Geog Korea Chapter 10 & 11
1/78
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
79 Terms
Gangbuk
north of the Han River
Gangnam
South of the Han River
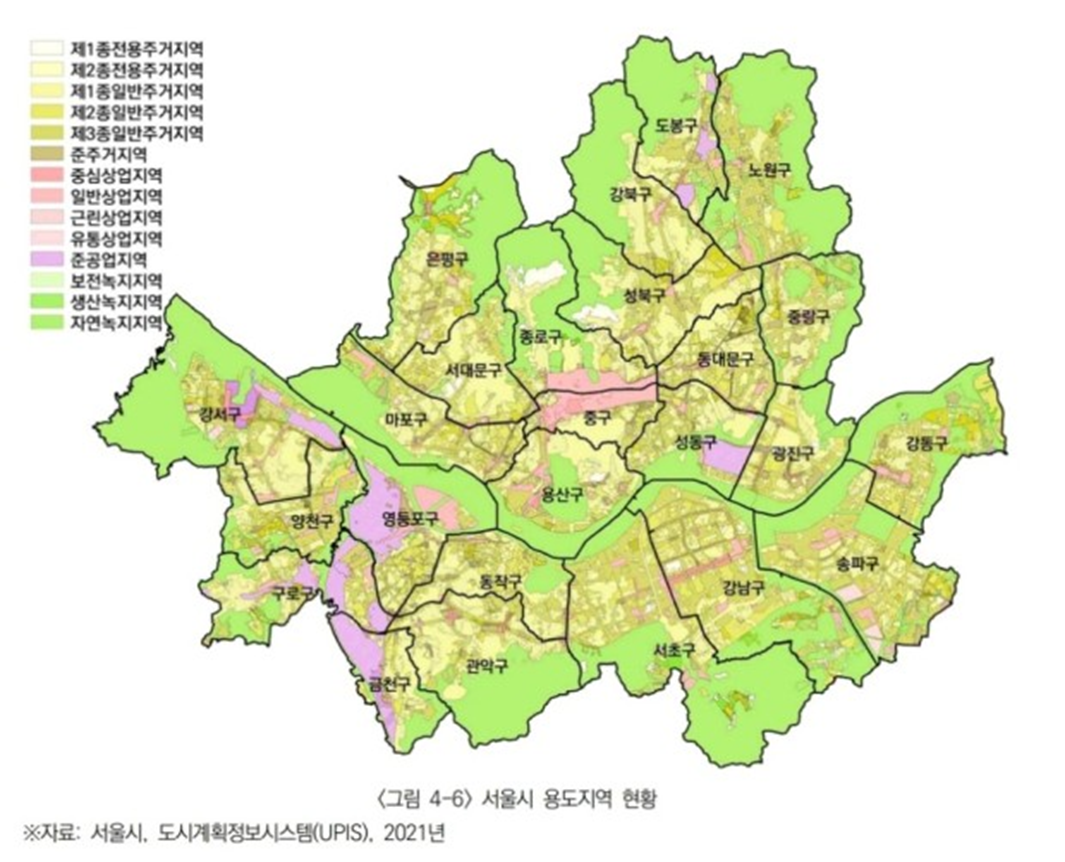
South Korea Urban Planning in the 1970s
•Classifying types of land use and implementing green belt
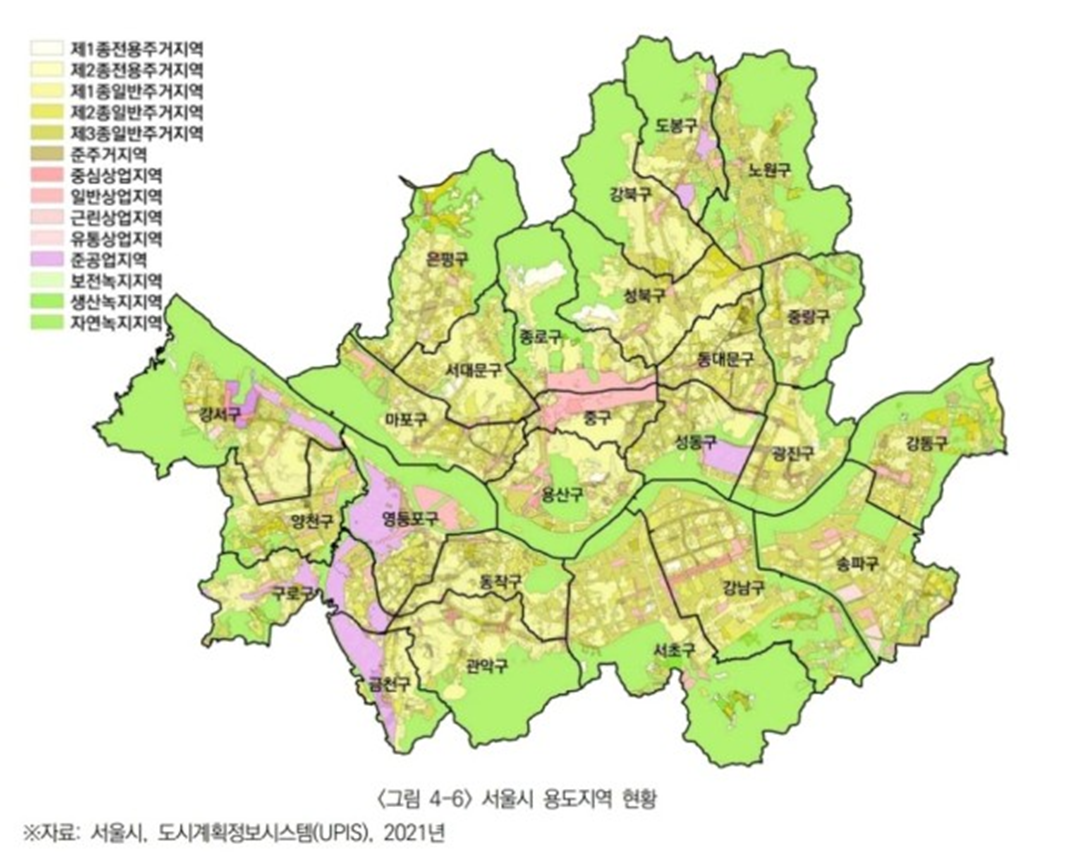
South Korea Urban Planning in the 1980s
•Systematizing basic urban planning over 20 years periods
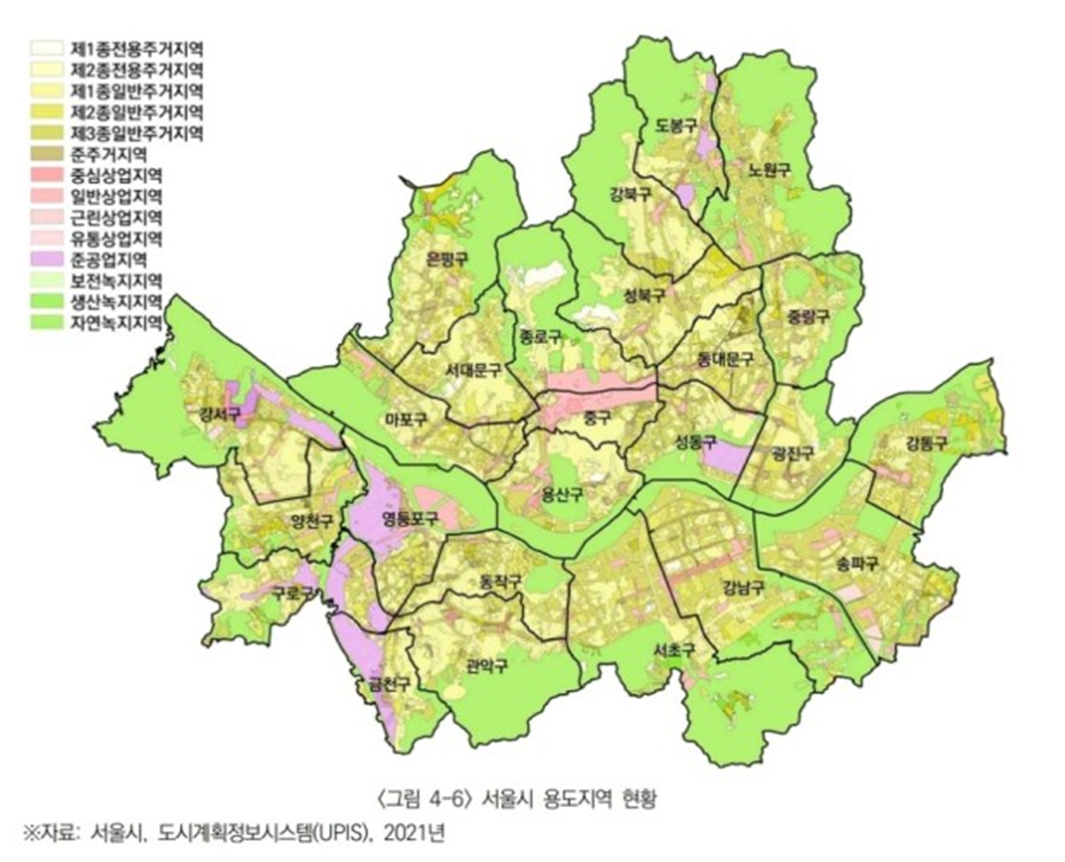
South Korea Urban Planning in the 1990s
•Focusing on balanced development and quality of life
•Sustainable urban planning with local citizen’s participation
CBD Redevelopment
•Land use change from residential to commercial area
•Efficient land use by skyscrapers.
