astrophysics ughhh
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What is the life cycle of a star?
Nebula attracted to each other due to their gravitational force (protostar)
Cloud becomes hotter and more dense until fusion occurs and becomes a main sequence star
Main sequence star is stable as long as outward pressure from fusion is balanced with inward gravitational force
Star dies and outward pressure increases, causing it to expand and turn into a red giant (similar size to the sun) or a super red giant (when star is larger than our sun)
Red giant will collapse into a white dwarf when fuel for fusion has run out. It becomes a black dwarf once cooled
A super red giant will explode into a supernova, producing heavy elements and new nebula. It leaves a dense neutron star at the middle, and a black hole. Nebula formed as nuclei fuse together due to immense energy from a Supernova
Whay is luminosity?
Total radiative power output of a star, given by stefan’s law luminosity = stefan constant x surface area (4 pi r 2) x surface temp in K ^4
How do we model stars?
As black bodies (emitting and absorbing all wave lengths)
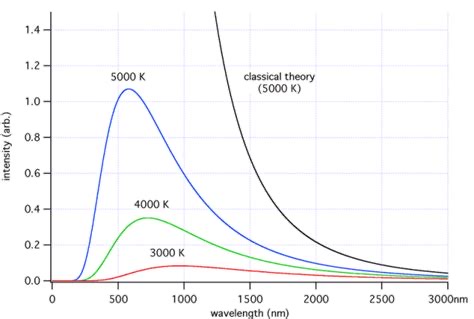
What is wein’s law?
The wavelength as which the most energy is emitted is called wavelength peak or max. The hotter the star, the shorter this wavelength
Wavelength peak T = 0.0029
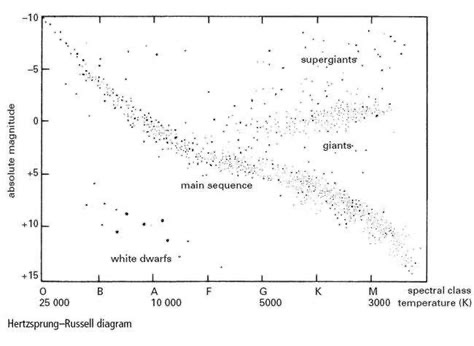
Hertz spring Russel diagram
What is a parsec?
The distance at which 1 AU subtends an angle of 1 at second
What is an astronomical unit?
The mean radius of the earth’s orbit / distance to the sun
What is a light year?
The distance light travels in a year
What is red shift?
Wavelengths of radiation from other galaxies are red shifted because they’re moving away from us. More distance galaxies appear more red shifted. This is evidence that they all originated from the same point in space, and is therefore evidence for the Big Bang theory
Evidence for the Big Bang theory
red theory
Cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBRh
What is Doppler shift equation?
Z = V / c = change in wavelength / wavelength = change in frequency / frequency
What is a binary star system?
two stars orbiting each other. Causes spectral lines to split and recombine periodically due to their changing recessional velocity
What is hubble graph?
The recessional velocity of galaxies and its distance from our galaxy. Gradient is Hubble constant. V = h0 d. The reciprocal theoretically gives you the age of the universe. Hubble constant is in seconds ^ -1
How do things orbit?
Centripetal motion, velocity always perpendicular to force
What is a UV catastrophe?
Theoretical is assuming black body