Disorders of Iron Kinetics and Heme Metabolism
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What is the most abundant heavy metal in the body?
iron
2/3 or more of total body iron in _______________.
RBCs
Each mL of RBC contains 1 mg of iron
Distribution of iron ~4000 mg total
Iron intake pattern:
Increases in first few years of life untill teen life. Female adults stay ~18 mg while male adults ~8 mg. Older adult females ~8mg.
iron in Bone Marrow:
~300 mg
iron in Duodenum:
~1-2 mg
Iron in liver:
~1000 mg
iron in myoglobin:
carries and stores oxygen for muscle contraction
~200 mg
iron in transferrin:
~4 mg
it binds to iron and shuttles it to tissues
iron in macrophages:
~600 mg
iron in RBC:
~2500 mg of Ferris 2+
What type of iron is in the blood?
Ferris 2+
how much iron do you usually lose a day?
*What are some causes of loss?
1-2 mg per day
*Sloughed cells
*menstruation
How is iron absorbed?
- Transferrin is secreted by enterocytes into the lumen of the small intestine
- Transferrin binds iron (Fe3+)
- Transferrin-iron complex binds receptor
- Fe3+ transformed to Fe2+ is Taken into cells by receptor-mediated endocytosis
- Some iron is stored in enterocytes as ferritin
- Some iron is transported into blood: bound to transferrin
Ferrous Iron
Fe2+
Ferric Iron
Fe3+
when iron levels are high, what is released?
Hepicidin
