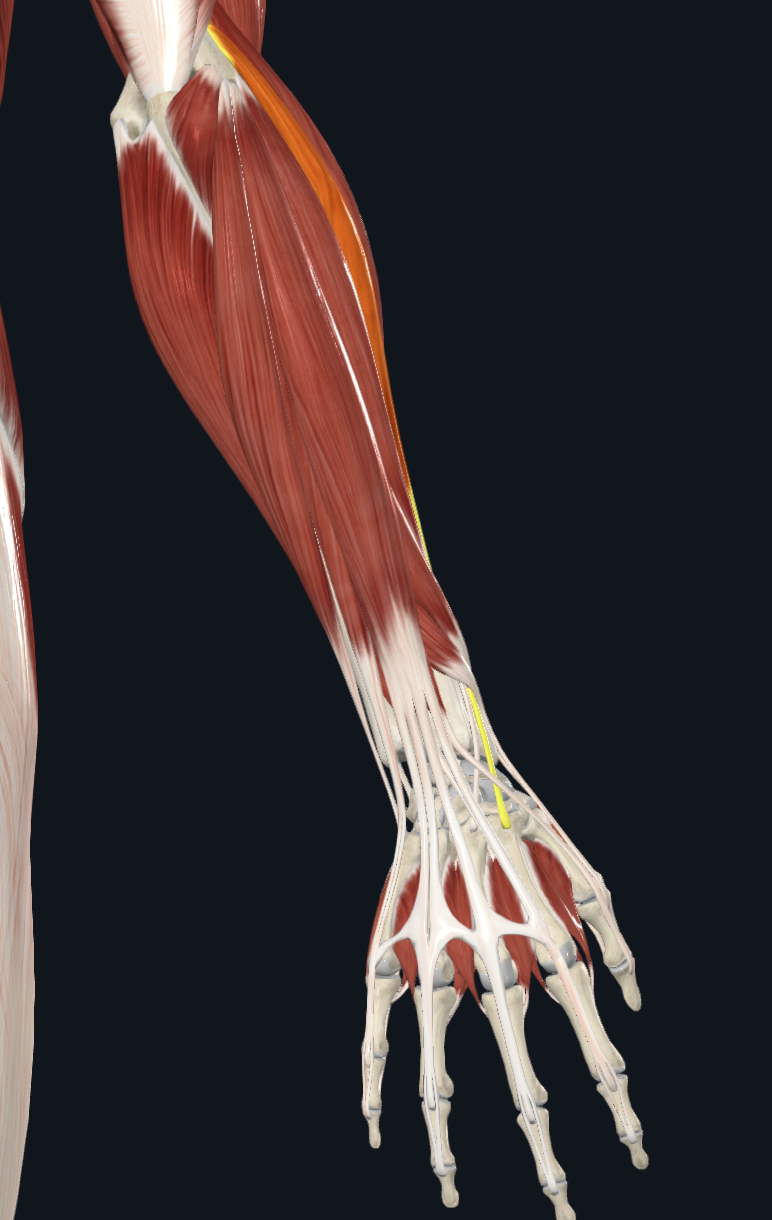
extensor carpi radialis brevis
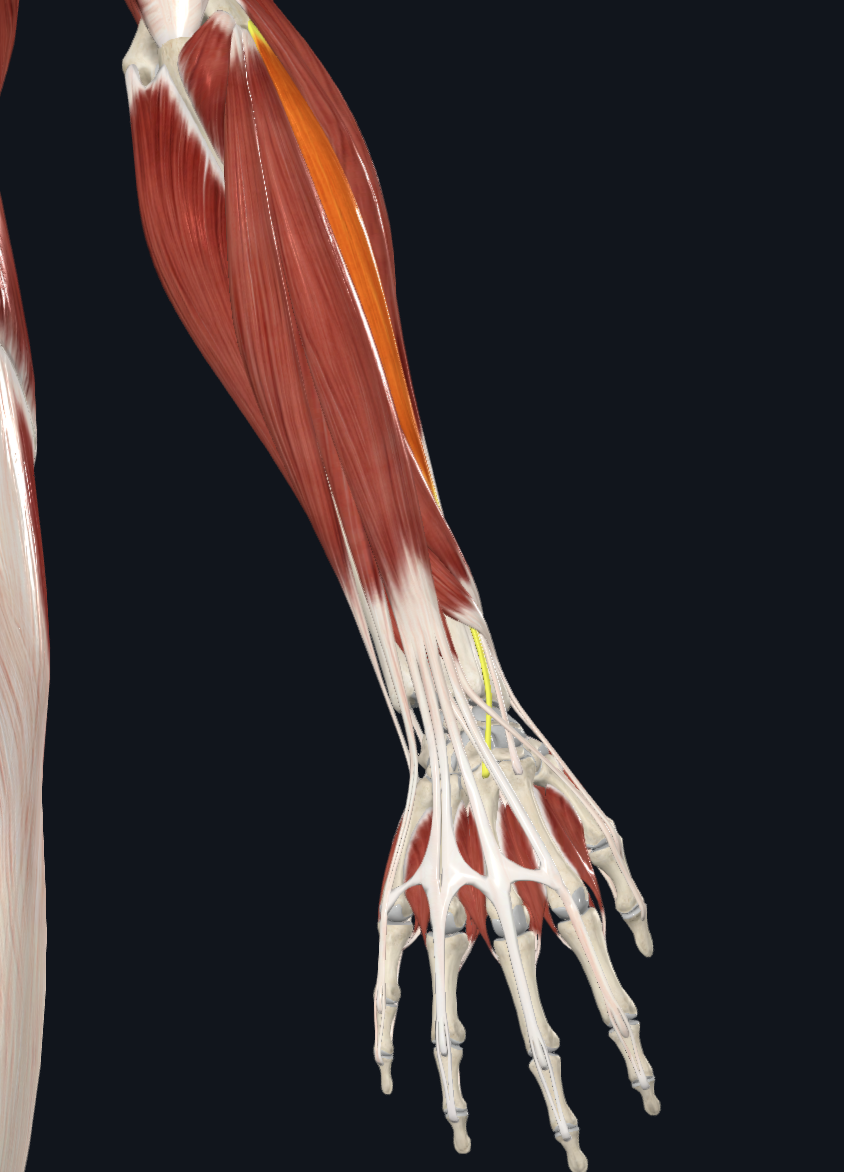
flexor digitorum profundus
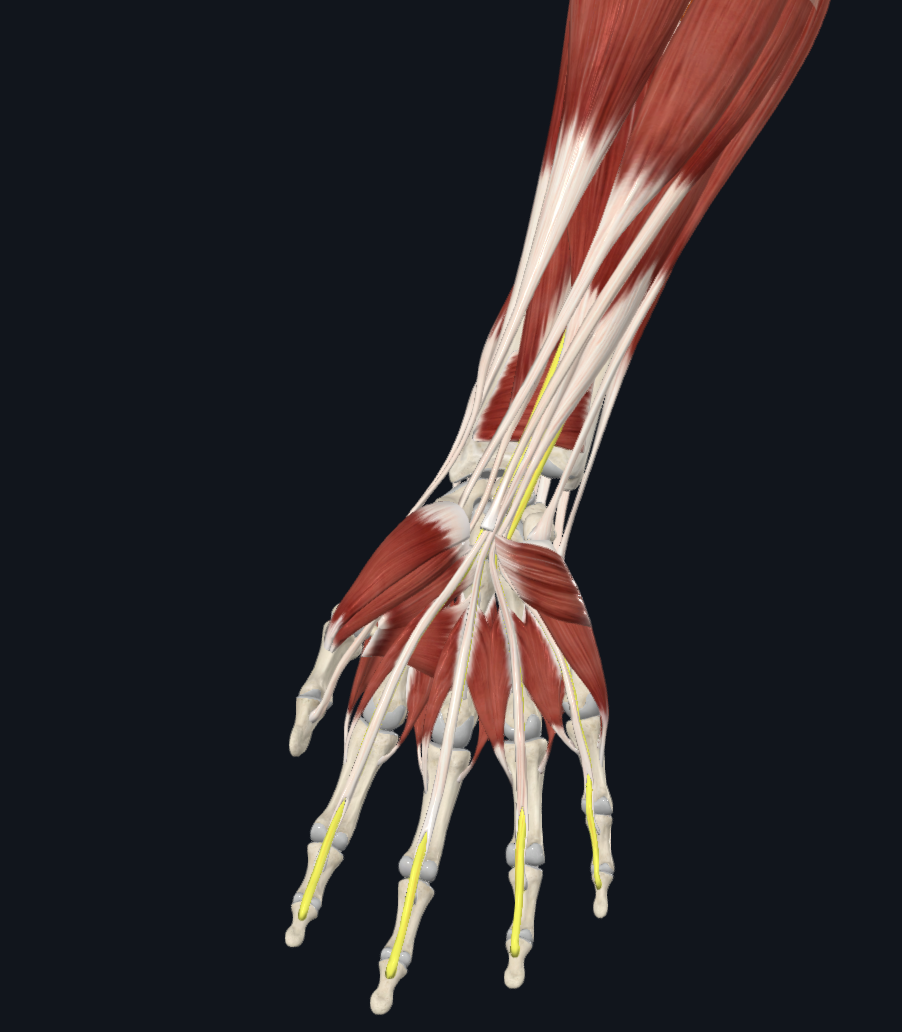
extensor pollicis brevis
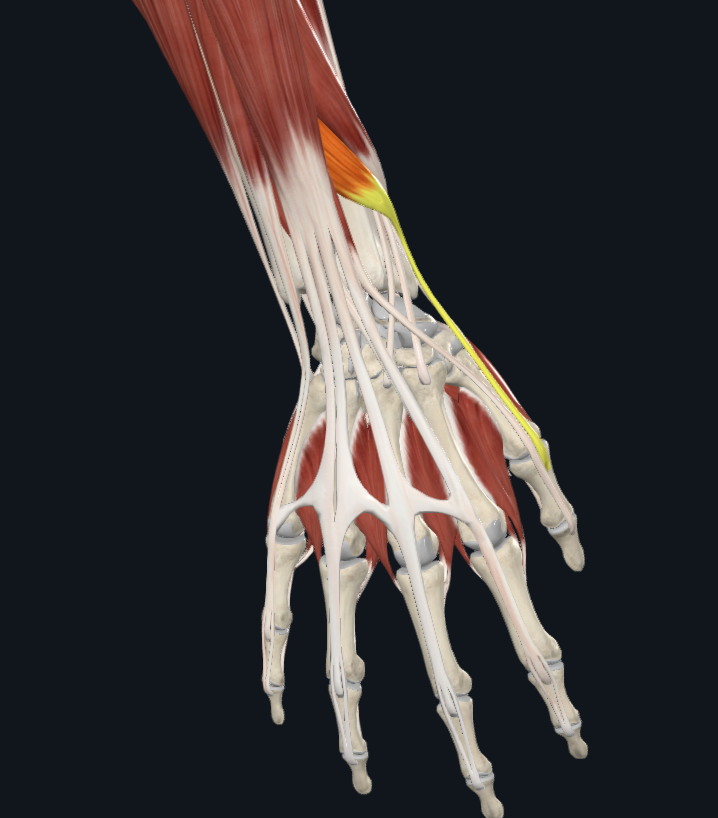
extensor pollicis longus
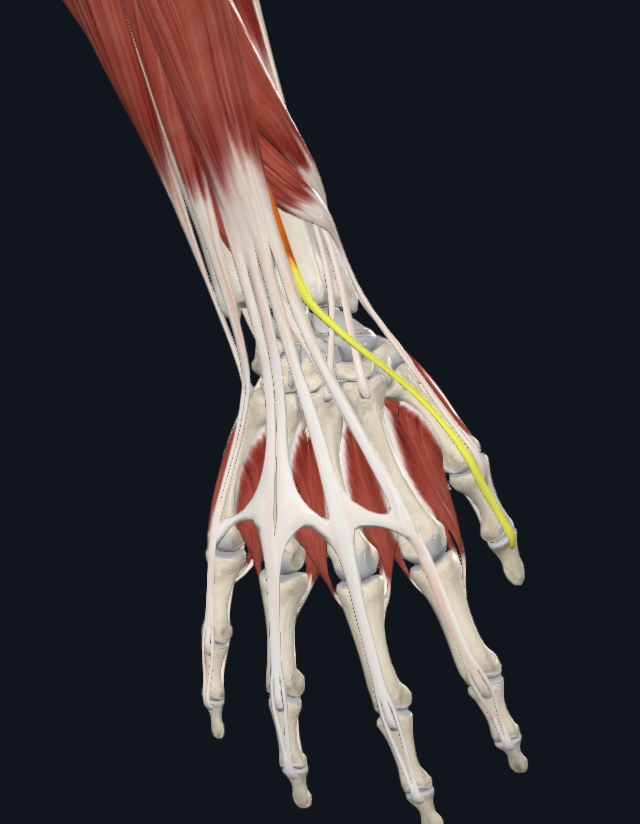
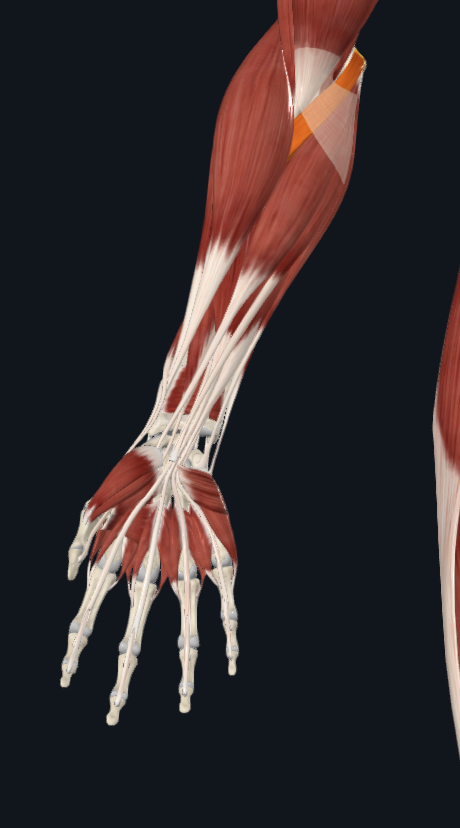
pronator teres
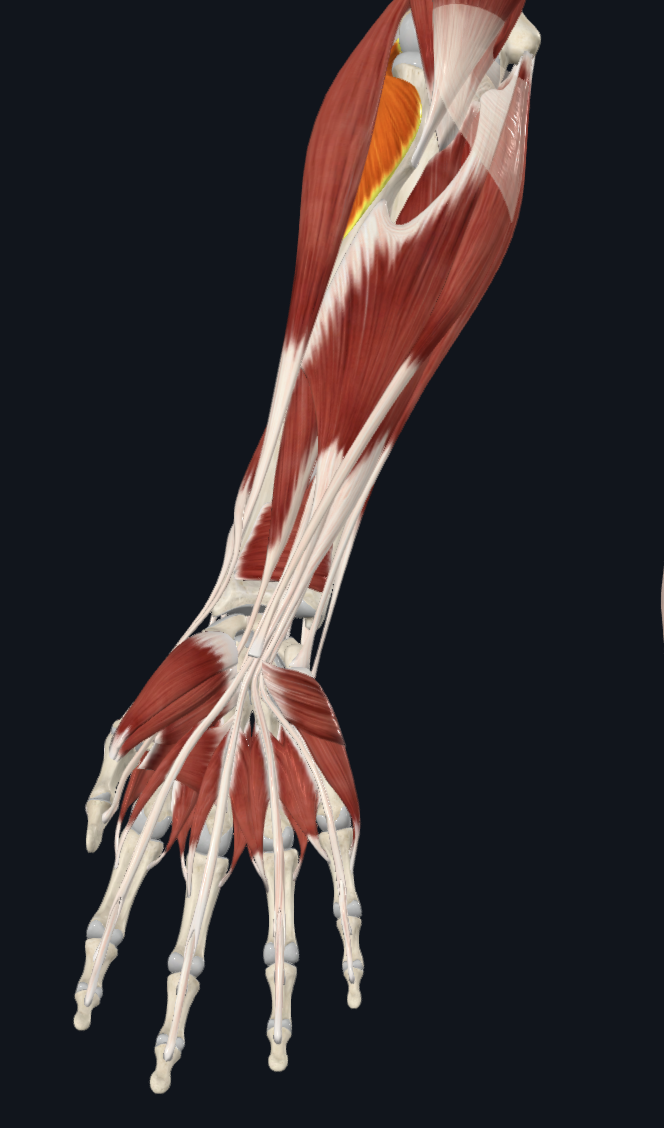
supinator
lumbricals
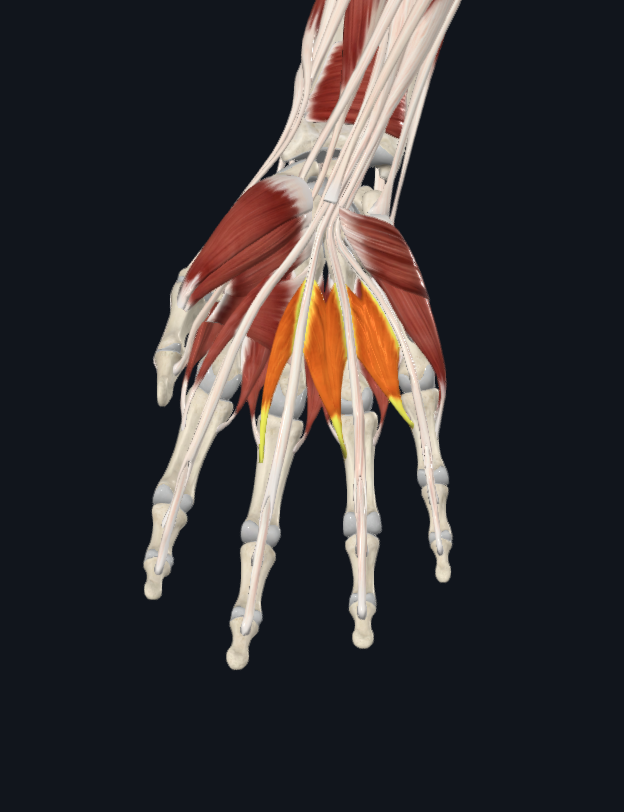
interossei
between fingers below the lumbricals
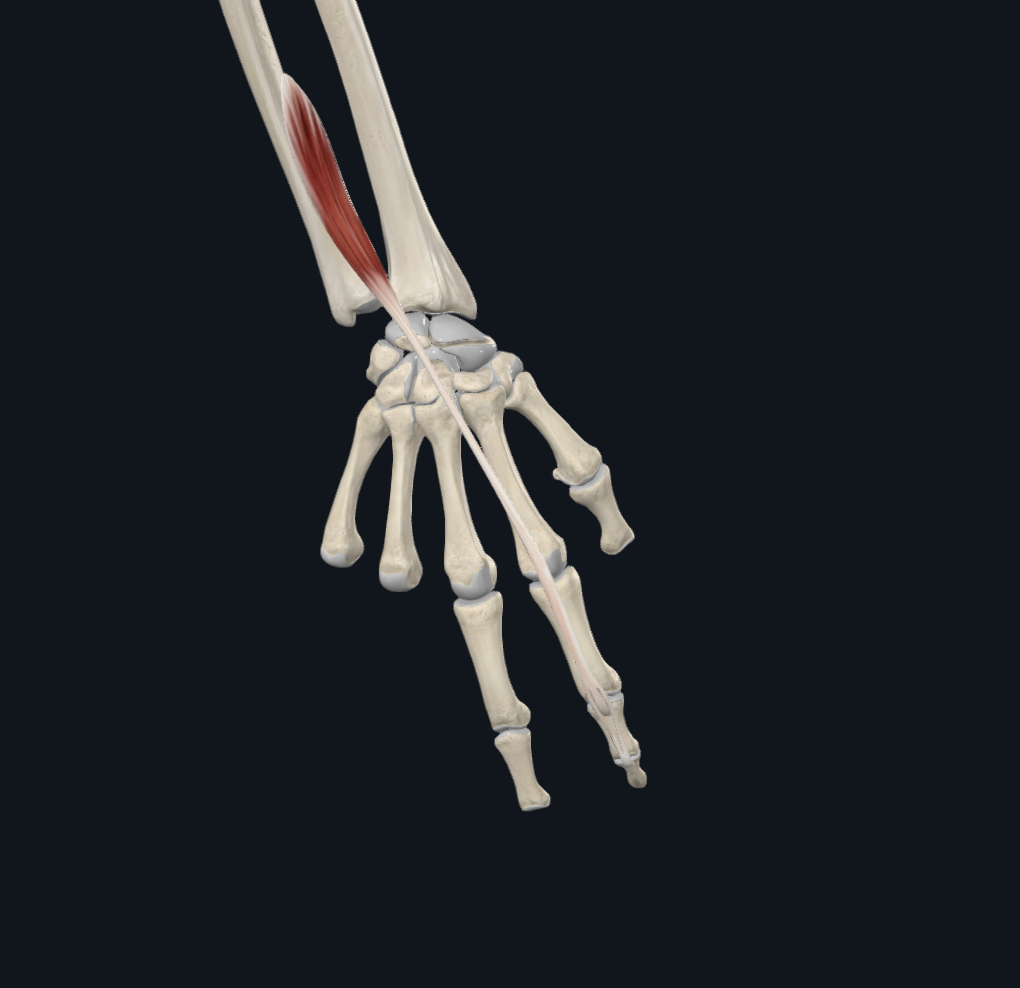
extensor indices
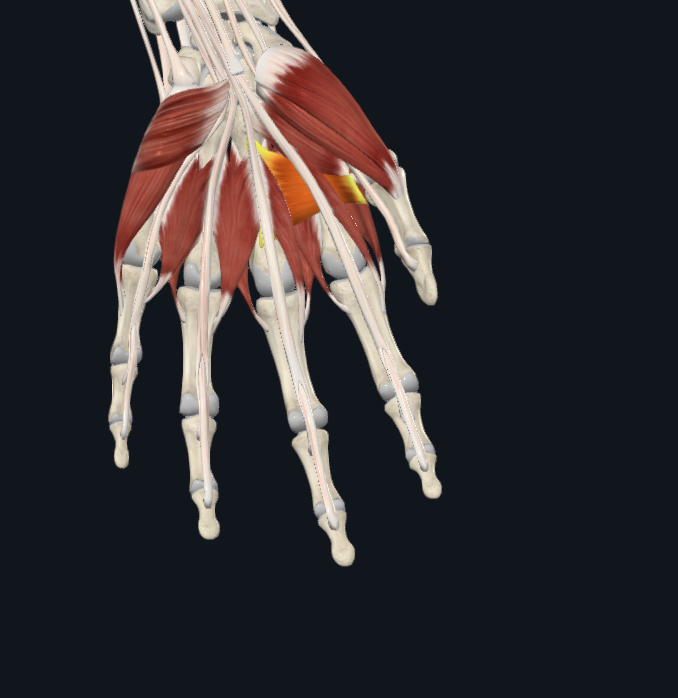
transverse adductor pollicis
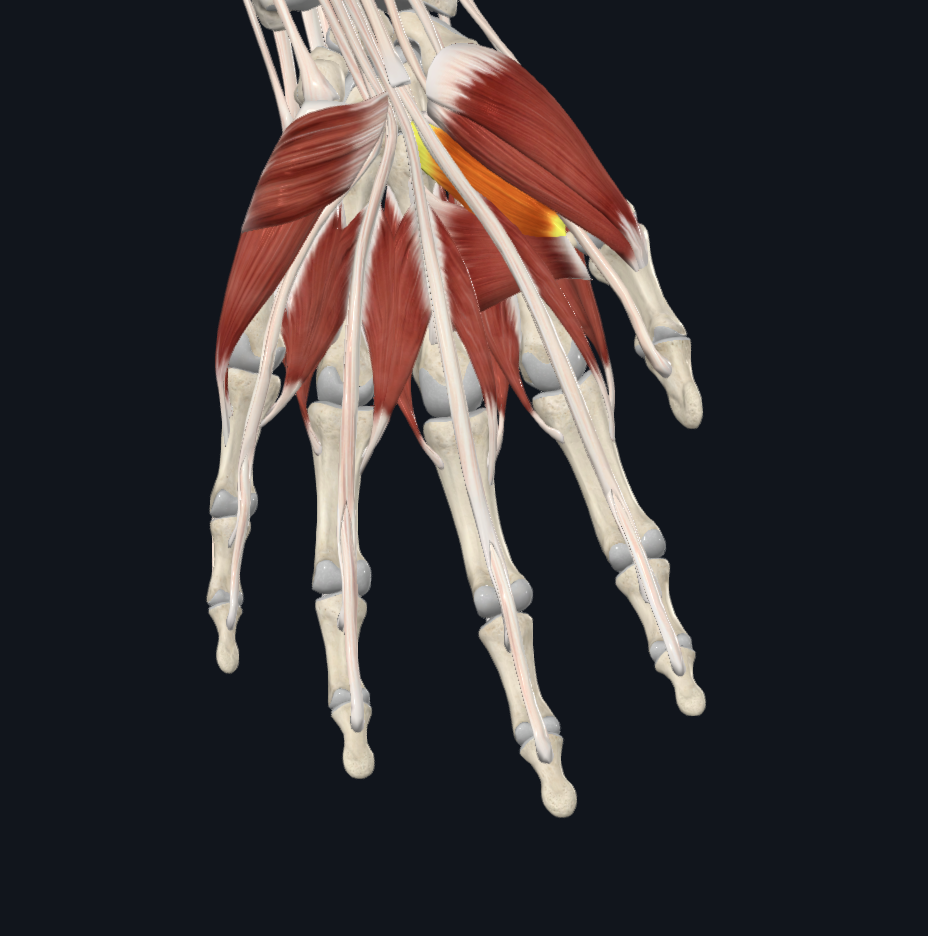
oblique adductor pollicis
What are the structures of the thoracic cage?
thoracic vertebrae, sternum and costal cartilages, ribs
What are the general functions of the thoracic cage?
protect vital organs of thoracic cavity, support shoulder girdle and upper limb, provides attachment sites of muscles of neck/back/chest/shoulders
true ribs
1-7 attached via hyaline cartilage
