Drug analysis in Forensic Science
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
define forensic science?
• Forensic – used in connection with courts of law.
• Forensic Science: science applied to legal problems.
• 3 important areas,
Forensic chemistry.
Forensic toxicology.
Forensic biology.
Forensic chemistry, drugs
• Drug analysis 80-90% of work,
o Illicit substances eg. cocaine, LSD, heroin, cannabis.
o Licit substances abused – benzodiazepines, opiates.
o Pharmaceuticals.
forensic chemistry?
• Fire Investigation.
• Physical evidence,
o Glass comparison by refractive index.
o paint comparisons by infrared spectroscopy.
• Unknown chemical analysis,
o Analysis of pepper or CS sprays (identify as firearm).
o Vandalism.
forensic toxicology?
• Involves analysis of drugs and poisons in biological specimens,
Blood, urine.
Liver, bile, stomach contents.
Vitreous humour/
Hair, saliva.
• Requires a knowledge of analytical chemistry, pharmacology.
forensic biology?
• Blood spatter analysis.
• DNA.
• Hair/fibre analysis.
• Links with other areas including,
Odontology.
Anthropology.
Entomology.
drug legislation?
• Misuse of Drugs Act 1971:
• https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/1971/38/contents
• Updates to an act are known as a Statutory Instrument (SI).

misuse of drugs regulations 2001
https://www.legislation.gov.uk/uksi/2001/3998/contents/made
Important Points
• Definitions.
• Schedules 1-5 (Regulations), Classes (Act).
• Generic controls.
psychoactive substances Act 2016

forensic chemistry: abused drugs
• Typically, a seized material is brought to forensic laboratory,
o Follows chain of custody.
• Packaged securely at scene.
• Transported to laboratory.
• Logged at lab reception and stored.
• Analysis carried out.
forensic chemistry: sources of information
• United Nations Office of Drugs and Crime (UNODC), www.unodc.org
Detailed methods for drug analysis, online manuals.
World drugs report – statistics, trends.
• US Drug Enforcement Agency, https://www.dea.gov/law-enforcement/forensic-sciences
Microgram bulletin.
International narcotics Control Board, www.incb.org
laboratory procedure
• Detailed notes at every stage.
• Mistakes- score once and initial.
• Examination:
Security of packaging,
Is packaging secure.
Tampered – reject/note.
Description of contents.
Weights.
drug identification?
• Normally 3 separate parameters are required,
o 2 chromatographic,
Gas chromatography (GC).
High performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
Thin layer chromatography (TLC).
o Mass Spectrometry (MS).
• For example,
o GCMS (2 parameters).
o HPLC (1 parameter).
identification continued:
• Pharmaceuticals – size, shape, colour and manufacturers mark.
• Unknowns – rule out controlled drugs.
• Colour tests are carried out,
Not a parameter.
Guide for subsequent analysis.
Exception – cannabis.

pharmaceutical preparations, legislation?

TICTAC drug identification:

Illicit Pharmaceuticals?
• Many pharmaceuticals are copied and available on black market,
No guarantee of strength.
Other compounds added.
commonly used colour test?
Reagent | Compounds |
Van Urk Reagent | Indole alkaloids: LSD and Psilocin: grey/violet. |
Modified Scott | Cocaine: blue/pink
|
Duquenois - Levine Reagent | Cannabis products
|
marquis reagent ?
Most commonly used reagent is Marquis reagent.
Mixture of conc. H2SO4 and formaldehyde.
Colour Change | Drug Substance |
Orange | Amphetamines |
Blue-black | Ring substituted amphetamines |
Shades of purple | opiates |
drug substances, Heroin?
Latex sap of opium poppy (Papaver somniferum),
Raw opium.
Average constituents.
Alkaloid | % |
Morphine | 11.4 |
Codeine | 3.5 |
Thebaine | 3.1 |
Papaverine | 3.2 |
Noscapine | 8.1 |
product of Heroin?
- Extraction of morphine from opium as HCl salt.
- Structurally related compounds also extracted.
- Acetylation using acetic anhydride.
structurally related compounds?
- Other compounds may also be acetylated for example codeine.
- Partial acetylation is also possible at 3- and 6- positions of morphine.
- Thebaine, noscapine and papaverine are not acetylated.
