types of maps/ map projections/ and vocab
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
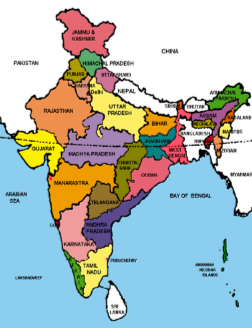
Political map
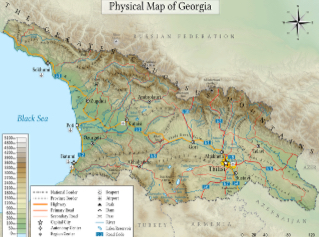
Physical Map
Shows and labels the natural features, such as mountains, rivers, and deserts.
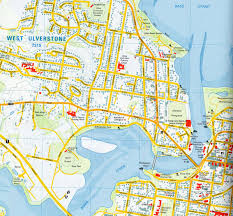
Large scale map
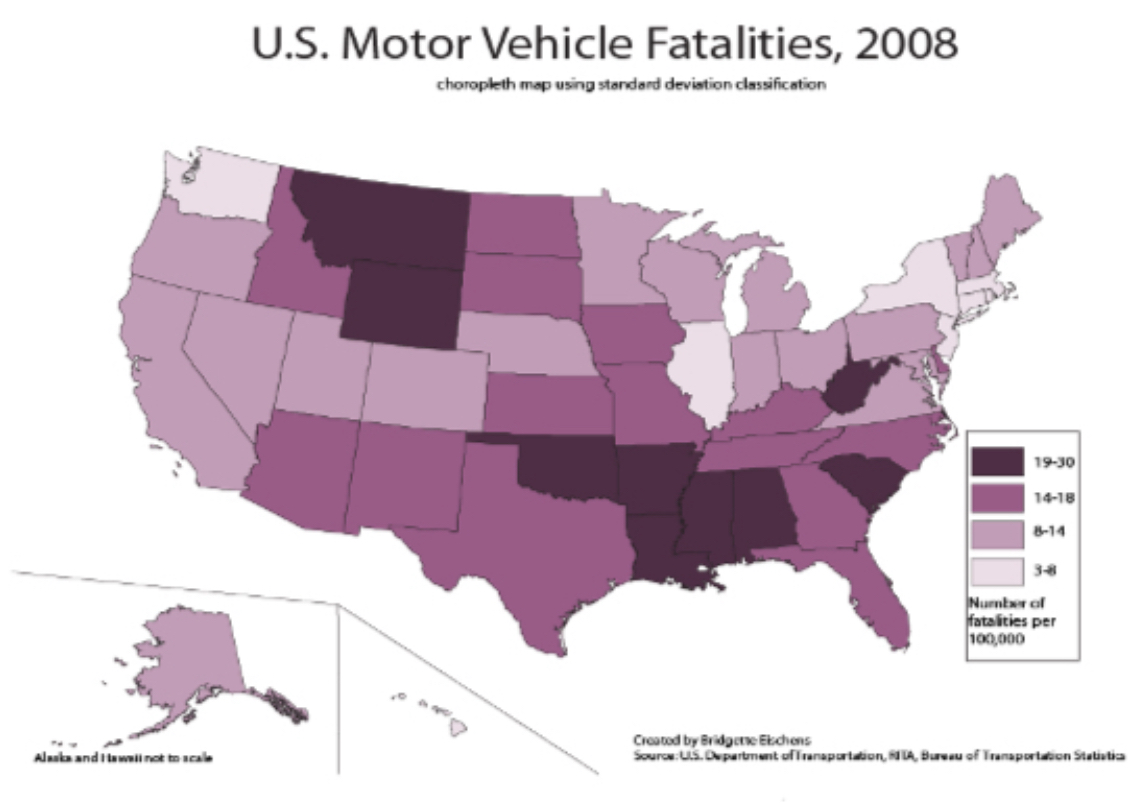
Choropleth Map
Uses various colors, shades of one color, or patterns to show the location and distribution of spatial data.
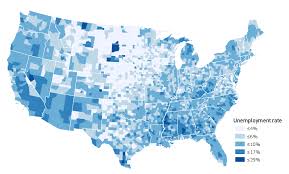
Thematic maps
show spatial aspects of information or of a phenomenon.
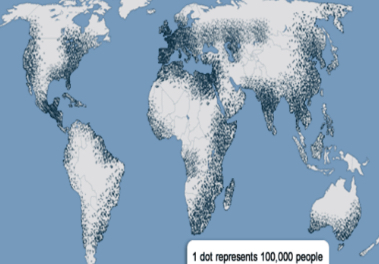
Dot Map
Used to show the specific location and distribution of something across the territory of the map. Each dot represents a specified
quantity.
