VET 215 - Laboratory Animal Medicine - Gerbils
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards related to gerbils.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Meriones unguiculatus
Scientific name for the Mongolian gerbil.
AKA: jird or desert rat
Agouti
Most common coat color in gerbils.
Radiobiology
A research use for gerbils, due to their resistance to radiation.
Endocrine studies
A research use for gerbils, due to their low water intake and concentrated urine.
Lipid metabolism
A research use for gerbils, due to their high serum and hepatic cholesterol levels.
Infectious diseases
A research use for gerbils, due to their low occurrence to natural disease.
Stroke studies
A research use for gerbils, due to anatomic variations that make them susceptible.
Epilepsy Studies
A research use for gerbils, due to their propensity for spontaneous seizures and neurophysiological similarities to humans.
Monogamous pairs
Gerbils form these and mate for life.
Foot stomping
A behavior used by gerbils of hind limbs to attract attention.
Hardwood chips, wood shavings, composite recycled paper pellets or sand NOT CEDAR
Acceptable bedding materials for gerbils.
Cedar bedding
A type of bedding that is not recommended for gerbils due to irritation of skin and mucous membranes.
Pelleted rodent chow
Main component of a gerbil's diet.
5-7 g/day
Supplement diet with small amounts of: sunflower seeds, lettuce, spinach, apple, and carrot once a week
Typical food consumption for gerbils.
3-6 ml/day
Typical water consumption for gerbils.
46-131g
Adult body weight of a male gerbil.
50-55 g
Adult body weight of a female gerbil.
Life span of Gerbil
typically 2-4 years.
Body temp of Gerbil
99-101 deg F
Heart rate of Gerbil
260-600 bpm
Respiratory rate of Gerbil
85-160 bpm
Long tail that is fully furred
Sebaceous gland used for marking on abdomen, ventral midline (more prominent in males) used for marking territory
Non-glandular forestomach & glandular stomach (inability to regurgitate)
Practice coprophagia
Adrenal glands large relative to total BW
Has a thymus
Produce small quantities of highly concentrated urine
Anatomy of gerbils.
2 (I 1/1, C 0/0, P 0/0, M 3/3)
Incisors continuously grow
Typical gerbil dental formula
Non-glandular forestomach & glandular stomach
Anatomical feature that results in inability to regurgitate in gerbils.
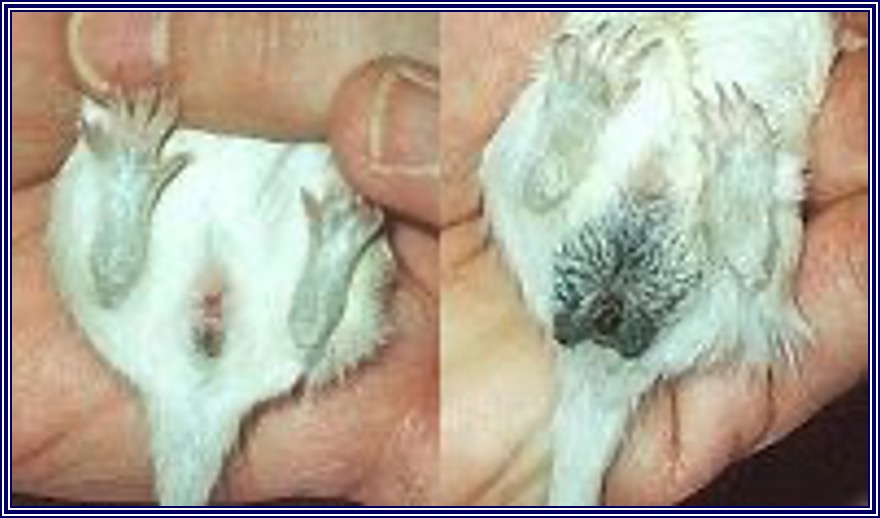
Greater anogenital distance in males
females have 4 pairs of teats
Distinguishing feature when sexing gerbils.
23-26 days
Gestation period for gerbils.
Breeding onset for male gerbils
9-18 weeks
Breeding onset for female gerbils
9-12 weeks
Polyestrus, spontaneous ovulators
can have Postpartum estrus
Breeding characteristics of female gerbils.
Estrous cycle length for gerbils
4-7 days
Tail slip/degloving
Potential injury when handling gerbils by the end of their tail.
Lift by carefully grasping the base of their tail
Retroorbital sinus, Lateral metatarsal vein, Tail vein, Cardiac puncture (terminal procedure)
Blood collection sites for gerbils.
Blood Volume
Total blood volume 4.4-8.0 ml
Single sample 0.3 ml
Exsanguination 2-4 ml
SQ
Route of injectable drug administration in gerbils with a max volume of 1-2 mls.
IM
Route of injectable drug administration in gerbils that is rare due to small muscle mass, max 0.1 ml.
IP
Best route of injectable drug administration in gerbils, max 2-3 ml.
IV
difficult/small veins, lateral metatarsal
ketamine + xylazine or ketamine + diazepam
Pre-anesthetic fasting not recommended
Inhalation anesthesia: Plastic syringe case as mask
Ophthalmic ointment
Circulating H2O pad
Post Op
–Recover in warm, quiet place (escape proof incubator)
–Turn every 30 – 60 minutes
–Analgesics if needed
Anesthesia protocols for gerbils.
70% carbon dioxide
Overdose of inhalant anesthetic
Sodium Pentobarbital IP
Acceptable methods of euthanasia for gerbils.
In general, gerbils do not contract many diseases
In general, gerbils do not contract many diseases
Tyzzer’s Disease
–Clostridium piliforme
–Common
–High mortality in young
–Poor sanitation & stress contributing factors
–Clinical signs:
•Rough hair coat
•Listlessness
•Weight loss
•Sudden death
Parasitic Diseases
•Demodex (mite)
–Clinical signs
•Alopecia
•Dermatitis
–Stress and age predispose
–Rare
•Pinworms
–Syphacia spp.
–Do not usually cause clinical problems
•Tapeworms
–Hymenolepis nana (dwarf tapeworm)
–Subclinical
–Zoonotic potential
Epileptiform seizures
Initiated by handling, stress or new environment in gerbils, no treatment recommended.
Porphyrin production by harderian gland
Cause of Chromodacyorrhea in ill or stressed gerbils.
Scent Gland tumors
Squamous cell carcinoma(SCC), More common in males, Seen on ventral marking gland
Aural cholesteatoma
Only non-human animal known to spontaneously develop this condition, excess keratin build up in middle ear