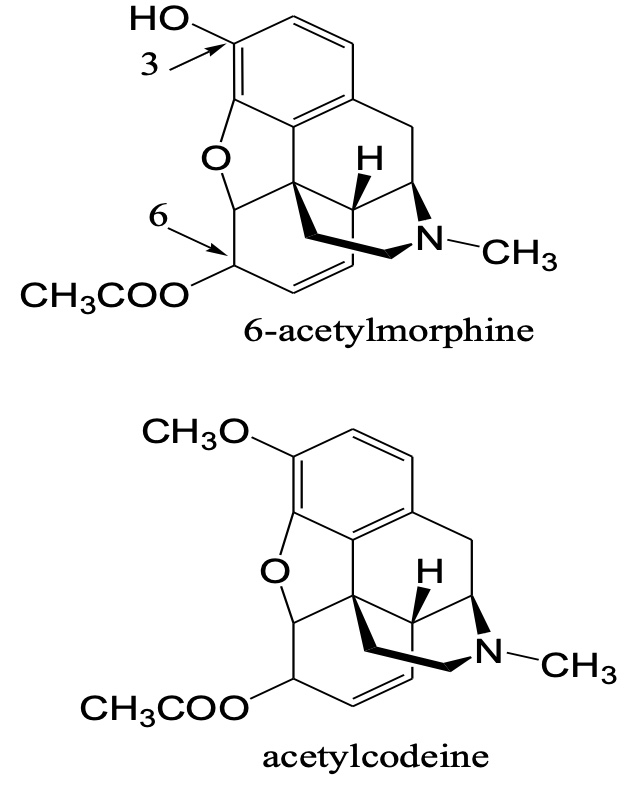
commonly used analytical techniques?
• Gas Chromatography (GC),
Detectors include FID (flame Ionisation detection), NPD (nitrogen phosphorus detector), ECD (electron capture detector).
Mass spectrometry (i.e. GCMS).
• HPLC high performance liquid chromatography,
Detectors include UV (ultraviolet), fluorescence, electrochemical.
Mass spectrometry (i.e LCMS).
Gas Chromatography – Mass Spectrometry (GCMS) Analysis?
GCMS diagram?
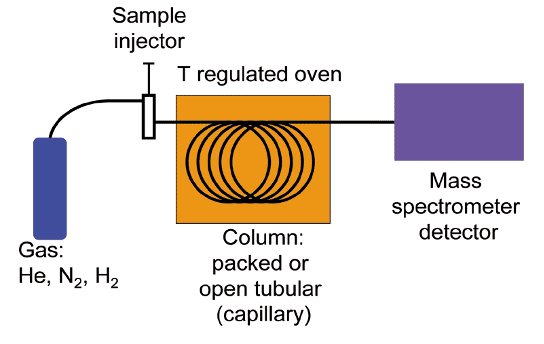
GCMA : Heroin
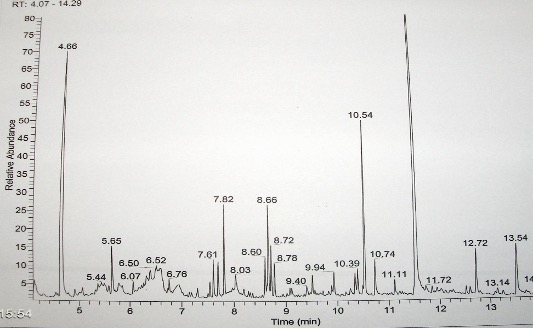
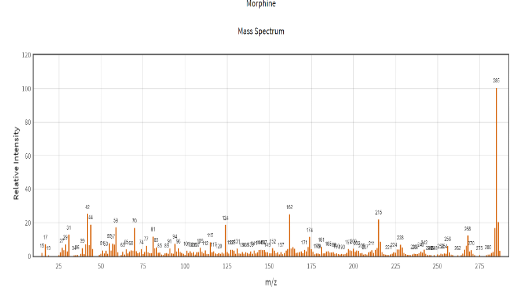
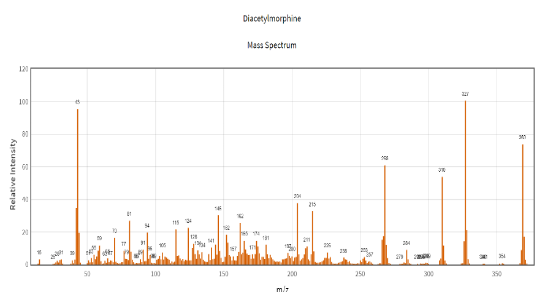
GCMS heroin components:
Cannabis, Sativa plant has provided a source of:
• Cannabis Sativa plant has provided a source of:
o Fuel.
o Textiles.
o Paper.
o Rope.
o Medicines.
o Intoxication.
definition, Misuse of drugs act?