•Parking space and pedestrian space
•Public space (urban parks)
Residential Redevelopment
•Shift of residential areas from single family to apartments
•Razing deteriorated residential areas
Industrial Redevelopment
•Renovation of dilapidated industrial complexes and traditional markets
Positives of Redevelopment
Efficiency
Urban landscape
Transportation infrastructure
Better quality of life
Negatives of Redevelopment
Dismantled community
Gentrification conflict
Constructive Redevelopment Strategies
Partnership among local people, government and developers
Distributive and procedural justice
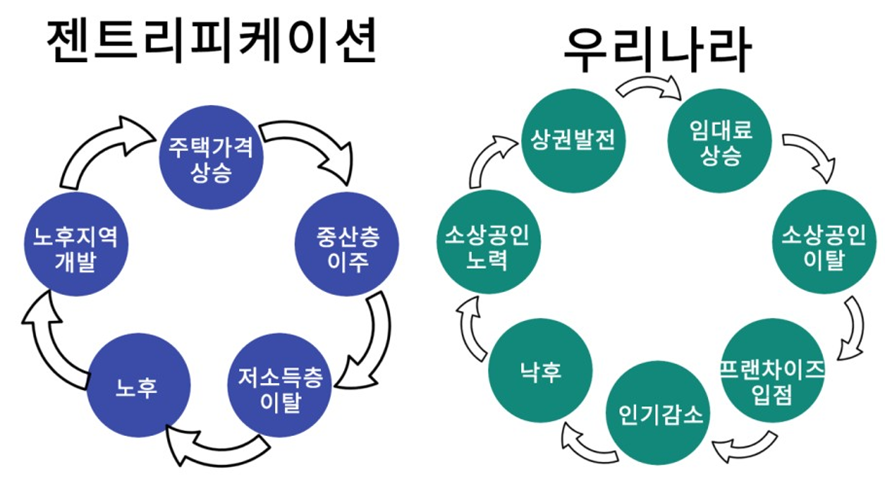
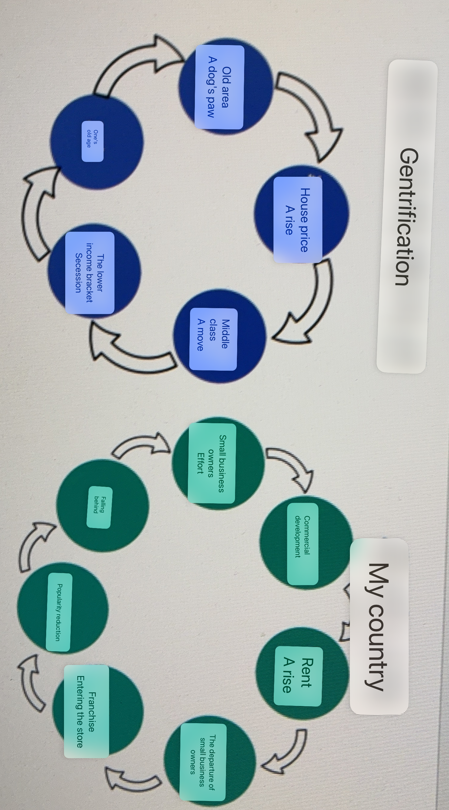
Gentrification
a process in which a poor area (as of a city) experiences an influx of middle-class or wealthy people who renovate and rebuild homes and businesses and which often results in an increase in property values and the displacement of earlier, usually poorer residents
Regional Development
•Improving quality of life
•Maximizing (economic) growth
•Minimizing regional polarization
Growth pole direction
top-down
Balanced direction
bottom up
growth pole countries
developING
Balanced countries
developED
growth pole method
focused (concentrated) Investment
balanced method
Investment for depressed regions
Goal of growth pole
•Maximizing economic growth
•Ripple effect
Goal of Balanced
•Economic equity
•Balanced development
Strengths of Growth Pole
Efficient investment
Strengths of Balanced
Democratic investment
Weaknesses of Growth Pole
•Economic polarization
•Lack of local people’s participation
Weaknesses of balanced
•Inefficiency
•Regional collective selfishness