**shuts down ferroportin channel reducing iron release to the body-holds iron in storage form in cells
**produced in the liver
What is the ferroportin chanel?
Transports iron(Fe2+) to the body
What is ferritin?
storage form of iron
What converts Fe3+ to Fe2+ on an enterocyte?
duodenal cytochrome B (Dcytb)
**ferric reductase enzyme on border of enterocyte
What channel allows Fe2+ to enter the enterocyte?
DMT 1
In a RBC, how is Fe3+ converted to Fe2+?
Steap 3
AKA a ferreductase
Iron Deficiency Anemia Etiology
-Inadequate intake
-Increased need (pregnancy)
-Impaired absorption (celiac disease)
-Chronic blood loss
Iron Deficiency Anemia 3 stages:
Stage 1—progressive loss of storage iron
Stage 2—exhaustion of iron storage pool
Stage 3—frank anemia
Stage 1 IDA:
RBC development normal
Patient is asymptomatic
Serum ferritin is low
Latent, subclinical
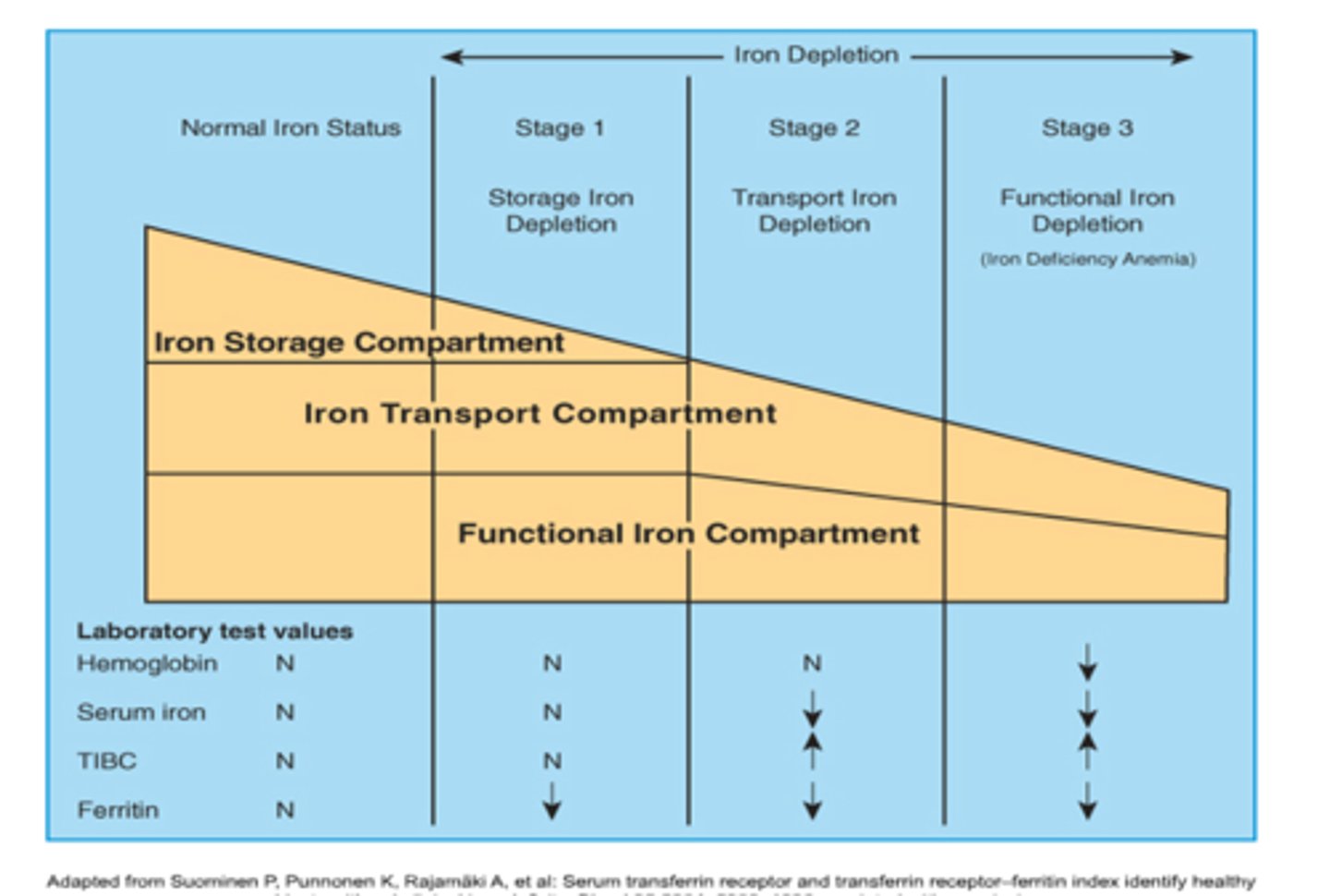
Stage 2 IDA:
-Hgb content of retics decreaase Hgb on hemogram/CBC is normal
-RDW may be increased
-Serum iron and ferritin decreased
-Total Iron Binding Capacity increased
-sTR’s increase
-Prussian blue stain of BM is negative
-Iron deficient erythropoiesis
-Hepcidin decreased
Stage 3 IDA:
-Frank Anemia
-H/H decreased
-Hypo/micro
-FEP and sTR increase
-Ferritin decreased (more iron distribution)
-Hepcidin decreased
-Serum iron decreased
-TIBC increased
-Patient is symptomatic
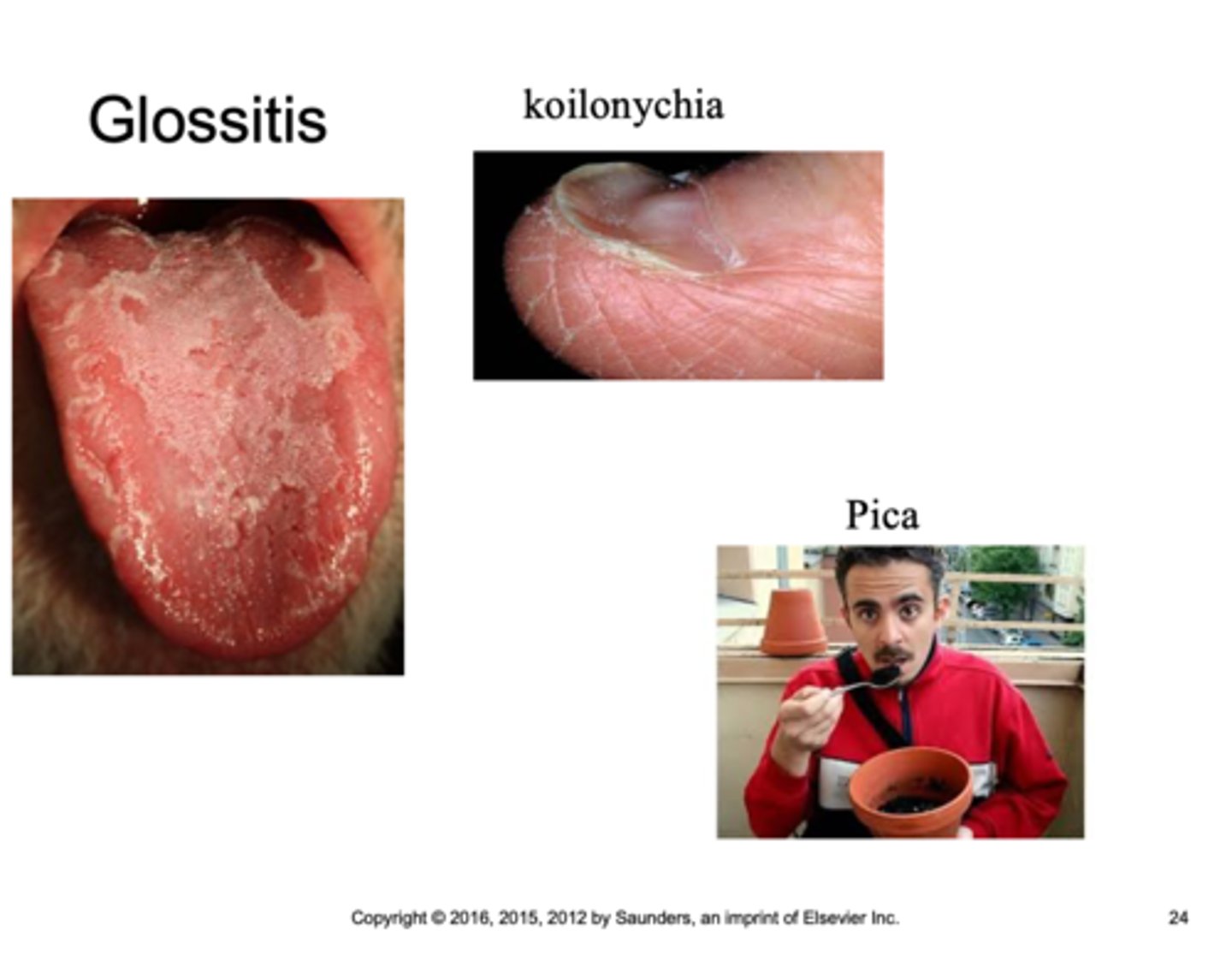