false ribs
8-12. not directly attached
floating ribs
11, 12. not attached
What structure of the rib articulates with the transverse costal facet of the vertebrae?
tubercles of rib
Head of rib articulates with what structure?
costal facets
pectoralis major OIA
o-clavicle and sternum, I-greater tubercle, a-flexion/adduction/medial rotation at shoulder
pectoralis minor OIA
o-ribs 3-5, I-coracoid process of scapula, a-protracts and depresses shoulder with ribs fixed pulls scapula forward
serratus anterior OIA
o-ribs 1-9, I-medial border of scapula, a-rotates and protracts scapula
What are the muscles of respiration? accessory structures?
diaphragm and external intercostals and primary respiratory muscles. internal intercostal are acccesory
What structures are included in the lower respiratory system?
larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, bronchioles, alveoli
Thyroid cartilage is what type of cartilage?
hyaline cartilage
What type of cartilage is the epiglottis composed of?
elastic cartilage
cricothyroid ligament
connects the thyroid cartilage and the cricoid cartilage
What are the true vocal cords? False cords?
vocal folds (the medial) are true, vestibular folds (lateral) are false
What are annular ligaments; What do they connect?
connects rings of tracheal cartilages
W hat type of epithelium would you find in the mucosa of the trachea?
pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
What is the trachealis muscle? Location?
located on the posterior side of the cartilage ring. allows for constriction and dilation of the trachea
Where does the trachea branch in two? What new structures form from the branching of the trachea?
trachea branches at the carina. branching forms the left and right main bronchi
What is the structural difference between the right and left main bronchi?
right main bronchus is steeper and larger than the left
Identify the lobar branches of the right and left main bronchi?
right-superior, middle, inferior. left-superior and inferior
Segmental (Tertiary) bronchi branch into what structures?
branch into the bronchopulmonary segments
How many bronchopulmonary segments does the right lung contain? Left lung?
right lung has 10. left lung has 9
Bronchioles are classified as airways smaller than?
passageways less than 1mm in diameter. end at a terminal bronchiole
Terminal bronchioles are classified as airways smaller than?
less than 0.5mm in diameter. terminate at respiratory bronchioles
Identify the structures of the respiratory zone?
respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs
What are alveoli?
functional site of gas exchange. elastic fibers allow alveoli to stretch and recoil. wrap in capillaries
What structures comprise alveolar wall?
type 1 alveolar cells (simple squamous), type 2 alveolar cells (scattered cuboidal)
What respiratory tissue is targeted by Sars-CoV-2?
any tissue with ACE2 receptor. alveolar cells of lungs
Does the virus alone damage respiratory tissue?
response is ARDS (acute respiratory distress syndrome) which leads to a cytokine storm (build up of fluid)
What is the inflammatory response created by Sara-CoV-2 called?
