AP Psychology Unit 2: Cognition
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
Cognition
the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating

Metacognition
awareness and understanding of one's own thought processes.
selective attention
the focusing of conscious awareness on a particular stimulus

inattentional blindness
a failure to perceive objects that are not the focus of attention

change blindness
failing to notice changes in the environment; a form of inattentional blindness
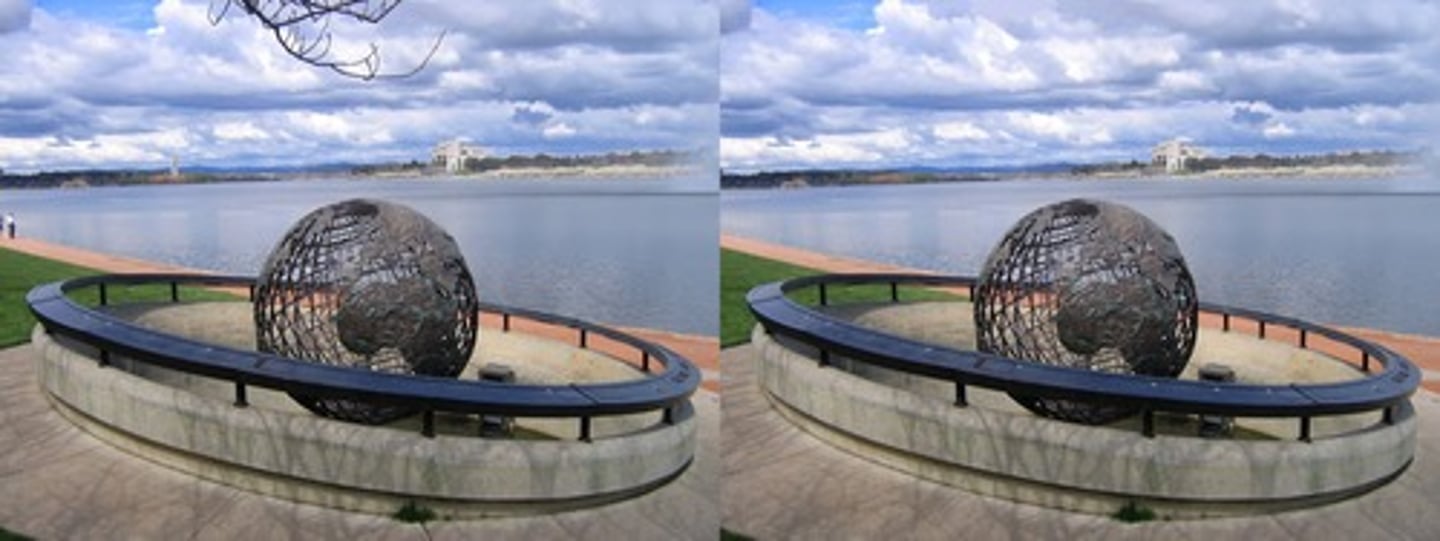

perceptual set
a readiness to perceive a stimulus in a particular way

gestalt
an organized whole that is perceived as more than the sum of its parts.
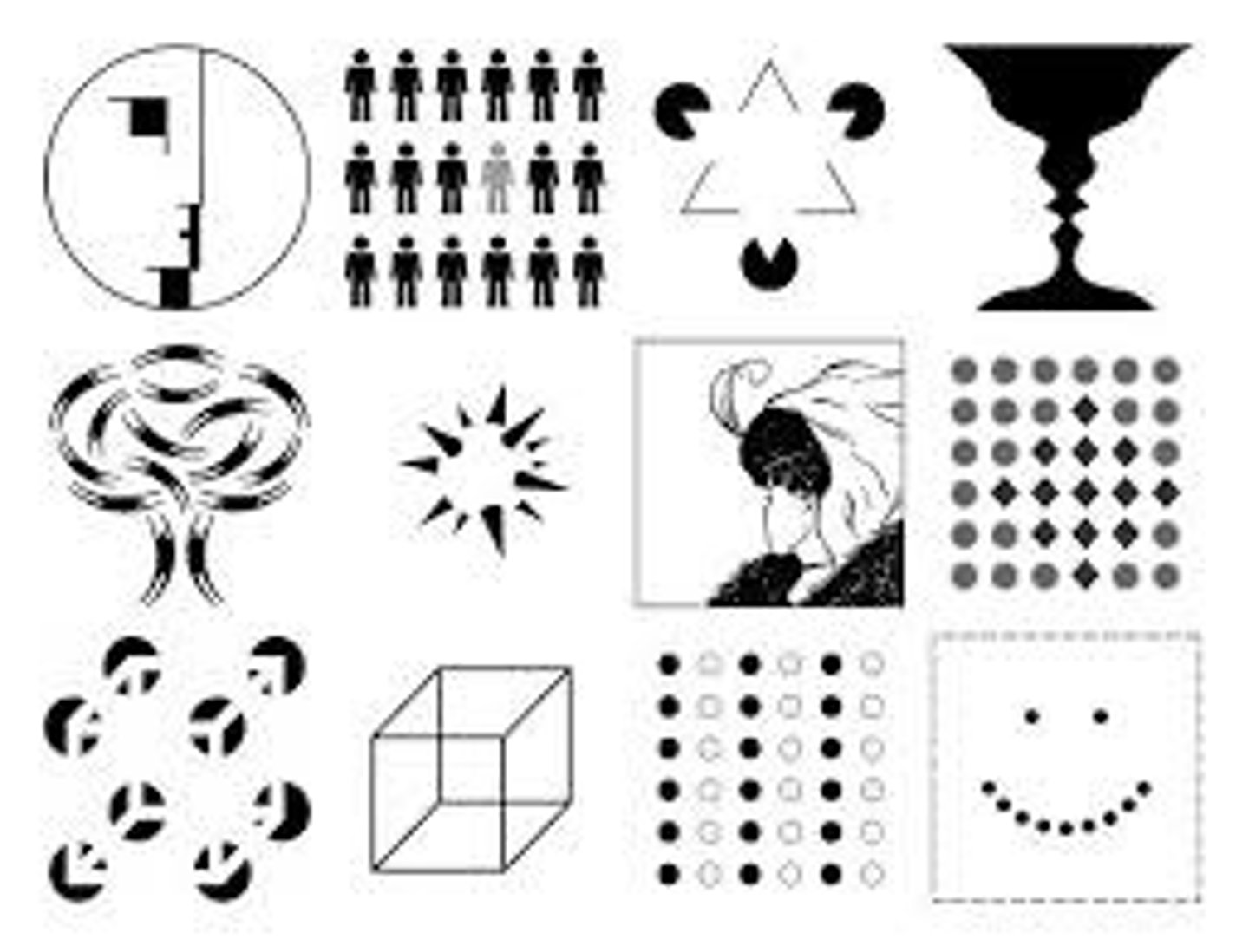
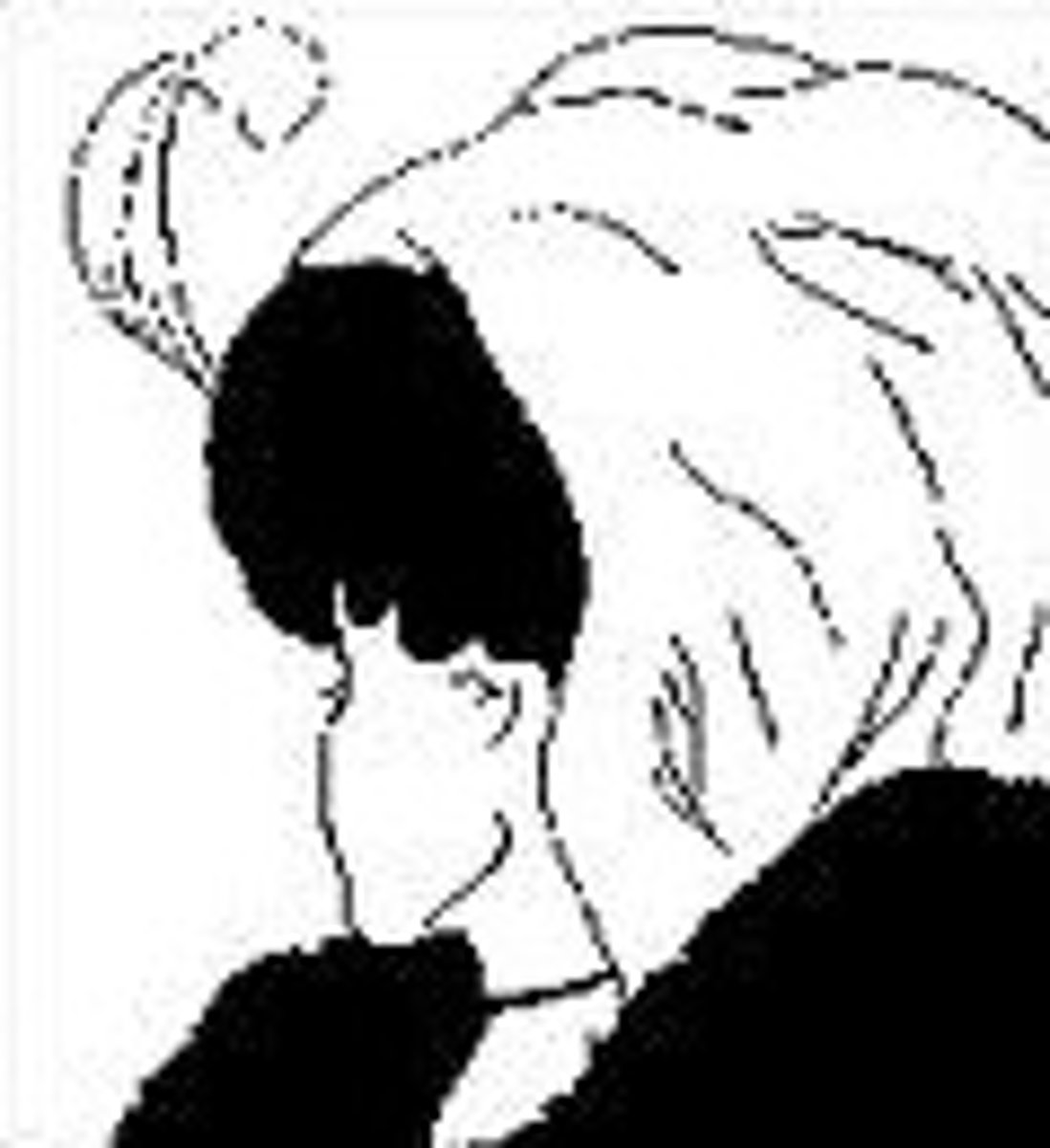
figure-ground
the tendency to perceive objects, or figures, as existing on a background

