Week 8-9: Dressings & Wound Management
1/341
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
342 Terms
Goal for a wound dressing
Moist wound environment
Moist wound environment can reduce
pt pain
Moist wound environment taps
endogenous enzymes for autolytic debridement
How do wound dressings promote endogenous growth?
They trap endogenous enzymes that are used for autolytic debridement
Moist wound environment preserves
endogenous growth factors
A Moist wound environment facilitates...
all 3 phases of wound healing
Autolytic debridement
using body's enzymes to break down tissue and self debride
How do wound dressings effect scar formation?
Promotes formation of a more cosmetically appealing scar
Too moist of a wound enviroment
maceration
Skin damage
Increased risk of infection
Maceration
softening or dissolution of tissue after lengthy exposure to fluid
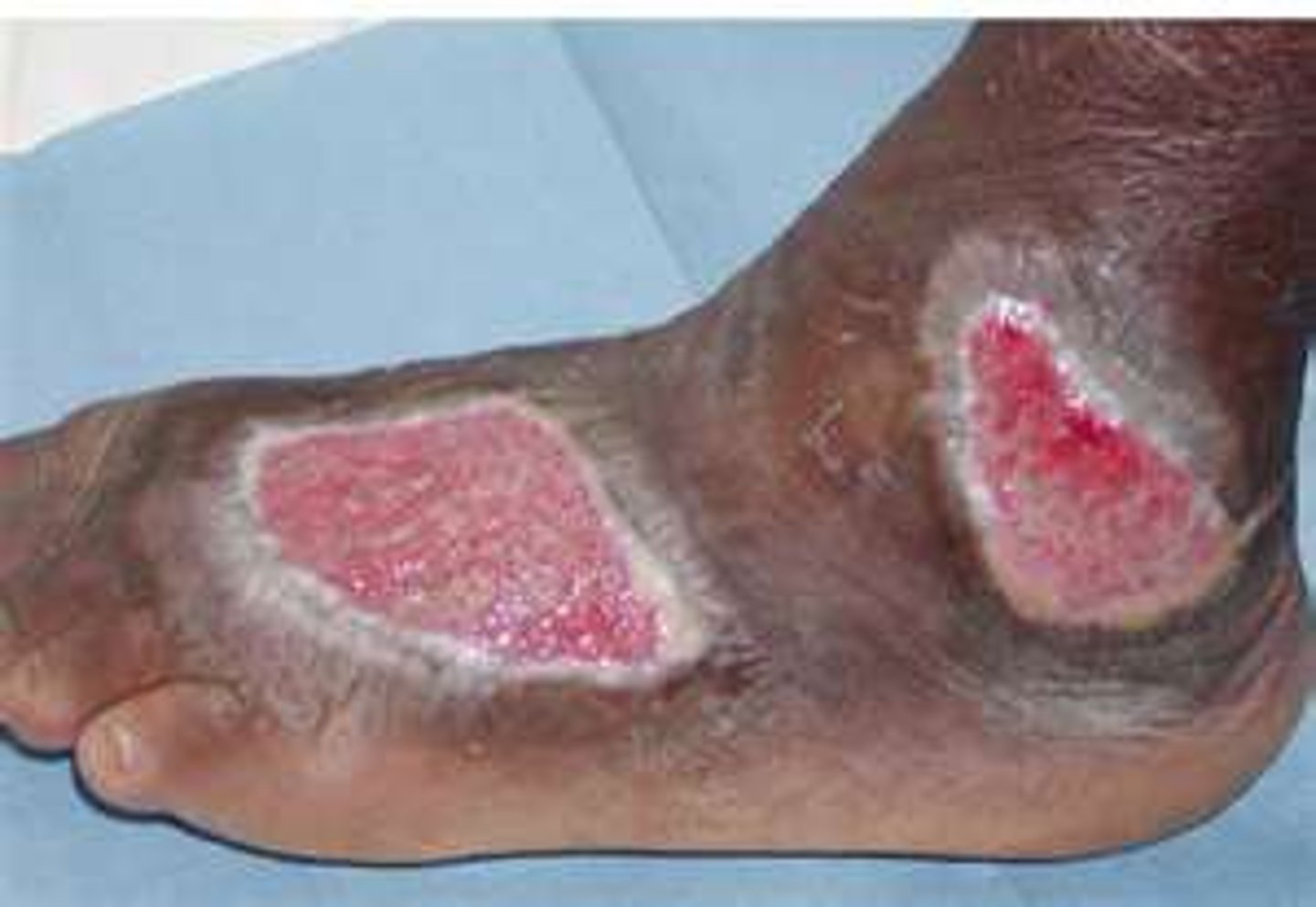
Too dry of a wound environment
desiccation
decreased enzyme/ growth factors
Scab/crust formation
Wound dressing purpose
-Create/Maintain a moist environment
-Absorb drainage/exudate
-Fill dead space
-Debride necrotic tissue
-Provide thermal insulation
-Prevent or treat infections
-Promote homeostasis
We pack the wound dead space to
heal it faster and stop abscesses from forming
Dressings have to be
-user friendly
-affordable
· Able to remain in place for long periods of time
· Non-traumatic
· Thermally insulating
What affects the cost of dressings
o Type of dressing
o Size
o Additional features (adhesive boarder)
o Local coverage decisions
Local coverage decisions
· Informs of dressings covered and at what rate
Primary dressing
Contact layer, comes in contact with wound surface
Secondary dressing
Wound dressing placed over the primary dressing that provides increased protection, cushioning, absorption, and/or occlusion.
Primary dressings do not always need
secondary dressings
tertiary dressing