Identify the lobes and fissures of the right and left lungs?
right lung= superior, middle, inferior, horizontal and oblique fissure. left=superior and inferior lobe, oblique fissure, cardiac notch
What is the hilum of the lungs?
groove on the mediastinal surface of lungs. site of entry for main bronchi, pulmonary arteries and veins, nerves
Identify the pleural membranes
What are the three pulmonary circuits?
pulmonary, systematic, and coronary
What is the definition of an artery and a vein?
arteries carry blood away from heart and have thicker muscle for vasodilation. he tunica intima (inner layer), tunica media (middle layer), and tunica externa (outer layer)
How does blood flow through the heart?
right atrium → right ventricle → lungs → left atrium → left ventricle → body
Which ventricular wall has a thick myocardium?
left, to pump blood all throughout body
What is the cardiac skeleton?
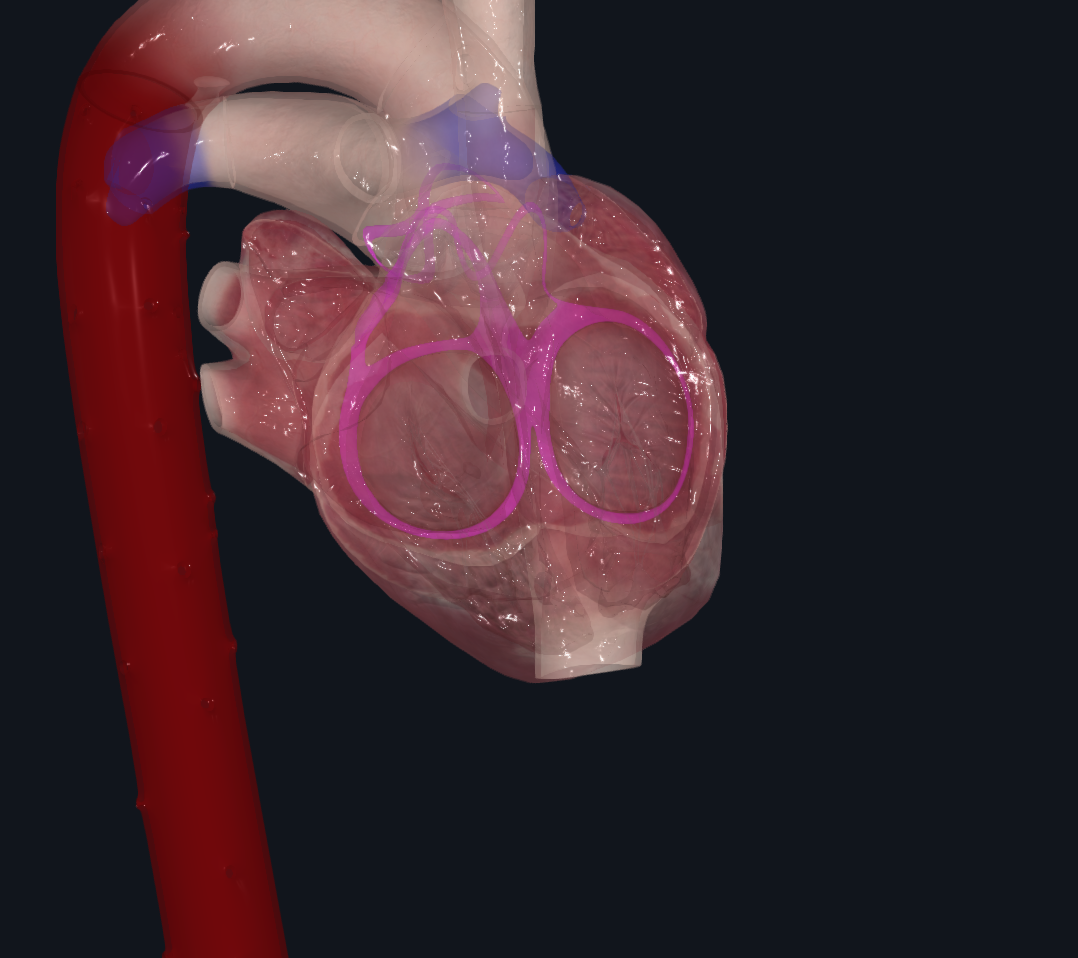
Identify the structures of the conduction system of the heart?
sa node, av node, fiber system (av bundle, left and right bundle branches, purkinje fibers)
Describe the basic process of heart development? What does the sinus venosus become?
heart is derived from mesoderm, begins as two chambers that fuse to form single actively pumping chamber, 4 chambered heart. sinus venous starts off at bottom then gives rise to right atrium, coronary sinus, and sa node
What is the function of the ductus arteriosus and foramen ovale in the fetal heart?
