Chapter 6 – Skeletal System Scintigraphy
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Which of the following is a malignant bone disease?
Ewing’s sarcoma
A three-phase bone scan is often done to differentiate:
Osteomyelitis vs. cellulitis
The presence of gastric and thyroid activity on a bone scan signals:
Free pertechnetate
Purpose of a reducing agent in a Tc-99m diphosphonate kit:
Both
What is the dose of Tc-99m MDP most often prescribed for a planar bone scan?
20-30 mCi
Which of the following is least likely to cause an artifact on a bone scan:
Colostomy bag
What is not an indication for a bone scan?
Osteoporosis
The presence of free pertechnetate on a bone scan may be the result of:
Both
What is the purpose of hydration and voiding after an injection for a bone scan?
Reduce radiation dose to the bladder
Cause of generalized diffuse abdominal activity:
Malignant ascites
Timing protocol best describing a four-phase bone scan:
During injection, immediately following, 2–4 h and 18–24 h
A focal hot spot near the left femur shows up on a bone scan. What is/are the best way/ways to proceed?
Both
A bone scan showing relatively uniformly increased skeletal uptake of radiopharmaceutical with almost absent renal and bladder activity is usually referred to as a:
Superscan
The glove phenomenon is usually the result of:
Arterial injection
What are common sites of bony metastasis?
All of the above
Purpose of stannous ion in a diphosphonate kit:
Acts as a reducing agent
The appendicular skeleton includes the following bones, except:
Skull
The axial skeleton contains:
All of the above
By what mechanism do diphosphonates localize in the bone?
Ion exchange
Which of the following describes a pediatric bone scan?
Increased uptake along epiphyseal plates
The first phase of a three-phase bone scan is best performed by:
Bolus injection + dynamic 2-s images for 60 s
What pharmaceuticals may be used for bone marrow imaging:
Both
What is often used in imaging-suspected avascular necrosis of the hip?
Pinhole collimation (also SPECT)
Splenic uptake on a bone scan is often associated with
Sickle cell disease
The bone is made of:
Hydroxyapatite + collagen
Osteoblastic activity refers to:
New bone formation
Osteoclastic activity refers to:
Destruction and reabsorption of bone
Function of the skeleton:
All of the above
Which group shows the highest rate of primary bone tumors?
Children
The radiation dose from a bone scan is highest to the:
Bladder
When performing a bolus injection for a three-phase bone scan, why would the tourniquet be released and injection delayed for 1 min?
Reduce transient hyperemia
What is an advantage of spot planar imaging over whole body imaging for a bone scan?
Decreased patient-to-detector distance
Reason not to inject in right antecubital fossa:
Suspicion of osseous abnormality there
The preparation for a bone scan is:
None of the above
Metastases usually affect the axial skeleton before the appendicular skeleton.
True
The advantage(s) of bone scanning over plain radiography is:
All of the above
The mechanism of localization for bone marrow scanning is:
Phagocytosis
A large amount of diffuse soft tissue activity present on a bone scan at 4 h frequently represents:
Renal insufficiency
What imaging agent can be used to image the skeleton as well as myocardial infarction?
Tc-99m PYP
Rib fractures often show up as:
Multiple focal hot spots located in consecutive ribs
Cold defect in left proximal humerus is most likely from:
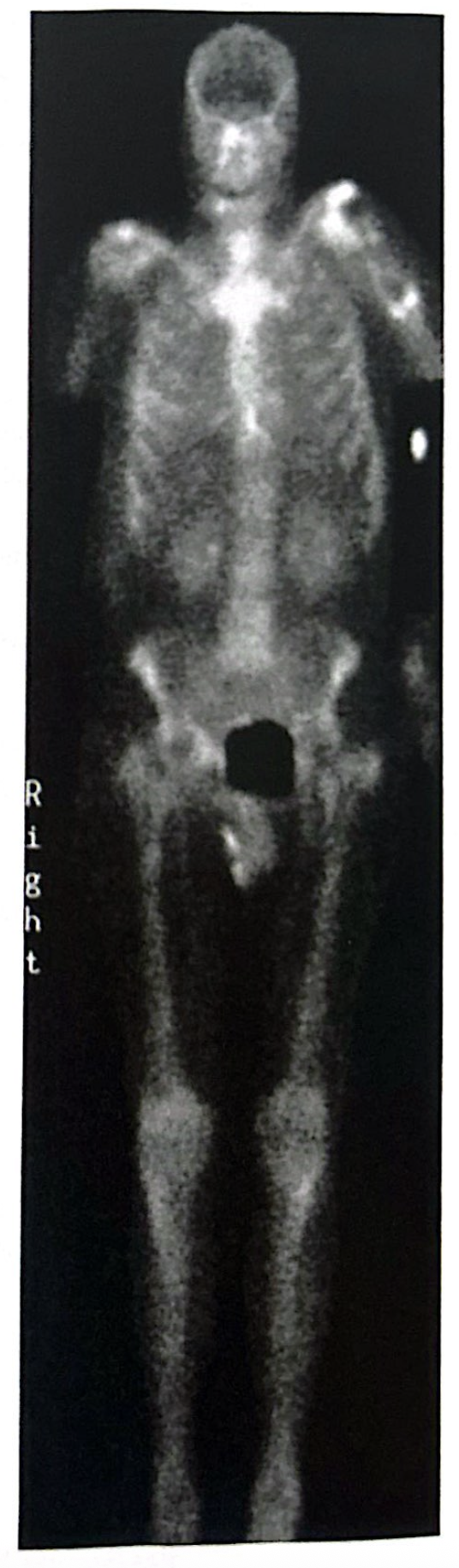
Surgically implanted metal