not always necessary, could be what holds the dressing in place or a compression wrap
Medication/topicals are NOT
a dressi g
Frequency for dressing changes
Minimize changing frequency
Why do you want to minimize the changing frequency?
It can change the temperature and wound environment
Dressings most absorptive to least
1. Alginates
2. Semipermeable foams
3. Hydrocolloids
4. Hydrogels
5. Semipermeable films
Gauze dressing most absorptive to least
1. Layers of gauze dressing
2. Gauze pad
3. Nonwoven gauze
4. Woven gauze
Composite dressings
Multilayer dressing made from a combination of wound dressing categories
Interactive dressings
Dressings that create a moist environment and interact with the
wound they cover to stimulate cell activity and growth
Occlusive
Blocks air and gas exchange
Permeable
penetrable; porous; allowing liquids or gas to pass through
Occlusiveness rankings
1. Hydrocolloids
2.Hydrogel sheets
3. Semipermeable foam
4. semipermeable film
5. Impregnated gauze
6. Calcium alginates
7. Fine-weave gauze
8-Loose weave gauze
Absorptive Moisture retentive dressings
Alginates>semipermable foam>hydrocolloids>hydrogels>semipermable fims
Absorptive Gauze dressings
Woven
When do you need to change a wound?
As the wound changes
Things to Remember
· Dressing needs change as a wound changes
· There can be several dressing recipes that are appropriate for a wound
· There is NO one dressing that works for all wounds
· Choices of dressings will depend on what is available to you in clinic/facility
· You must know WHY you are using what you are using
Factors to consider for wound dressing
o Amount of wound drainage
o Condition of wound bed (granular or necrotic)
o Presence of wound infection
o Periwound Skin condition (can it tolerate adhesives?)
o Frequency of dressing changes
o Availability of wound dressings
o Cost of dressing
o Wound location
o What WAS the patient using?