Some symptoms of stage 3 IDA:
Fatigue
Weakness
pallor
glossitis
koilonychia
pica
Groups more at risk for IDA:
•Menstruating women
•Adolescent females
•Pregnant and nursing women
Factors increasing risk of IDA
•Socioeconomics
•Iron absorption
Iron Deficiency Levels:
Serum Ferritin:
Serum iron:
TIBC:
transferrin saturation:
BM Iron:
Serum Ferritin: decreased
Serum iron: decreased/normal
TIBC: increased
transferrin saturation: decreased
BM Iron: no stainable iron
Thalassemia Minor Levels:
Serum Ferritin:
Serum iron:
TIBC:
transferrin saturation:
BM Iron:
Serum Ferritin: increased/normal
Serum iron: increased/normal
TIBC: none
transferrin saturation: increased/normal
BM Iron: increased/normal
Anemia of Chronic Inflammation Levels:
Serum Ferritin:
Serum iron:
TIBC:
transferrin saturation:
BM Iron:
Serum Ferritin: increased/normal
Serum iron: decreased
TIBC: decreased
transferrin saturation: decreased/normal
BM Iron: increased/normal
Sideroblastic Anemia Levels:
Serum Ferritin:
Serum iron:
TIBC:
transferrin saturation:
BM Iron:
Serum Ferritin: increased
Serum iron: increased
TIBC: decreased/normal
transferrin saturation: increased
BM Iron: increased
What kind of cells would you expect to find on the peripheral blood smear of someone with IDA?
Shistocytes
PLT
ovalocyte
helmet cell
target cell
tear drop cell
In a patient with IDA, how would an erythroblast present on a Bone marrow smear?