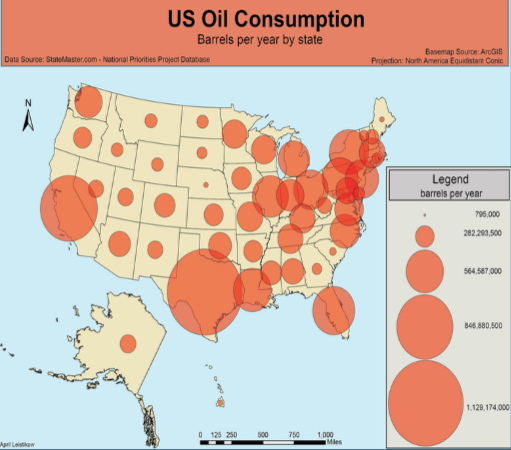
Proportional (Graduated) Symbol Map
Arranged in a series or according to a scale. Uses symbols of different sizes to indicate different amounts of something.
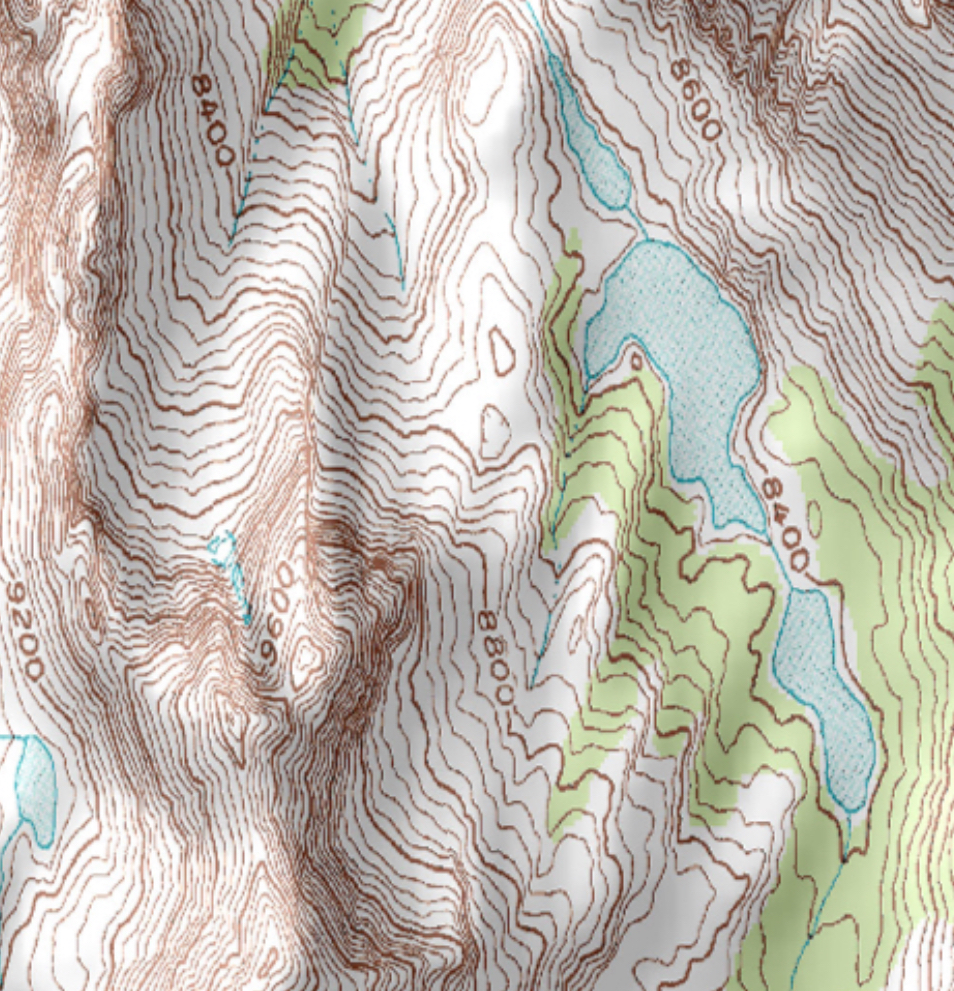
Isoline Map
Uses lines that connect points of equal value to depict variations in the data across space. Where lines are close together, change is rapid and where the lines are far apart, the phenomenon is relatively the same.