cannabis form?
• Cannabis refers to the plant,
o Skunk: strains bred for higher content of main active ingredient (THC).
• Controlled under drug law,
o Leaf.
o Flowering tops.
• Often not controlled,
o Seeds.
o Stalk.

form of cannabis: Resin?
• Collection of resin,
Brush past plants with rubber sheets.
Scrape resin from sheets.
• Blocks of compressed resin,
Typically wrapped in plastic.
Logos.
Approx. 250g (±10g).
Divided using hot knife.

form of cannabis: oil?
• Solvent extract of:
o Cannabis.
o Cannabis resin.
o Concentrated.
Form | % Main active component THC
|
Cannabis | 1-3 |
Cannabis resin | 4-9 |
Cannabis oil | = 20-50 |
constituents of cannabis?
• Cannabinoids – active constituent of cannabis.
• ›300 compounds,
o Approx. 60 potentially active,
5 numbering systems – 2 are commonly used.
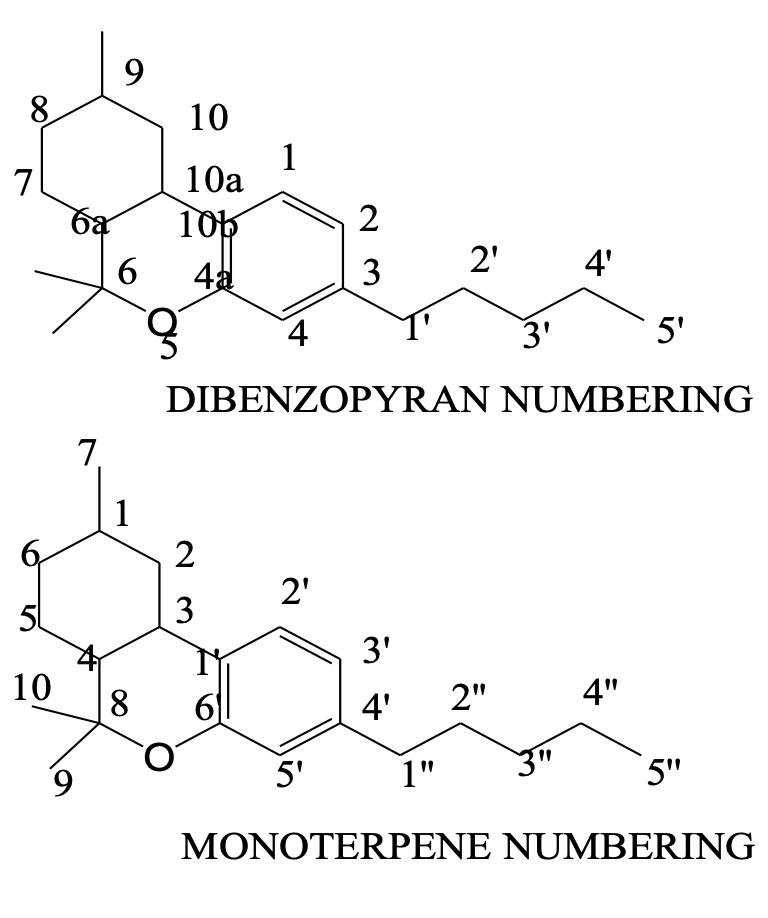
Constituents: ∆-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol
• ∆-9-THC, or THC,
o Dibenzopyran system.
• ∆-1-THC,
o Monoterpene system.
• Main active ingredient in cannabis.