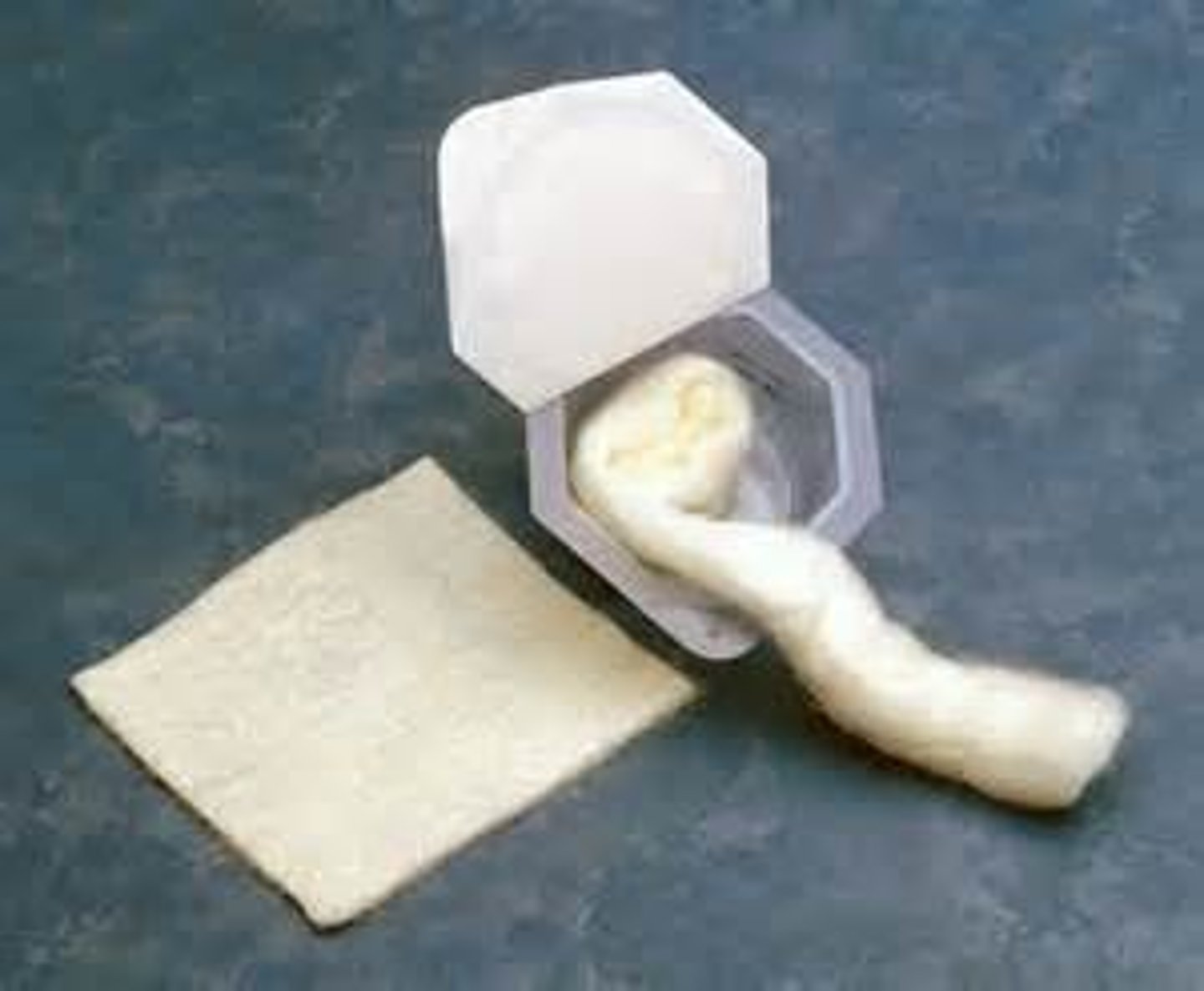
Alginate
Most absorptive dressing made from alginic acid from brown seaweed, fibers create a hydrophilic gel

Alginates are
Most absorptive and are semi occlusive
Hydrocolloids are very
occlusive
Alginates are available in
ribbons, rope, and calcium alginate tipped applicators
Alginate tipped applicators are used for
tunnels
Alginate Fibers react with wound exudate and form a
hydrophilic gel to provide a moist wound environment
Hydrophilic gel
absorbs and retains large amounts of moisture, forming a gel-like substance creating moist wound environment
Why is alginate not used for wounds with o with exposed tendon, joint capsule or bone
§ Because they would dry that area out
Fluff don't stuff
§ Don't stuff in bottom of wound
Advantages of alginate
can absorb 20x it's weight, easy to use in filling cavities or irregular wounds, encourages autolytic debridement, works well under compression, hemostatic
o Can remain on wound for several days
o Fibers will NOT cause irritation if left in wound- they emulsify
Can alginate be used on infected wounds?