grouping
tendency to organize stimuli into coherent groups
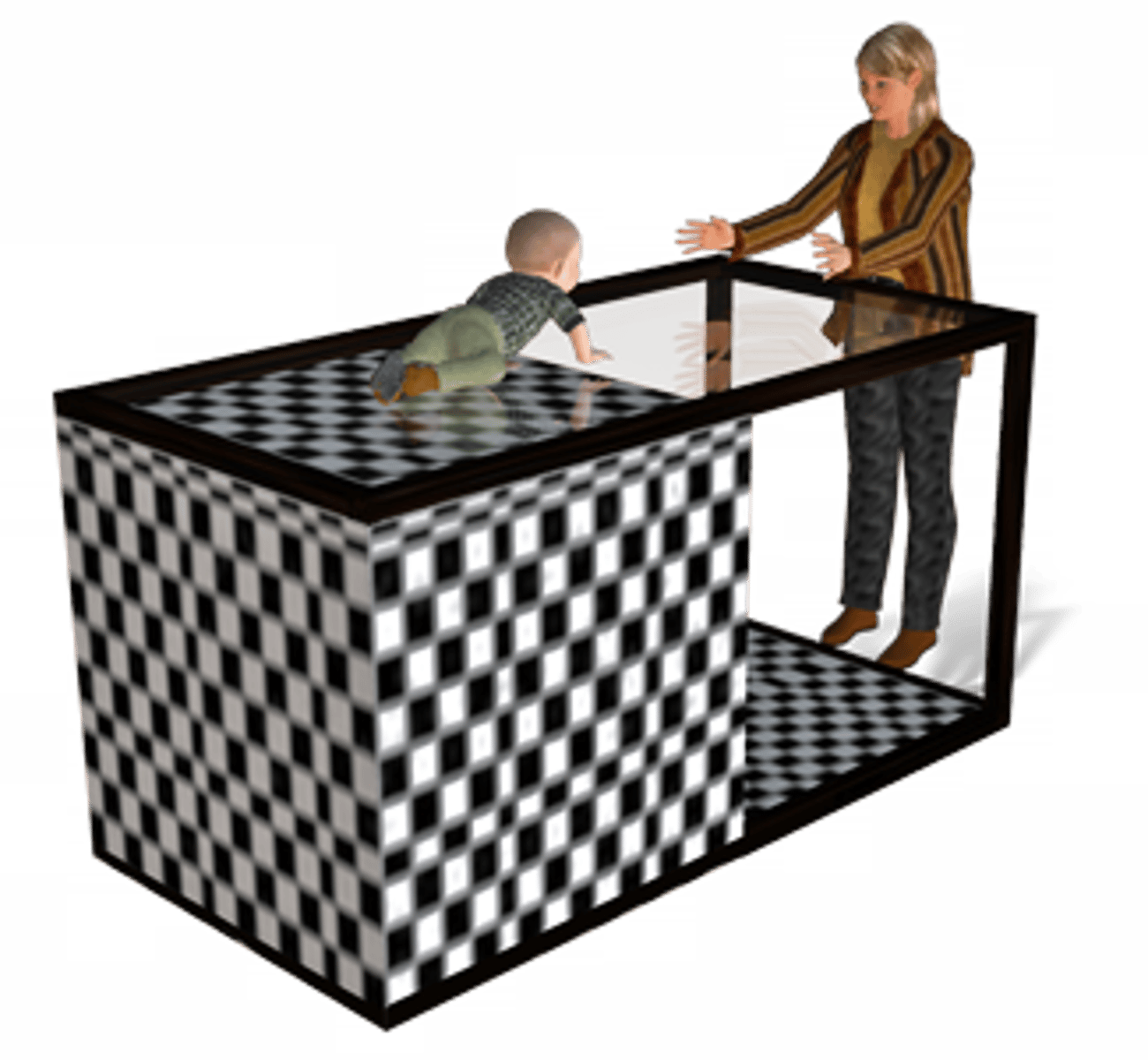
depth perception
the ability to perceive the world in three dimensions

visual cliff
a lab device for testing depth perception in infants and young animals
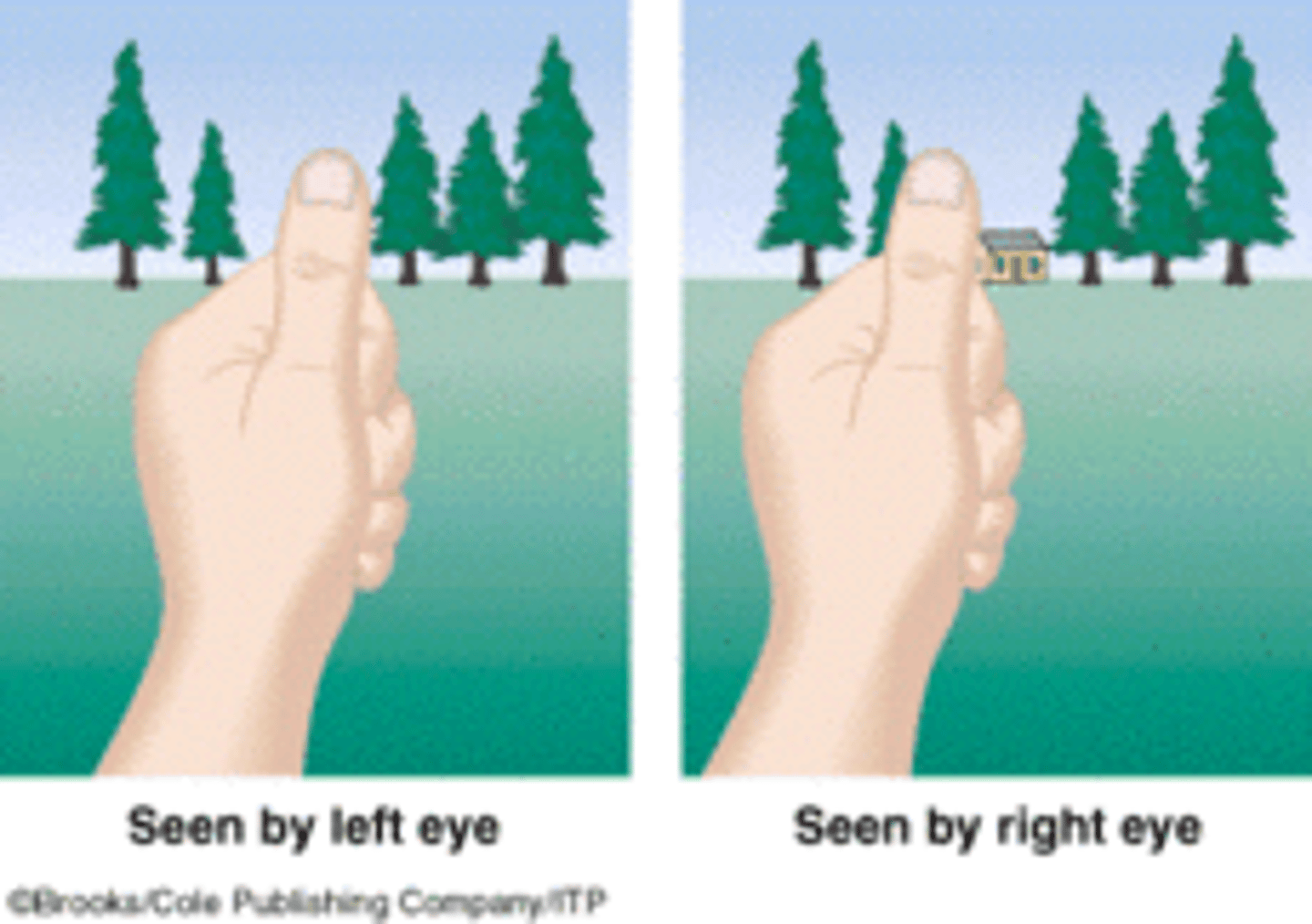
binocular cue
a depth cue that requires the use of both eyes

convergence
A binocular cue for perceiving depth; the extent to which the eyes converge inward when looking at an object

retinal disparity
a binocular cue for perceiving depth by comparing images from the retinas in the two eyes, the brain computes distance—the greater the disparity (difference) between the two images, the closer the object.
monocular cue
a depth cue, such as interposition or linear perspective, available to either eye alone

stroboscopic movement
the brain's perception of continuous movement in a rapid series of slightly varying images; this is how we perceive motion in film and animation
phi phenomenon
an illusion of movement created when two or more adjacent lights blink on and off in quick succession
autokinetic effect
The tendency to perceive a stationary point of light in a dark room as moving
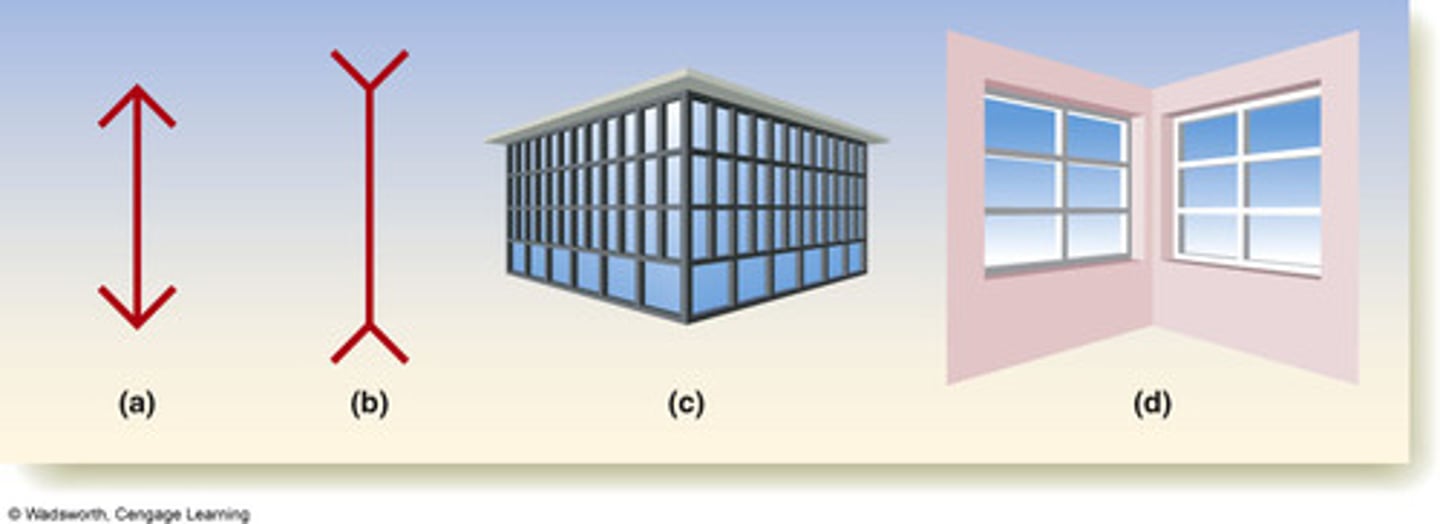
perceptual constancy
perceiving objects as unchanging even as illumination and retinal images change
metacognition
awareness and understanding of one's own thought processes.
concept
a mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, or people

prototype
a mental image or best example of a category

Jean Piaget
Known for his theory of cognitive development in children and how schemas are developed.

schema
a conceptual framework a person uses to make sense of the world
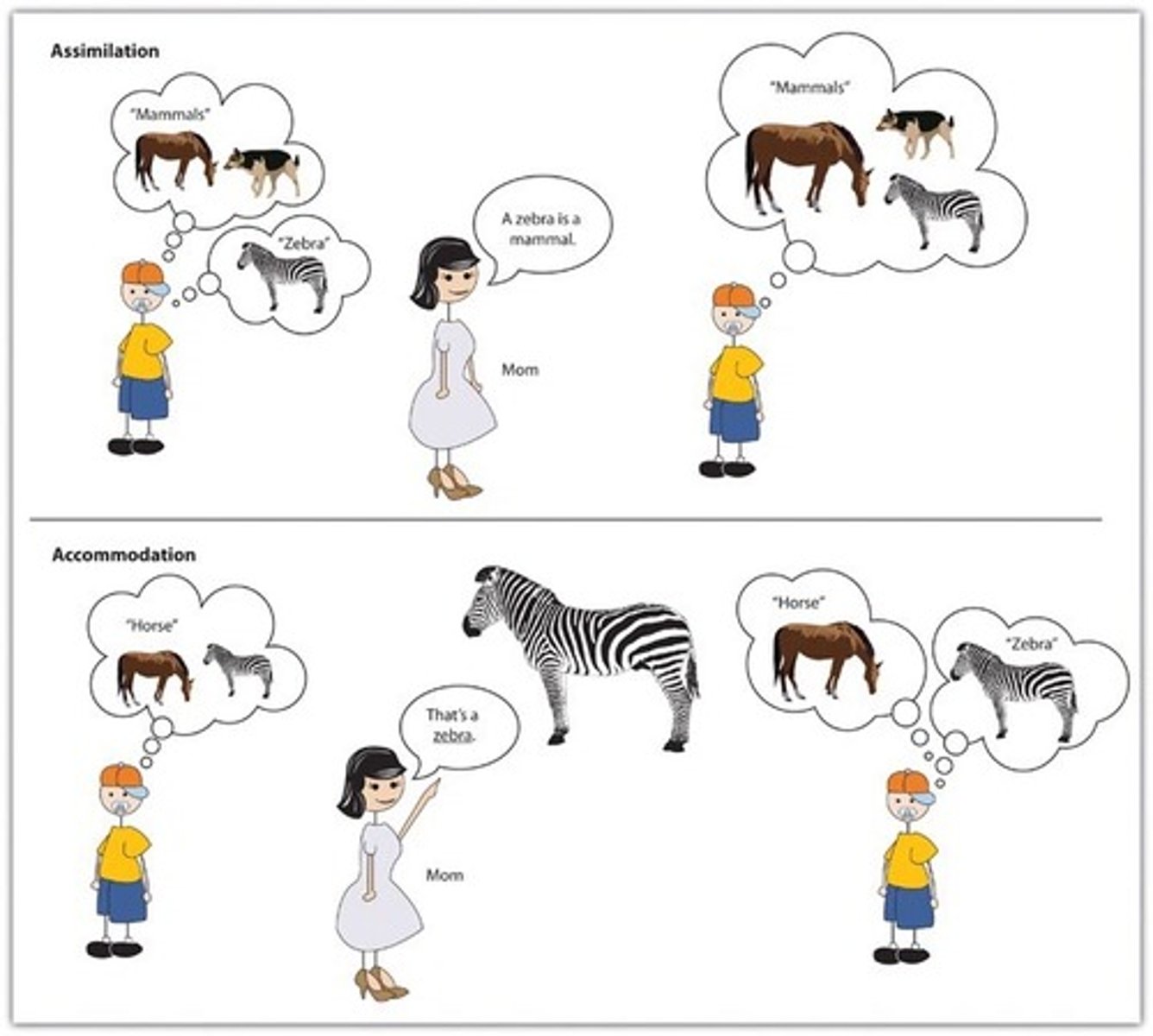
assimilation
interpreting our new experiences in terms of our existing schemas

accomodation
adapting our current understandings (schemas) to incorporate new information
creativity
the ability to produce novel and valuable ideas

divergent thinking
expands the number of possible problem solutions (creative thinking)

convergent thinking
narrows the available problem solutions to determine the single best solution

