Molecular Genetics Lecture 13 - Epigenetics
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
Why does gene expression need to be regulated?
all cells in an organism contain the same gene (DNA) and whenever cells need the protein the genes are turned on and vice versa and there are signals that induce gene expression
What are the two ways genes are tightly regulated?
temporal regulation, spatial regulation
What is temporal regulation?
specific proteins are required at specific times only and cells do not always need all the proteins
What is spatial regulation (cell or tissue specific expression)?
specific proteins are needed in only specific cell or tissue types, not all the proteins need to be expressed in all tissues or organs
What are the steps of gene expression
epigenetics/transcriptional regulation
mRNA processing
regulation of mature mRNA
regulation of translation
post-translational regulation
What is epigenetics?
heritable changes in phenotypes caused by mechanisms independent of DNA sequence (not by mutations or changes in nucleotide of DNA)
What is DNA methylation?
when DNA methyl transferase (DNMT) enzyme catalyzes the transfer of methyl groups to the 5’ carbon of cytosine nucleotide
What recognizes CG dinucleotide clusters (CpG islands) recognized?
DNMTase (p-phosphodieaster bond)
How are genes repressed (OFF)?
high DNA methylation in CpG sequences
How are genes active (ON)?
no DNA methylation in CpG sequences
Transposons and repeat sequences are silenced by ________
DNA methylation
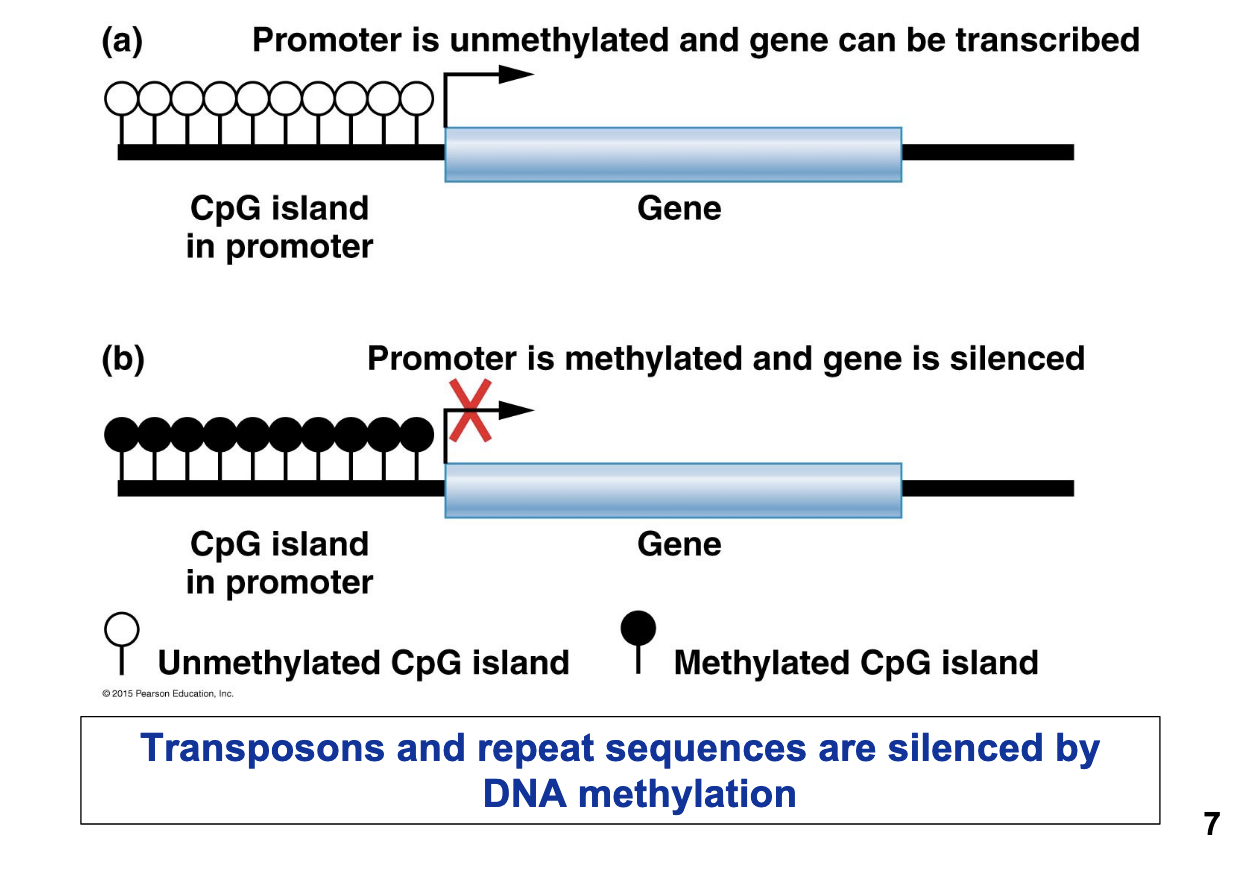
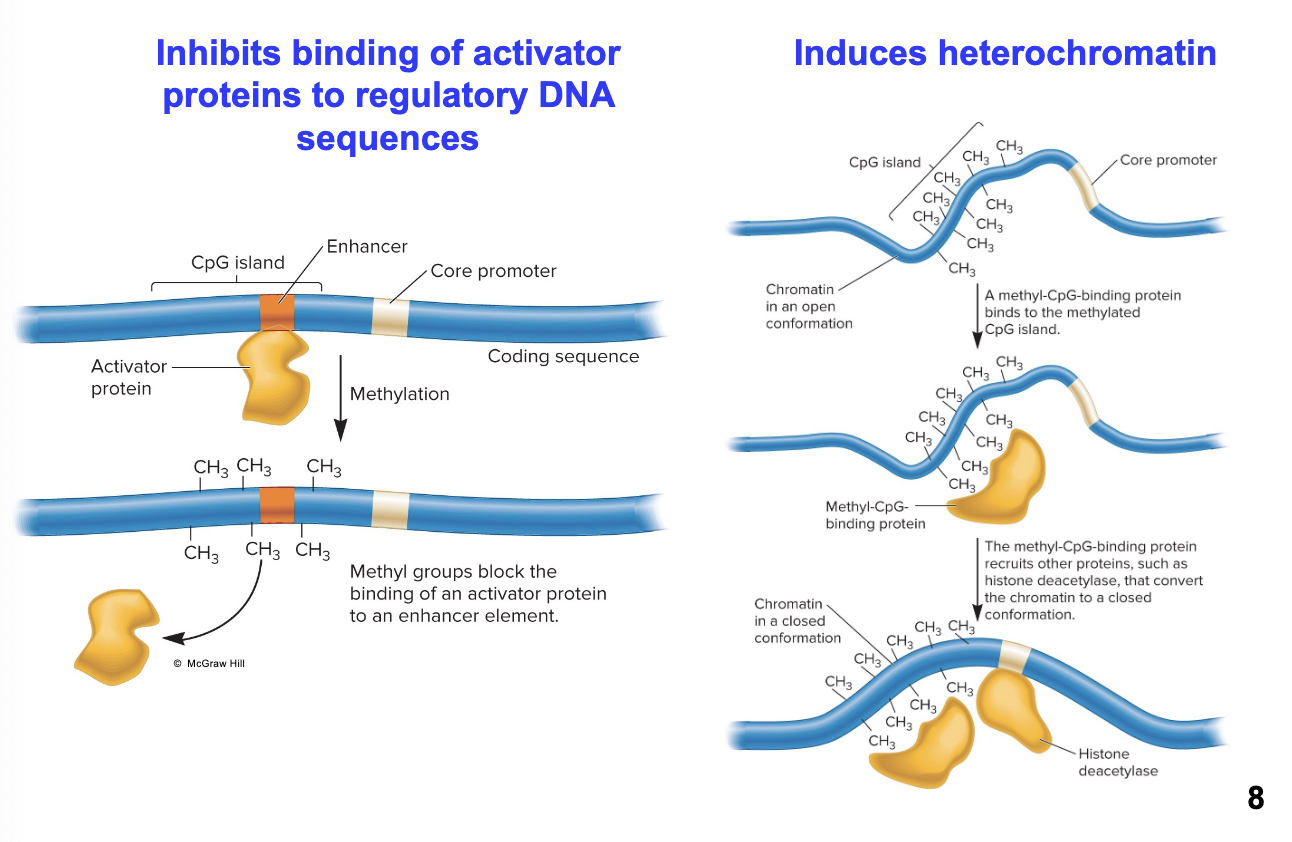
What are two mechanisms of repression by DNA methylation?