Yes
hemostatic
controls or stops bleeding
Disadvantages of alginate
dehydrate since its so absorptive, non-adherent = requires secondary dressing, requires irrigation to remove
Alginates work well for
VI ulcers
Semipermeable foams
nonstick, absorbant, spongelike polymer
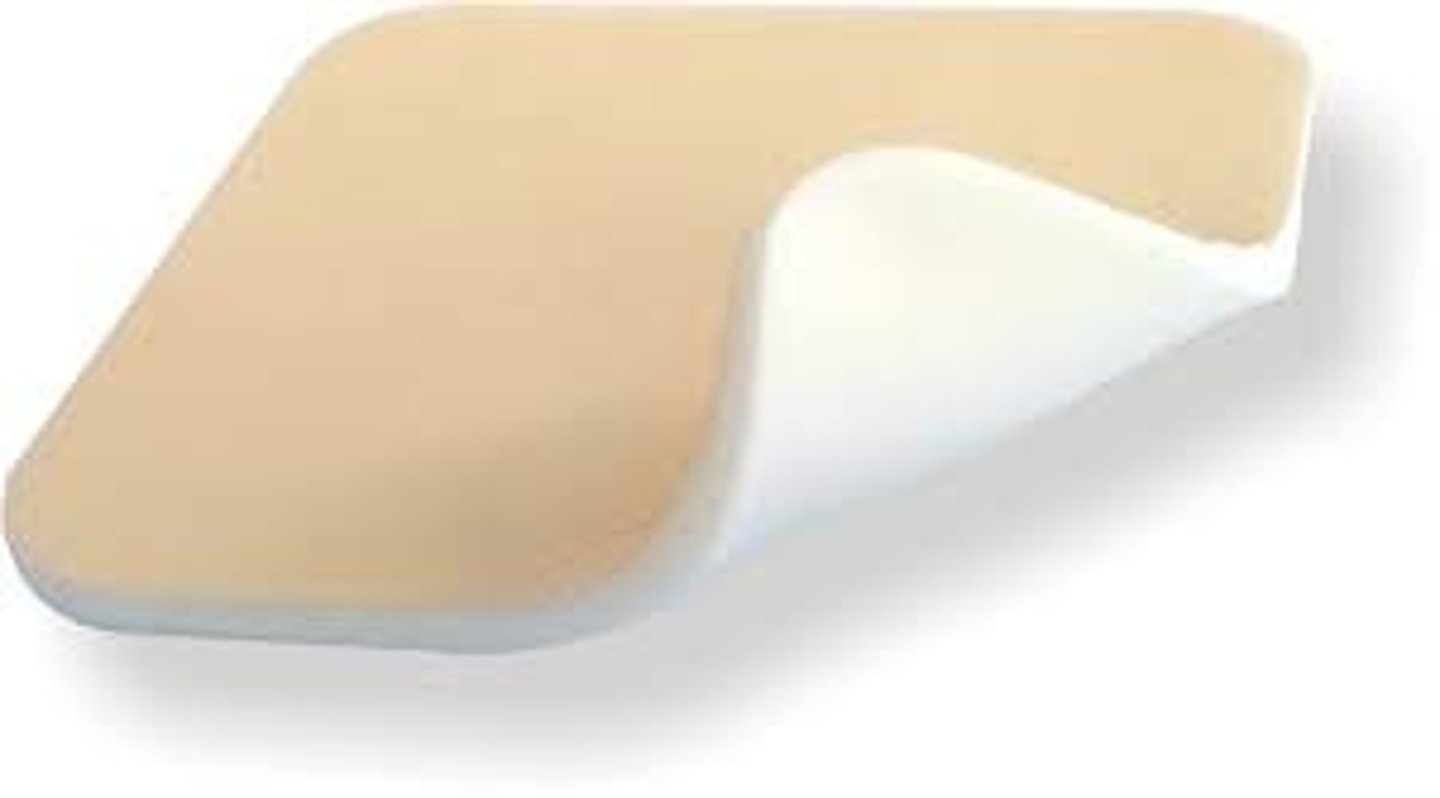

Semipermeable foam may have adhesive borders for
absorbing exudate
Semipermeable foam waterproof outer layer
o to prevent strike through drainage
strike through drainage
drainage visible through last layer of dressing (unable to be contained by the dressing)
Do we use semipermeable foams on infections?
