VITAMINS part 1 (fat-soluble)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/47
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
1
New cards
Emergence of Vitamins
100 years ago
2
New cards
Accessory food factors
Vitamin (Casimir Funk (1912)
3
New cards
Vita: Essential 4 life
Amine: contain nitrogen
4
New cards
Vitamins (1970)
* not classified into groups
* classified according to **biological functio**n in body
* not classified into groups
* classified according to **biological functio**n in body
based on **physical-chemical** properties
* water-soluble
* fat-soluble
* water-soluble
* fat-soluble
5
New cards
Vitamins
* potent organic compounds → unrelated chemical composition
* minute quantities
* small amounts →specific regulatory functions
* minute quantities
* small amounts →specific regulatory functions
6
New cards
Vitamins provide Energy
ingested preformed
7
New cards
**Organic Compounds**
All Vitamins contain C,H,O in chemical composition
8
New cards
Water-soluble vitamins
NITROGEN in chemical composition
9
New cards
Vitamins vs. Proteins
Nitrogen in Vitamins - not occur as building units of proteins
10
New cards
Vitamins vs. Minerals
All **Vitamins** are ORGANIC
All **Minerals** are INORGANIC
All **Minerals** are INORGANIC
11
New cards
Potent Minute Quantities
very small concentrations of vit. → maintain life / normal growth.
12
New cards
Potent Minute Quantities
micronutrients
13
New cards
Potent Minute Quantities (Measurement)
* **MICRO**GRAMS (mcg – one **millionth** of a gram)
* **MILLI**GRAM (mg- one **thousand** of a gram)
* **MILLI**GRAM (mg- one **thousand** of a gram)
14
New cards
Dietary Essentials
Distinguishes Vitamins from hormones
15
New cards
**PRE-CURSORS/PROVITAMINS**
changed into active vitamins
16
New cards
**PRE-CURSORS/PROVITAMINS (ex.)**
✓ Carotene & Cryptoxanthin -> Vitamin A
✓ Ergosterol -> Vitamin D
✓ Tryptophan -> Niacin
✓ Ergosterol -> Vitamin D
✓ Tryptophan -> Niacin
17
New cards
PREFORMED VITAMINS
* **Naturally-occurring** in active form, ready for biological role
18
New cards
AVITAMINOSIS (condition)
* lack of vitamin in body
* nutritional deficiency disease is recognizable
* nutritional deficiency disease is recognizable
19
New cards
HYPERVITAMINOSIS (Vitamin Toxicity)
* excessive **accumulation** of vitamin **A**
* chronic **intake** of vitamin **more** **than** **recommended** dietary allowance (RDA)
* chronic **intake** of vitamin **more** **than** **recommended** dietary allowance (RDA)
20
New cards
VITAMIN MALNUTRITION
too much / too little - not good 4 health
21
New cards
VITAMIN-LIKE COMPOUNDS
* **physiological** roles like vitamins
* present in **larger** amounts
* partially **synthesized** in body
Ex. Choline: as essential with B-vitamins
* present in **larger** amounts
* partially **synthesized** in body
Ex. Choline: as essential with B-vitamins
22
New cards
ANTI-VITAMINS / VITAMIN ANTAGONISTS
* interfere w/ normal functioning of a Vitamin
Ex:
* **dicumarol** against Vitamin **K**
* **avidin** against **biotin**
* **thiaminase** against thiamin or **B2**
Ex:
* **dicumarol** against Vitamin **K**
* **avidin** against **biotin**
* **thiaminase** against thiamin or **B2**
23
New cards
SYNTHETIC VITAMINS (Man-made)
* experimental/therapeutic purposes
24
New cards
VITAMERS
Multiple forms of a Vitamin
25
New cards
Fat-Soluble Vitamins (A, D, E, K)
* pro-vitamins
* deficiencies are slow
* needed daily from food sources
* stable in ordinary cooking methods
* deficiencies are slow
* needed daily from food sources
* stable in ordinary cooking methods
26
New cards

VITAMIN A
* Promotes vision; light & color; Visual purple (rhodopsia)
* Promotes growth, reproduction, immunity
* Prevents drying of **skin** & eyes
* Promotes resistance to bacterial infection
* Possible aid in treating cancer patients.
* Promotes growth, reproduction, immunity
* Prevents drying of **skin** & eyes
* Promotes resistance to bacterial infection
* Possible aid in treating cancer patients.
27
New cards
VITAMIN A (malnutrition)
Deficiency
* Night blindness
* Xeropthalmia
* Poor Growth
* Dry Skin
Toxic
* Fetal malformations
* Hair loss
* Skin changes
* Pain in bones (beyond 3000 RE per day
* Night blindness
* Xeropthalmia
* Poor Growth
* Dry Skin
Toxic
* Fetal malformations
* Hair loss
* Skin changes
* Pain in bones (beyond 3000 RE per day
28
New cards
VITAMIN A (dietary allowance)
* mcg (microgram) RE (recommended energy)
* Male: 19 years n over: 550 mcg RE
* Female: 19 years n over: 500 mcg RE
* Male: 19 years n over: 550 mcg RE
* Female: 19 years n over: 500 mcg RE
29
New cards
VITAMIN A (excess intake) Hypervitaminosis A
* **carotenemia** - yellow skin discoloration
* bone fragility / painful swellings
* Dry, itching skin, coarse sparse hair •
* Nausea, Headache, Irritability
* bone fragility / painful swellings
* Dry, itching skin, coarse sparse hair •
* Nausea, Headache, Irritability
30
New cards
VITAMIN A sources
Liver • Butter • Fortified milk • Fortified Margarine • Carrots • Greens • Broccoli • Sweet potatoes • Spinach • Papaya • Cantaloupe • Apricots
31
New cards
Vitamin A, Beta-Carotene, and Cancer
* low risk lung cancer
* ^ beta-carotene → 46% die lung cancer
* smokers + beta caro = lung cancer
* beta-carotene rarely advisable
* ^ beta-carotene → 46% die lung cancer
* smokers + beta caro = lung cancer
* beta-carotene rarely advisable
32
New cards

