BIO224A: Chapter 16, Endocrine System (Day 2, NO DIAGRAMS)
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
Calcitonin
produced and secreted by parafollicular cells; decreases blood calcium levels
What must be released when calcium ion level in blood is above normal?
calcitonin
How does calcitonin affect osteoclast activity?
inhibits osteoclast activity allowing osteoblast activity
How does osteoblast activity affect calcium ion levels?
They keep taking calcium out of the blood and using it to build bone, so calcium levels decrease
parathyroid gland
3-5 separate glands on posterior surface of thyroid gland
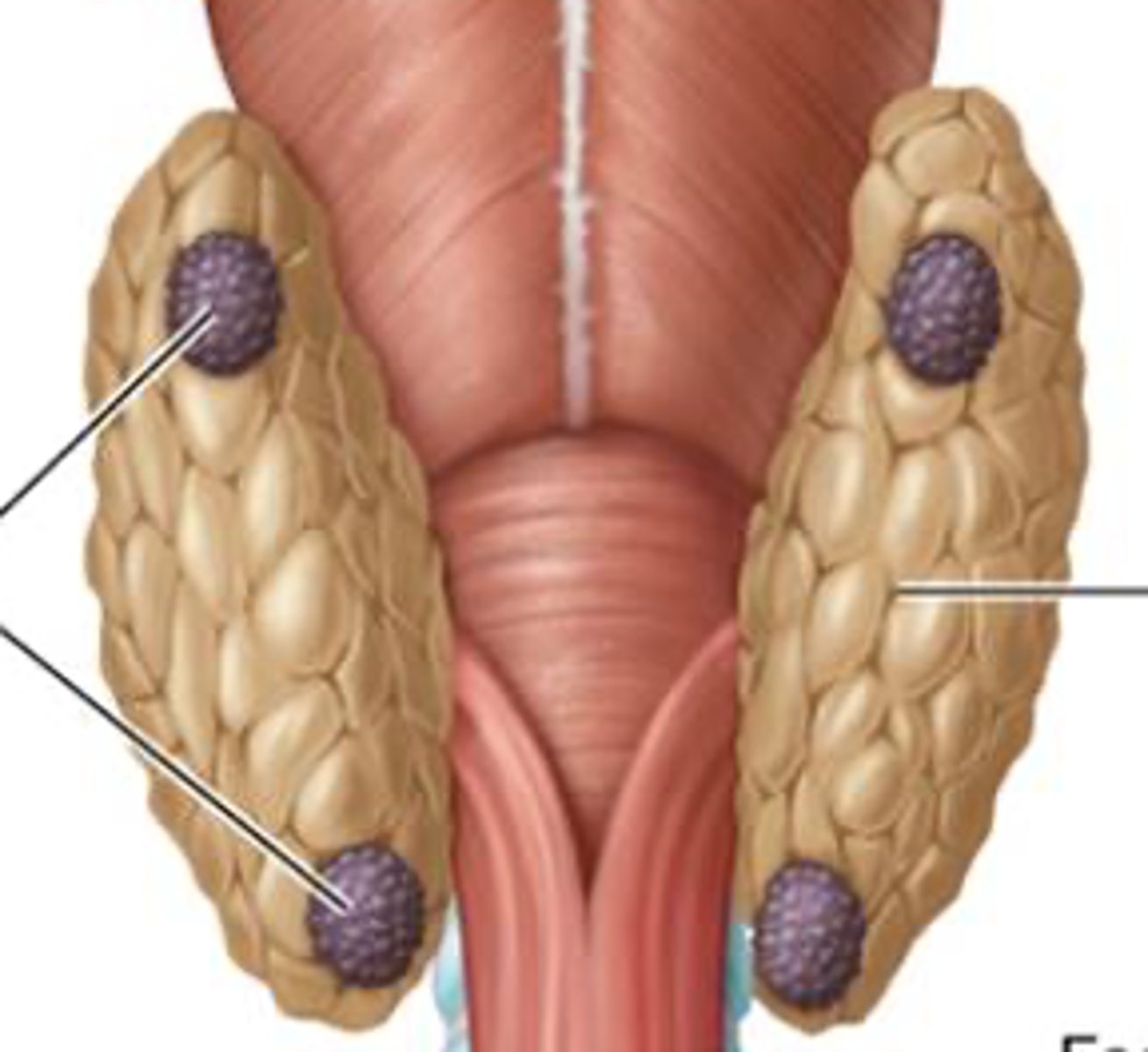
Where is the parathyroid from?