No, unless changed daily
Semipermeable foams advantages
o Keeps wound moist & warm
o Provides cushioning
o Permeable to gas but not bacteria
o Promotes autolytic debridement
o Can be left in place for several days
o Can be used under compression dressings
Semipermeable foams permeablity
Permeable to gas but NOT bacteria
Semipermeable foams absorption
Will absorb moderate amount of drainage but not dry out a minimally draining wound if left on for extended period of time
Semipermeable foams disadvantages
o Adhesive type may damage Periwound
o Can roll at edges
o May need secondary dressing
o May macerate Periwound as it absorbs fluid if it doesn't have wicking qualities
Wicking qualities
ability to draw moisture away from the skin and towards the outer surface of the fabric, where it can evaporate more quickly
Hydrofibers
composed of carboxymethylcellulose fibers form gel after contact with exudate
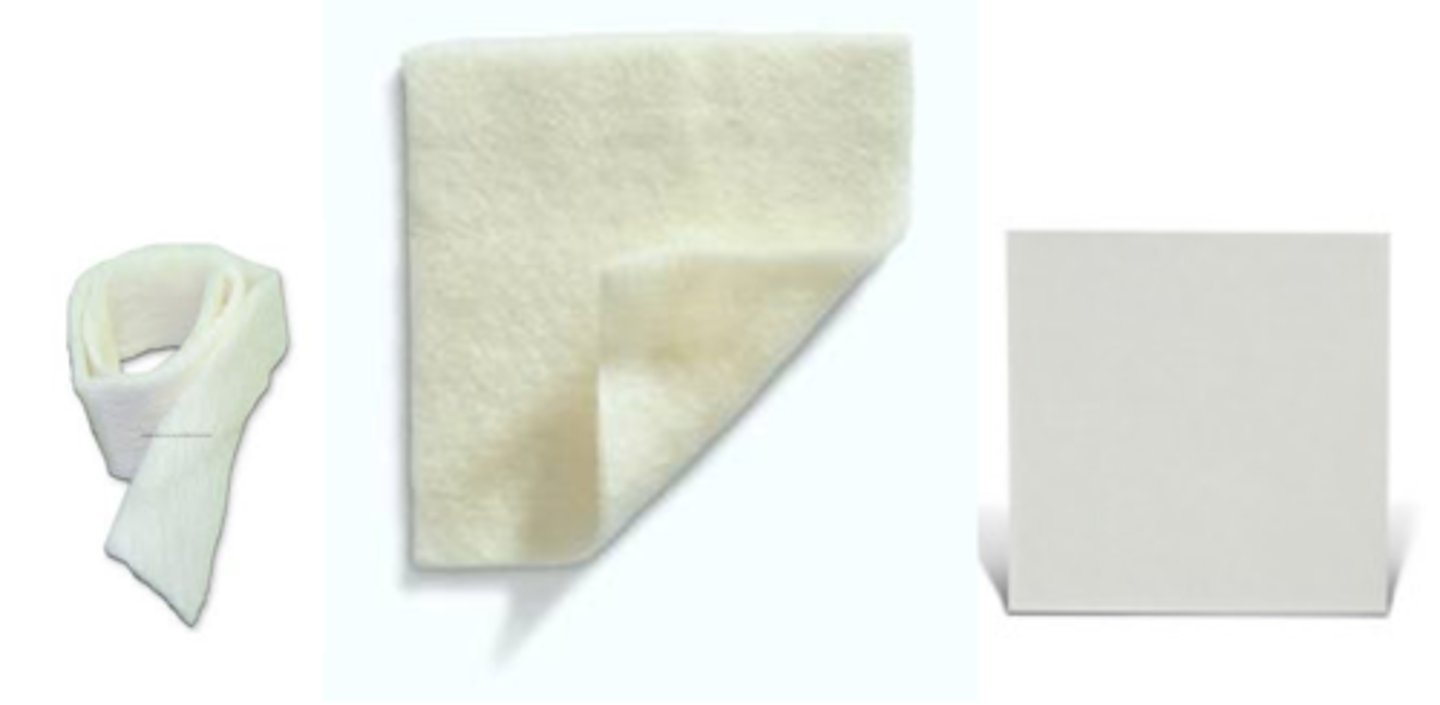

Hydrofibers are neither
o an alginate or a hydrocolloid but it has benefits of both
Hydrofibers advantages
o Absorbs moderate to large amounts of drainage
o Works well under compression dressings
o Can stay in place for several days
o Interaction with wound exudate forms a gel
Hydrofibers disadvantages
May fuse to bloody wound base
can dehydrate the wound
Hydrocolloids
Adhesive wafer composed of gelatin, pectin, and carboxymethyl-cellulose
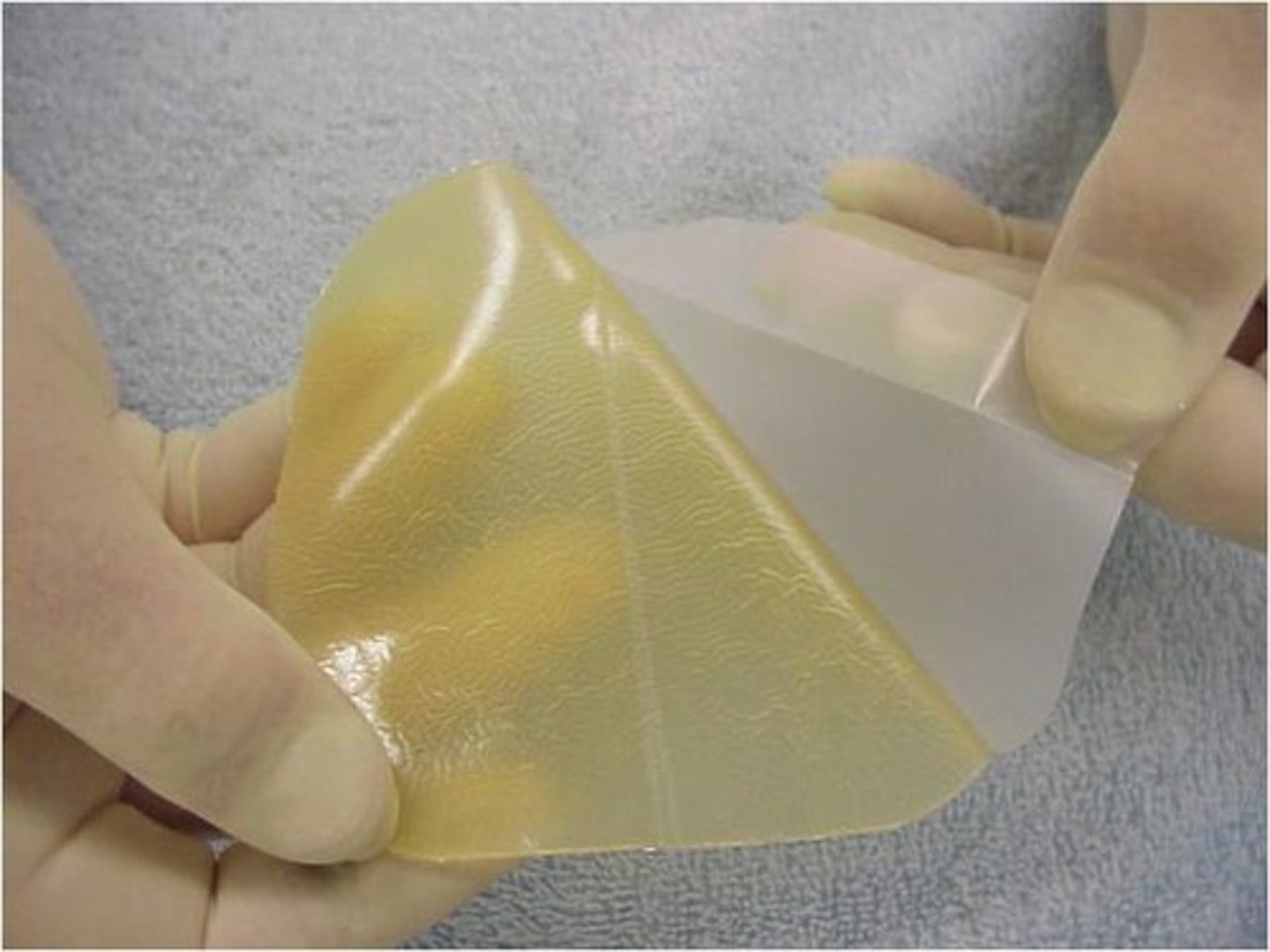

What should you do before application of hydrocolloid?
