Molec Cell: Ch. 2 pt. 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/48
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
1
New cards
The information in DNA and RNA is conveyed…
by the order of the bases.
2
New cards
DNA is made up of __. The bases are on the __, joined by __ btween _____ base pairs
DNA is made up of two polynucleotide chains. The bases are on the inside, joined by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs.
3
New cards
Complementary base pairing
one strand of DNA (or RNA) to act as a template for synthesis of a complementary strand.
4
New cards
Nucleic Acids
self-replication
5
New cards
The information carried by and ___ directs _____ of specific ______, which control __________.
The information carried by DNA and RNA directs synthesis of specific proteins, which control most cellular activities.
6
New cards
Other important nucleotides include:
* ATP
* some act as signaling molecules within cells
* some act as signaling molecules within cells
7
New cards
_______ are the most diverse of all macromolecules.
Proteins
8
New cards
Each cell contains ______ different proteins.
Each cell contains several thousand different proteins.
9
New cards
Proteins direct _______.
Proteins direct virtually all activities of the cell.
10
New cards
Functions of proteins include:
* structural components
* transport and storage of small molecules (O2)
* Transmit information between cells (protein hormones)
* Defense against infection (antibodies)
* Enzymes
* transport and storage of small molecules (O2)
* Transmit information between cells (protein hormones)
* Defense against infection (antibodies)
* Enzymes
11
New cards
Proteins are polymers of _____.
Proteins are polymers of 20 different amino acids.
12
New cards
What does each amino acid consist of?
* *a* carbon bonded to a carboxyl group (COO-)
* amino group (NH3+)
* hydrogen
* distinctive side chain
* amino group (NH3+)
* hydrogen
* distinctive side chain
13
New cards
Amino acids are grouped based on what? What are some examples?
Amino acids are grouped based on characteristics of the side chains:
* Nonpolar side chains
* polar side chains
* side chains with charged basic groups
* acidic side chains terminating in carboxyl groups
* Nonpolar side chains
* polar side chains
* side chains with charged basic groups
* acidic side chains terminating in carboxyl groups
14
New cards
What are some basic amino acids?
* Lysine (Lys) K
* Arginine (Arg) R
* Histidine (His) H
* Arginine (Arg) R
* Histidine (His) H
15
New cards
What are some acidic amino acids?
* Aspartic Acid (Asp) D
* Glutamic Acid (Glu) E
* Glutamic Acid (Glu) E
16
New cards
How to join the amino acids?
Peptide bonds
17
New cards
Polypeptides
chains of amino acids, hundreds or thousands of amino acids
18
New cards
What are the on the ends of a polypeptide?
* One end of a polypeptide terminates in an *a* amino group (N terminus)
* Other ends in an *a* carboxyl group (C terminus)
* Other ends in an *a* carboxyl group (C terminus)
19
New cards
What do amino acid sequences define?
characteristics of proteins
20
New cards
What did Frederick Sanger do in 1953?
Worked out the amino acid sequence for insulin
21
New cards
How are protein sequences now deduced from?
Sequences of mRNAs
22
New cards
Complete amino acid sequences of over _____ proteins have been established.
100,000
23
New cards
Insulin consists of____. The side chains of three pairs of ___ are joined by _______.
Insulin consists of two polypeptide chains. The side chains of three pairs of cysteine residue are joined by disulfide bonds.
24
New cards
How are the sequences are amino acids in a protein determined by?
the order of nucleotide bases in a gene
25
New cards
Proteins also have distinct ________ that are critical to their ____.
Proteins also have distinct 3D conformations that are critical to their function.
26
New cards
The shape and functions of proteins are determined by….
The shape and functions of proteins are determined by their amino acid sequences.t
27
New cards
What did Chirstian Anfinsen do?
* demonstrated the importance of the 3D structure.