Shagged outer cytoplasm
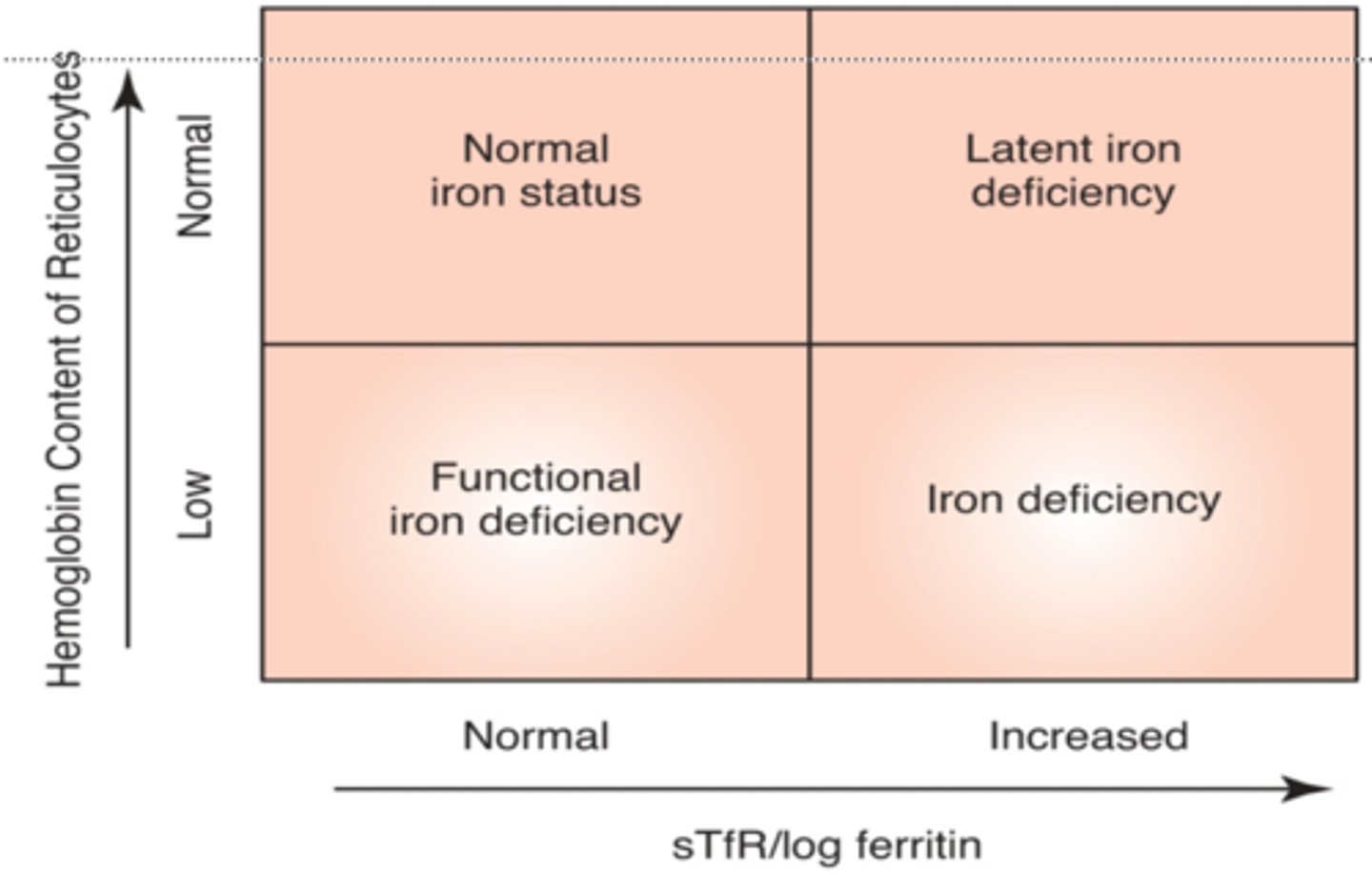
The Thomas plot measures:
Hemoglobin content of retics against sTfR/log ferritin to measure iron status and deficiency
Screening tests for Diagnosing IDA:
•Abnormal complete blood count (CBC) results
•Blood smear abnormalities
Diagnostic testing for IDA:
•Serum iron
•Total iron-binding capacity (TIBC)
•Transferrin saturation
•Ferritin
•Reticulocyte Hb content
Specialized tests for Dx IDA:
•Evaluation of heme synthesis
•Free erythrocyte protoporphyrin
•Soluble transferrin receptors (sTfR)
•Bone marrow evaluation ? not necessary
treatment for IDA:
•Treat underlying cause
•Ferrous sulfate oral supplements
•Iron dextran parenteral administration
•Monoferric (FDA approved) given IV
•RBC transfusion
Measuring response to treatment for IDA
•Reticulocyte Hb content
•Relative and absolute reticulocyte counts
•Hb
•MCV
•Peripheral film smear evaluation
In which stage of IDA is the hemoglobin on CBC normal, serum iron decreased, ferritin decreased, sTfR increased, and TIBC increased?
