AP Psych - Unit 1
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Psychoanalysis Perspective
Freud; focus on the id-ego-superego interactions and childhood experiences on the unconscious
Cognitive Perspective
Focus on the mind and thinking processes; emphasizes memory, perception, and problem-solving.
Behavior Perspective
Focus on the relationships between reward/punishments on behavior
Humanist Perspective
Emphasizes individual potential, self-actualization, and personal growth. Assumes that all individuals have an inherent tendency to be good
Biopsychological Perspective
Focuses on the interactions of biology and the mind; emphasis on brain functions, genetics, neurotransmitters, and the nervous system
Evolutionary Perspective
Explains behavior through the lens of evolution, suggesting that human thoughts and actions are influenced by adaptations that have evolved over time for survival and reproduction
Sociocultural Perspective
Explains behavior by examining the influences of social and cultural environments, including norms, values, and interactions with others; individualism v. collectivism
Biopsychosocial Perspective
Integrates biological, psychological, and social factors to explain mental health and behavior; emphasizes the interaction of these domains in understanding individuals.
Falsifiable
An idea, hypothesis, or theory can be disproven; allows for testing and validation of the theory
Operational Definition
Specific statement of procedure; defines how the variable is measured
Case Study
Studies one person in depth to reveal a truth about everyone or unique behavior/phenomena
Naturalistic Observation
Observation of subjects in natural environments
Meta-Analysis
Combination of several studies to form an overall conclusion
Survey
Participants self-report data through questionnaires or interviews.
Wording Effect
The influence the phrasing of a question might have on respondents answers, lead to false interpretations
Self-Report Bias
Inaccurate memories or reports; correlates with tendency to only remember extremes
Social Desirability Bias
Respondents change answers in order for answers to appear normal to others
Random Sampling
All populations have a fair chance of inclusion
Generalizbility
The extent to which the results apply to the rest of the population
Placebo Effect
Results caused by the expectancy that the treatment will cause results
Placebo
Substance of treatment designed to have no effect
Single Blind Procedure
Participants don’t know what they are receiving, but experimenters do
Double Blind Procedure
Neither participants nor experiments know what participants are receiving
Confounding Variable
A factor other than the one being studied influencing results
Quantitative Research
Uses numerical data
Qualitative Reseach
Uses narrative data
Mean
Average; sum of values divided by the number of values
Median
Middle point of data distribution
Mode
Most frequent value
Range
Distance between the lowest and highest value
Standard Deviation
How much scores vary around the mean
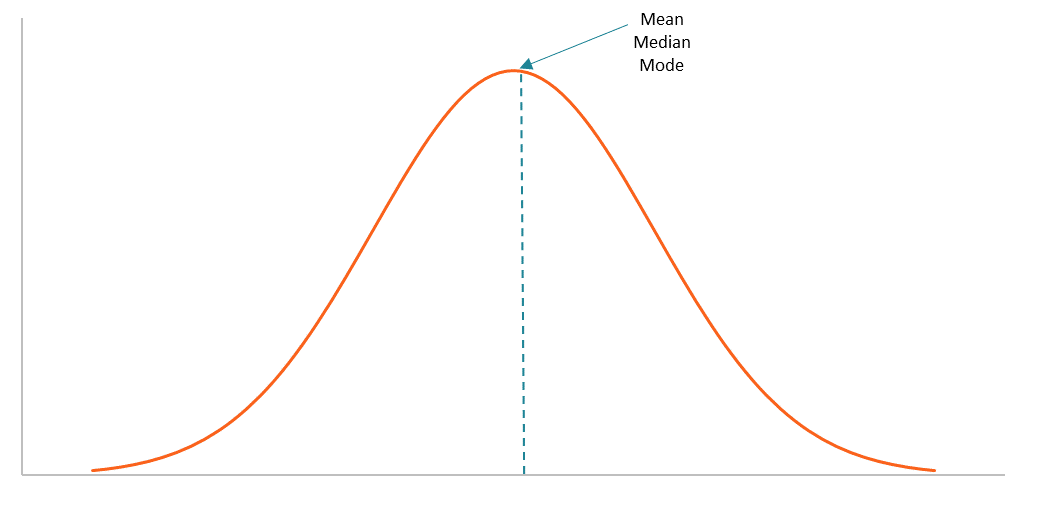
Normal/Bell Curve
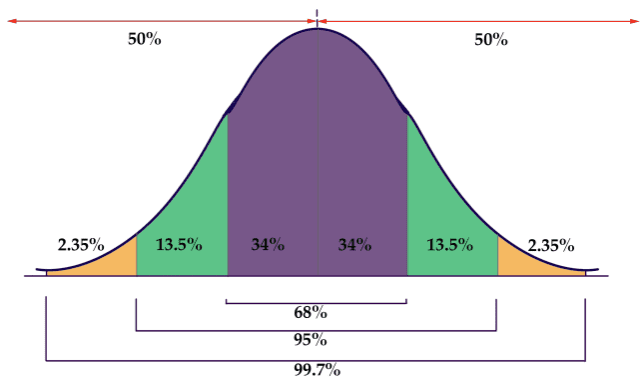
Empirical Rule
2.35%, 13.5%, 34%, 34%, 13.5%, 2.35%
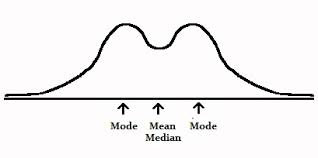
Bimodal Distribution
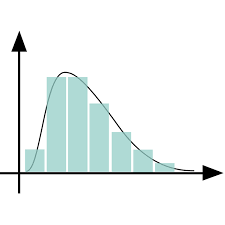
Positively Skewed Curve
Negatively Skewed Curve
Correlational Coefficients
Statistical index of the relationship between two things on the scale -1.00 to +1.00
Illusory Correlation
Perceiving a relationship where none exists
Regression Toward The Mean
Extreme observation tend to turn back toward the mean
Statistically Significant
Result was likely not due to chance; p-value less than 5%
p-value
probability that the null-hypothesis is true
Effect Size
Indicates the strength of the variable
Informed Consent
Potential participants have enough information to decide whether they want to participate
Deception
Cause someone to believe something that isn’t true; often uses confederates