Ch. 14: Cnidarians and Ctenophores
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/77
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A look into the phylogeny of corals, sea anemones, jellies, and others.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
1
New cards
radiates
animals displaying radial or biradial symmetry
diploblastic (ectoderm and endoderm)
no cephalization
diploblastic (ectoderm and endoderm)
no cephalization
2
New cards
The radiates clade of animals contains…
phylum Cnidaria and Cnetophora
3
New cards
phylum Cnidaria
sea anemones, jellyfish, corals, etc.
have cnidocytes for defense and/or offense
ancient group of animals, with fossils from 700 mya
mostly marine and sessile
sometimes lives symbiotically with other organisms
have cnidocytes for defense and/or offense
ancient group of animals, with fossils from 700 mya
mostly marine and sessile
sometimes lives symbiotically with other organisms
4
New cards
cnidocytes
defensive cells seen in phylum Cnidaria
has discharging organelles
has discharging organelles
5
New cards
cnidocyte type example
nematocyst
6
New cards
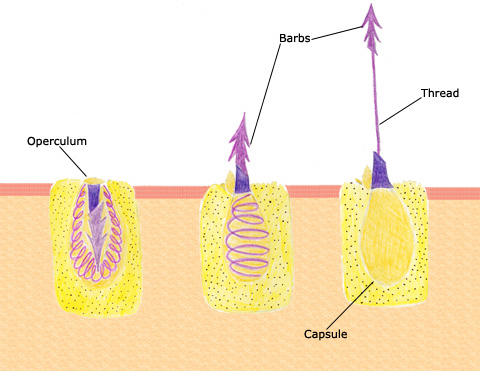
nematocyst
a type of cnidocytes
injects toxin for prey capture or defense through hollow filament
sometimes has barbs to latch into victim
usually triggered by cnidocil
injects toxin for prey capture or defense through hollow filament
sometimes has barbs to latch into victim
usually triggered by cnidocil
7
New cards
Are nematocysts single use or reuseable structures?
single-use
once they have been launched, they cannot go back in
cnidarians can shed these cells and make new nematocysts
once they have been launched, they cannot go back in
cnidarians can shed these cells and make new nematocysts
8
New cards
phylum Cnidaria classes and description of what’s included
Hydrozoa - hydras
Scyphozoa - the true jellies
Cubozoa - box jellies, sea wasps
Anthozoa - anemones, corals, and other related things
Staurozoa - very few species of medusa-like animals (not much focus in this course)
Myxozoa - highly modified parasitic forms (very different from rest of the phylum)
Scyphozoa - the true jellies
Cubozoa - box jellies, sea wasps
Anthozoa - anemones, corals, and other related things
Staurozoa - very few species of medusa-like animals (not much focus in this course)
Myxozoa - highly modified parasitic forms (very different from rest of the phylum)
9
New cards
phylum Cnidaria body plans
dimorphic: polyp and medusa forms
10
New cards
physical relationship of polyp and medusa form
polyp is the sessile, “upright” form
medusa is the free moving, “downward” form
can show with your hand: polyp form is palm facing up, medusa form is palm facing down, and your fingers are the tentacles.
medusa is the free moving, “downward” form
can show with your hand: polyp form is palm facing up, medusa form is palm facing down, and your fingers are the tentacles.