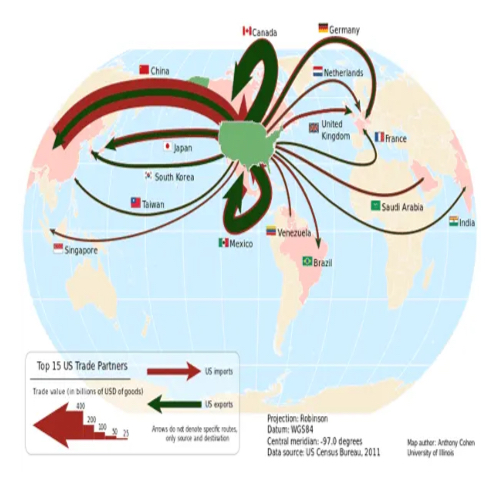
Flow Line
Represent the movement of goods, weather phenomena, people and other living things with line symbols of different widths.
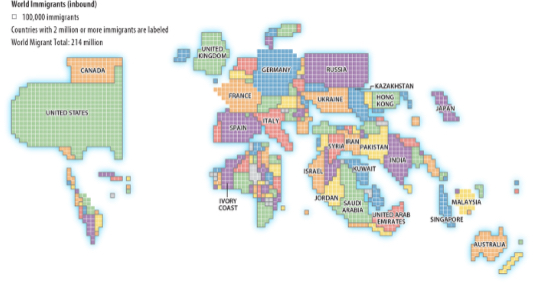
Cartogram
Sizes of countries are shown according to some specific statistic.
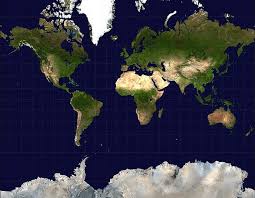
Mercator projection
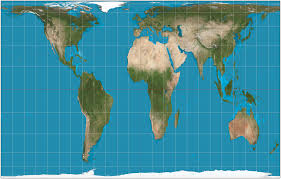
Peters
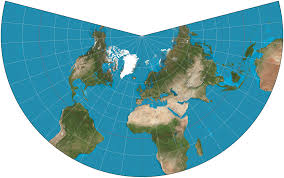
Conic
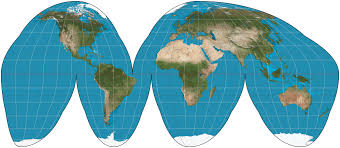
Goode homolosine
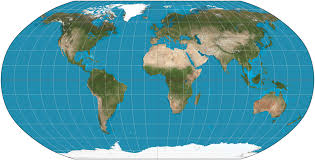
Robinson
Scale
The relationship of the size of a map to the area it represents.
Cartographic Scale
Refers to the way the map communicates the ratio of its size to the size of what it represents. Ex. Large scale maps show less area in greater detail.
Geographic Scale
The total amount of territory the map represents, from local to global.
Scale of Analysis
The level at which data is displaced on a map.
Geo-Inquiry Process
the process that describes how geographers find specific places for specific things (ask, collect, visualize, create, and act.)
Quantitive data
uses numbers to describe what is observed
Qualitative
Data in the form of recorded descriptions rather than numerical measurements.
Census
the official count of a population
Geographic Information System (GIS)
A computer system that stores, organizes, analyzes, and displays geographic data.
Topography
the shape and steepness of the landscape
Remote Sensing
The acquisition of data about Earth's surface from a satellite orbiting the planet or other long-distance methods.
Global Positioning System (GPS)
A system that determines the precise position of something on Earth through a series of satellites, tracking stations, and receivers.
cartographer
a person who makes maps
Absolute Distance
The distance that can be measured with a standard unit length, such as a mile or kilometer.
Relative Distance
Distance measured in terms such as cost or time which are more meaningful for the space relationship in question
Absolute Directions
the cardinal directions north, south, east, and west
Relative Directions
Directions commonly given by people, such as right, left, up, and down, among many others.
Map Scale
The relationship between the size of an object on a map and the size of the actual feature on Earth's surface.
Large Scale
A relatively small ratio between map units and ground units. Usually have higher resolution and cover much smaller regions than small-scale maps.
Small Scale
A map scale ratio in which the ratio of units on the map to units on Earth is quite small usually depict in large areas.
Reference Maps
Maps that show the absolute location of places and geographic features determined by a frame of reference, typically latitude and longitude
Thematic Maps
Maps that tell stories, typically showing the degree of some attribute or the movement of a geographic phenomenon