inhibiting the binding of activator proteins to regulatory DNA sequences and inducing heterochromatin
What is imprinting?
marks that are recognized and inherited
Genomic imprinting is an epigenetic phenomenon controlled by
DNA methylation
What is genomic imprinting?
expression of identical copies of a gene depends on whether it’s maternal or paternal
What is maternal imprinting?
mother’s copy of the gene is inactive/silenced
What is paternal imprinting?
father’s copy of the gene is inactive/silenced
The silencing of imprinted genes are caused by _______ NOT by _______
caused by DNA methylation, not by nucleotide changes/mutations
IGF2 is _______ imprinting because ….
maternal because the gene from the mother never expresses the phenotype since it is silenced by DNA methylation
The IGF2 gene is only expressed if it is inherited from the _____
father
H19 gene is _____ imprinting because…
paternal because the gene is only expressed if it is inherited from the mother and the gene is inactive from the father
What does the H19 gene control?
body weight and also affects cancer
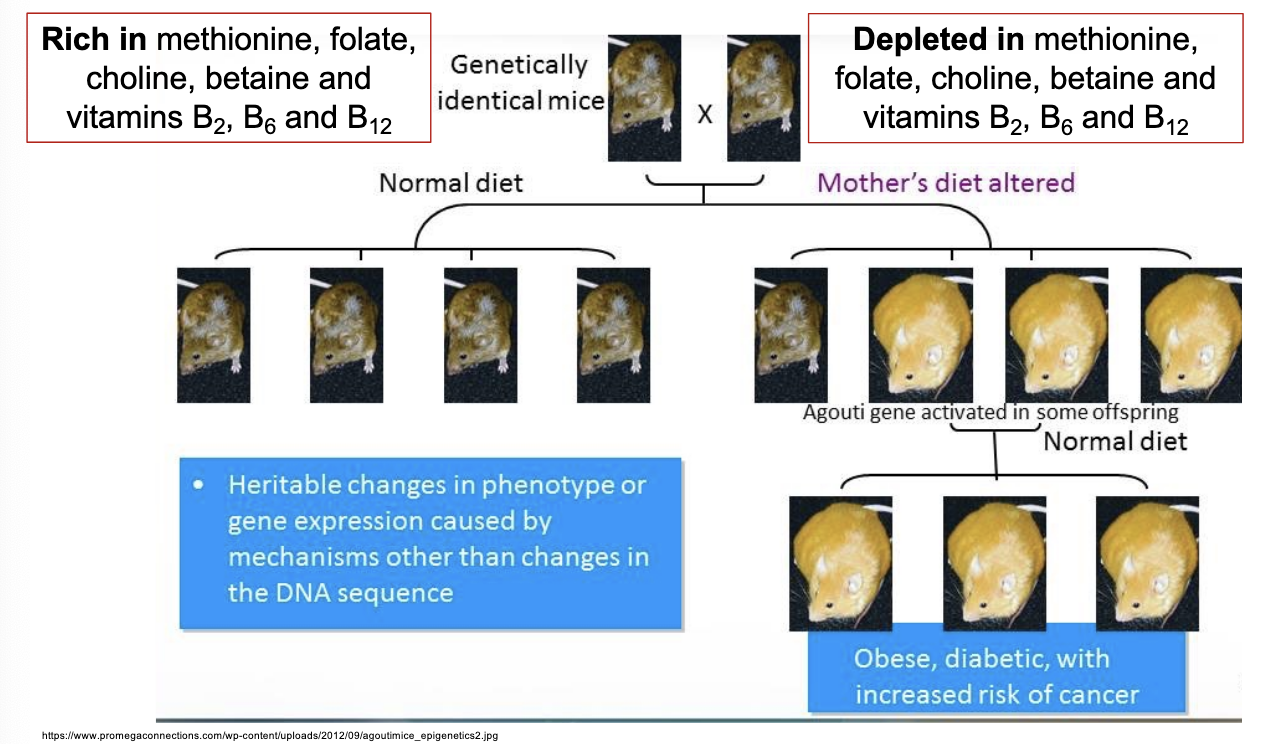
The aguoti mouse are an example of what type of epigenetic inheritance?
transgenerational epigenetic inheritance
What is the universal donor of methyl group?
S-adenosyl methione (SAM)
What hyperactivates the agouti gene constitutively in all cells which leads to the yellow mouse phenotype?
IAP promoter
What silences the UAP promoter which results in the brown mouse phenotype controlled by its own hair-cycle specific promter?
