Econ test 4
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Expansionary Policy
An economic policy aimed at increasing aggregate demand through government spending, tax cuts, and lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth.
Contractionary Policy
An economic policy aimed at reducing aggregate demand, typically through decreases in government spending, increases in taxes, and higher interest rates to control inflation.
Conventional Monetary Policy Tools
o Adjustments in open market operations
o Reserve requirements
o Discount rate
Unconventional Monetary Policy Tools
o Large-scale security purchases (quantitative easing)
o Payment of interest on reserves that depository institutions hold at federal reserve banks
OMO’s
Purchases and sales of short-term treasury securities and other securities on the secondary market.
Defensive Open Market Operations
Operation intended to offset temporary fluctuations in the demand or supply of bank reserves, rather than carrying out permanent changes in bank reserves
Repurchase Agreements
Increases bank reserves, trading desk will purchase short-term securities from a bank, for a specified price at an agreed-upon date in the future, subject to resell
Reverse Repurchase Agreement
Decreases bank reserves, the trading desk sells short-term securities to a bank, agreeing to buy them back at a specified future date for a specified price. indicator of excess liquidity in a banking system.
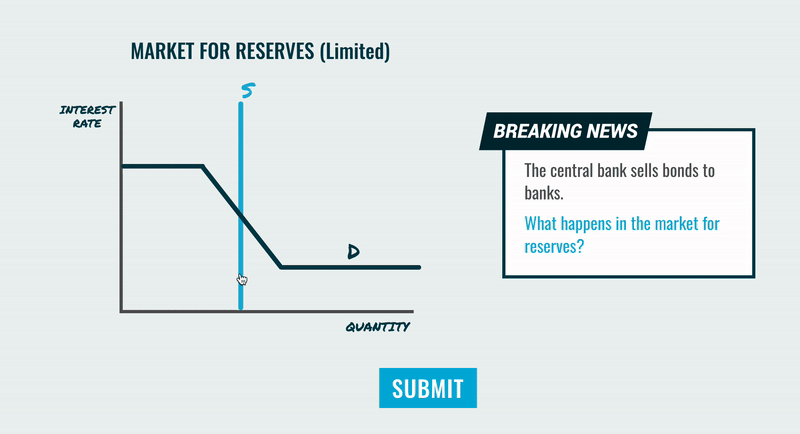
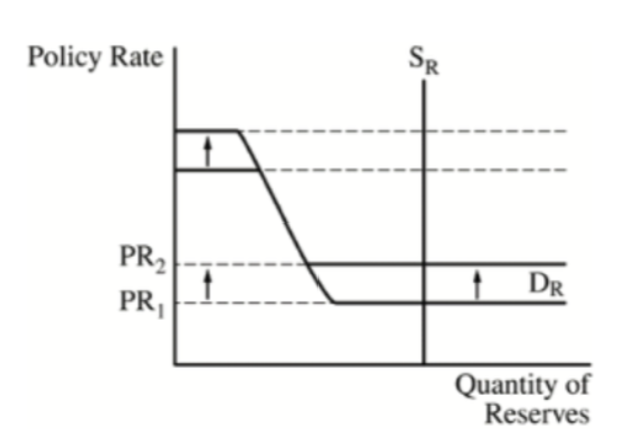
Reserve Market
A market where banks lend and borrow reserves primarily to meet their required reserve ratios or manage their liquidity.
Limited Reserve Market Graph
Ample Reserve Market Graph
Inflation Targeting
Fed strategy of stating an inflation rate as a goal and enacting monetary policy to realize that rate. Currently at 2%.
Taylor Rule
A guideline that the Fed can use to adjust interest rates to stabilize the economy
Taylor Rule Formula
Federal Funds Rate Target = Equilibrium real interest rate + inflation rate + weighted average of 2 gaps
2 Gaps
Inflation Gap = current - target inflation
Output Gap = Real GDP - Potential GDP
Recognitional Lag
Time delay between when an economic shock occurs and when policymakers understand its implications
Operational Lag
The period between when monetary authorities enact a change in policy and when it takes full economic effect
Cyclical Asymmetry
The phenomenon where monetary policy may have a different effect during economic expansions compared to contractions, often leading to ineffective responses during recessions.
Rules
Wages + prices are flexible so economy will self adjust
lags, data, recognition, legislative implications, effectiveness
Fed may not have current data / relative info
Fed may not have a full understanding economy
Discretion
Wages and prices are sticky so self-adjustment is very slow
Flexible / prevents fluctuations due to unforeseen circumstances
Paul Volcker, Inflation of the 70’s
Period great Inflation - The period during the 1970s to the early 1980s that was characterized by an increasing inflation rate. In the late 1970s and early 1980s, Federal Reserve Chair Paul Volcker curbed the Great Inflation by dramatically raising interest rates, pushing the federal funds rate as high as 20% to break inflationary expectations.
The 2001 Attack on America
Following the 2001 terrorist attacks, the Federal Reserve swiftly stabilized the U.S. economy by injecting liquidity into financial markets, cutting interest rates, and ensuring the smooth operation of banking systems. These actions helped restore confidence, prevent a financial panic, and support economic recovery during a time of national crisis.
The Great Recession of 2007–2009
During the Great Recession of 2007–2009, the Federal Reserve took aggressive measures to stabilize the economy by slashing interest rates to near zero and launching unprecedented programs like quantitative easing to inject liquidity into the financial system. These actions helped restore confidence, support credit markets, and pave the way for economic recovery.
COVID-19 Pandemic
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the Federal Reserve took swift action to stabilize the economy by slashing interest rates to near zero and launching massive asset purchase programs to ensure liquidity in financial markets. It also implemented emergency lending facilities to support businesses, households, and municipalities, helping to prevent a deeper economic collapse.