NSCI 2101 Exam 3 Locomotion
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What are some different types of Gaits?
Gaits: how you use limbs to move
Walking
Running
Skipping
Hopping
Trotting
Swimming
etc
T/F are gaits typified by rhythmic coordination of various limbs?
T
How are rhythmic motor patters of locomotion generated?
Central Pattern Generators
How are rhythmic motor patterns of locomotion modulated for complex locomotion?
By ascending and descending input
What is a Central Pattern Generator (CPGs)?
CPG is a network of neurons, typically in spinal cord, that are capable of generating rhythmic patterns of activity without requiring sensory feedback.
What is rhythmic coordination is required for Locomotion?
The rhythmic coordination of flexor( bending the limb) and extensor (straightening the limb) muscles
How does rhythmic coordination happen?
Mutually inhibiting spinal networks utilizing excitatory and inhibitory interneuorns
What does Mutual Inhibition coordinate?
ipsilateral flexor/extensor opposition as well as contralateral opposition
What does activation of the EphA4 receptor do?
repels axon growth, preventing excitatory interneurons from crossing.
No EphA4 gene → growth of excitatory interneuron across spinal cord → contralateral excitation.
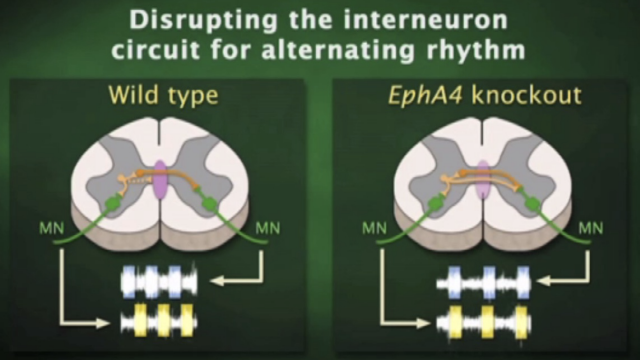
What would happen if instead of contralateral inhibition, the spinal walking circuit gave rise to contralateral excitation?
you have to hop
What does sensory feedback do with locomotion?
Modulates timing, amplitude of steps, and allows coordination in the motor cortex to plan future movements.
How does Proprioceptive information allows the automatic movements of walking?
Ia afferents from muscle spindles (muscle stretch reflex) notice foot is moving far back so it stretches
ib afferents from Golgi Tendon Organs (Muscle contraction) contracts leg muscle
Proprioceptive Information
Stretching the hip flexor muscle → activates muscle spindle in felxor muscle → Excite MN to contract flexor muscle → inhibit MN to relax extensor muscle
What does the Golgi Tendon Organ (GTO) do when it is squeezed during muscle contraction?
Sends signals to the spinal cord and transmits information on muscle load.
what does the Mesencephalic Locomotor Region (MLR) do?
Initiate walking, even in decerebrated prep.
MLR → Reticular formation (medulla) (axons in ventrolateral funiculus) → Central Pattern Generators (CPG)
What is involved in gait modulation but not critical for initiation?
Subthalamic locotomor region (in the subthalamic nucleus)
Pontine pedencular nucleus (in the pons)
What can modulate the speed of walking?
Stimulation of Mesencephalic locomotor region with higher intensities → faster speed
What do descending pathways need to activate to initiate walking?
Required glutamatergic activation
What neurotransmitters are sufficient to initiate stepping but not necessary?
Norepinephrine and serotonin
What information does the Cerebellum receive from the spinocerebellar tract?
Dorsal spinocerebellum tract: proprioception
Ventral spinocerebellum tract: afferents from Central Pattern Generators.
Gives the cerebellum information on where the limbs are in space and what the pattern of limb movement is
How does the Cerebellum fine-tune locomotor patterns?
Cerebellum receives descending motor information from motor cortex and transmits plans for intended and upcoming motor movements
What information does the Cerebellum combine for fine-tuned locomotor patterns?
Current limb position
current motor pattern
intended motor commands
upcoming motor commands
What is necessary for stepping over an object?
Visuomotor coordination and the motor cortex. When stepping over an object, its position relative to the limbs is kept in working memory and the posterior parietal cortex is critical for this function