FIRST Comprehensive National Physical (Land) Development (South Korea) - type
Growth Pole/Top Down
FIRST Comprehensive National Physical (Land) Development (South Korea) - period
1972~1981
FIRST Comprehensive National Physical (Land) Development (South Korea) - policies
•Exports-oriented industrialization
•Water resource development
•Social capital (infrastructure)
SECOND Comprehensive National Physical (Land) Development (South Korea) - type
Region-Wide
SECOND Comprehensive National Physical (Land) Development (South Korea) - period
1982~1991
SECOND Comprehensive National Physical (Land) Development (South Korea) - policies
•Population dispersion
•Welfare
•Natural Environment
THIRD Comprehensive National Physical (Land) Development (South Korea) - type
Balanced
THIRD Comprehensive National Physical (Land) Development (South Korea) - period
1992~1999
THIRD Comprehensive National Physical (Land) Development (South Korea) - Policies
•Promotion of regional development
•New-industrial zone
•Inter-Korean exchange
FOURTH Comprehensive National Physical (Land) Development (South Korea) - type
Green & balanced
FOURTH Comprehensive National Physical (Land) Development (South Korea) - period
2000~2020
FOURTH Comprehensive National Physical (Land) Development (South Korea) - policies
•Globalization
•Climate change
•Sustainable
FIFTh Comprehensive National Physical (Land) Development (South Korea) - type
from development to management
FIFTh Comprehensive National Physical (Land) Development (South Korea) - period
2020~2040
FIFTh Comprehensive National Physical (Land) Development (South Korea) - policy
•Population decrease
•Climate change
•Utilitarianism
Negative Side Effects of Development