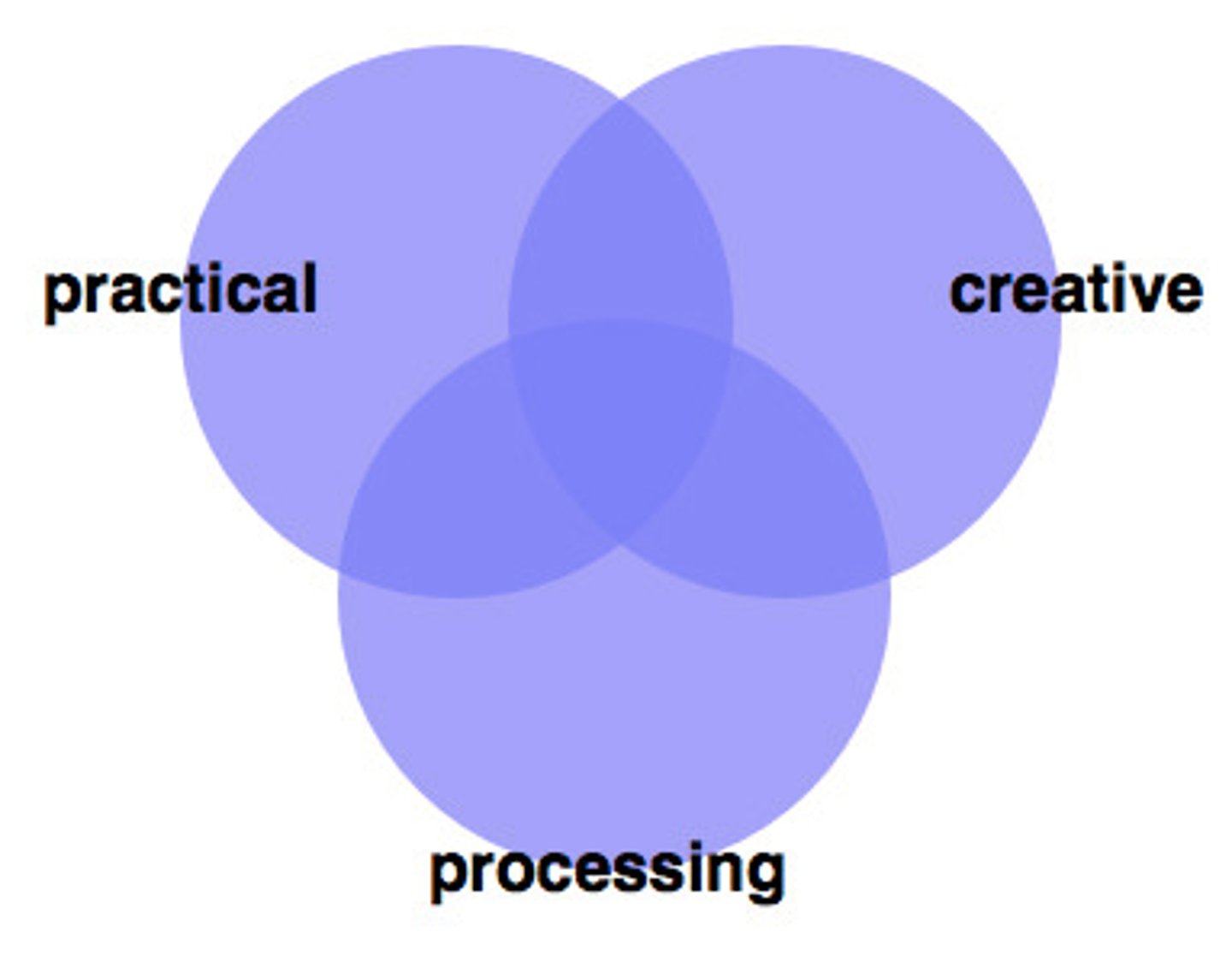
Robert Sternberg
intelligence; devised the Triarchic Theory of Intelligence (academic problem-solving, practical, and creative)
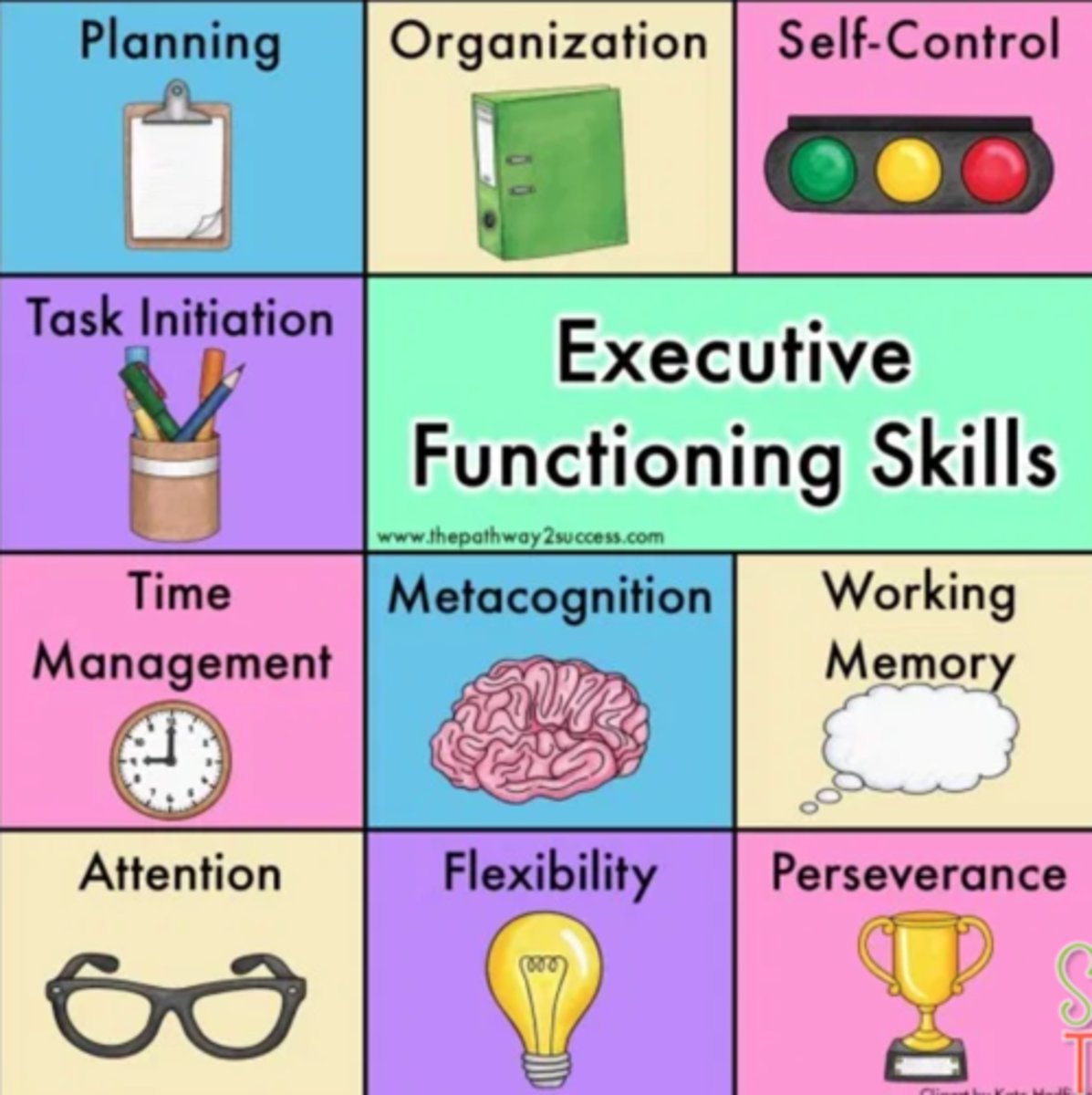
executive functions
higher order thinking processes that include planning, organizing, inhibition, and decision-making
algorithm
A methodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem.

heuristic
a simple thinking strategy that often allows us to make judgments and solve problems efficiently; usually speedier but also more error-prone than algorithms

insight
a sudden realization of a problem's solution

Wolfgang Kohler
considered to be the founder of Gestalt Psychology

confirmation bias
a tendency to search for information that supports our preconceptions and to ignore or distort contradictory evidence

fixation
the inability to see a problem from a new perspective, by employing a different mental set
mental set
a tendency to approach a problem in a particular way, often a way that has been successful in the past

intuition
an effortless, immediate, automatic feeling or thought, as contrasted with explicit, conscious reasoning

Amos Tversky
Worked with Daniel Kahneman to identify representative heuristics and availability heuristics

Daniel Kahneman
an Israeli psychologist and Nobel laureate, who is notable for his work on the psychology of judgment and decision-making, behavioral economics and hedonistic psychology.

representativeness heuristic
estimating the likelihood of events in terms of how well they seem to represent, or match, particular prototypes; may lead us to ignore other relevant information

availability heuristic
making a decision based on the answer that most easily comes to mind.

overconfidence
the tendency to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgments.

belief perseverance
tendency to stick to our initial beliefs even when evidence contradicts them
framing
the way an issue is posed; how an issue is framed can significantly affect decisions and judgments.

nudge
a slight push or shake
memory
the persistence of learning over time through the encoding, storage, and retrieval of information

recall
A measure of memory in which the person must retrieve information learned earlier, as on a fill-in-the-blank test.

recognition
a measure of memory in which the person need only identify items previously learned, as on a multiple-choice test

relearning
a measure of memory that assesses the amount of time saved when learning material for a second time

Herman Ebbinghaus
He was a German psychologist who pioneered the experimental study of memory, and is known for his discovery of the forgetting curve and the spacing effect. He was also the first person to describe the learning curve.

encoding
the processing of information into the memory system

storage
the retention of encoded information over time

retrieval
the process of getting information out of memory storage

parallel processing
the processing of many aspects of a problem simultaneously;