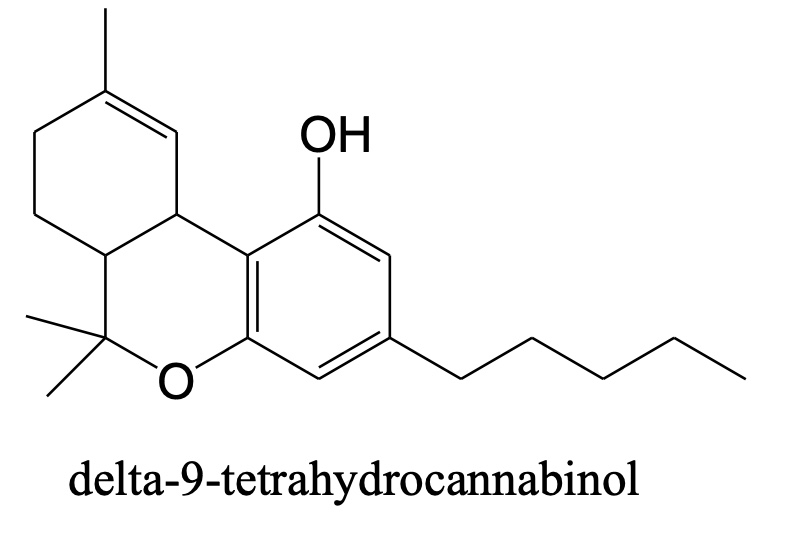
other important constiuents?
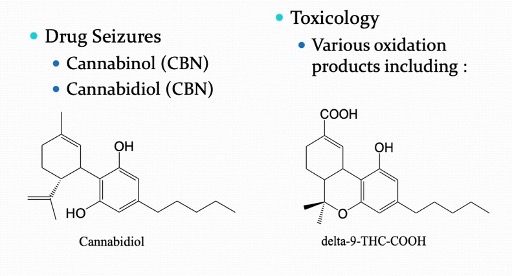
laboratory analysis of Cannabis?
• 3 parameters for identification,
o Chemical colour test.
o Thin layer chromatography.
o Microscopy.
• All of these tests are carried out on cannabis, cannabis resin and oil.
• Some labs carry out GCMS.
Problems with fresh cannabis
| solution |
Chlorophyll masks colour test. | Dry sample in oven and repeat. |
Packaged in plastic – mould can cause asthma. | Package in paper (breathable) carry out analysis in fume hood. |
chemical colour test?
• Duquenois - Levine Test.
• Shavings (using scalpel) are added to test tube.
• Add 5 drops of Duquenois – Levine reagent (vanillin/acetaldehyde/ethanol)
and equal volume of conc. HCl.
• Purple colour within 2 minutes.
• Add CHCl3 and shake.
• Both layers should be purple.
interferences - colour test?
• Tea – purple colour, but no coloured chloroform layer.
• Nutmeg – murky blue colour, lilac coloured chloroform, only after standing for at least 30 minutes.
• Some herbs and spices.
• Generally other parameters will also rule these out.
thin layer chromatography?
• 2 or 3 drops of petroleum ether added to sample – extracts non-polar cannabinoids.
• THC, CBN, CBD spotted to plate.
• Toluene used as developing solvent.
• Plates dried and sprayed with fast blue RR salt or fast blue B salt solutions.
• Highly coloured bands.
• Measure Rf’s.
microscopy?
• Shavings of sample placed on microscope slide.
• Add drops of chloral hydrate.
• Place cover slip.
• Heat gently over spirit burner, moving cover slip.
• Remove from heat and exam at magnification 10-50X.
• 3 main features:
o Cystolithic trichomes (CT).
o Non cystolithic trichomes (NCT).
o Multicellular glandular trichomes (MCGT).
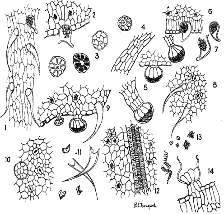
features?
• 5,14,3 stages of multicellular glandular trichomes.
• 6,7 cystolithic trichomes.
• 9,11 non cystolithic trichomes.
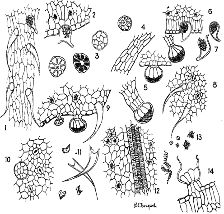
lab analysis: interpretation?
It is vital that the scientist can distinguish between the three types below:
Cannabis Resin | Cannabis | Active Principles |
Characteristic appearance of resin. | Appearance of plant substance | Too small to see or badly charred |
+ ve Duquenois | + ve Duquenois | + ve Duquenois |
3 botanical features (CT, NCT, MCGT) | 2 botanical features (CT, NCT) MCGT as 3rd if mature plant | Botanical features absent or badly charred |
TLC: 3 standards shown (THC, CBN, CBD) | TLC: at least THC | TLC: 3 standards shown |
stimulants: phenethylamine derivatives?
• Broadly subdivided,
o Amphetamine type,
Stimulant properties.
o Ring substituted amphetamine type,
Stimulant properties.
Hallucinogenic from side chain.