VITAMIN D
* Facilitates absorption of calcium & phosphorus
* optimal calcification of bones
* optimal calcification of bones
33
New cards
VITAMIN D (forms)
* calciferol - fish oils and eggyolk, added to margarine and milk
* cholecalciferol - sunlight hit skin; UV rays react w steroid
* ergocalciferol - synthesized plants exposed to sunlight
* cholecalciferol - sunlight hit skin; UV rays react w steroid
* ergocalciferol - synthesized plants exposed to sunlight
34
New cards
VITAMIN D
* require bile salts → absorbed store in liver
* mainly absorb calcium n phosphorus
* make cell membrane permeable
* mainly absorb calcium n phosphorus
* make cell membrane permeable
35
New cards
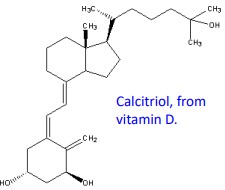
VITAMIN D
* VDP “vitamin D binding protein” - target organs
* pheromone; is not active
* modified to yield biologically active forms, such as
* Calcitriol - transcription factor
* immune system function
* pheromone; is not active
* modified to yield biologically active forms, such as
* Calcitriol - transcription factor
* immune system function
36
New cards
VITAMIN D deficiency
* rickets, bone loss, osteomalacia
Toxic
* Growth Retardation • Kidney damage • Deposits in soft tissue • Toxicity beyond 2000 IU/day
Toxic
* Growth Retardation • Kidney damage • Deposits in soft tissue • Toxicity beyond 2000 IU/day
37
New cards
VITAMIN D (RDA)
* 100-400 IU
* Infants, children, adolescents: 5 mcg
Adults:
* – Male & Female (19-49 yrs.): 10 mcg
* – Male & Female (50-64 yrs.): 15 mcg
* Infants, children, adolescents: 5 mcg
Adults:
* – Male & Female (19-49 yrs.): 10 mcg
* – Male & Female (50-64 yrs.): 15 mcg
38
New cards
VITAMIN D sources
Vitamin D fortified milk • Fortified margarine • Fish oils • Sardines • Salmon
39
New cards
VITAMIN E
* Act as an anti-oxidant
* Prevent breakdown of Vitamin A, Vitamin K and unsaturated fatty acids
* Prevent breakdown of Vitamin A, Vitamin K and unsaturated fatty acids
40
New cards
VITAMIN E
* Retard spoilage in commercial products
* Preserve the integrity of RBC walls
* Protect muscle tissue from degeneration
* Protect unsaturated fatty acids from oxidative breakdown
* antioxidant, protects tissues/membrane against damage of oxidation.
* normal functioning of the immune system
* Controls blood platelet aggregation during formation of blood clots
* metabolism of nucleic acids and proteins
* mitochondria function and production of different hormones regulation
* Protects vitamin A from oxidative damage
* Preserve the integrity of RBC walls
* Protect muscle tissue from degeneration
* Protect unsaturated fatty acids from oxidative breakdown
* antioxidant, protects tissues/membrane against damage of oxidation.
* normal functioning of the immune system
* Controls blood platelet aggregation during formation of blood clots
* metabolism of nucleic acids and proteins
* mitochondria function and production of different hormones regulation
* Protects vitamin A from oxidative damage
41
New cards
VITAMIN E deficiency
* Hemolysis of red blood cells • Nerve destruction
* Muscle weakness • Headaches • Fatigue • Blood clots • Toxic beyond 1200 IU/day
* Muscle weakness • Headaches • Fatigue • Blood clots • Toxic beyond 1200 IU/day
42
New cards
VITAMIN E (RDA)
* Muscle weakness, Headaches, Fatigue, Blood clots
* Toxic beyond 1200 IU/day
* more than rda - improves the immune system in the elderly
* Toxic beyond 1200 IU/day
* more than rda - improves the immune system in the elderly
43
New cards
VITAMIN E sources
Vegetable oils • Some greens • Some fruits • Wheat germ • Peanuts • Olive Oil • Eggyolk • Liver • Butter • Milk
44
New cards

VITAMIN K
Help form prothrombin & other factors for blood clotting & bone formation
45
New cards
VITAMIN K
* Important for the synthesis blood-clotting protein
* regulate normal clotting of blood
* Increases calcium absorption
* Maintains strong healthy bones
* regulate normal clotting of blood
* Increases calcium absorption
* Maintains strong healthy bones
46
New cards
VITAMIN K deficiency
* Hemorrhage
* Anemia & Jaundice (for medicinal forms only)
* Anemia & Jaundice (for medicinal forms only)
47
New cards
VITAMIN K sources
soybean oil, green leafy vegetables, cabbage, liver, cauliflower, tomatoes and egg yolk.
48
New cards
VITAMIN K (RDA)
* Average mixed diets - normal vitamin K intake
* Normal dose: 1-2 mg for prophylaxis
* Male adults (19 years & older): 59 mcg
* Female adults (19 years & older): 51 mcg
* Normal dose: 1-2 mg for prophylaxis
* Male adults (19 years & older): 59 mcg
* Female adults (19 years & older): 51 mcg