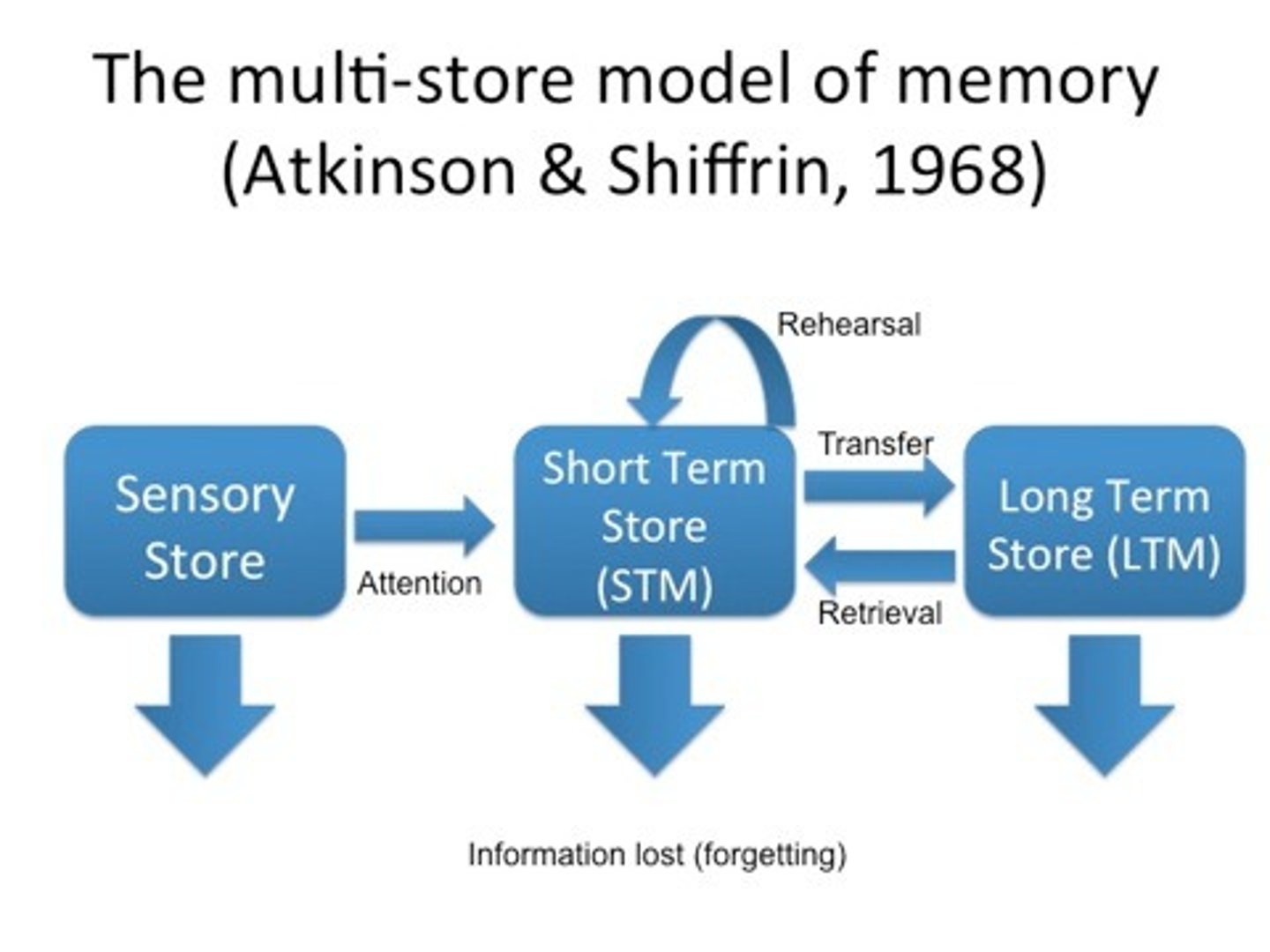
Richard Atkinson
Worked with Shiffrin to explain our memory forming process with a model
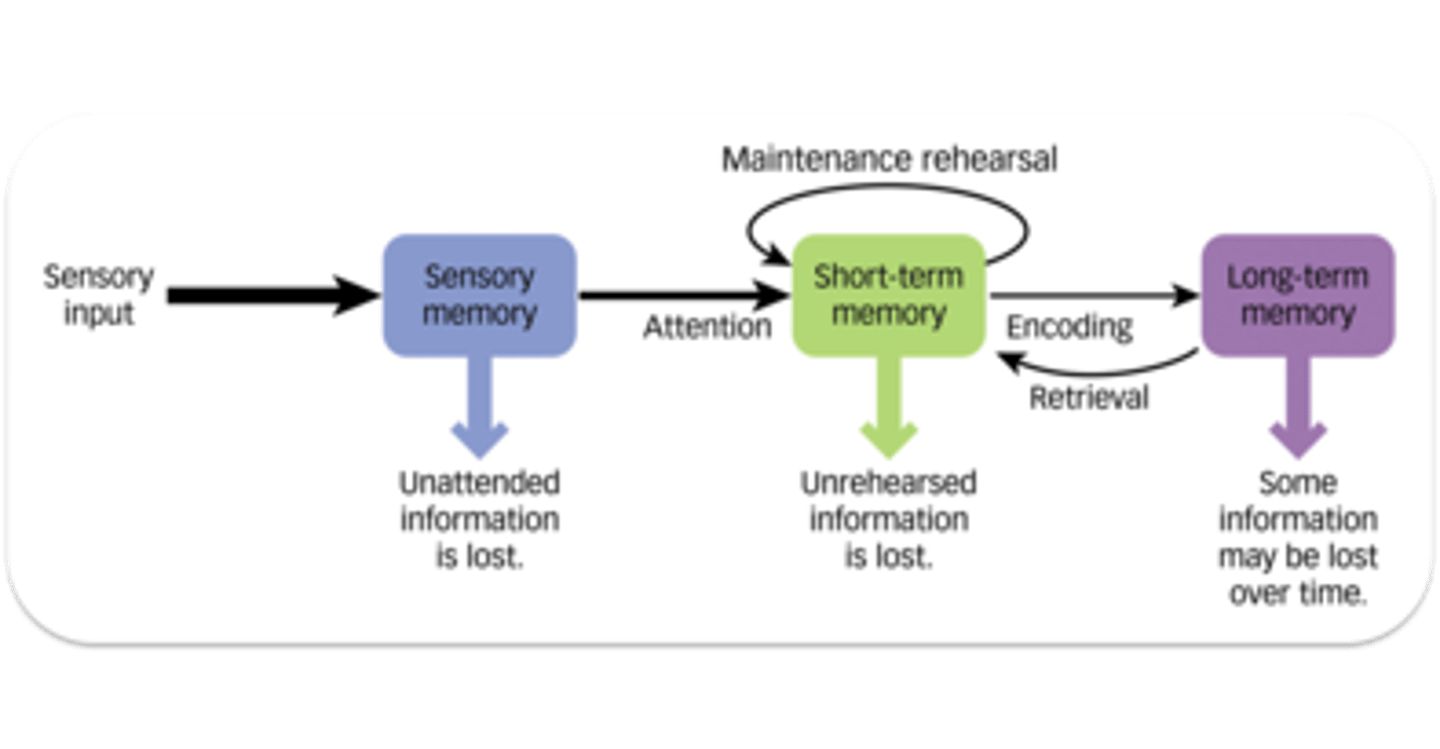
Richard Shiffrin
Worked with Atkinson to explain our memory forming process with a model
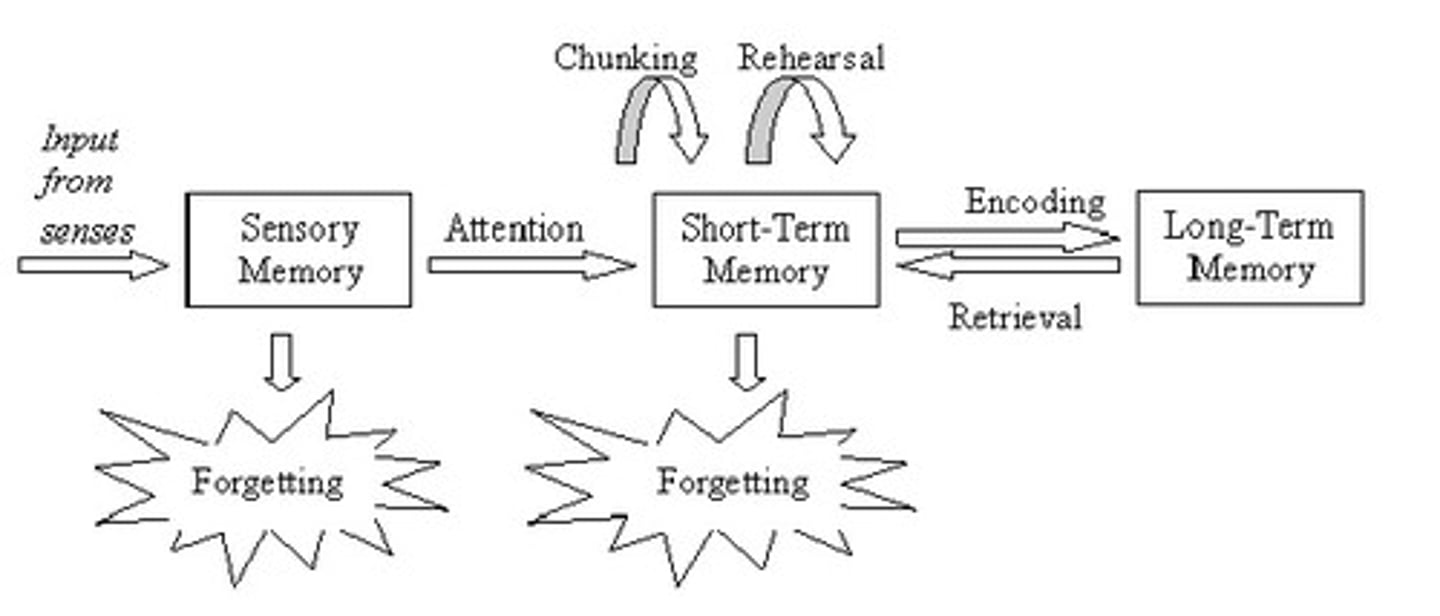
sensory memory
the immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system
short-term memory
activated memory that holds a few items briefly, such as the seven digits of a phone number while dialing, before the information is stored or forgotten