in South Korea
Spatial Inequalities between capital and other regions due to top down strategy
Negative Side Effects of Development
in South Korea
Spatial Inequalities between urban and rural regions due to urban focused growth
•Environmental Inequality
Spatial discord between environmental beneficiaries and victims due to development
NIMBY
Not In my backyard
PIMBY
Please in my backyard
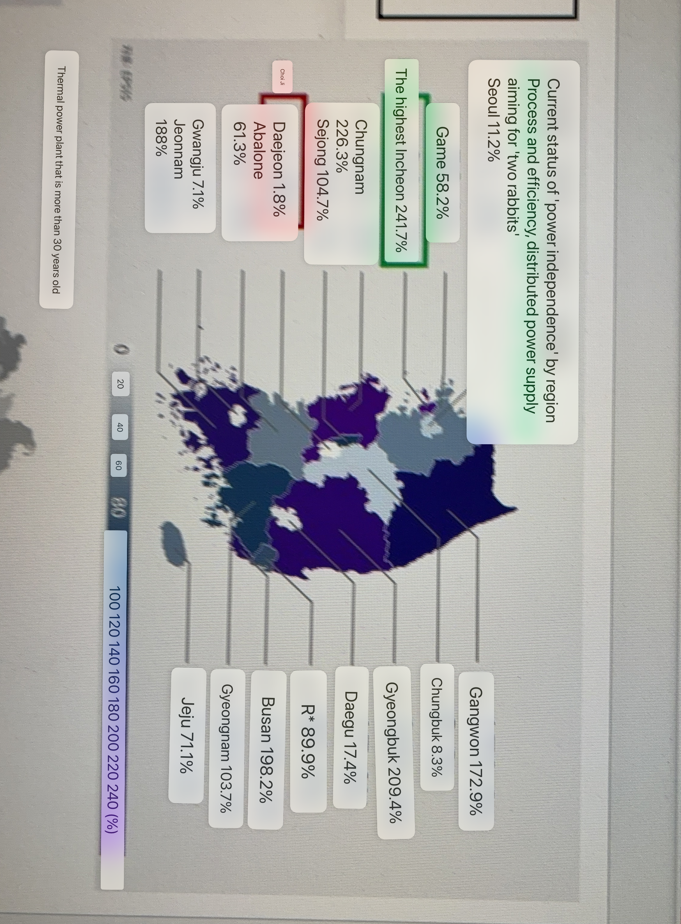
What region has the highest power independence
Incheon
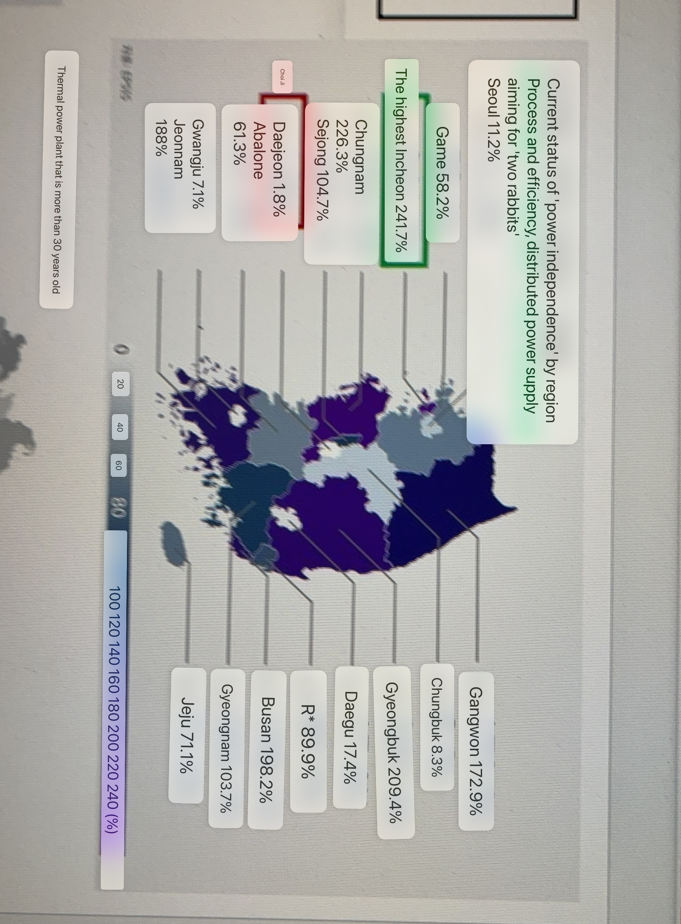
What region has the lowest power independence
Daejeon
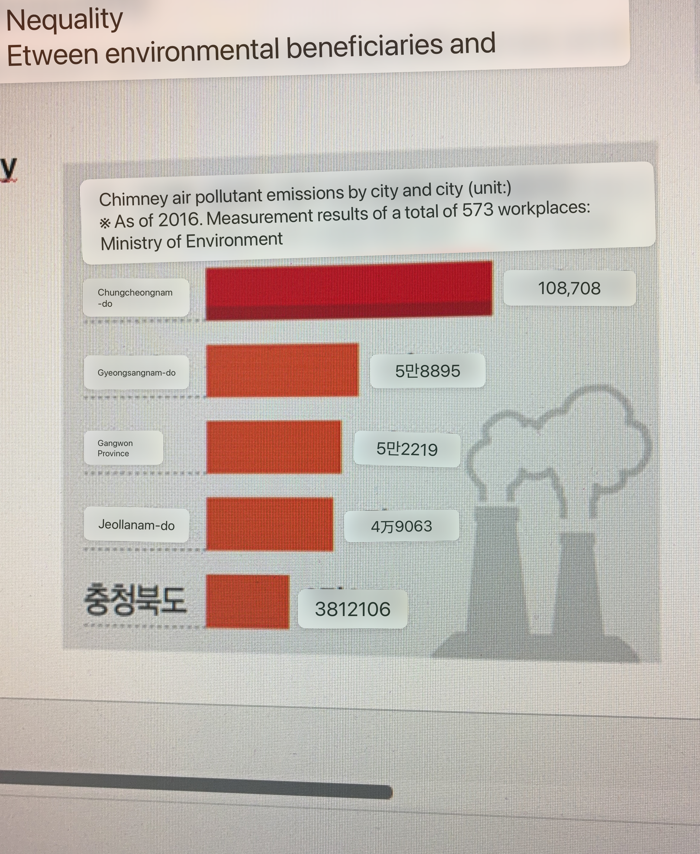
What region has the worst air pollutant emissions
Chungcheongnam-do
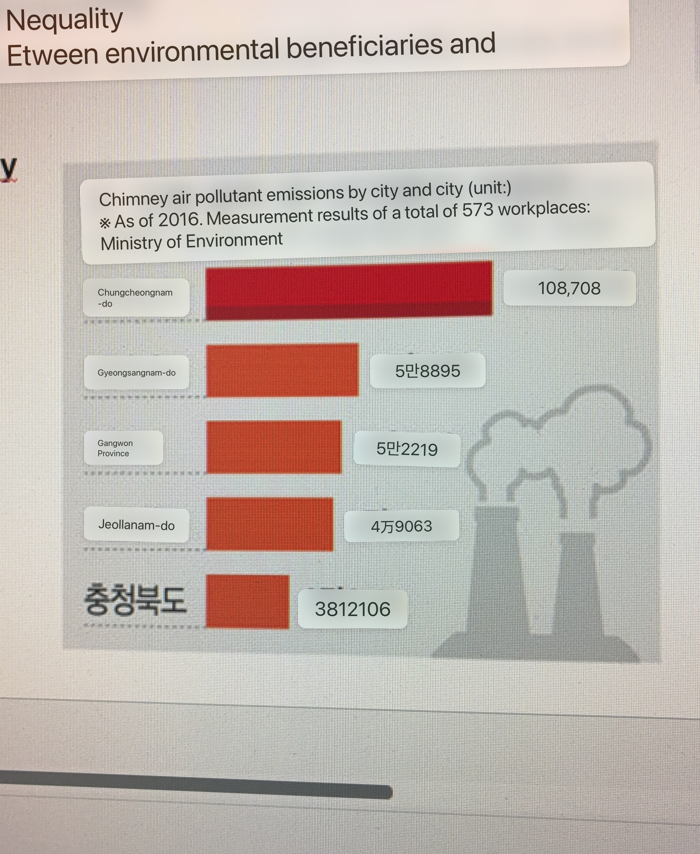
What region has the best air pollutant emissions
Chungcheongbuk-do
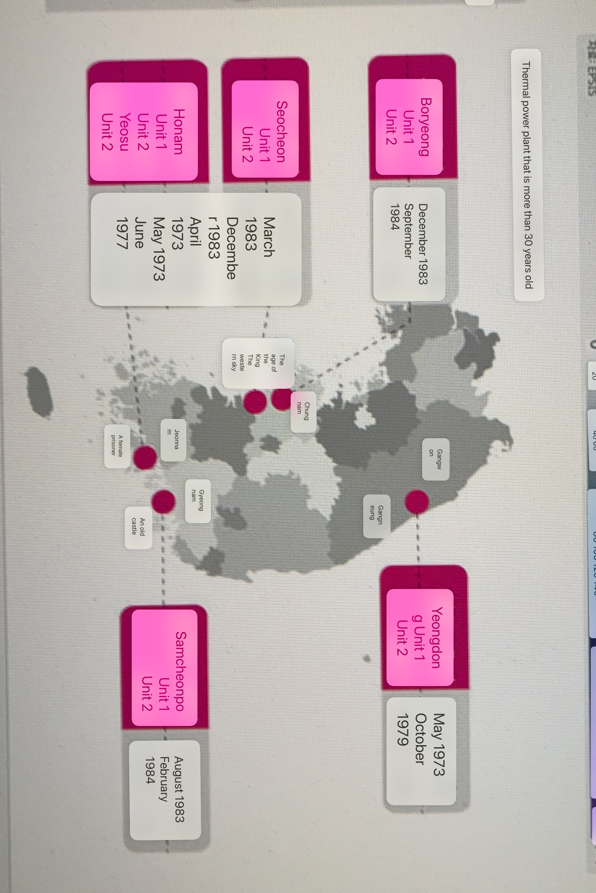
Old power plants in South Korea
Gentrification Diagram
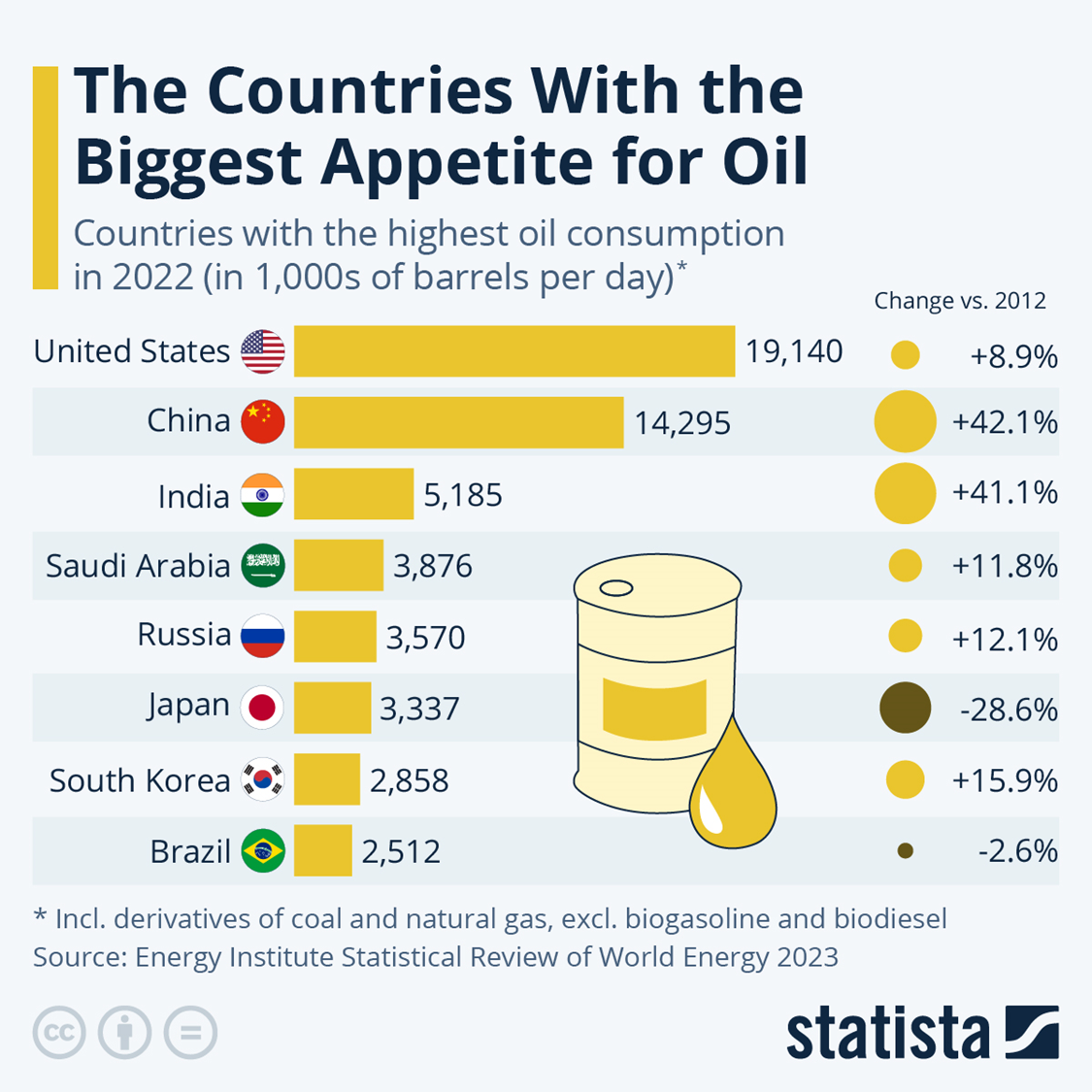
Leonard Maugeri
Theorized we will use up all oil in 20 years

Even though SK does not produce much oil, it is in the top 10 consumer countries, and has changed ____ from 2012
15.9%
resources have a _________ based on technology, economic conditions and cultural backgrounds
changeable value
which mineral does SK have the most of?
Limestone
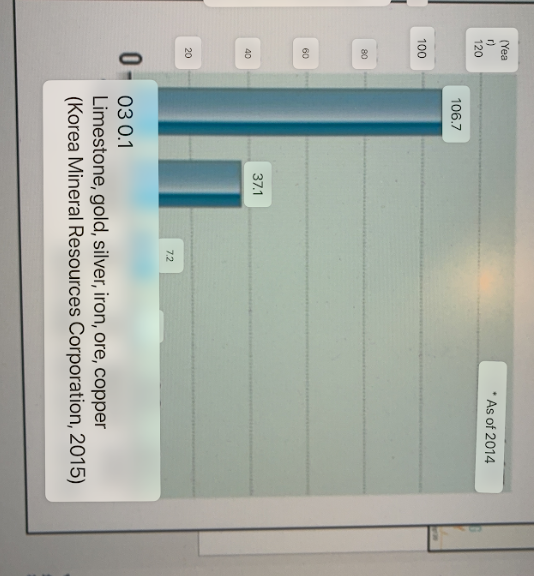
Resource nationalism
refers to the various forms of state involvement in extracting, processing, and marketing natural resources. It is a neutral concept that aims to give resource-rich countries more control and a higher share of profits from their natural resource wealth.
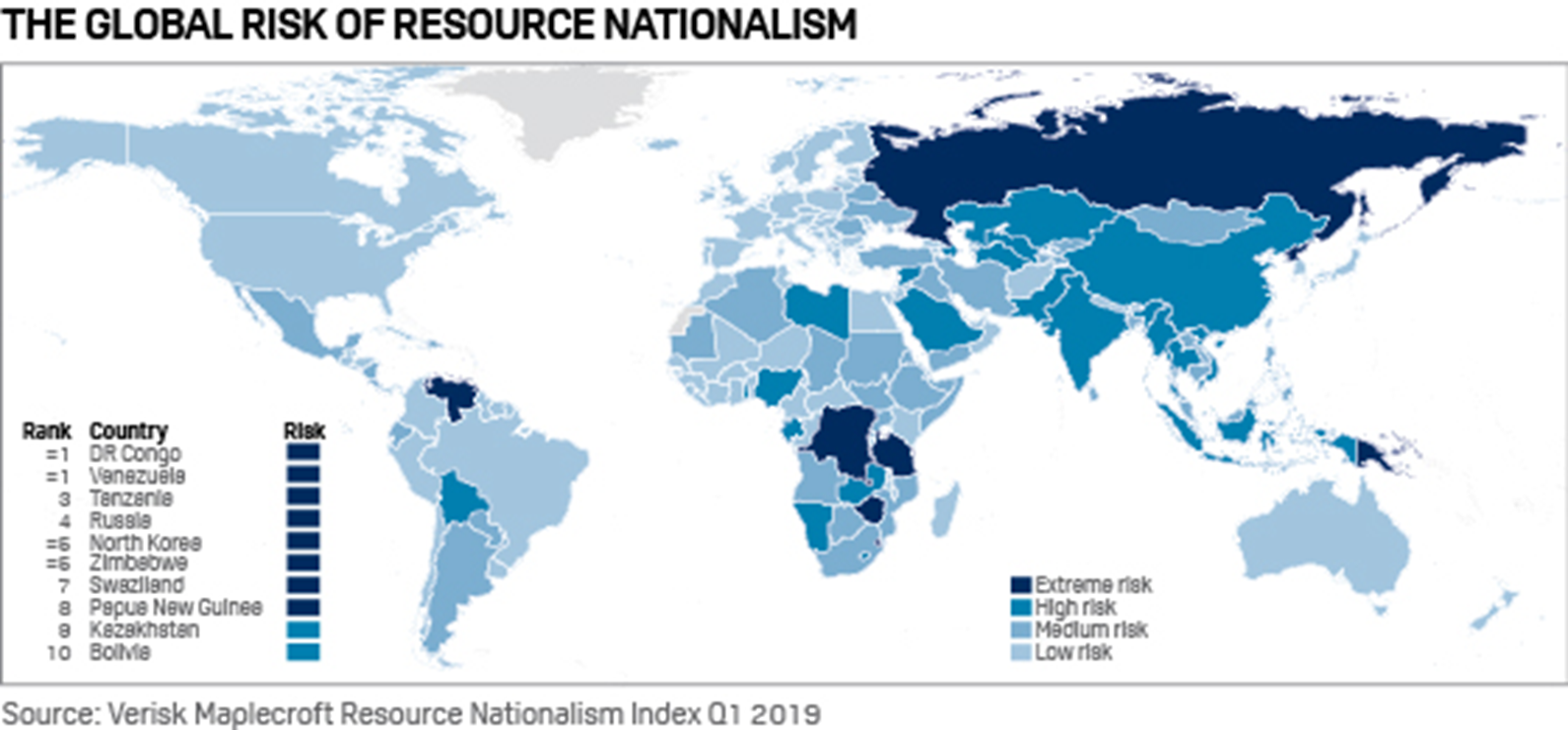
What country has the highest risk of resource nationalism?
Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC)
Why does DRC have the highest risk of resource nationalism
Cobalt mining for battery and electronic components
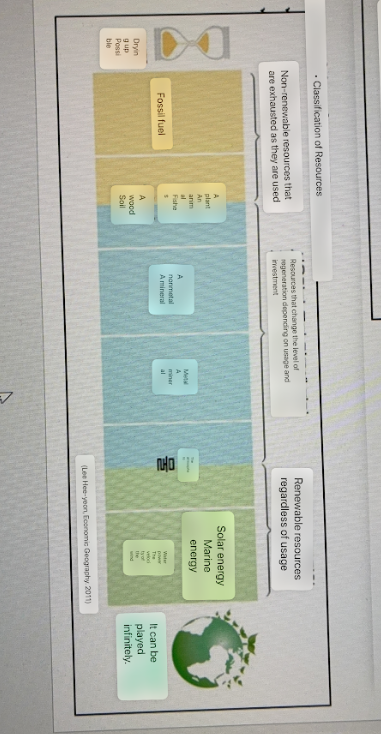
Classification of resources
natural, human, cultural
renewable, nonrenewable, inbetween
South Korea has _____ non metallic minerals than metallic
more
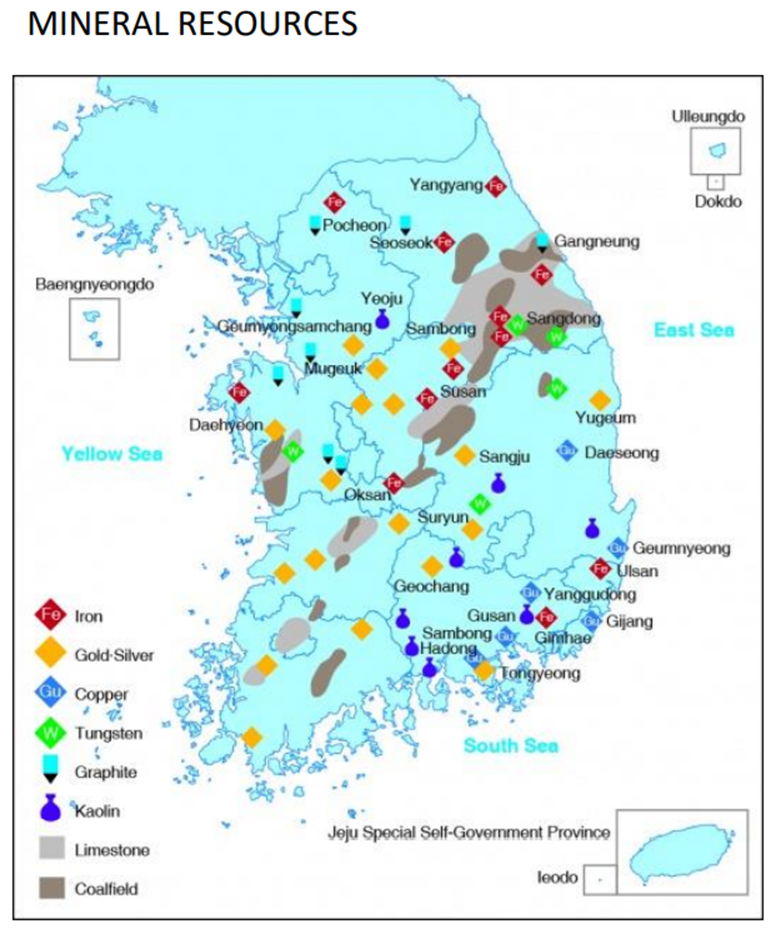
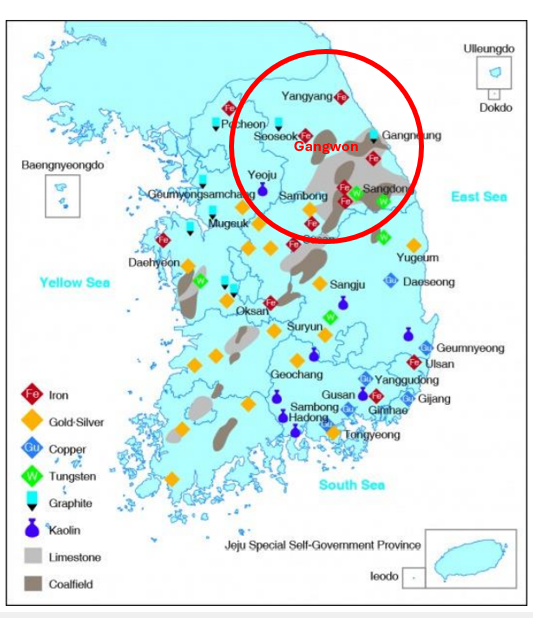
Iron Ore Provice
Gangwon
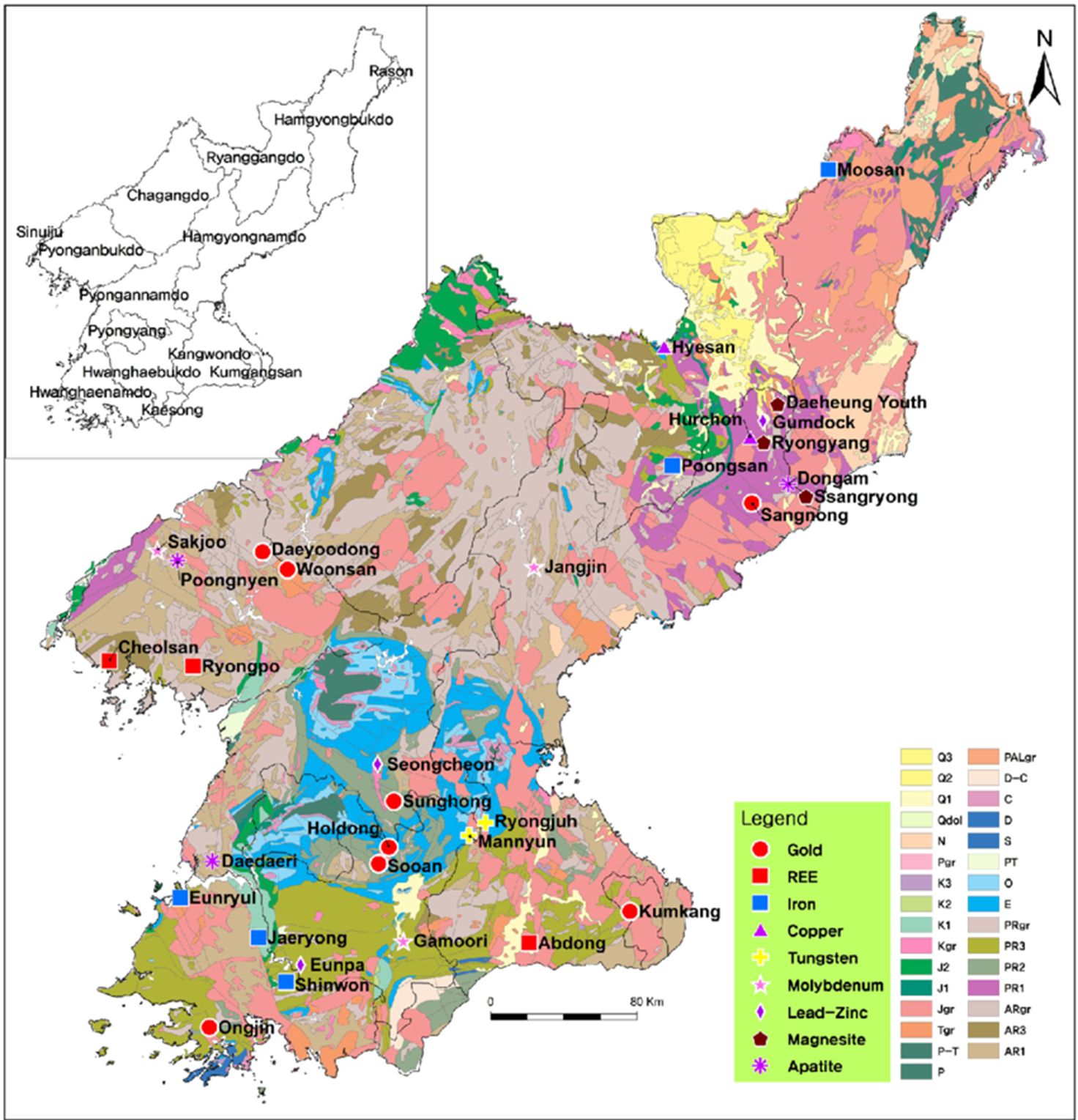