bypass pulmonary circulation because the fetus does not need oxygen in womb
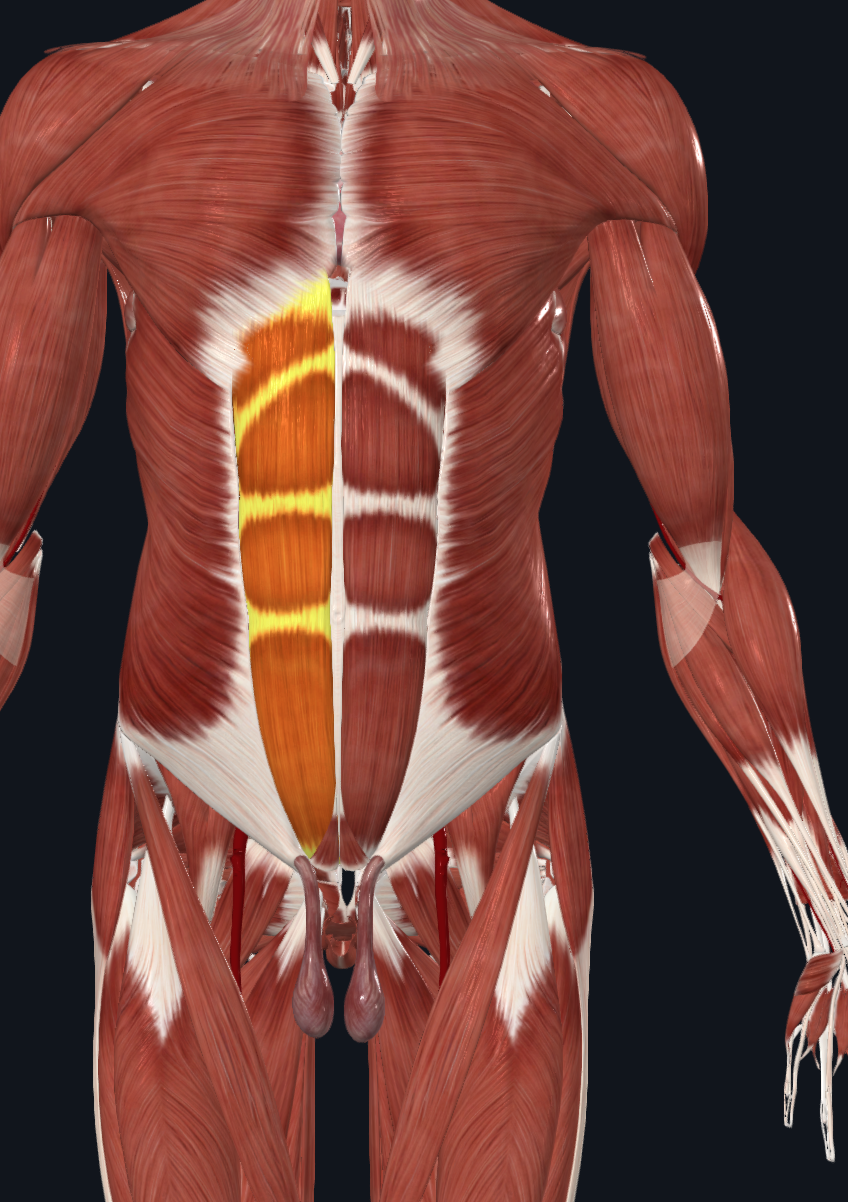
Rectus abdominis
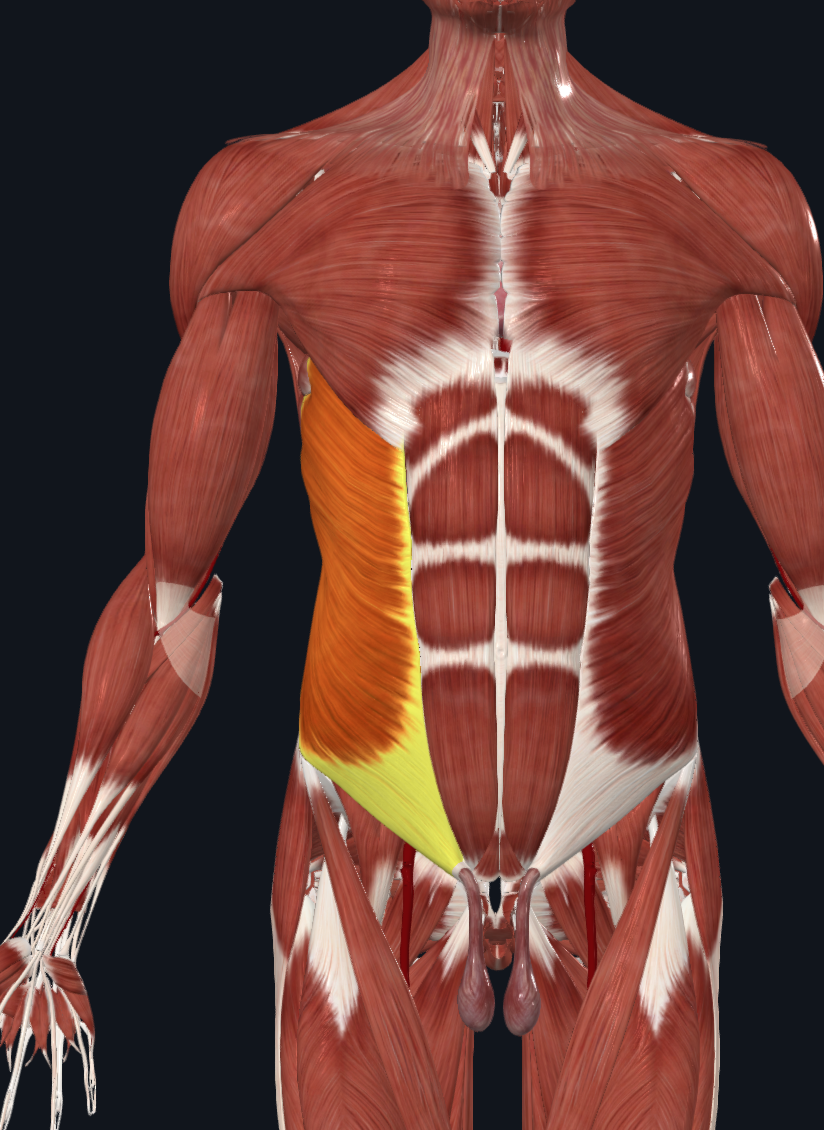
External Obliques
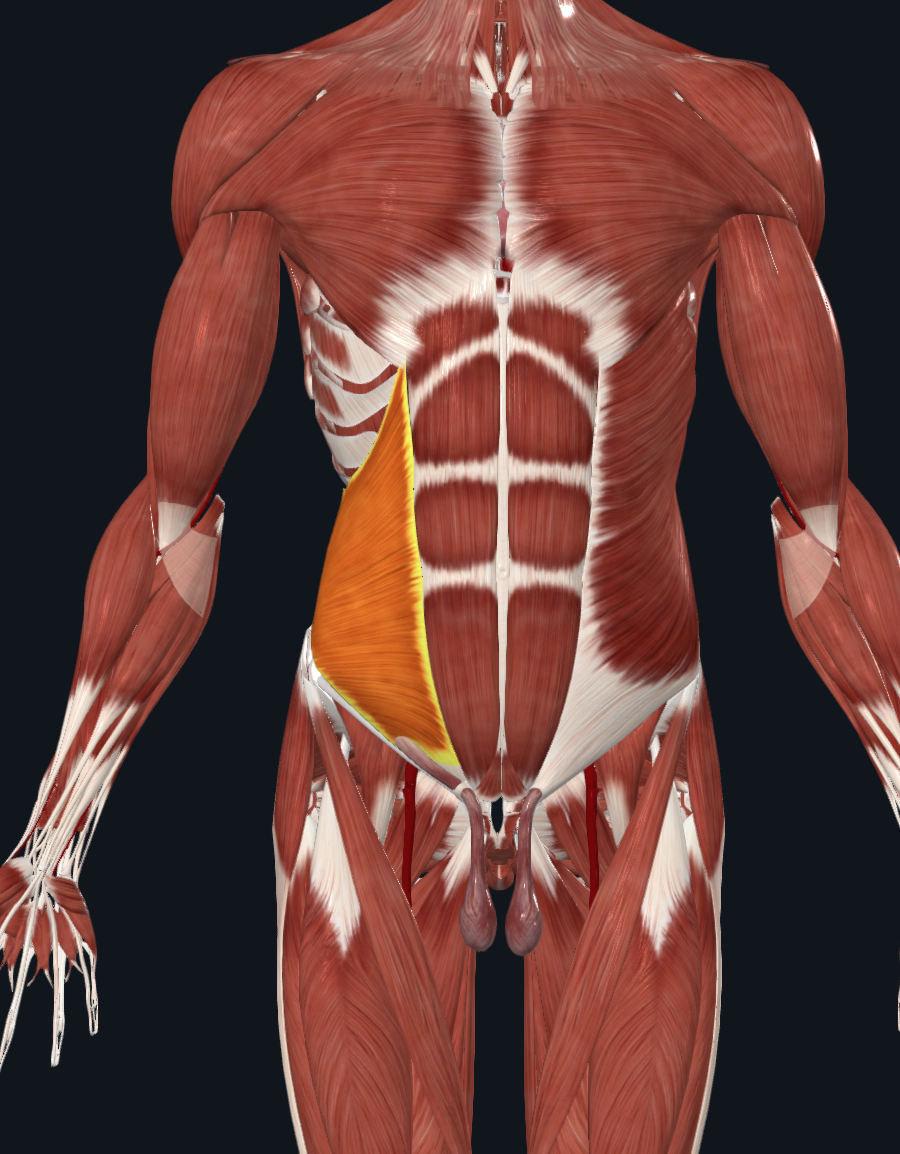
Internal Obliques
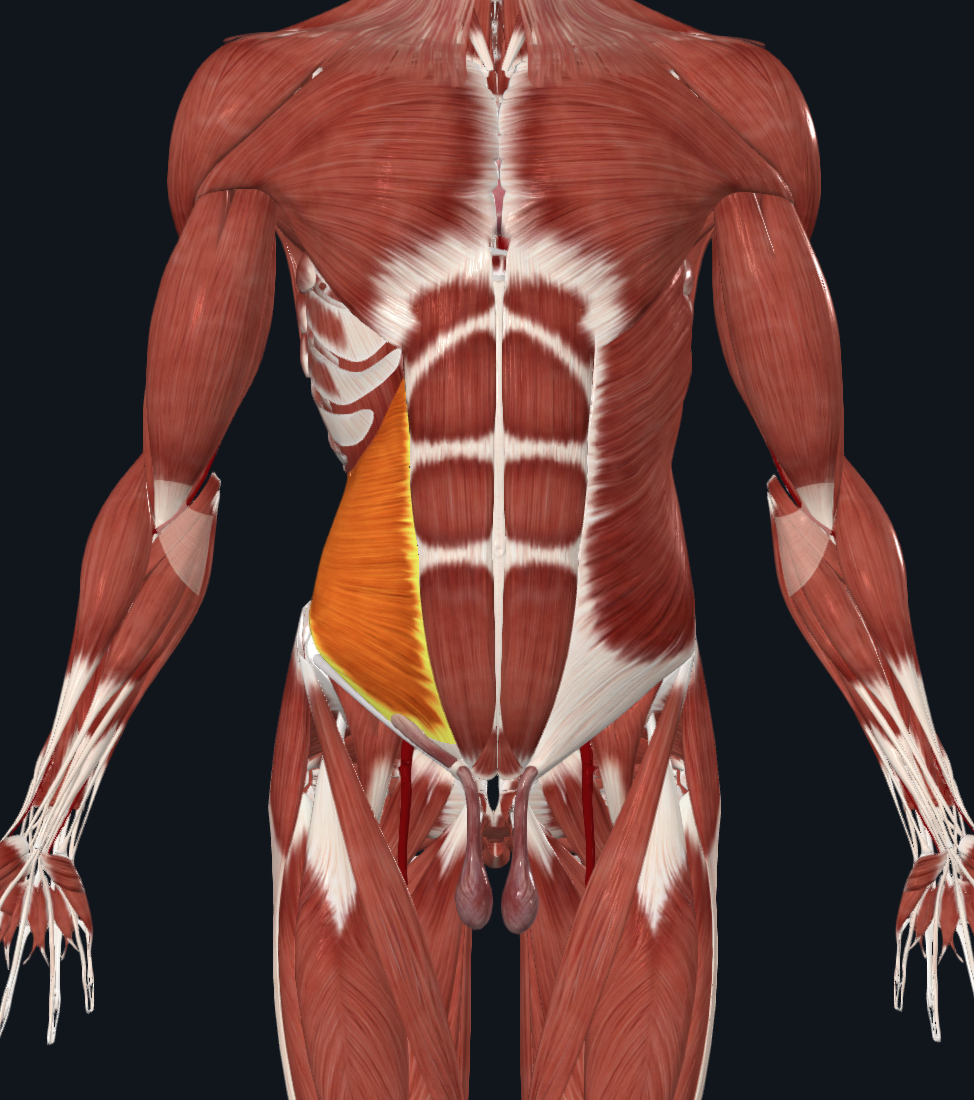
Transversus Abdominus
Visceral and Parietal peritoneum