11
New cards
dimorphic
an animal having two separate forms
12
New cards
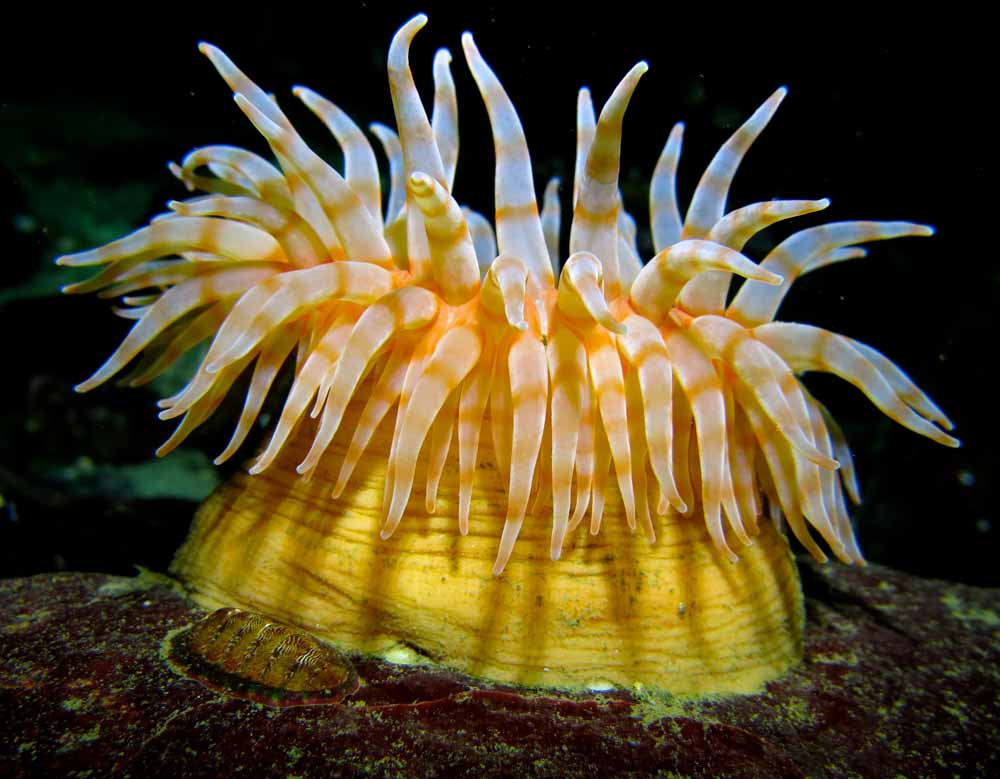
polyp
typically tubular
blind gut
sessile
reproduces asexually
colonies may have several morphologically distinct polyps
blind gut
sessile
reproduces asexually
colonies may have several morphologically distinct polyps

13
New cards
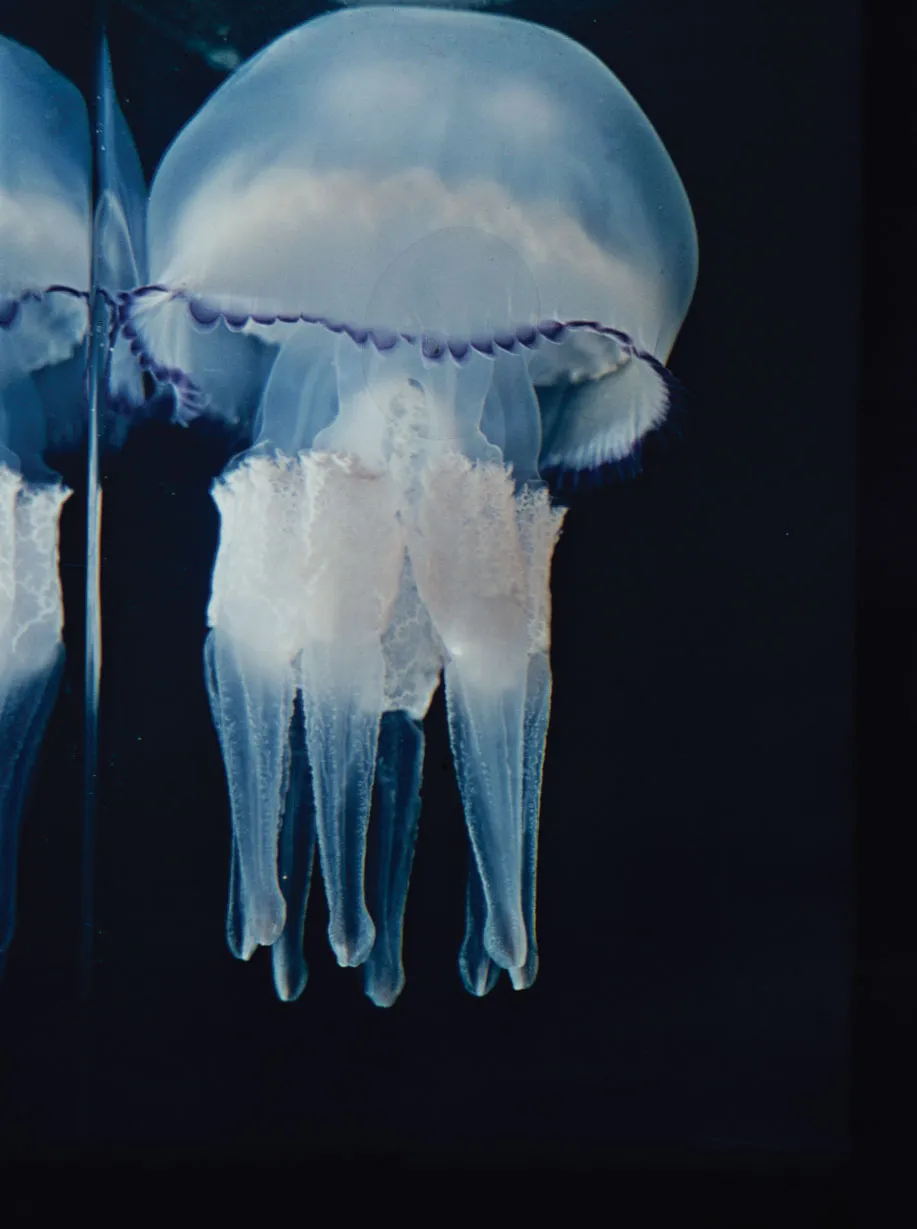
medusa
the “jelly” form
bell or umbrella shaped
usually free-swimming
mouth is directed downwards
tentacles may extend down
sensory structures for sensing orientation and light
sexually reproduce to make polyps
* linked to motor response via nerve ring at the base of the bell
bell or umbrella shaped
usually free-swimming
mouth is directed downwards
tentacles may extend down
sensory structures for sensing orientation and light
sexually reproduce to make polyps
* linked to motor response via nerve ring at the base of the bell