* disrupted proteins by treatments such as heating, which breaks non-covalent bonds (denaturation)
* disrupted proteins by treatments such as heating, which breaks non-covalent bonds (denaturation)
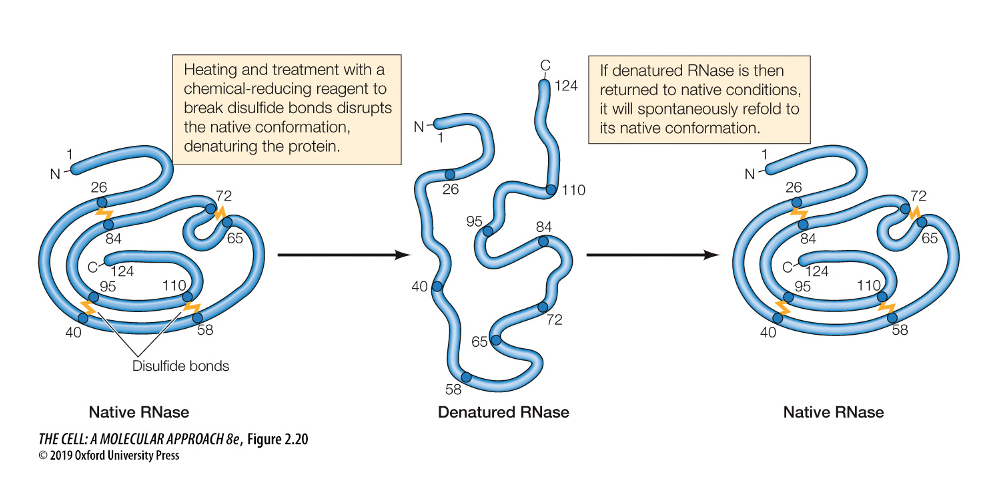
28
New cards
All the information required to specify the correct 3D conformation of a protein is contained in its ___ _____ ___ ____.
All the information required to specify the correct 3D conformations of a protein is contained in its primary amino acid sequence.
29
New cards
Primary Protein Structure
the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain
30
New cards
Secondary Protein Structure
Regular arrangement of amino acids within localized regions
* Two common types:
* *a* helix
* *B* sheet
* both are held together by H bonds between CO and NH groups of peptide bonds
* Two common types:
* *a* helix
* *B* sheet
* both are held together by H bonds between CO and NH groups of peptide bonds
31
New cards
Tertiary Protein Structure
The folding of the polypeptide chain due to interactions between side chains of amino acids in different regions of the chain
32
New cards
Domains
The basic units of tertiary structure; are folded 3D structures usually containing between 50-200 amino acids
33
New cards
What are the 3 critical determinants of tertiary structure?
* Hydrophobic amino acids: in the interior of the protein
* Hydrophilic amino acids: on the surface - interact with water
* Loop regions - connect the elements of secondary structure
* Hydrophilic amino acids: on the surface - interact with water
* Loop regions - connect the elements of secondary structure
34
New cards
Where are the critical determinants of tertiary structure?
They are on the surface of folded proteins, where the polar components of the peptide bonds form H bonds with water or with the polar side chains of hydrophilic amino acids.
35
New cards
Quaternary Protein Structure
Interactions between different polypeptide chains in proteins composed of more than one polypeptide.
36
New cards
Hemoglobin is composed of…
4 polypeptide chains
37
New cards
A fundamental role of proteins is to act as…
enzymes
38
New cards
Enzymes
Catalysts that increase the rate of all chemical reactions in cells
39
New cards
What would happen to most biological reactions without enzymes?
They would be so slow that they would not occur.
40
New cards
What are the two fundamental props of enzymes?
1. Increase rate of chemical reactions **without themselves being consumed** or permanently altered.
2. **Increase reaction rates** without altering the chemical equilibrium between reactants and products.
41
New cards
When a substrate (s) is converted to a product (P), the chemical equilibrium between S and P is determined by…
the laws of thermodynamics

42
New cards
If an enzyme is present, the conversion is ___ , but the equilibrium is ___.
If an enzyme is present, the conversion is accelerated, but the equilibrium is unaltered.
43
New cards
Equilibrium is determined by…
the final energy states of S and P
44
New cards
The substrate must first be converted to a higher energy state, the…
transition state
45
New cards
activation energy
energy requires to reach the transition state
46
New cards
Enzymes…
reduce the activation energy
47
New cards
What are enzyme-substrate complexes (ES)?
It is when enzymes bind their substrates to form an enzyme-substrate complex.
48
New cards
Active site
Where the substrate binds to a specific region of the enzyme
49
New cards
The substrate is converted to ___ while bound to the ____ ____, then _____.
The substrate is converted to product while bound to the active site, then released.