long-term memory
the relatively permanent storage of information

working memory
a newer understanding of short-term memory that focuses on conscious, active processing of incoming auditory and visual-spatial information, and of information retrieved from long-term memory
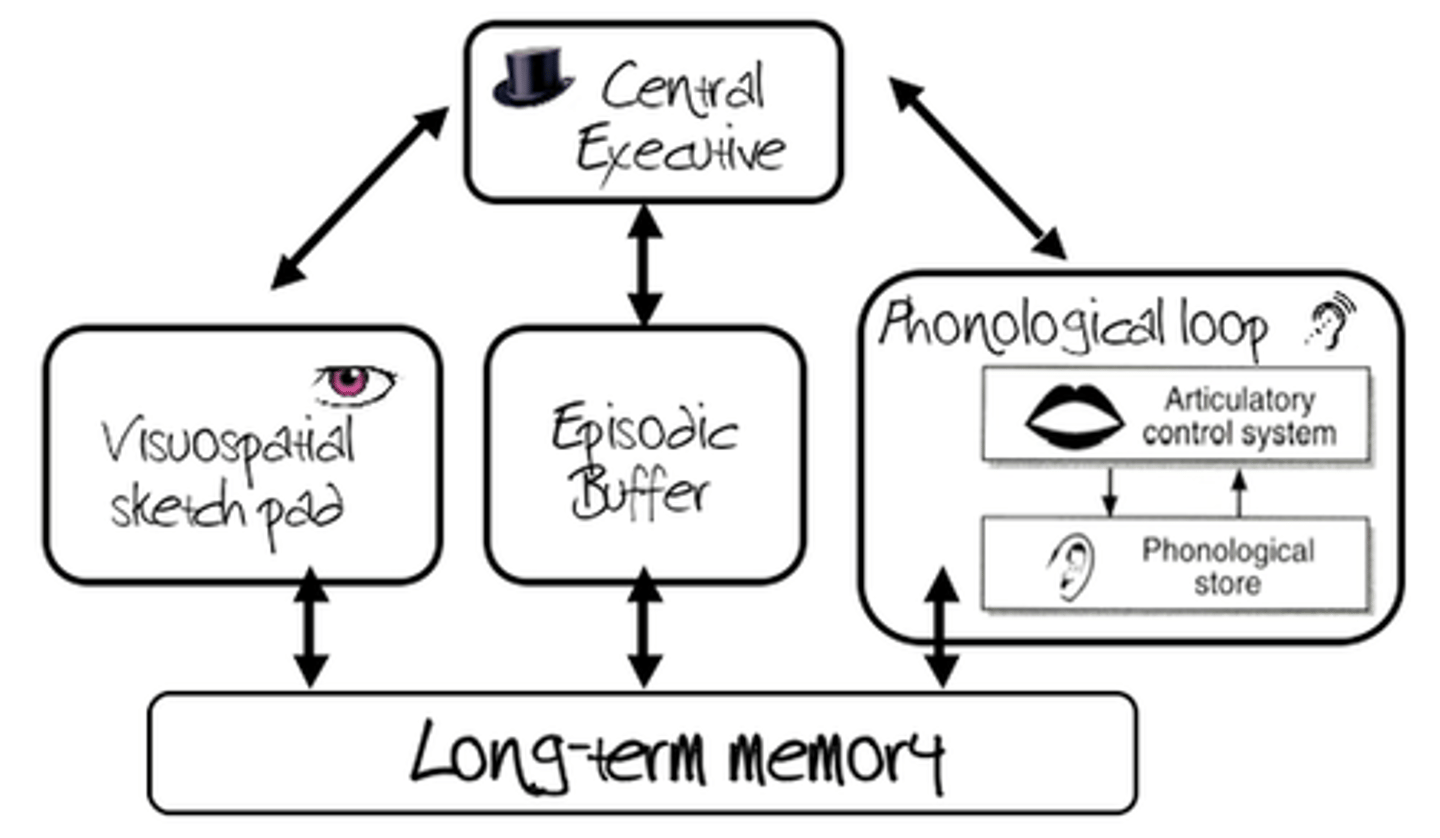
central executive
the part of working memory that directs attention and processing
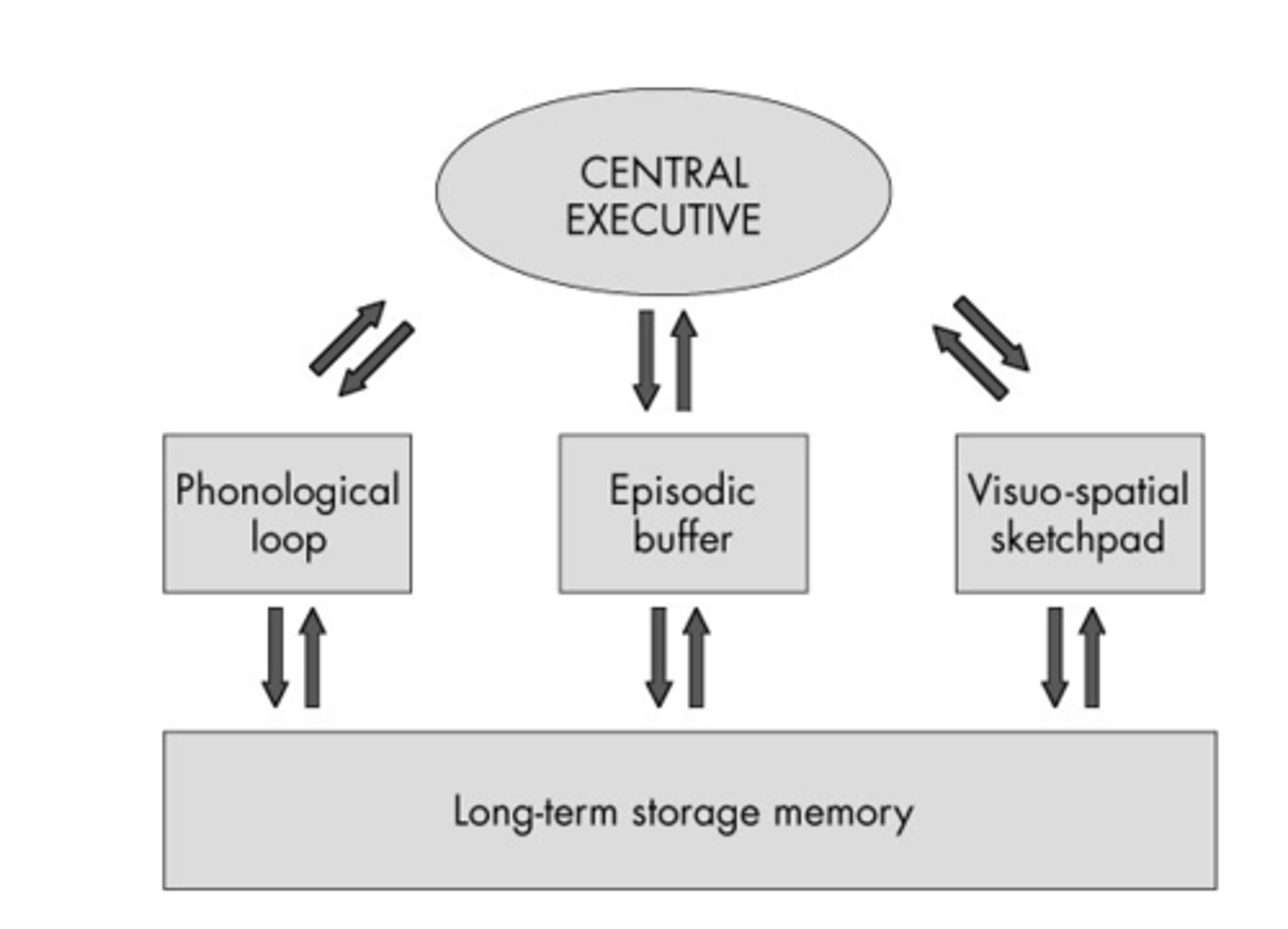
phonological loop
the part of working memory that holds and processes verbal and auditory information
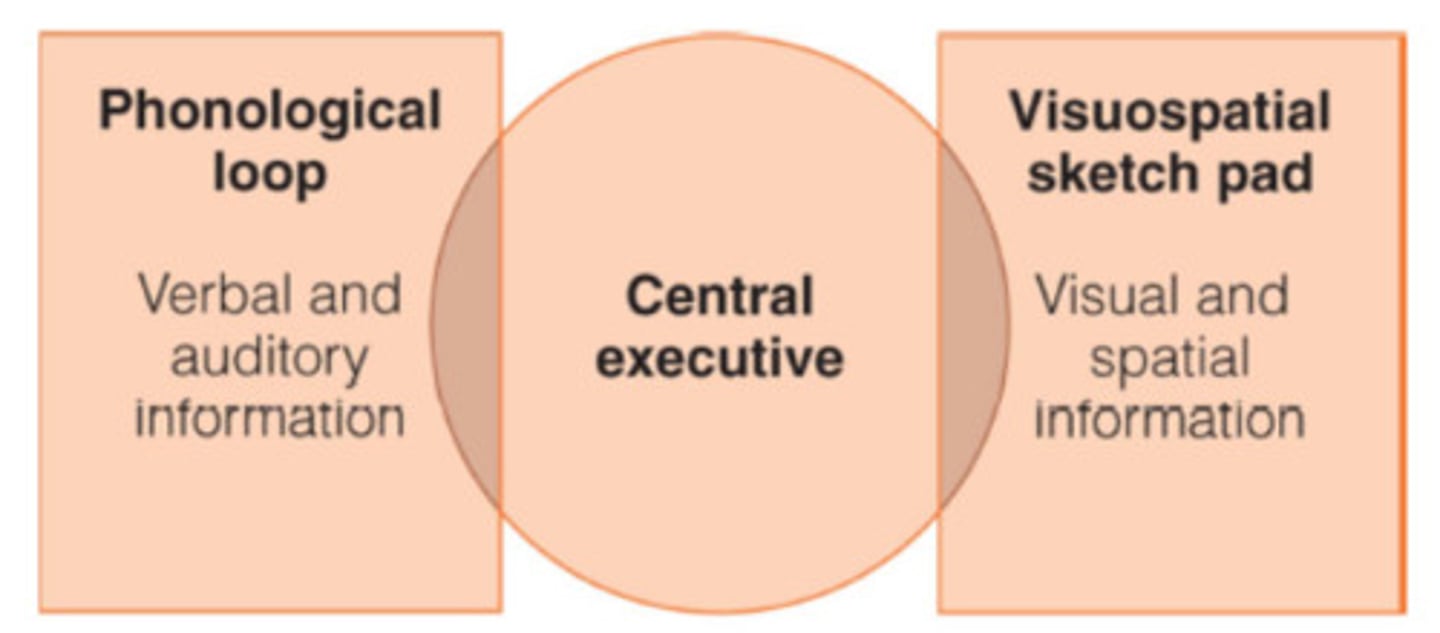
visual spatial sketchpad
a short-term storage system for visual and spatial information in working memory

neurogenesis
creation of new neurons in the adult brain

Working Memory Model
Baddeley Hitch (1974) developed this model of short term memory to address its limitations - they suggested it has a number of different stores.
Multi-Store Model of Memory
The memory model developed by Atkinson and Shiffrin (1968) that visualises memory as a system consisting of multiple memory stores through which a stream of data flows for processing.
Erik Kandel
psychologist who used sea snails to observe changes in the sending of neurons, aplysia research

long term potentiation
An increase in a synapse's firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation. Believed to be a neural basis for learning and memory.

explicit (declarative) memory
memory of facts and experiences that one can consciously know and "declare"

implicit memory
retention of learned skills or classically conditioned associations independent of conscious recollection
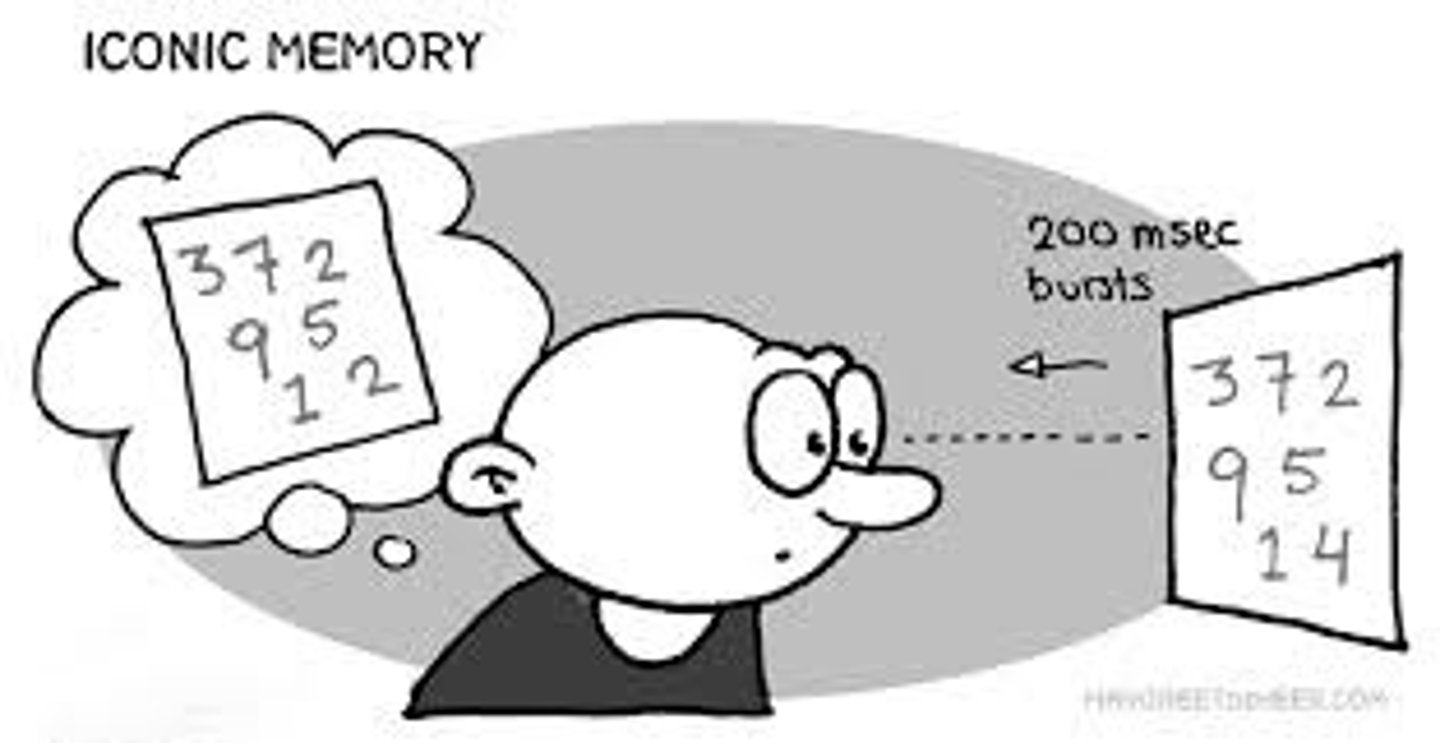
iconic memory
a momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli; a photographic or picture-image memory lasting no more than a few tenths of a second
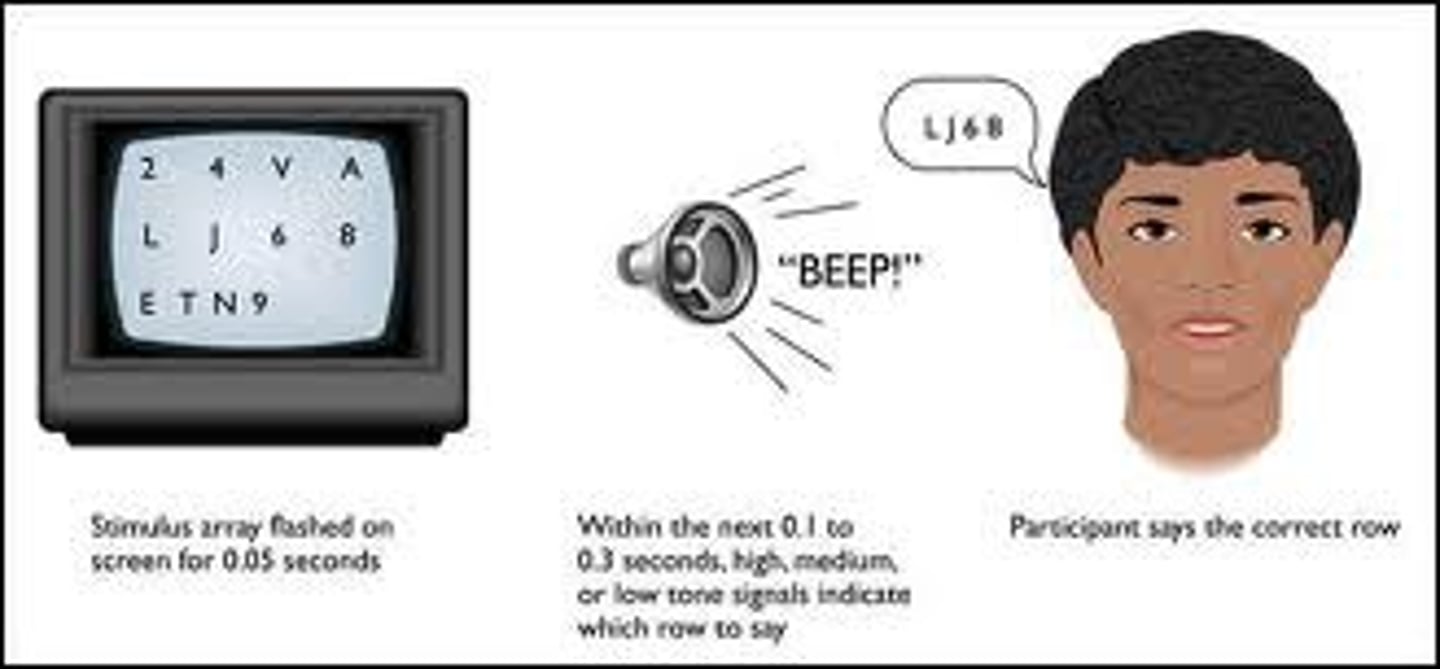
echoic memory
a momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli
George A Miller
Found that short term memory has the capacity of about 7 (+/- 2) items.