chief cells
Function of parathyroid hormone
increase blood calcium levels
Calcium ion homeostasis
1.) Para follicular cells secrete CALCITONIN to decrease blood calcium levels
2.) Parathyroid chief cells secrete PARATHYROID HORMONE to increase blood calcium levels
Adrenal glands
superior aspect of each kidney, pyramid shaped; produce catecholamine and steroid
Cortex
subdivided into three distinct zones
steroid hormones are derived from...
cholesterol
Outer zona glomerulosa
densely packed cells; produce mineralocorticoid hormones
middle zona fasciculata
cells stacked on one another in columns; secrete glucocorticoids and androgenic steroids
inner zona reticularis
thin layer of cells arranged loosely in clusters; secrete glucocorticoids and androgenic steroids
medulla
neuroendocrine organ that secretes neurohormones
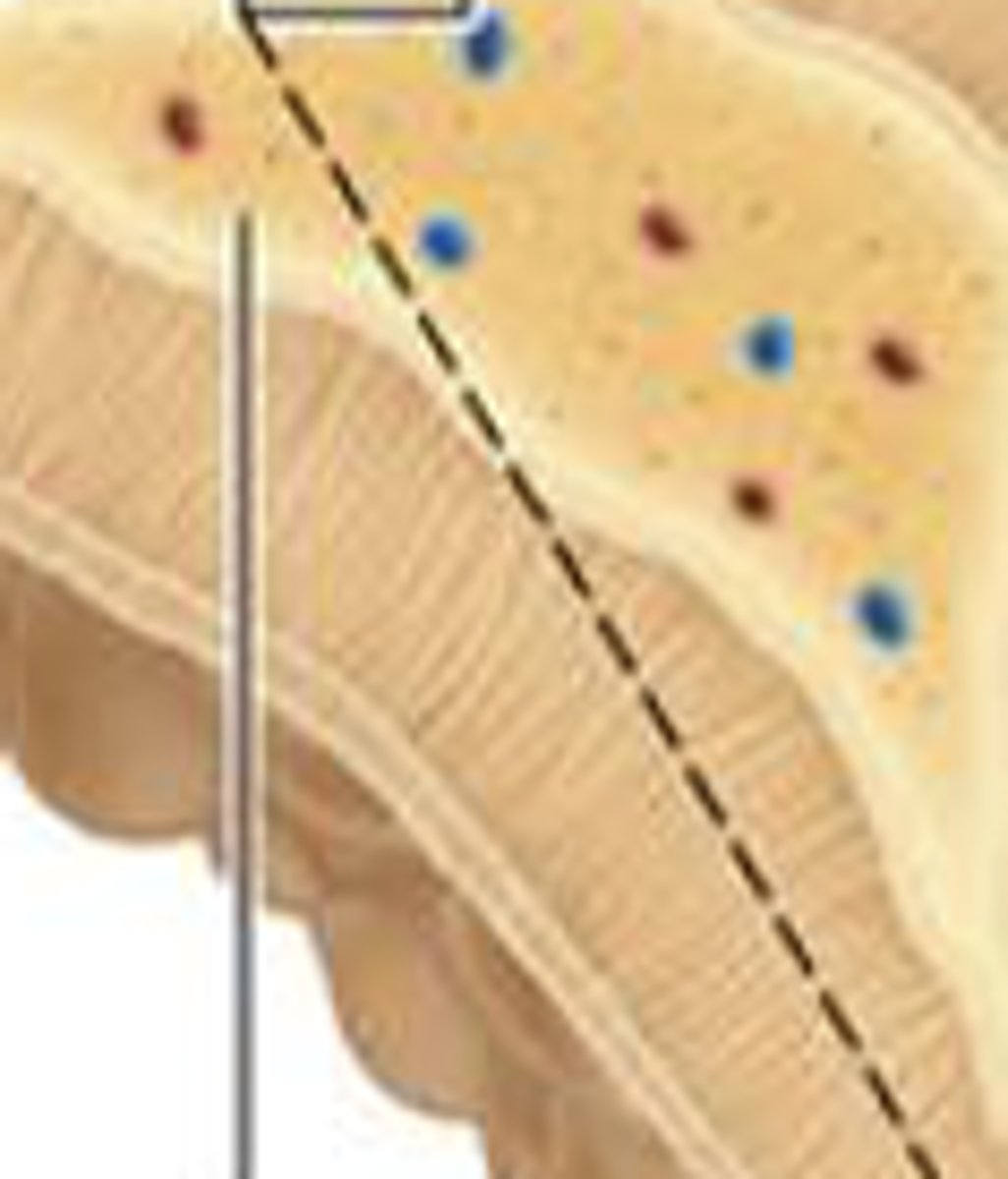
What are the three distinct zones of the cortex?
