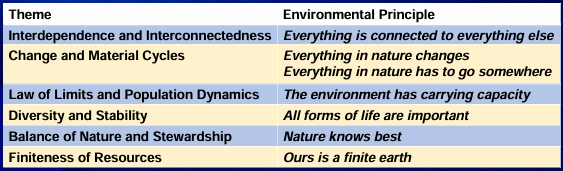
(1) Finiteness of Resources
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Mining
It is a process of mineral extraction from the surface of the Earth, either from land or from the seas.
Mineral Deposit
A confirmation of its presence
There is a natural occurrence of a useful material
Ore Deposits
It must denote a mineral deposit of sufficient extent and concentration for it to be extracted
Philippines Mineral Deposits
Data from the Philippine Statistic Authority revealed that copper accounted for the bult of metallic mineral resources of about 72 while nickel at 16%.
Philippines Mineral Deposits
For non-metallic mineral resources, limestone and marble accounted for 39 and 29%, respectively.
Philippines Mineral Deposits
Gold reserves of the Philippines amounted to about 240 metric tons of gold metal.
Philippines Mineral Deposits
is also has one of the largest chromite deposits in the world.
The Marcopper Mining Disaster
Occured in the island of Marinduque in 1996 is one of the worst thing and environmental disaster in Philippine history.
Fossil Fuel Depletion
Is the decline of available fossil fuel in a well, field or geographic area.
Fossil Fuel Depletion
The reality is not that oil is depleting but rather that we are transitioning from a period of easily-accessible oil at low prices to an era supply is finite.
Deforestation
Is caused by shifting cultivation, land use conversion, forest fires, illegal logging, and 40 million m3 of fuelwood harvested each year.
Importance of Forest Ecosystem:
Source of food
Source of raw materials
Climate control and modification
Disaster risk reduction
Source of medicine
Tourism value
Air and water purification
Social and cultural value
Overfishing
This happens when a particular type of fish from a body of water is removed at a higher rate than they replenished in time of given area.
Poverty, Hunger and threats to Food Security
With the increasing global population, the levels of natural resource depletion are also increasing. As a consequence, poverty rises. Poverty is a deprivation of one’s basic needs due to lack of money to buy services or a lack of access to services.a
Undernourishment
The share of the population that is undernourished
Ex.
- Whose caloric intake is insufficient:
Child wasting
Child stunting
Child mortality
Child Wasting
The share of children under the age of five who are wasted (i.e., who have low weight for their height, reflecting acute undernutrition)
Child Wasting
The share of children under the age of five who are wasted (Low weight for their height, acute undernutrition)
Child Stunting
The share of children under the age of five who are stunted (Low height for their age, chronic undernutrition)
Child Mortality
The mortality rate of children under the age of five (Fatal mix of inadequate nutrition and unhealthy environments)
Food Security and its Main Threats
It exists when all people, at all times, have physical, social, and economic access to sufficient, safe, and nutritious food that meets their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.
Food Security and its Main Threats
It is ensured when the following three conditions are simultaneously satisfied:
Physical food availability
Economical food availability
The health value of a single food product
Consumer food rations
Physical Food availability
The national food economy ensures meeting of at least the minimum physiological demand, and imports provide foods in excess of this minimum demand.
Economical Food Avalability
It means that the economically weakest households have access to essential food.
A consumer has the purchasing power to facilitate the purchase of the essential goods and services on the market.
The Health Value of a Single Food Product
This means that food products are free of any substances that are harmful to health.
Main Threat to Food Security
The food system is intensely challenged by the world population growth, increased food demands, scarcity of water and land resources, and the larger spread of arable land vis-a-vis bio-fuels, industry, and urbanization.
Ex:
Population growth
Increase demand for food
Food price
The disappearance of the variety of agricultural plant species
The increase in the area of scarce water and the limitation of the availability of land
The food losses and food waste