Iron Ore is mainly in
North Korea
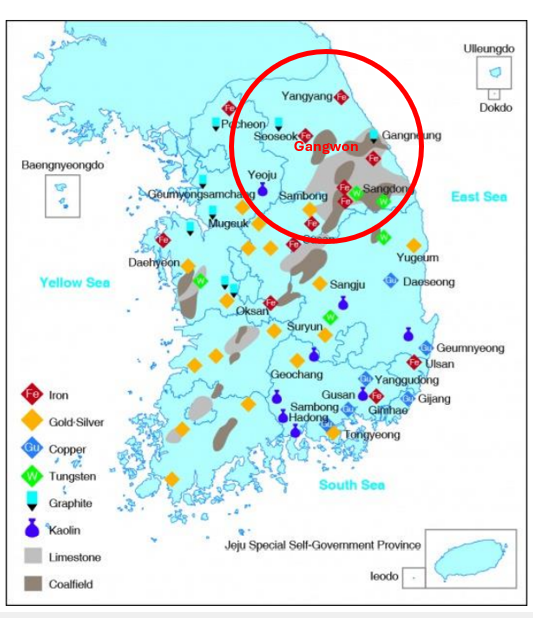
Tungsten Province
Gangwon
Tungsten Uses
Special steel, alloys
what two countries export a lot of tungsten
SK and China
Limestone provinces
Gangwon, Chungbuk
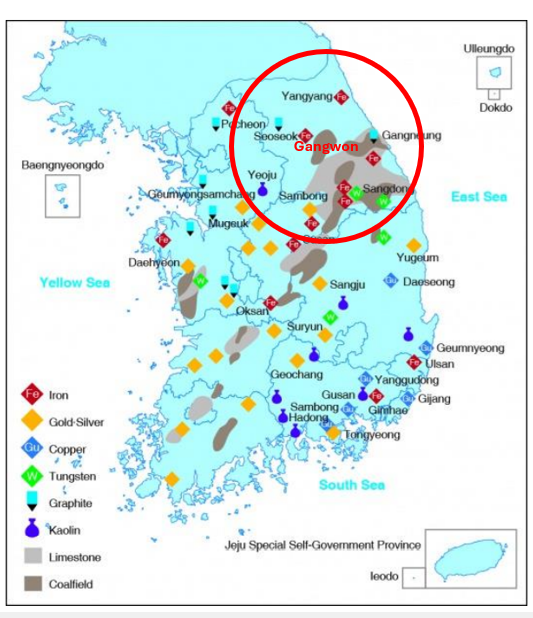
Limestone uses/advantages
Cement, long lifespan, high amount of production
limestone is found in the _____ layer
paleozoic
kaolin provinces
Gangwon, Kyungbuk, Kyungnam
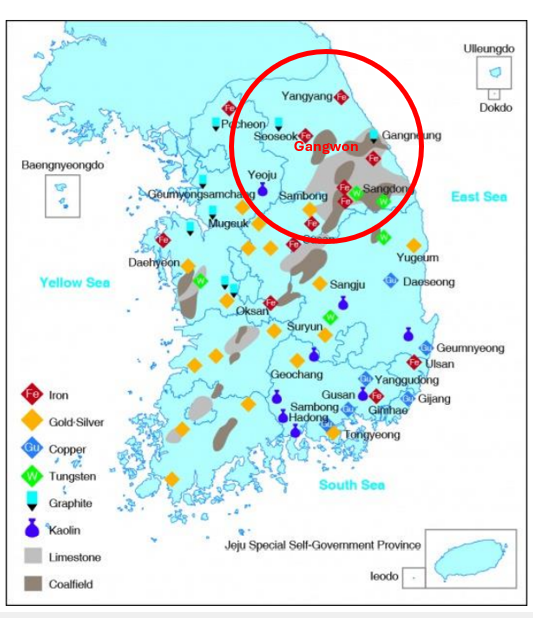
kaolin uses