Stage 2
Anemia of Chronic Inflammation Etiology
-Underlying condition
-Cell products involved
Pathophysiology of Anemia of Chronic Inflammation
-Impaired ferrokinetics
•Role of hepcidin
•Role of lactoferrin
•Role of ferritin
-Inflammatory cytokine production
Anemia of Chronic Inflammation
a type of anemia that affects people who have conditions that cause inflammation, such as infections, autoimmune diseases, cancer link, and chronic kidney disease
Laboratory diagnosis of Anemia of Chronic Inflammation
Hgb 8-10 g/dL
Absence of reticulocytosis
N/N ~ micro/hypo (a third of patients)
Low serum iron
Low TIBC
High ferritin
High FEP
•Failure to incorporate iron into heme molecule
How to Dx Iron deficient Anemia:
-decreased RBC
-Biochemical/clinical evidence of inflammation
-transferrin saturation
How to Dx anemia of inflammation
-decreased RBC
-Biochemical/clinical evidence of inflammation
-transferrin saturation
treatment for anemia of chronic inflammation
Erythropoietin
Ferrous sulfate
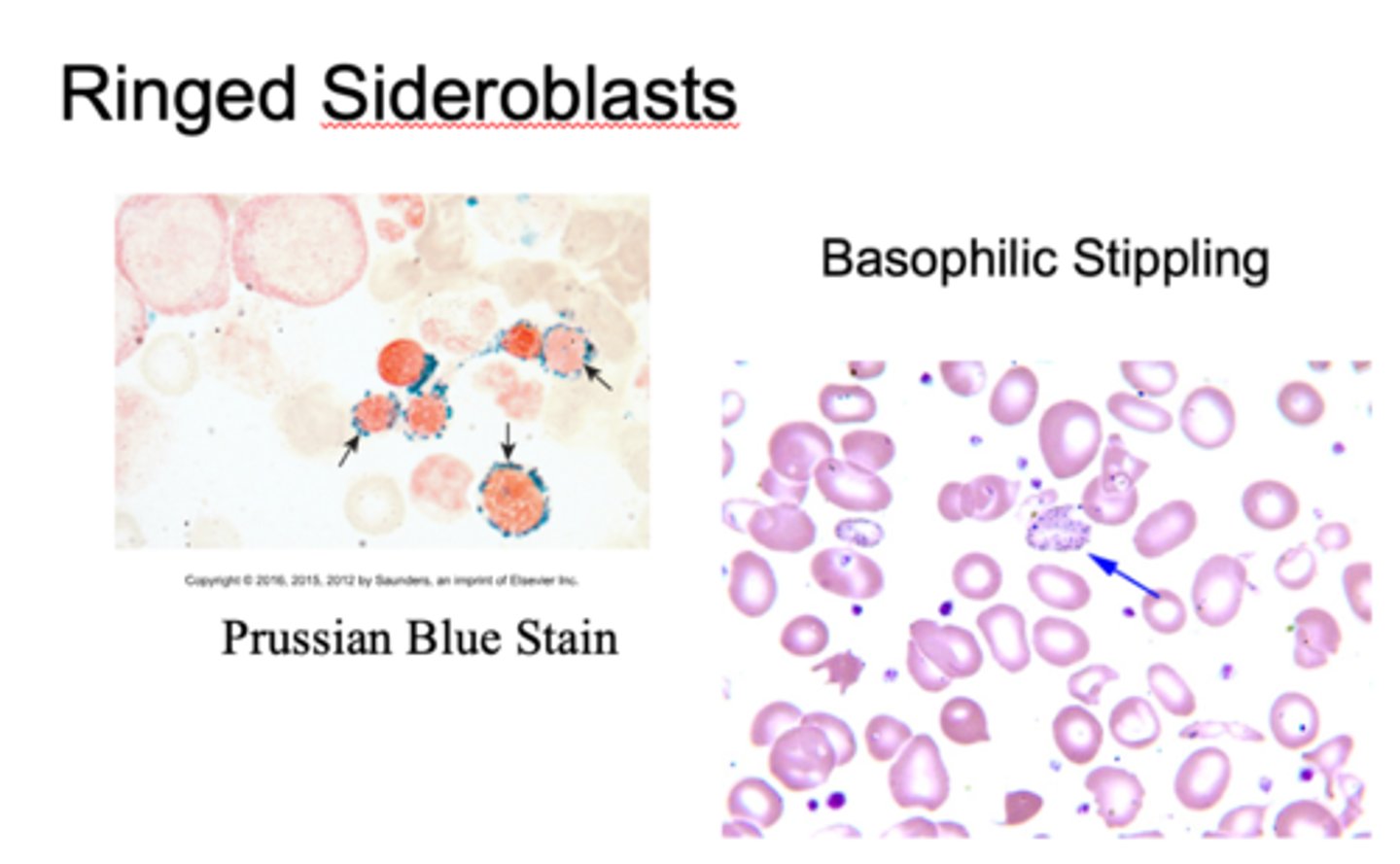
General features of Sideroblastic Anemias
Diverse group of diseases
Hereditary and acquired conditions
Iron deposits in mitochrondria of erythroblasts
Ringed sideroblasts ~ Hallmark
Hereditary Sideroblastic Anemias are
X linked or autosomal
Acquired Sideroblastic Anemias could be from
antitubercular drugs
chloramphenicol
alcohol
lead
chemo agents
Sideroblastic Anemia caused by lead poisoning
-Interferes in biosynthesis of heme
•Conversion of aminolevulinic acid (ALA) to porphobilinogen (PBG) by ALA dehydratase increasing aminolevulinic acid
•Incorporation of iron into protoporphyrin IX by heme synthase
-N/N ~ micro/hypo anemia
-Increased reticulocytes
-interferes with heme biosynthesis
-basophilic stippling