outer zona glomerulosa, middle zona fasciculata, inner zona reticularis
What does zona glomerulosa secrete?
aldosterone
Aldosterone disorders
Hyperaldosteronism can lead to
- hypokalemia
- hypernatremia
- hypertension
Hyperaldosteronism
hypersecretion of aldosterone
Hypokalemia
low potassium
hypernatremia
high sodium
hypertension
high blood pressure
Zona fasciculata secretes...
corisol
Stress response
events that maintain homeostasis when body is faced with stressor; regulation of blood glucose levels by cortisol
Corisol function
stimulates liver cells to synthesize enzymes of gluconeogenesis
gluconeogenesis
production of new glucose molecules from amino acids and fatty acids
How does gluconeogenesis affect blood glucose levels?
increases blood glucose levels
Besides rising glucose levels, what is the effect of gluconeogenesis on the body?
- induce protein breakdown by releasing free amino acids for glucose conversion
- acts on adipocytes to release fatty acids for fuel/glucose for glucose conversion in the liver
- decreases certain leukocytes, a anti-inflammatory agent
How are cortisol disorders caused?
oversecretion of cortisol or long-term administration ofcorticosteroids
Cushing's disease
oversecretion from adrenal cortex, usually from tumor

Iatrogenic Cushing's syndrome
disorder caused by long-term administration of glucocorticoid-containing drugs
Symptoms of cortisol excess
muscle wasting and sliming of limbs
muscle wasting
the result of the breaking down of proteins in muscle; causes hyperglycemia
hyperglycemia
fats and amino acids converted into glucose
Slight mineralocorticoid effect causes...
hypertension
Effect on leukocytes causes...
immunosuppression
Effect on osteoblast activity and calcium absorption may cause...
osteoporosis
Why do limbs become slim from cortisol excess?
Lipolysis release fatty acids in lower and upper limbs resulting in slim appearance; deposit adipose tissue in TRUNK, FACE, BACK OF NECK
moon facies
round face due to cortisol excess
buffalo hump
hump on back of neck due to cortisol excess
Androgenic steroids
steroid sex hormones that affect GONADS and other tissues
How does the adrenal cortex synthesize hormones?
In small quantities in both genders; mainly by products of cortisol synthesis pathway
How do you change androgenic steroids into other sex hormones?
it can be converted in circulation to androgen testosterone or female hormone estrogen
What can adrenal insufficiency result in?
Addison's disease leading individuals susceptible to adrenal crisis
What is Addison's disease?
hyposecretion of cortisol and mineralocorticoids
What is the result of adrenal crisis?
disruption of fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base homeostasis
What causes adrenal insuffciency?
abnormal development of adrenal gland, deficiency in certain enzymes required to produce steroid hormones, and destruction of adrenal glands by individual’s immune system
Chromaffin cells
derived from nervous tissue; secrete mostly epinephrine
Chromaffin cells function
mediate immediate responses to stressor
How do chromaffin cells create an immediate response to stressors?