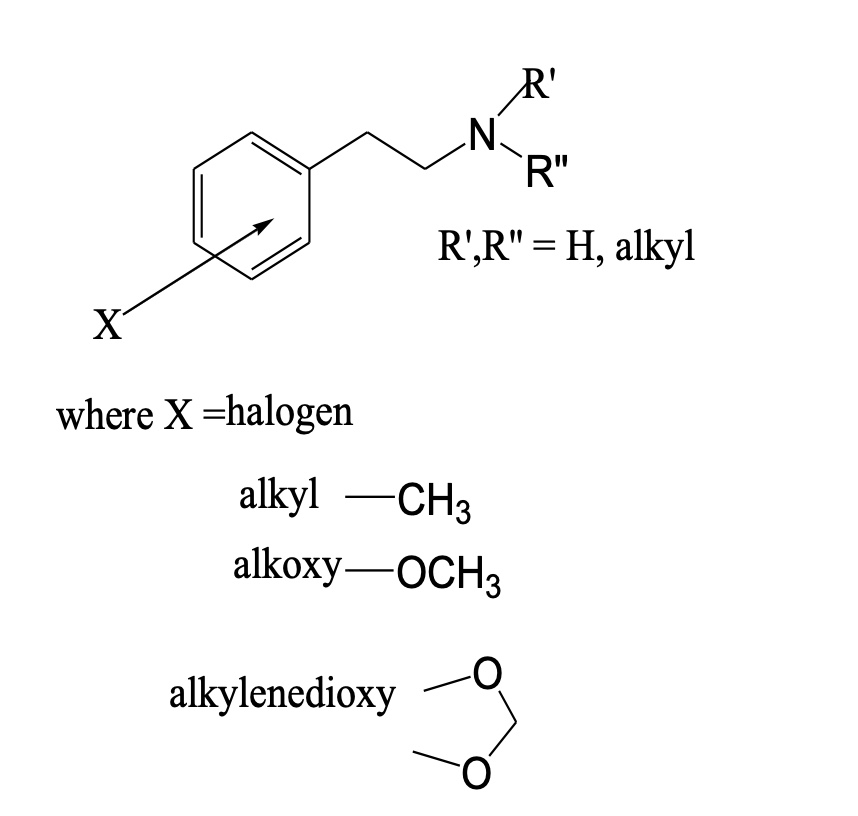
examples?
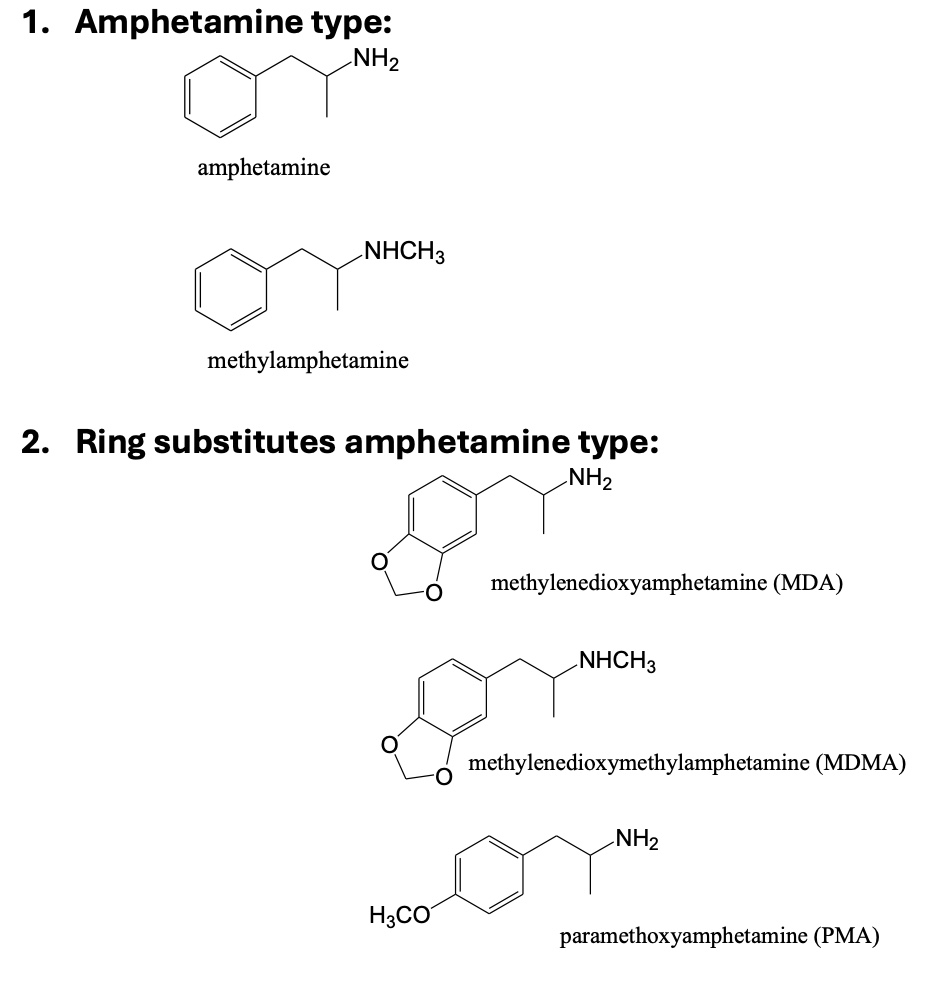
Typical forms of Amphetamine type stimulants?