Porcelain, brick, cosmetics
1960s energy source
coal and firewood
1970s-80s energy source
Oil
1990s and beyond energy source
moving to natural gas and renewable energy
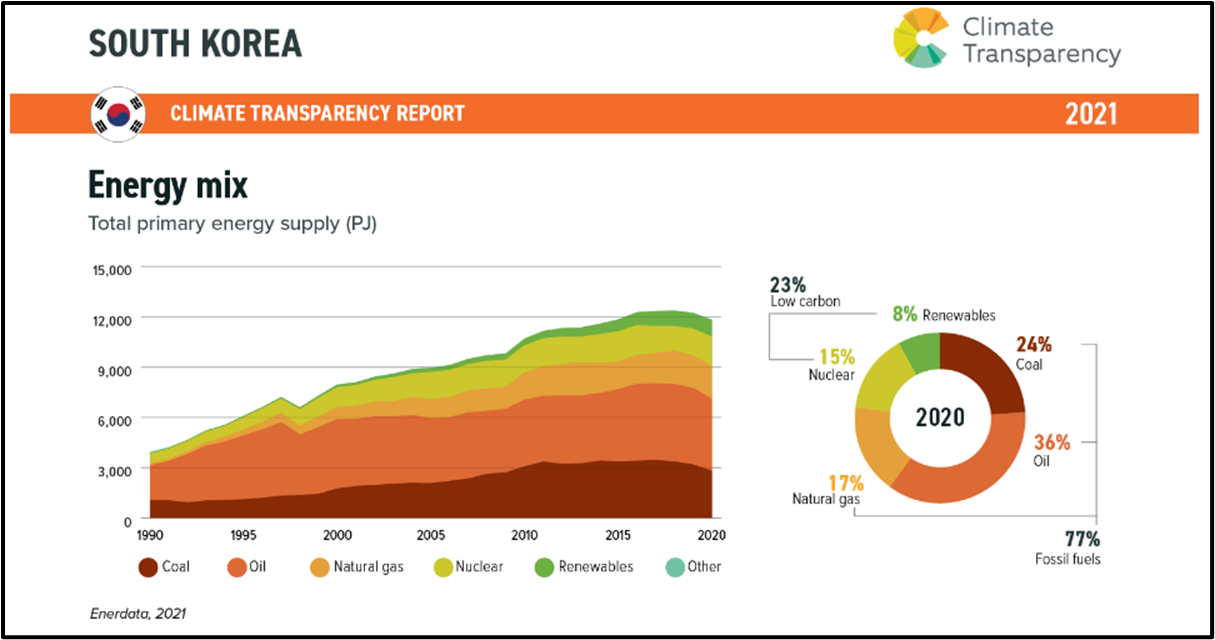
elecricity is mainly produced by
steam power and nuclear
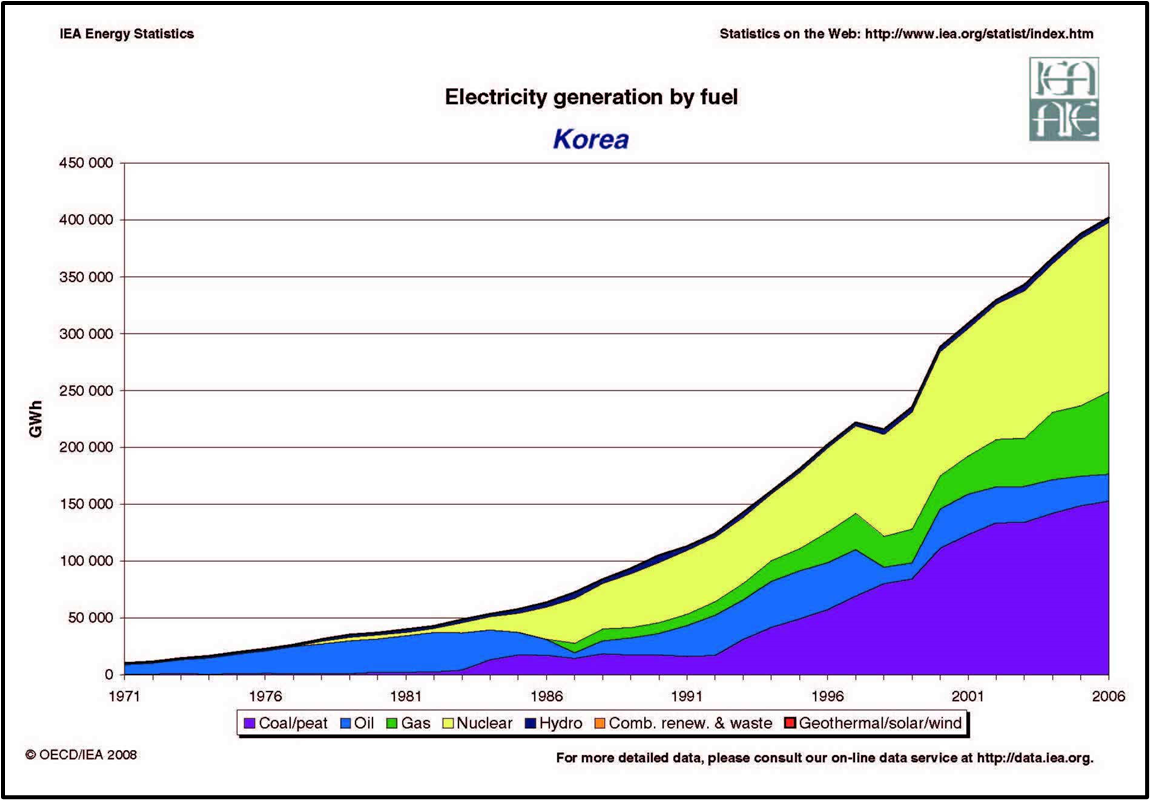
Geography of power plants
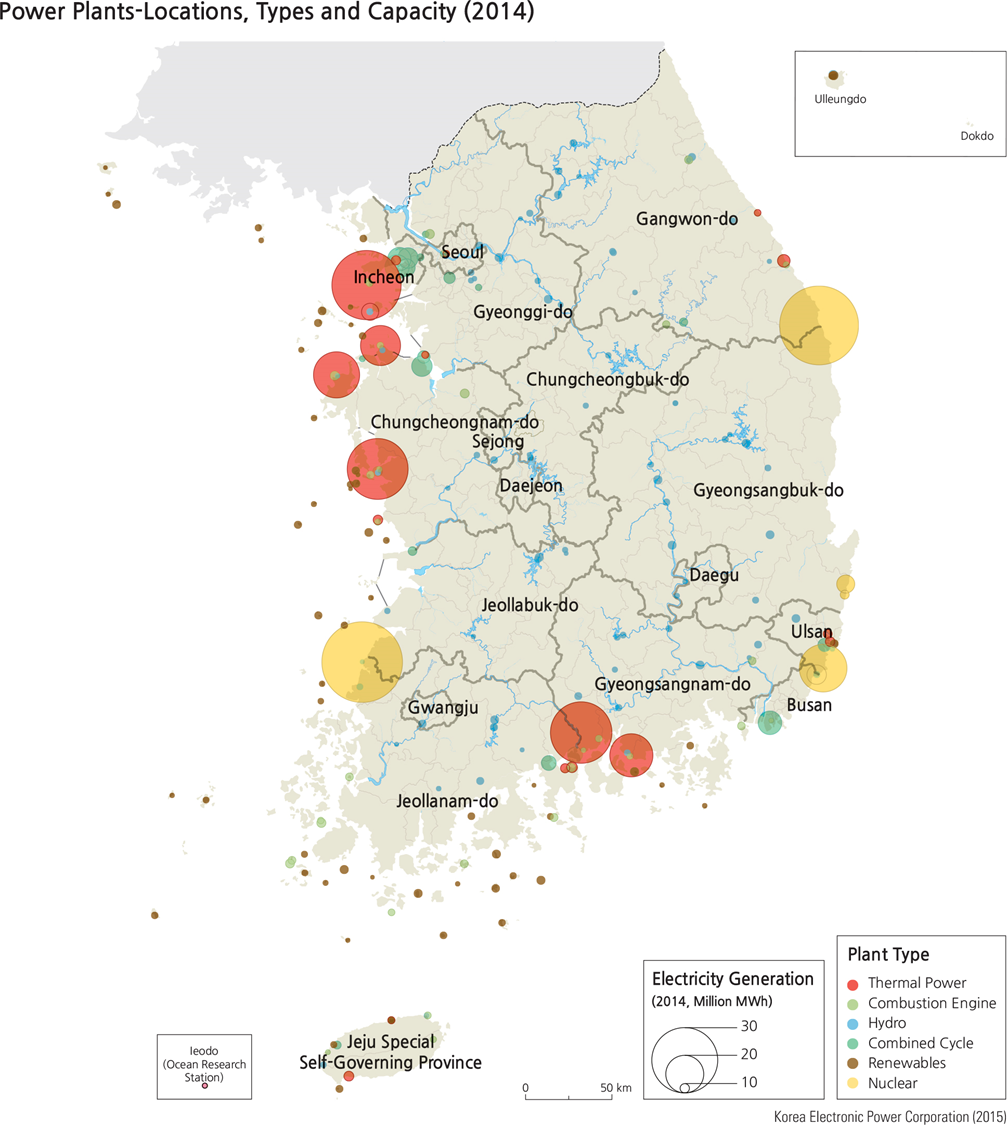
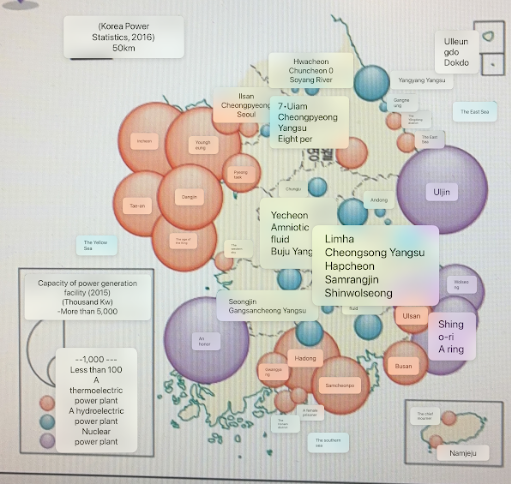
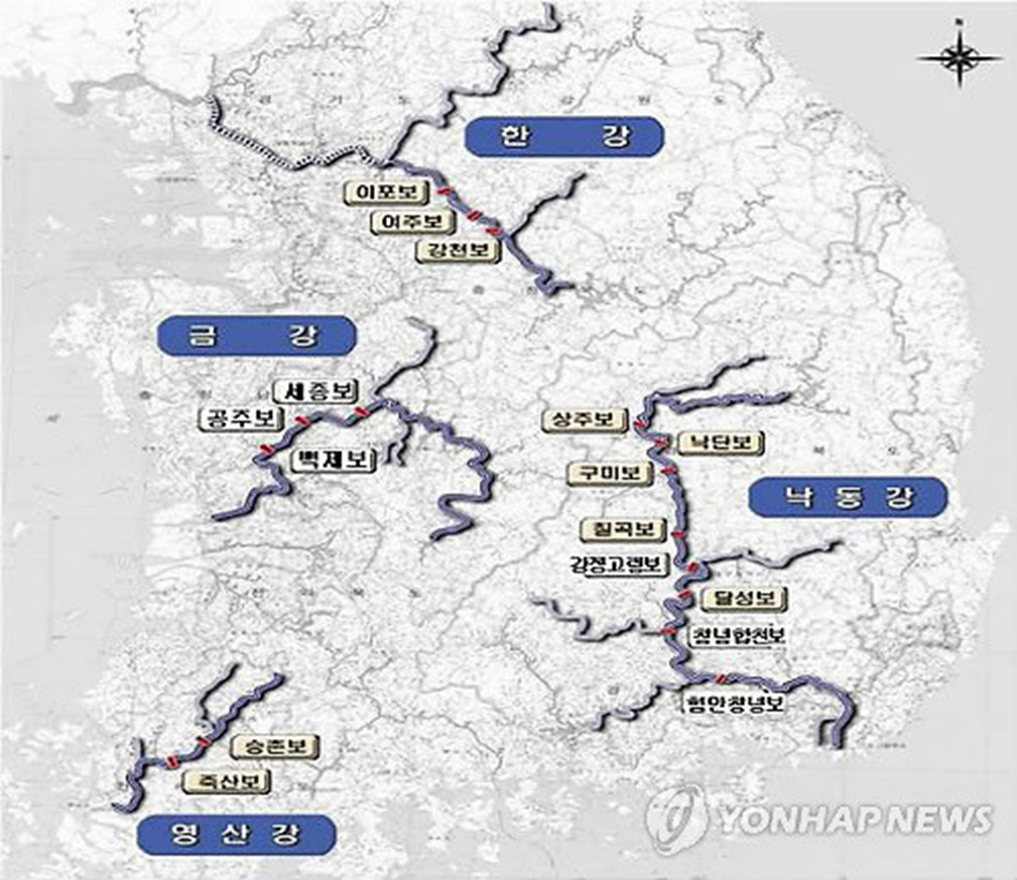
Where are hydroelectric plants located?