visceral=membrane on outside of digestive organs. parietal=membrane on inside of body wall
peritoneal cavity
fluid filled space between peritoneums. fluid lubricates mobile organs
what does retroperitoneal mean
outside of the peritoneal cavity
what is the mesentery
double layer of peritoneum. extends from body wall to digestive organs, provides routes for blood vessels/lymph/nerves, hold organs in place
identify the greater omentum and lesser omentum
greater omentum is off of greater curvature of stomach. lesser omentum is from lesser curve of the stomach to the liver and the duodenum
esophagus
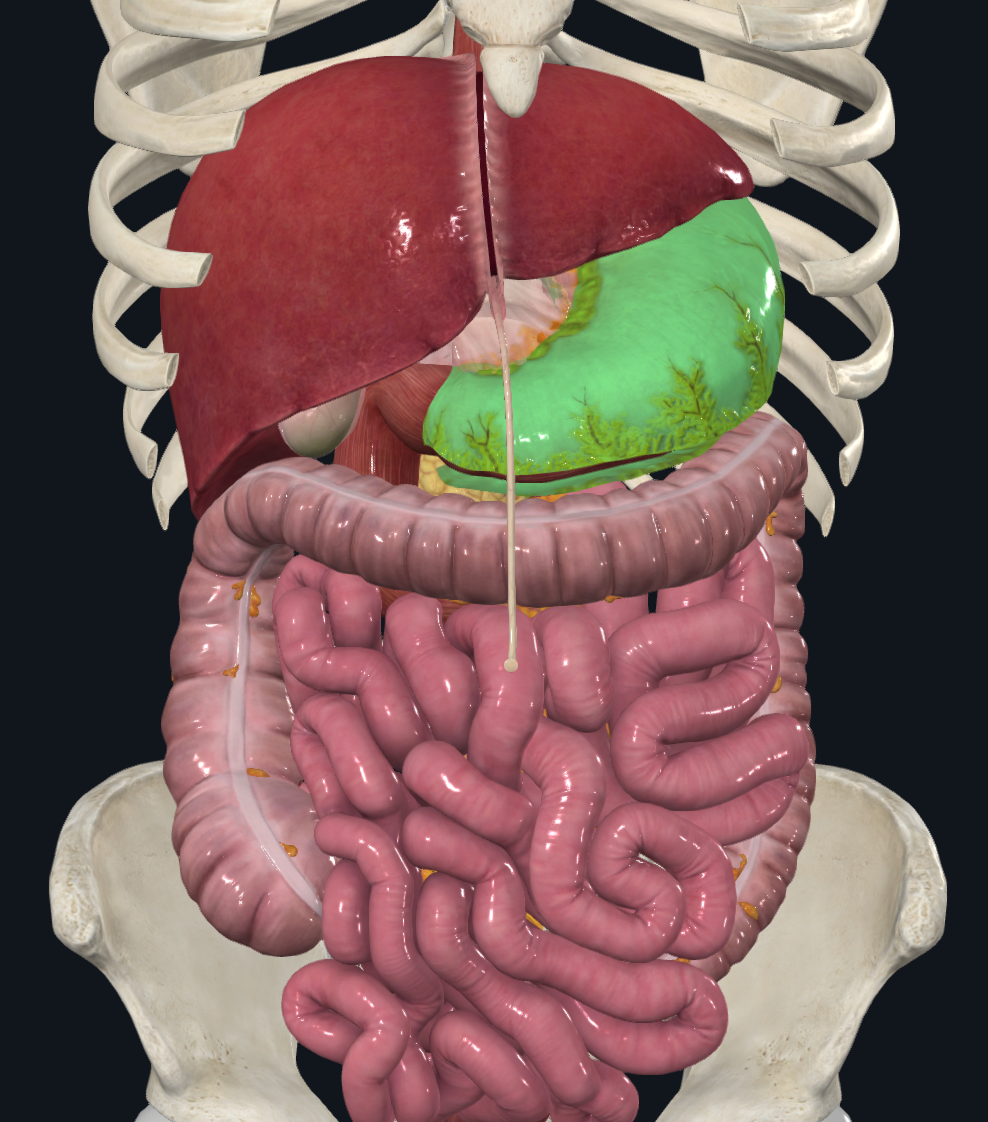
stomach
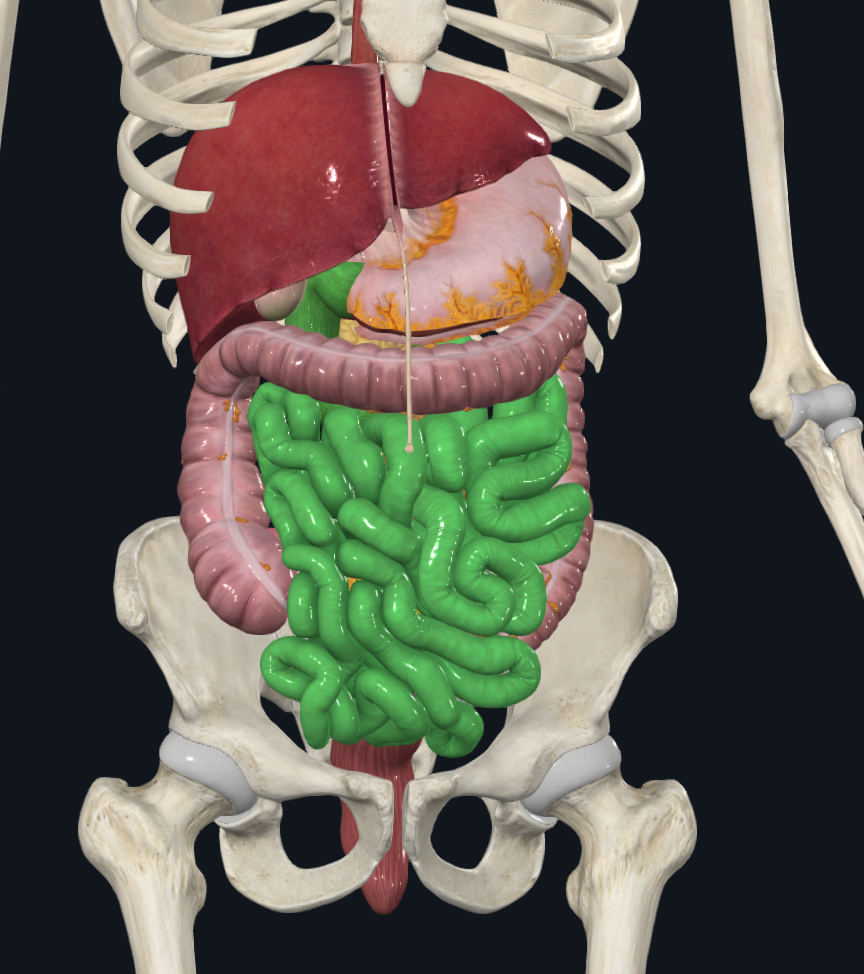
small intestine
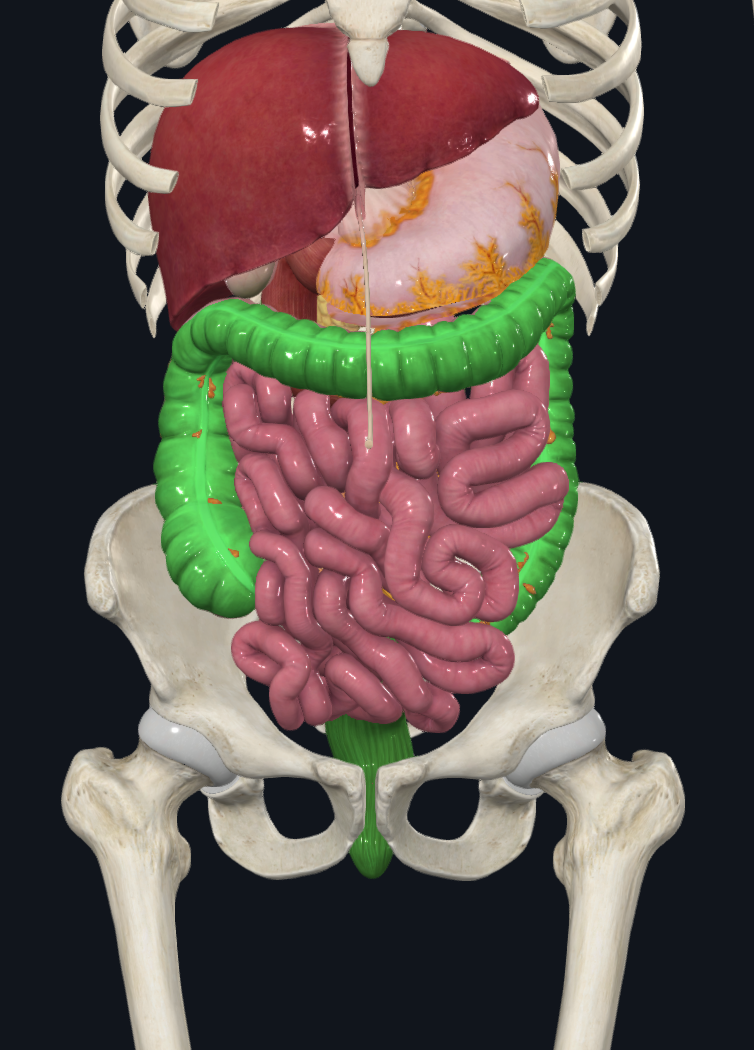
large intestine
liver