DNA methylation
DNA methylation silences transposon ______ of agouti gene.
upstream
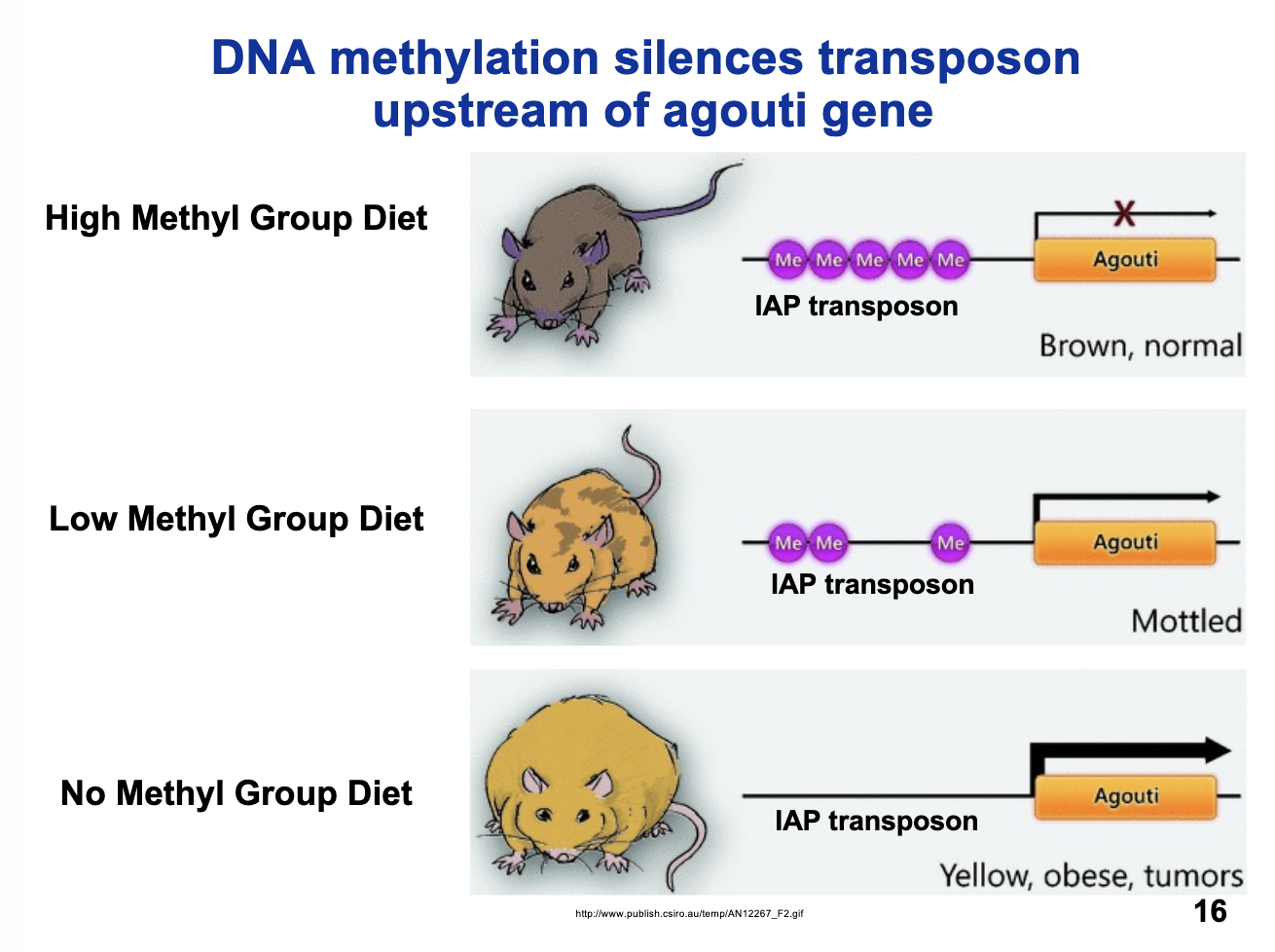
What is the phenotype of mice with a high methyl group diet?
brown, normal

What is the phenotype of mice with a low methyl group diet?
mottled
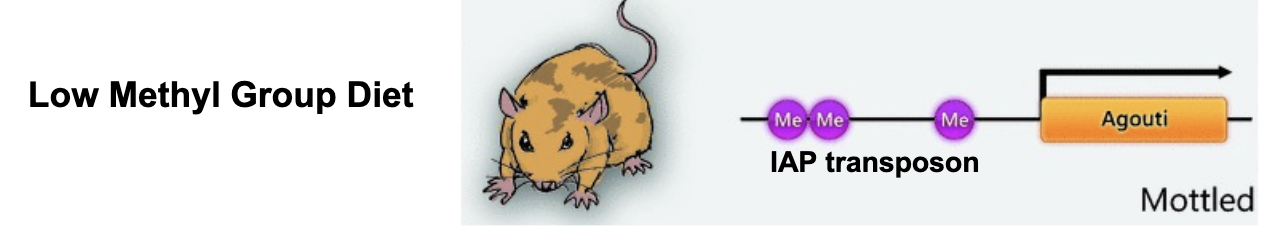
What is the phenotype of mice with a no methyl group diet?
yellow, obese, tumors

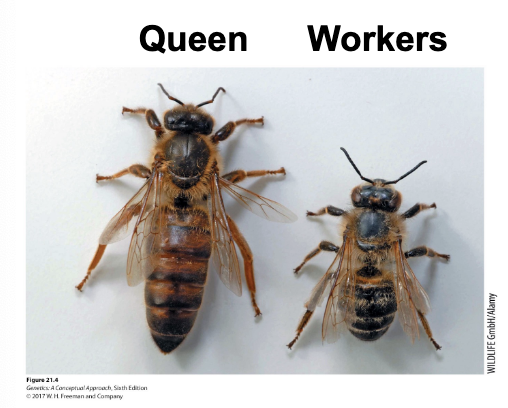
How do queen bees and worker bees differ?
only in diet, larvae feed with royal jelly develop into queen bees while larvae fed with honey develop into workers
Queen bees and worker bees are genetically identical, but have different phenotypes (anatomy, physiology, behavior). True or false.
True