Warm it first
Do you use hydrocolloids for infected wounds?
No
Duoderm
hydrocolloid dressing that is a barrier against incontinence and MRSA, hep-B, HIV, and pseudomonas
Should you use hydrocolloids for exposed tendons and fasica?
No its sticky
Hydrocolloid advantages
o Impermeable to bacteria and incontinence/ waterproof
o Encourages autolytic debridement
o Absorbs minimal amount of drainage
o Provides thermal insulation
Hydrocolloid disadvantages
Adhesive can damage periwound
Edges can roll
can cause hypergranulation
Pectin causes an odor upon removal (can be mistaken for infection)
Leaves residual in wound bed
How can using a hydrocolloid be mistaken as infection?
The pectin from the hydrocolloid leaves an odor which can be mistaken as infection
Can hydrocolloids be used on skin
yes
Hydrogel sheets are very
occlusive
Semipermable films allow for
gas exchange
Hydrogels
Water, glycerine based, sheet, or impregnated gauze
Hydrogels may require what else
skin sealant for periwound protection
Hydrogrels if not covered correctly
will dehydrate
Hydrogels used for infection?
no
Hydrogels commonly used for
Blisters, abrasions, skin tears, burns, donor sites, mastitis
Mastitis
inflammation/infection of the breast; most commonly occurs in women who are breastfeeding
Hydrogels are good for use with
arterial wounds
Hydrogel advantages
o Donates moisture to wound
• Good for arterial wounds
o Painless removal
o Can soften eschar
Application of amorphous hydrogel
Put hydrogel on applicator and then put applicator into wound
Change applicator each time applied
Hydrogels disadvantages
o Minimal absorptive qualities
o Non-adhesive requiring secondary dressing
o May macerate Periwound
Semipermeable films
transparent polyurethane membrane, breathes like skin allowing vapor exchange
Semipermeable films good for
minimally draining wounds
abrasions
skin tears
Partial thickness wounds
Too much drainage with semipermeable films can result in
the wound stopped air diffusion and can cause maceration
Semipermeable films application
Apply w/o tension or wrinkles
Semipermeable films for infection?
no
Semipermeable film indications for change
if wrinkle/channel develops
New varieties of semipermeable film
combine film with hydrocolloid or foam aka tegaderm
Semipermeable film advantages
o Self-adhering
o Can see wound
oWaterproof/incontinence proof
o Impermeable to bacteria
o May be used as secondary dressing
How long can a semipermeable film last for?`
5-7 days
Semipermeable disadvantages
o No absorptive qualities
o Poor thermal insulation
o May tear off periwound skin
Silicone dressing
Newer technology, thin and thick foam

silicon dressing brand name
mepilex
mepilex
foam dressing for wounds and ulcers
What dressing is beginning to replace hydrocolloids and transparent films?
Silicone dressings
Silicone dressings used for
Skin tears
Fragile skin (elderly)
Skin grafts
Silicon dressings can be used prophylactically to
reduce friction and sheer injuries