Porphyrias
-Impaired production of porphyrin component of heme
-When an enzyme in heme synthesis is missing the products from earlier stages in the pathway accumulate in cells and body tissues

Erythropoietic Porphyrias (EPP):
Enzyme affected:
Affected Gene:
Clinical features:
RBC:
Urine:
Feces:
Enzyme affected: Ferrochelatase deficiency
Affected Gene: FECH
Clinical features: photosensitivty, mild anemia
RBC(protoporphyrin): increased
Urine(porphobilinogen): normal
Feces(protoporphyrin): increased
Treatment for Erythropoietic Porphyrias (EPP):
Scenesse (FDA approved)
Iron Overload Etiology:
-Acquired
•Blood transfusions – transfusion-related hemosiderosis
-Hereditary
•Homozygous hemochromatosis (5 of 1000 northern Europeans)
•Heterozygous hemochromatosis (13%)
Hemochromatosis, Type 1 (HFE):
Affected gene:
Mutated protein:
normal function of affected protein:
Age of onset:
Affected gene: HFE
Mutated protein: hereditary hemochromatosis
normal function: inhibits TfR1, iron intake, regulates hepicidin
Age of onset: 30-40
Pathogenesis of Iron Overload
-In presence of oxygen ferrous iron initiates superoxide production which damages membranes
-Lysosomal enyzmes released
-Cell death
-"Bronzed diabetes"
*Tanning of the skin, joint pain

Laboratory diagnosis of Iron Overload
-Increased serum ferritin and transferrin saturation
-Genetic testing for mutation
Treatment for Iron Overload
-Hereditary hemochromatosis
•Therapeutic Phlebotomy
•Removal of ~ 500 mL blood per week
-Transfusion-related hemochromatosis
•Iron chelating drugs (e.g. Desferrioxamine)
In which iron disorder is the ferritin increased, serum iron increased, TIBC normal or decreased, FEP increased, and transferrin saturation increased?
Sideroblastic anemia