Han, Nakdong, Geum, and Youngnsan Rivers where there is large stream flow
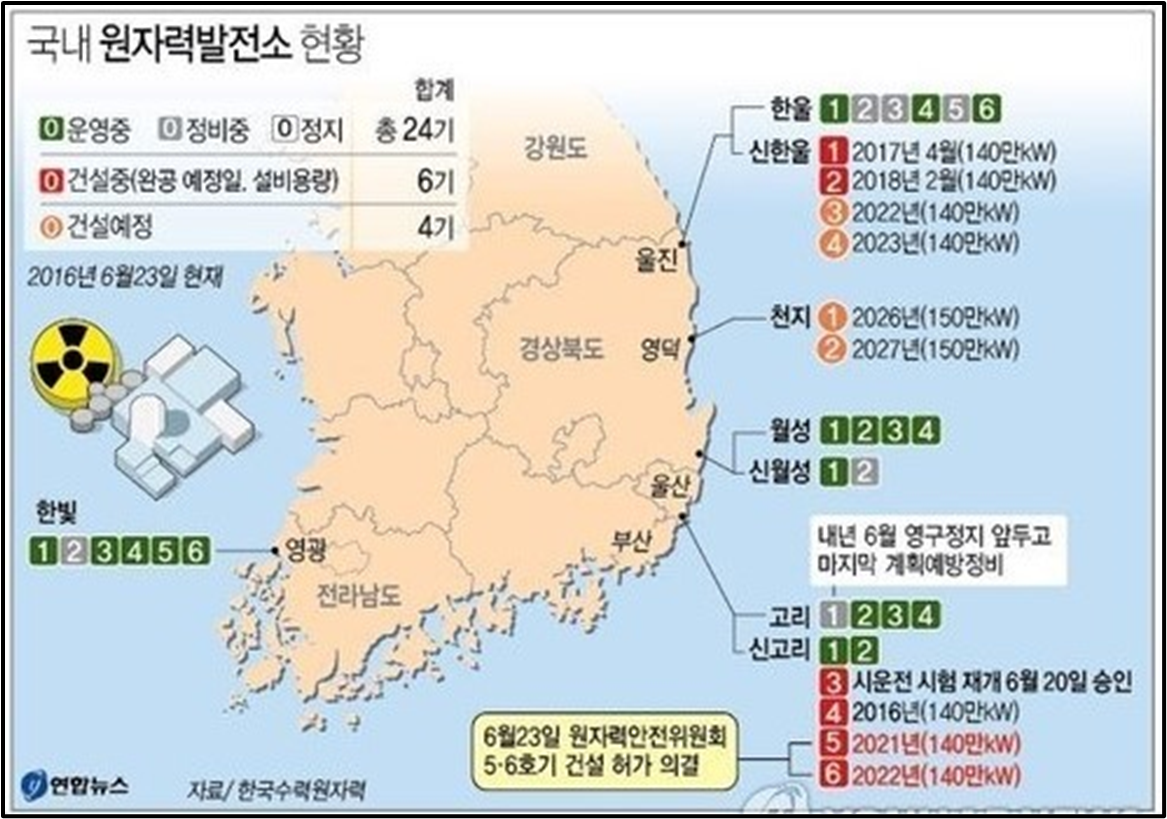
Where are nuclear plants located
•Uljin, Gyungju, Busan, Ulsan, where there is firm ground and water accessibility (coast)
where is steam power generated
•Free from natural environment
•Raw material-oriented
•Market-oriented (doesnt make sense but thats what the powerpoint says)
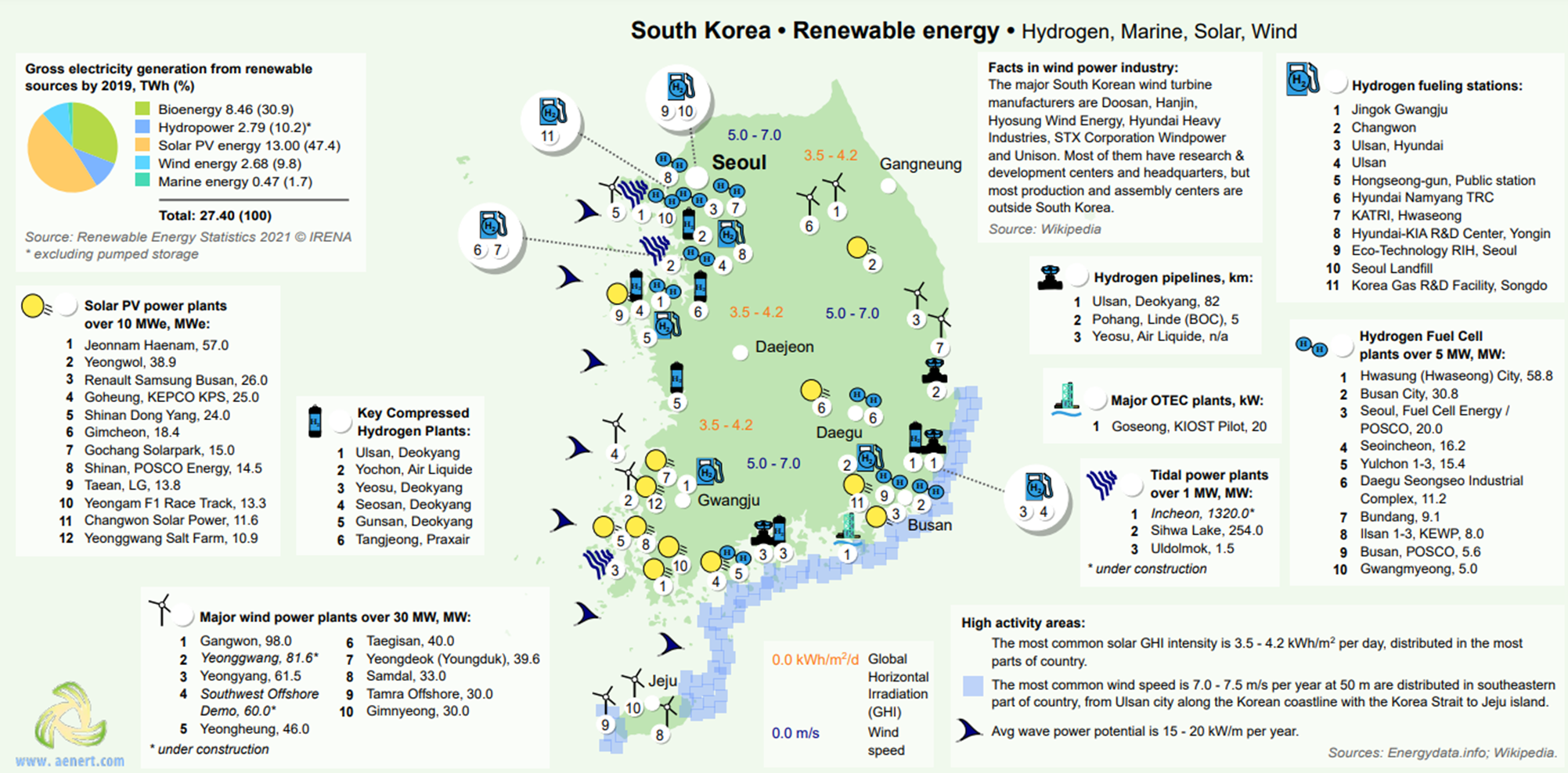
renewable energy geography