chunking
organizing items into familiar, manageable units

mnemonics
learning aids, strategies, and devices that improve recall through the use of retrieval cues

effortful processing
encoding of information that takes effort and attention

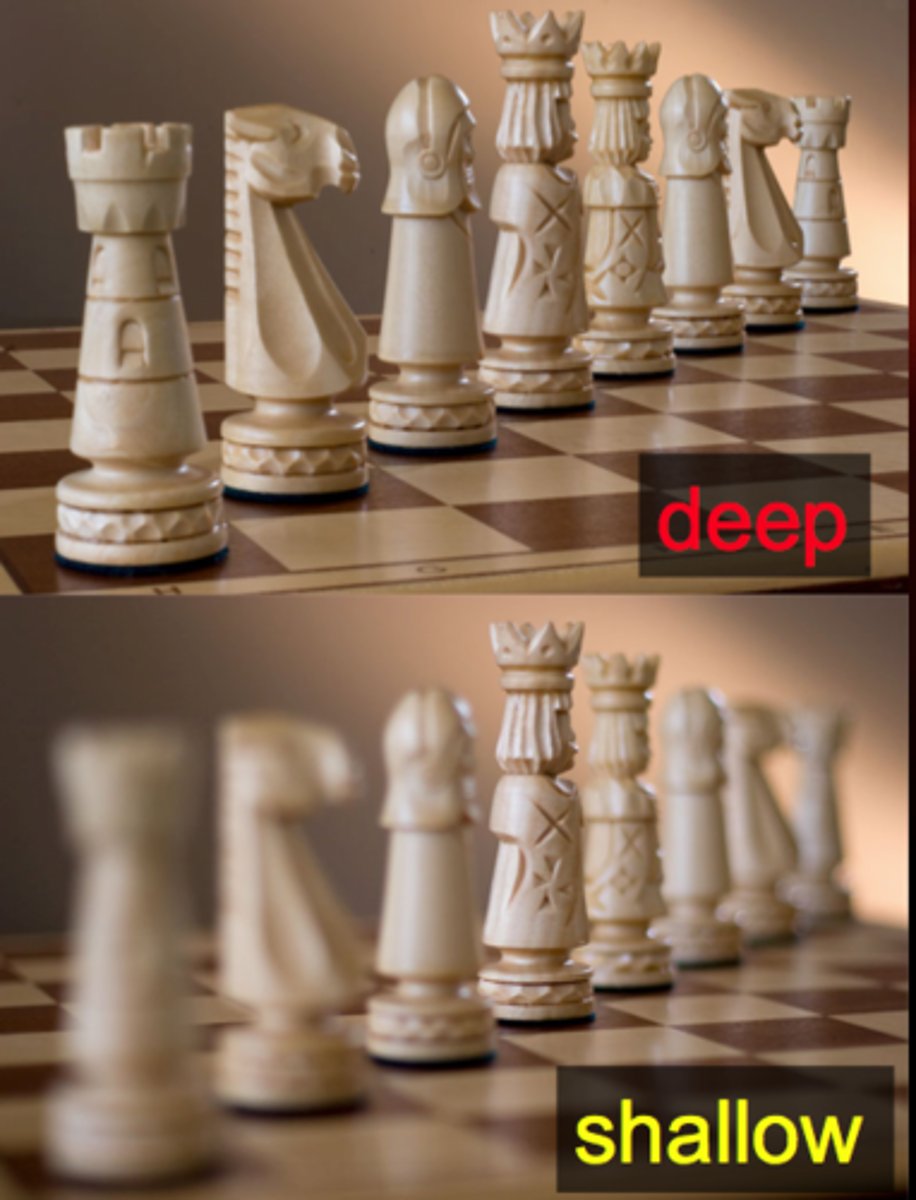
shallow vs deep processing
-shallow processing: e.g observe the type of text of a word
-deep processing: think about the meaning of the word or its use
-deeper processing--> better memory

testing effect
enhanced memory after retrieving, rather than simply rereading, information

semantic memory
a network of associated facts and concepts that make up our general knowledge of the world

episodic memory
memory for one's personal past experiences

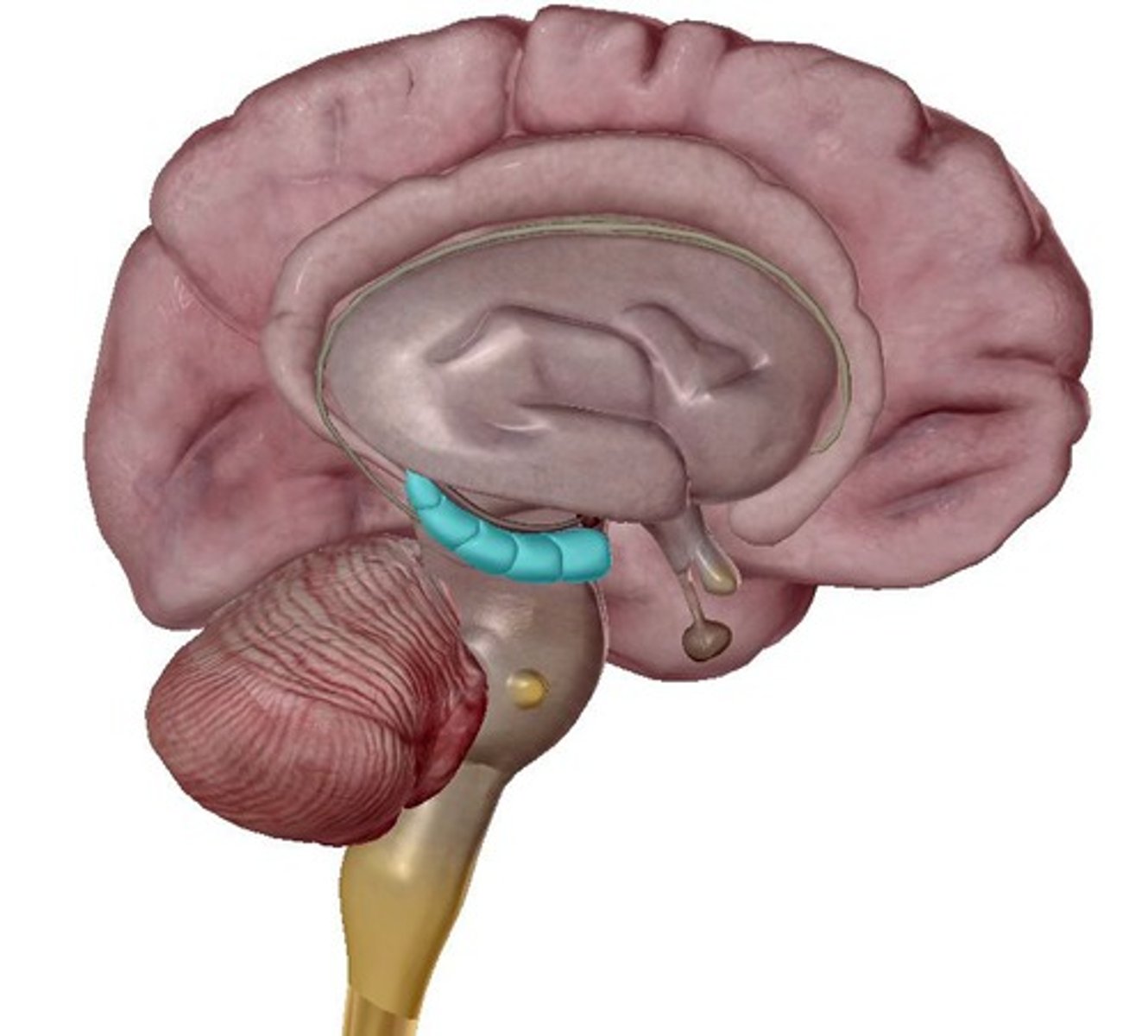
hippocampus and memory
A neural center located in the limbic system that helps process explicit memories for storage.
memory consolidation
the gradual, physical process of converting new long-term memories to stable, enduring memory codes
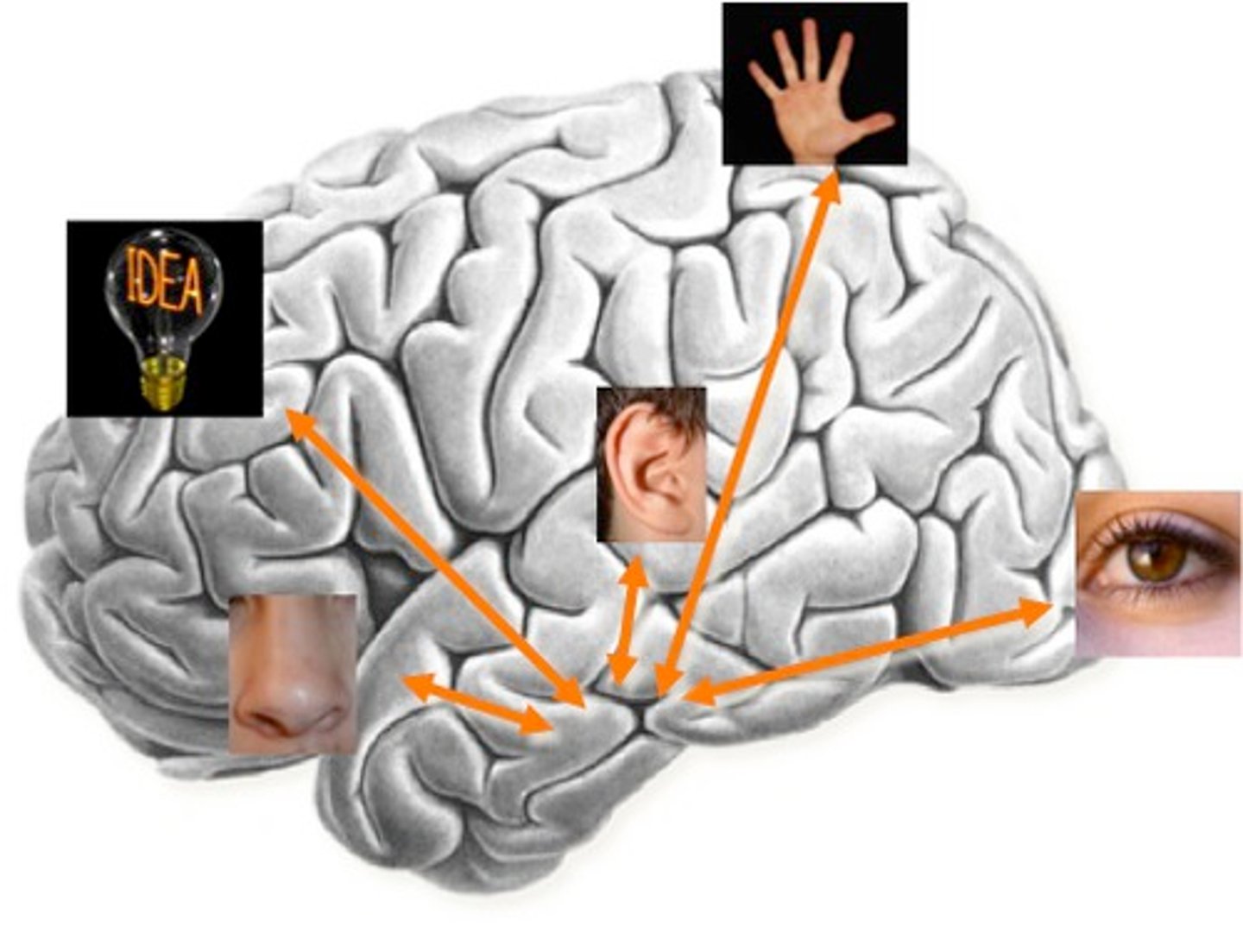
flashbulb memory
A clear and vivid long-term memory of an especially meaningful and emotional event.