chemical analysis?
• Colour test : Marquis reagent,
o Orange : amphetamines.
o Blue black : ring substituted.
• GCMS analysis,
o Compounds have polar groups and do not chromatograph well.
o Small molecules M/Z ions not specific.
• Therefore, chemical derivatisation is carried out.
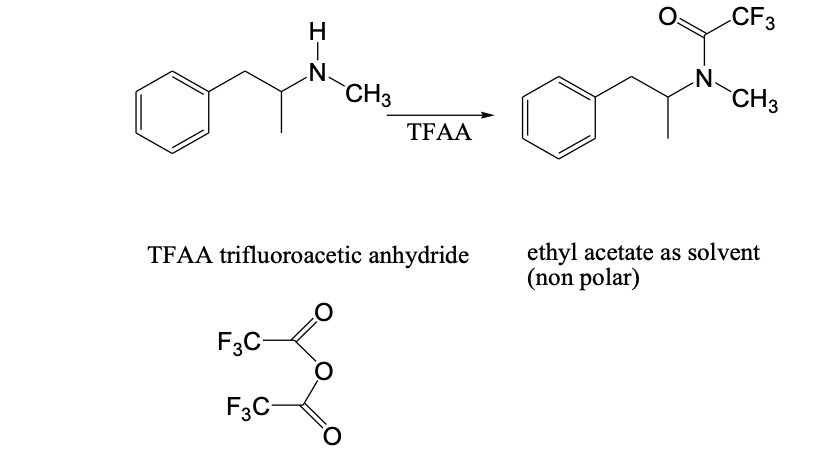
chemical derivatisation?
• Decreases polarity on active hydrogen atoms (OH, NH, SH).
• Improves chromatography.
• May improve stability/detectability.
• Creates more distinguishable ions.
• Commonly,
o Sialylation (addition of –Si (CH3)3).
o Acetylation.
o Acylation (addition of alkyl group e.g. CH3).
Example: Acetylation of Methamphetamine:
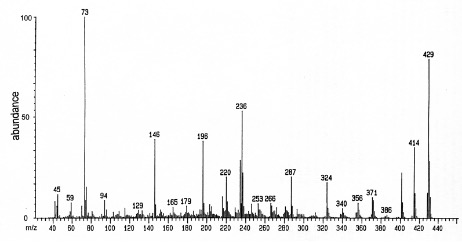
MS Spectra of Derivatised Morphine:
example package, sent to Cherie Blair?
• Former UK prime minister’s wife.
• Package posted,
o Consisted of bottle with commercial label, Eucalyptus oil.
o Typed instructions : rub on face.
o Intercepted at Downing Street sorting office as suspicious.
• Wooden board (backing of wardrobe) found in accused’s house with white staining.
Laboratory examination?
• Bottle contained white slurry,
o Slippery feel between finger of glove.
• High pH in solution (14).
• Flame test yellow,
o AAS confirmed high levels of Na.
• Thought to be NaOH.
• Analysis of white staining on board revealed similar results.
• Conclusion: although analysis was not totally exhaustive – gave police a lever in terms of gaining an admission from accused.
accused?
• 2 schoolboys.
• Other letters had been posted containing,
o Powders.
o Notes suggesting anthrax spores.
• One notable recipient Prince William,
o Studying at St Andrews University at the time.
• Schoolboys admitted charges,
o Blamed unknown internet anarchist for ideas.