1.) increase HR by force of contraction and dilate bronchioles in lung
2.) increase blood pressure via constriction of blood vessels of skin, digestive, and urinary organs
3.) dilate blood vessels supplying skeletal muscles
4.) dilate pupiles
5.) decrease digestive and urinary function
Pancreatic islets
small rounded islands populated by endocrine cells; secrete hormones into bloodstream
Three main cell types of Pancreatic islets
Alpha cells
Beta cells
Delta cells
Alpha cells secrete...
peptide hormone glucagon
Beta cells secrete...
protein hormone insulin
Delta cells secrete...
peptide hormone somatostatin
Exocrine acinar cells
clustered around small ducts to secrete enzymes and other products; delivered to digestive tract
What regulates concentration of glucose in blood?
insulin and glucagon
Glucagon's major target tissues
cells of liver, muscle tissue, and adipose
Glucagon function
promotes reactions that increase levels of glucose and metabolic fuels in blood
glycogenolysis
Breakdown of glycogen
gluconeogenesis location
Formation of new glucose in liver
How is glucagon secretion inhibited?
by both elevated blood glucose level and somatostatin
What is glucagon secretion triggered by?
- decrease in blood glucose
- sympathetic NS stimulation
- Circulating catecholamines from adrenal medulla
–Ingested protein; hormonal response maintains stable glucose levels during feeding
Hormones of the endocrine pancreas
insulin and glucagon
Insulin
antagonist of glucagon; produced and secreted from beta cells of pancreatic islets
What cells does insulin target?
liver, cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle, and parts of brain
Cell responses to insulin
- uptake and storage of ingested nutrients; lowers blood glucose levels
- synthesis or glycogen in liver
- synthesis of fat from lipids and carbohydrates
- satiety
Satiety
feeling of fullness
Hypoglycemia
low blood glucose
what is hypoglycemia caused by?
elevated insulin levels
Symptoms of hypoglycemia
weakness, dizziness, rapid breathing, nausea, and sweating
Symptoms of severe hypoglycemia
confusion, hallucinations, seizures, coma, and death
When do symptoms of severe hypoglycemia occur?
when the brain is deprived of adequate glucose since glucose is the primary fuel for its metabolic reactions
Hyperglycemia
blood glucose too high
Causes of chronic hyperglycemia
Type I diabetes mellitus, but also often congenital
congenital
often-inherited medical condition that occurs at or before birth
What occurs during congenital hyperglycemia?
- target cells cannot take in circulating glucose
- glucose over produced because of no insulin
- increased level of ketone bodies
What is the result of hyperglycemia?
glucose and ketones in urine; water drawn from ECF by osmosis.
- polyuria and polydipsia from dehydration
polyuria
frequent urination
polydipsia
excessive thirst
Type II diabetes mellitus
non-insulin dependent diabetes millitus
Type I diabetes mellitus
insulin dependent diabetes mellitus
Explain the pathogenesis of type I diabetes mellitus
caused by the destruction or lack of beta islet cells that produce and secrete insulin
Explain the pathogenesis of type II diabetes mellitus
insulin's target tissues are insensitive to insulin; insulin resistance occurs
insulin resistance
so target cells do not initiate proper response to blood glucose concentration
Which diabetes type is usually genetic?
type II diabetes
Which diabetes type is often lifestyle linked?
type II diabetes
What is the result of type II diabetes mellitus?
hyperglycemia, glucosuria, polyuria, poludipsia
glucosuria
excess glucose in urine
Which type of diabetes generally produce enough insulin to prevent ketoacidosis?
type II diabetes mellitus
What are the effects of chronic hyperglycemia?
- damage to blood vessels, decreased circulation in heart and lower limbs
- peripheral nerves, peripheral neuropathy in lower limbs
peripheral neuropathy
numbness, tingling, and burning pain in affected areas
In extreme cases, what are the consequences of hyperglycemia?
blindness and kidney failure
pineal gland
primary endocrine; component of epithalamus
What neurohormone does the pineal gland secrete?
melatonin
When does melatonin secretion occur the most?
secretion increases when dark (night)
Is the pineal gland a primary, secondary, or neuroendocrine organ?
neuroendocrine organ
What is melatonin's main target tissues?
sleep regulation centers in reticular formation of brainstem; adjusts sleep/wake cycle in individuals
Thymus
primary endocrine gland in mediastinum
Where do T lymphocytes mature?
thymus