priming
the activation, often unconsciously, of particular associations in memory
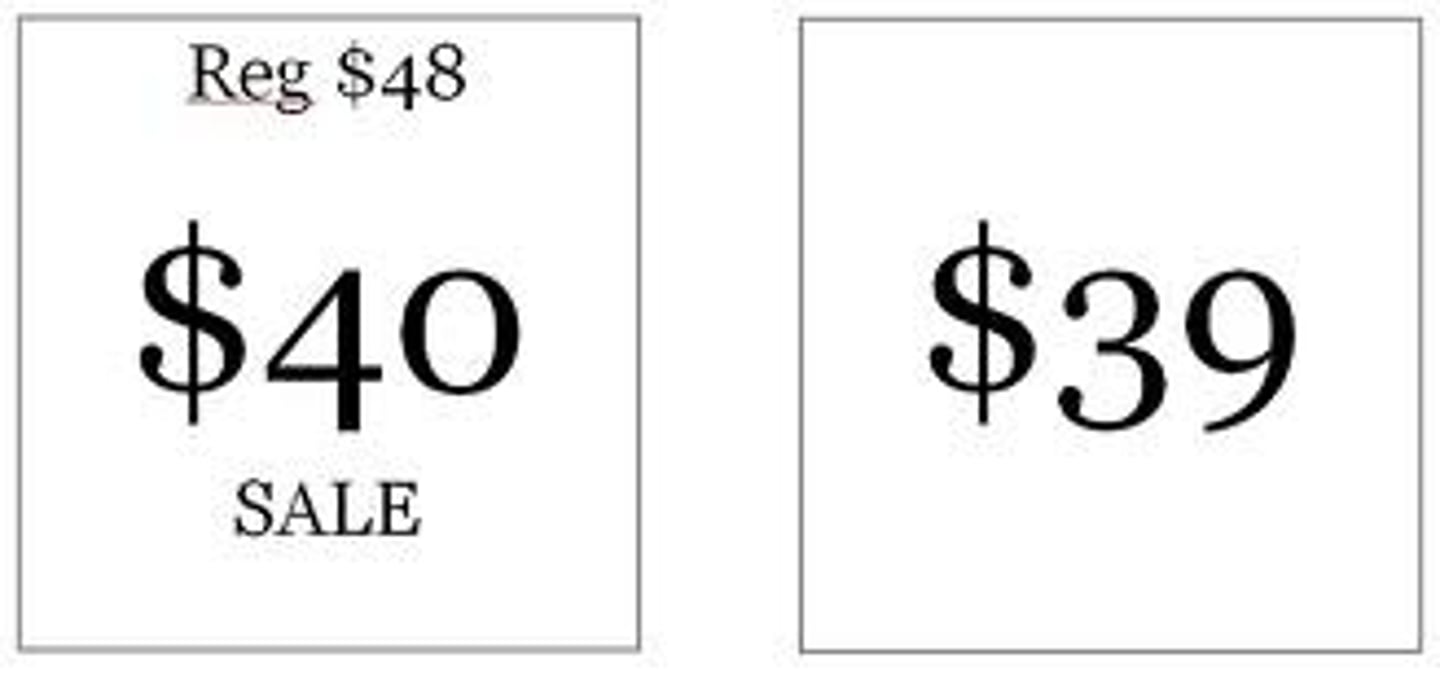
encoding specificity principle
the idea that cues and contexts specific to a particular memory will be most effective in helping us recall it

mood congruent memory
the tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one's current good or bad mood

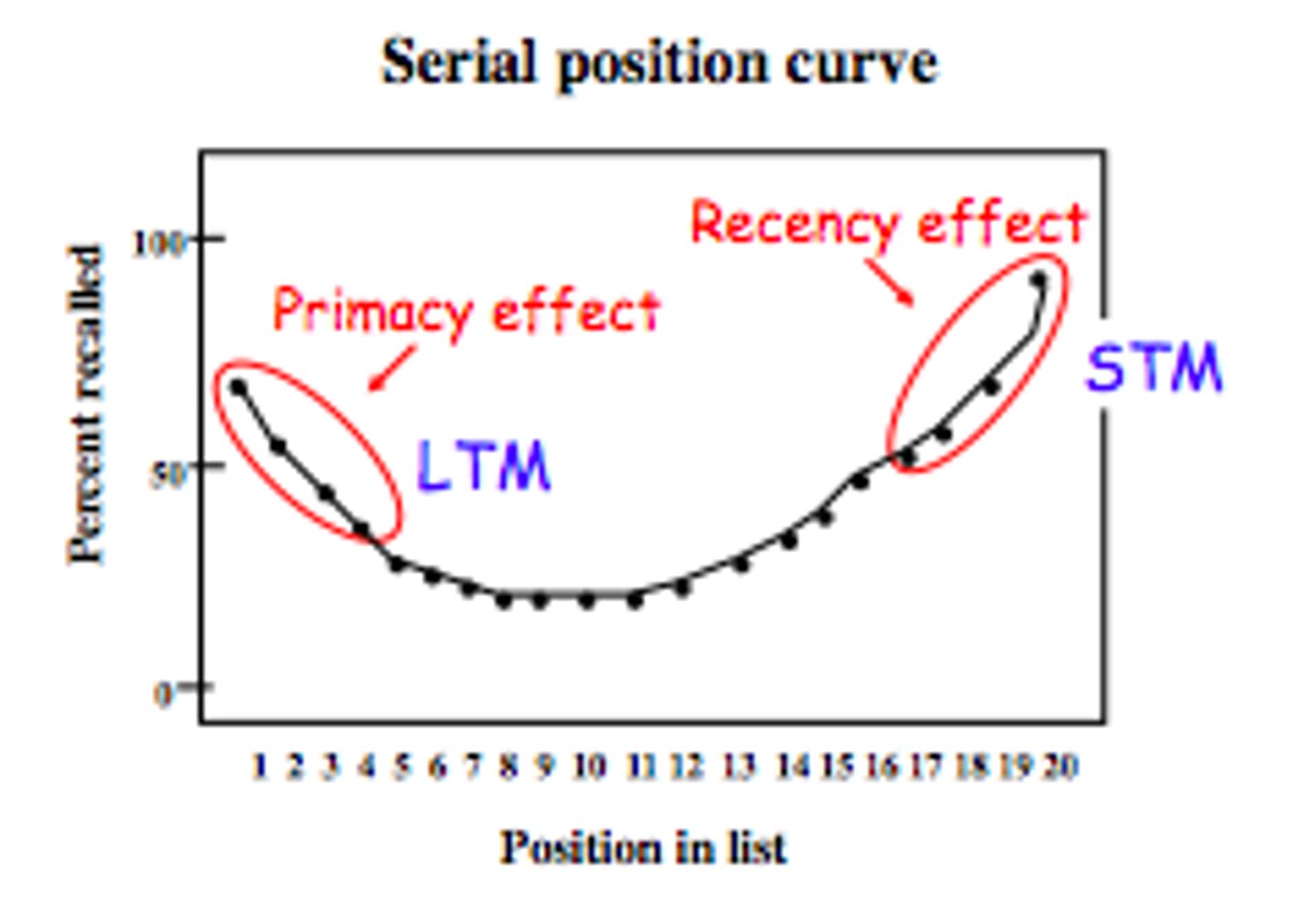
serial position effect
our tendency to recall best the last (a recency effect) and first items (a primacy effect) in a list
interleaving
a retrieval practice strategy that involves mixing the study of different topics.

anterograde amnesia
an inability to form new memories

retrograde amnesia
loss of memories from our past

proactive interference
the disruptive effect of prior learning on the recall of new information
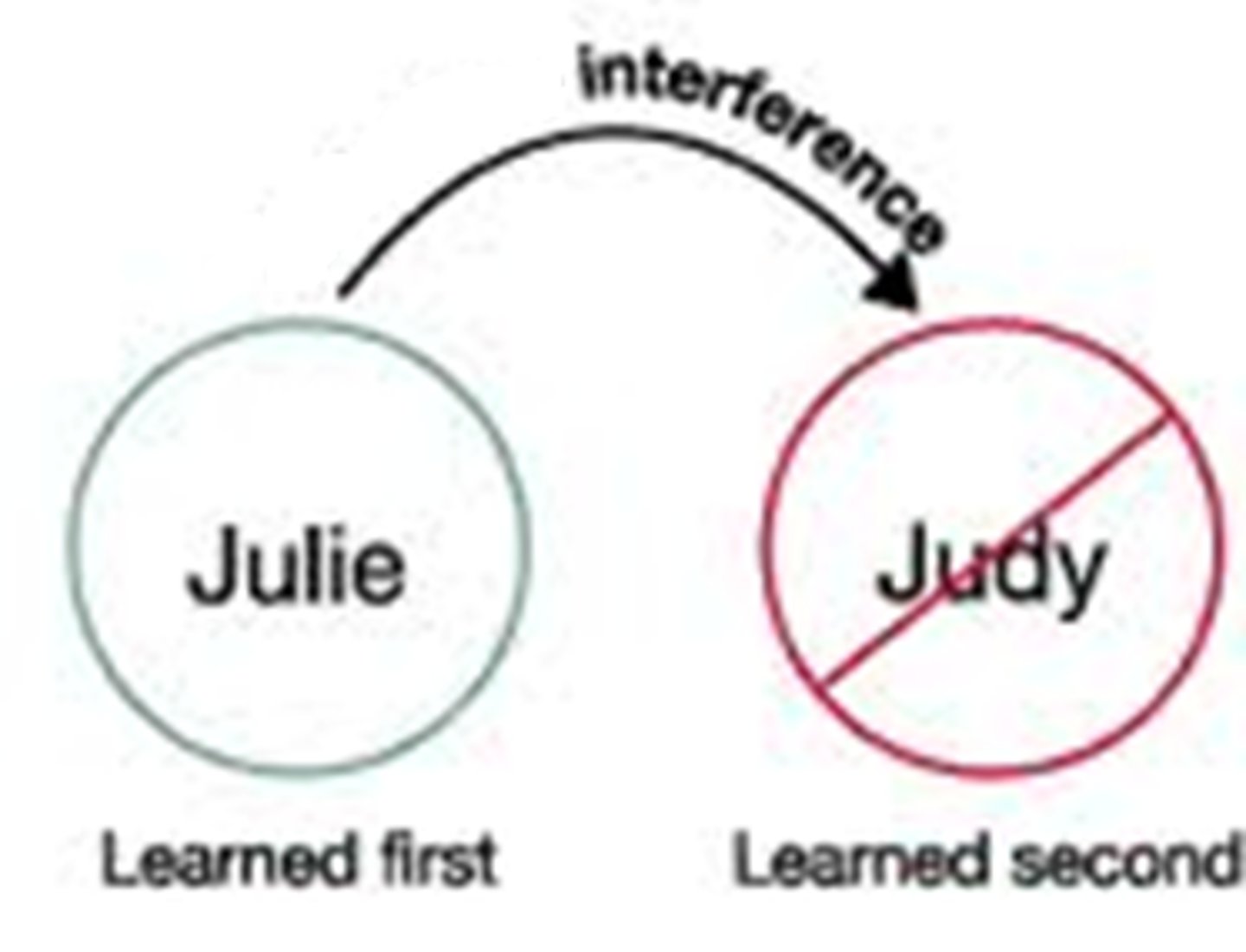
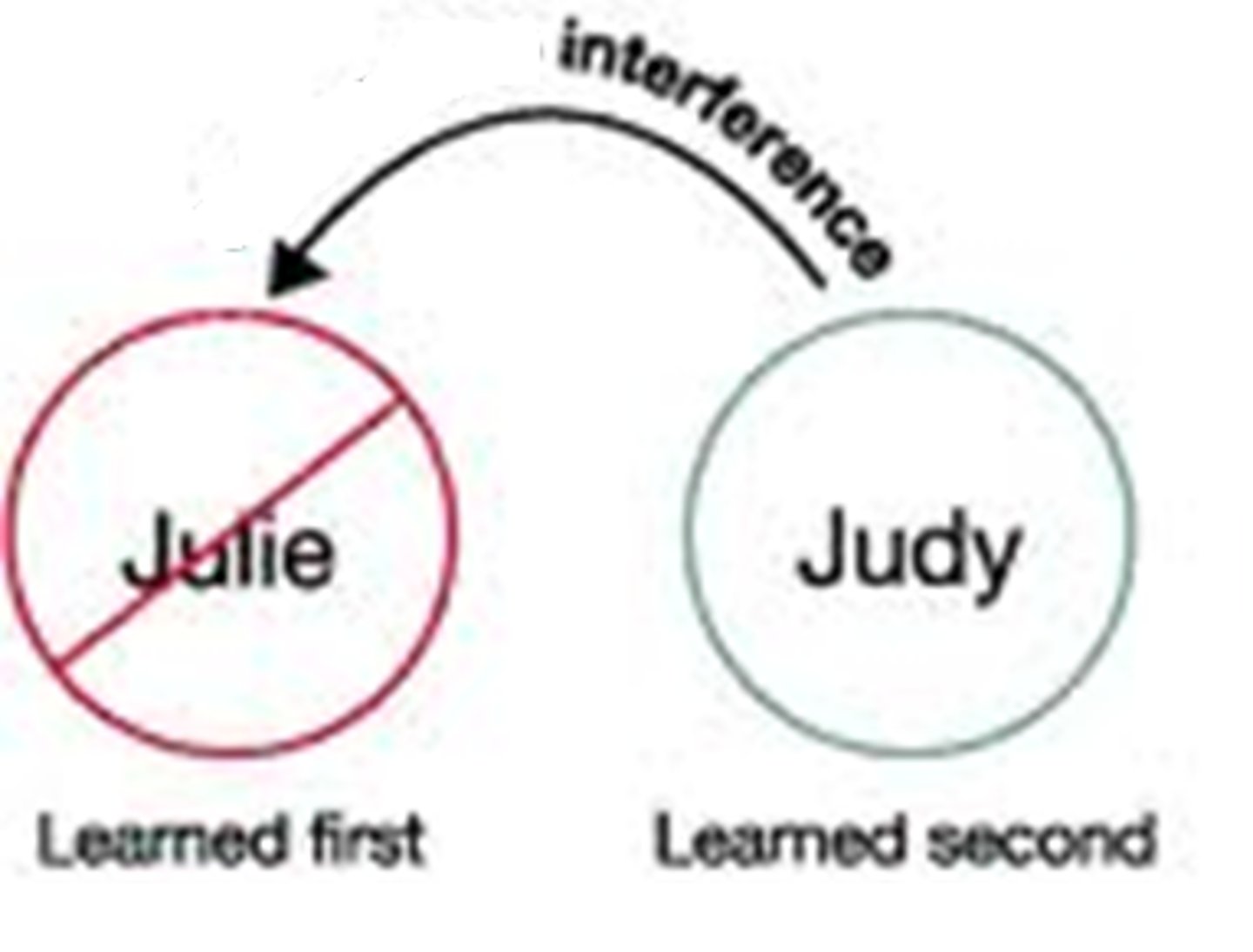
retroactive interference
the disruptive effect of new learning on the recall of old information
repression
keeping distressing thoughts and feelings buried in the unconscious

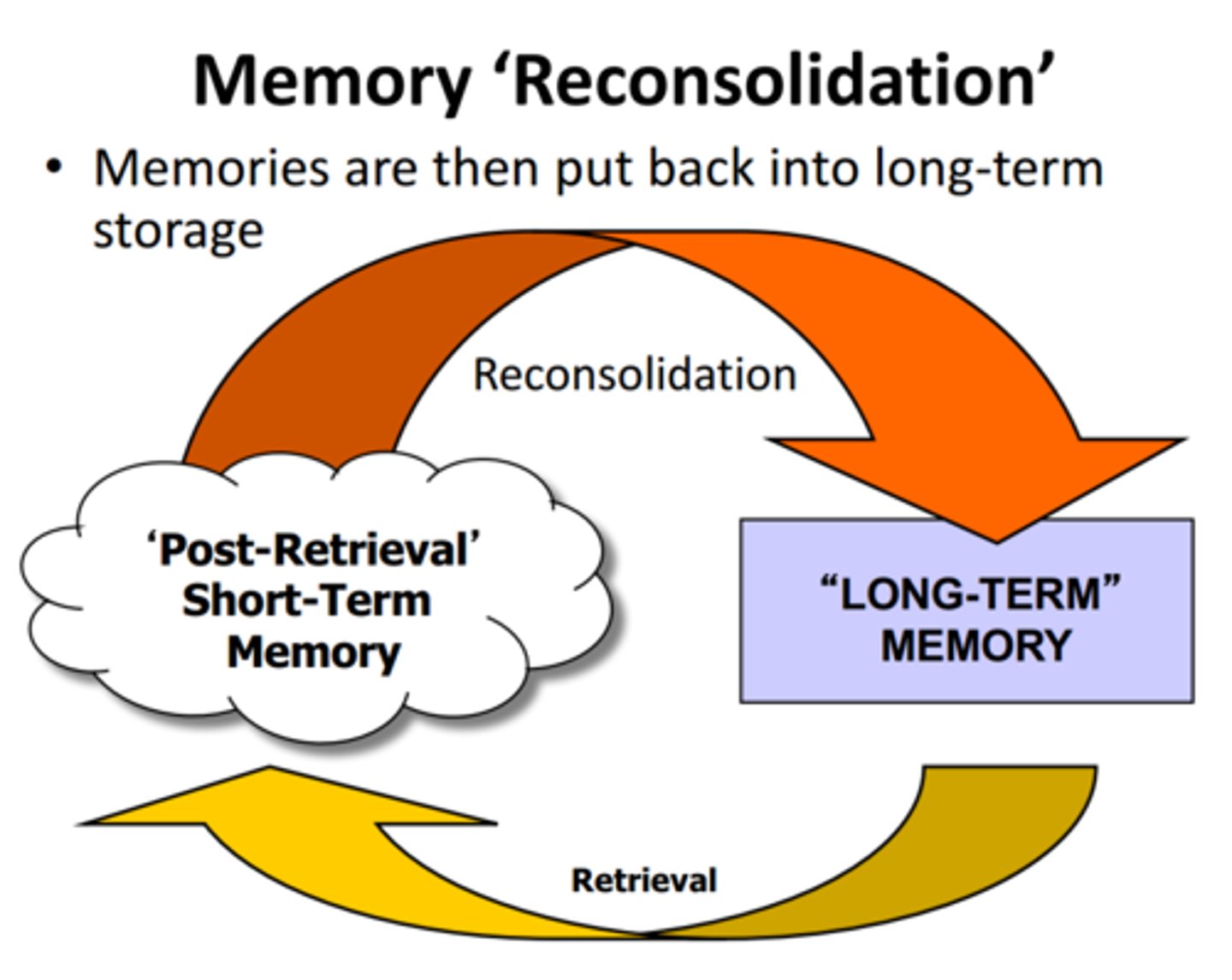
reconsolidation
memories can become vulnerable to disruption when they are recalled, requiring them to become consolidated again
Elizabeth Loftus
1944-present; Field: memory; Contributions: expert in eyewitness testimony (false memories or misinformation effect); Studies: Reconstruction of Auto. Destruction, Jane Doe Case (repressed memories of Nicole Taus' sex abuse)

misinformation effect
incorporating misleading information into one's memory of an event
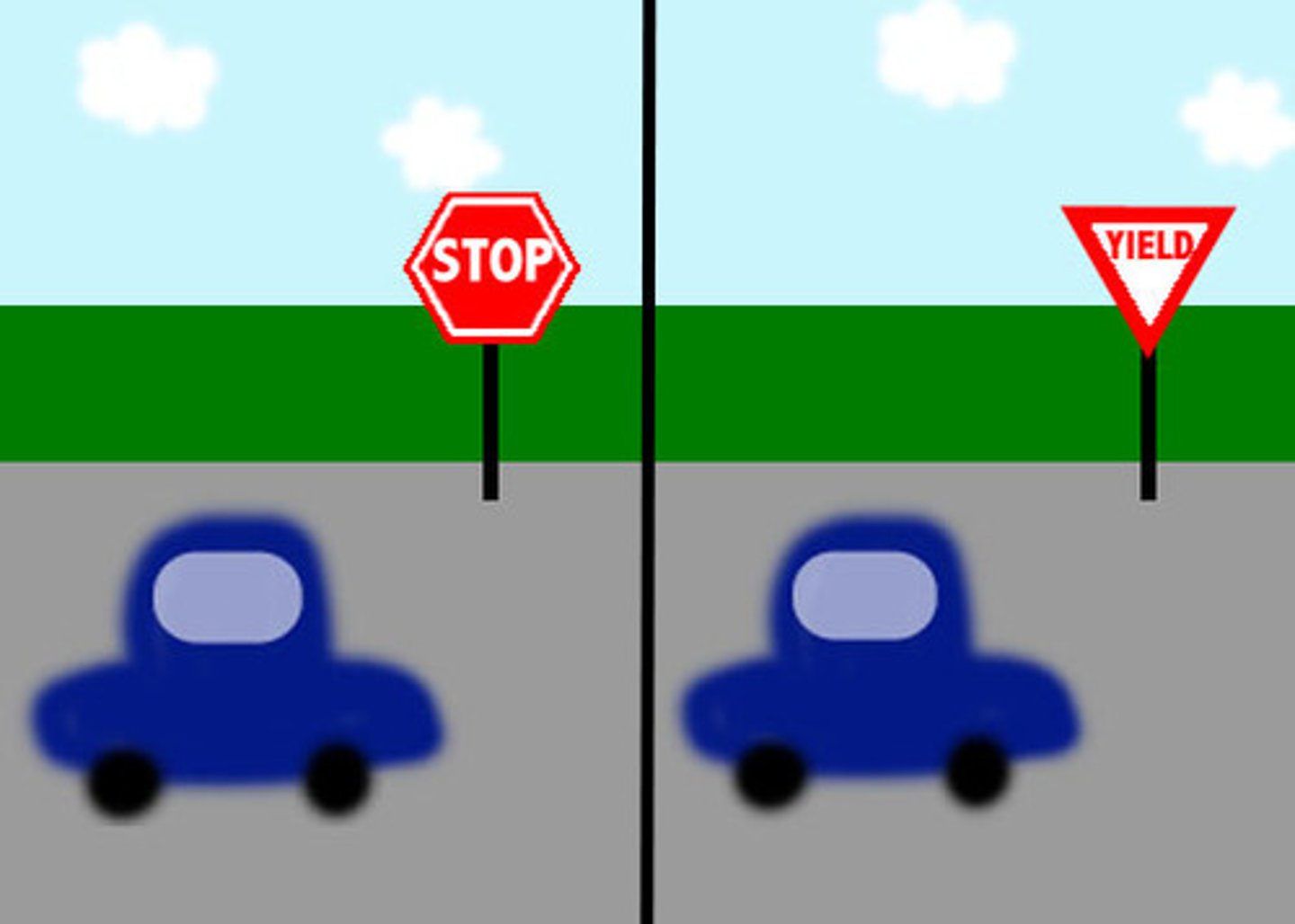
Source Amnesia
faulty memory for how, when, or where information was learned or imaginedFra

deja vu
The eerie sense that "I've experienced this before." Cues from the current situation may subconsciously trigger retrieval of an earlier experience