14
New cards
Are medusa forms dioecious or monoecious?
dioecious
15
New cards
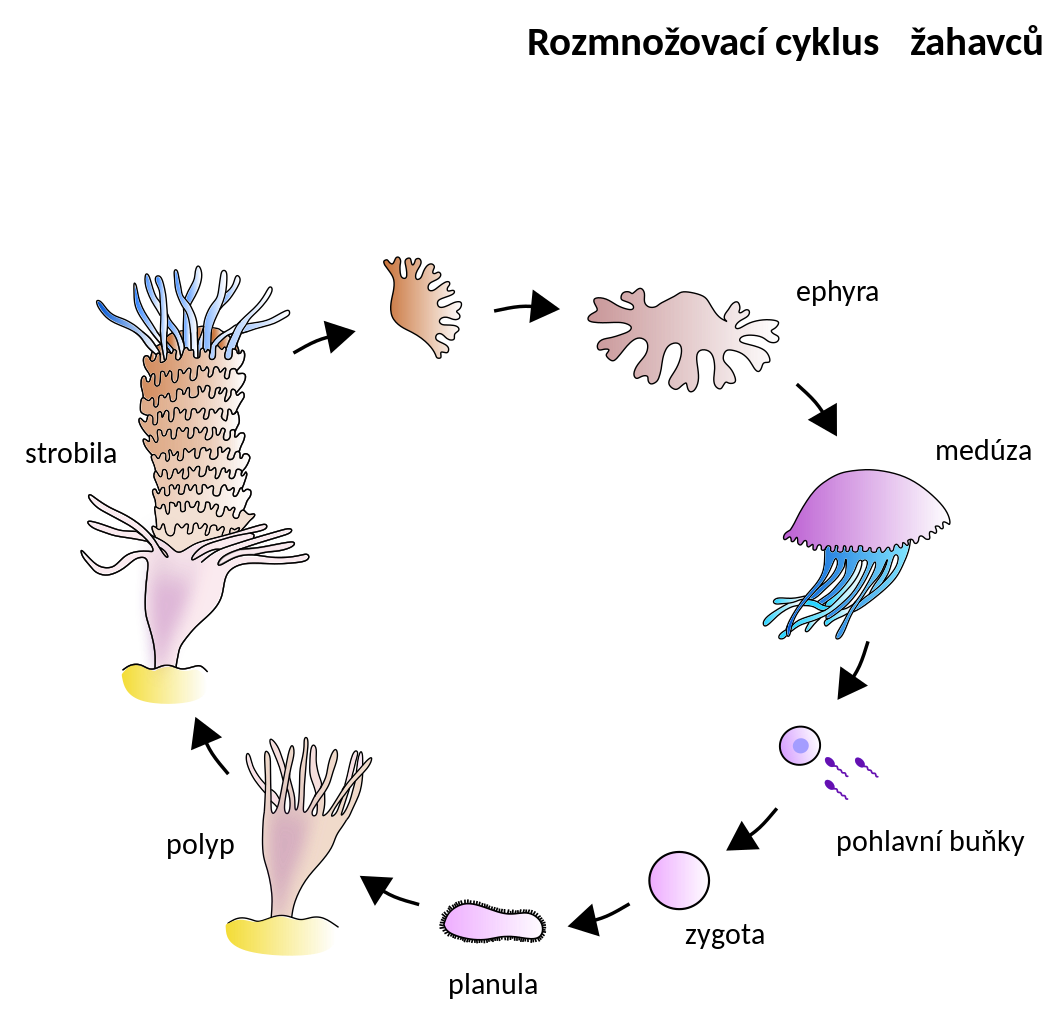
general life cycle of cnidarians
zygote → motile planula larva → planula larva settles, metamorphosis → polyp → asexually form medusa → mature medusa → sexually reproduce with other medusae and form a zygote
16
New cards
Polyps may form other polyps via…
asexual reproduction
17
New cards
planula larva
the larval stage between zygote and polyp in cnidarians
18
New cards
ephyra
a baby medusa that still needs to grow into a full size medusa
19
New cards
variations in life cycle in cnidarians
drifting polyp colony, or polyp/medusae colony
life cycles without medusae
life cycles without medusae
20
New cards
cnidarian cell layers
two cell layers:
* inner layer - gastrodermis
* outer layer - may have cnidocytes with nematocysts
has mesoglea between layers
* inner layer - gastrodermis
* outer layer - may have cnidocytes with nematocysts
has mesoglea between layers
21
New cards
gastrodermis
AKA inner layer or endoderm
digestion layer on the inside of the cnidarian
digestion layer on the inside of the cnidarian
22
New cards
epidermis
AKA ectoderm
may have cnidocytes with nematocysts in cnidarians
may have cnidocytes with nematocysts in cnidarians
23
New cards
mesoglea
gelatinous, buoyant filling between cell layers
supports the body
supports the body
24
New cards
organ systems of cnidarians
feeding and digestion
nerve net
nerve net
25
New cards
feeding and digestion in cnidarians
both stages carnivorous
coral also get carbon from algal symbionts
coral also get carbon from algal symbionts
26
New cards
nerve net
example of diffuse nervous system, *not* central
in medusae, nerve net and nerve ring function like a central nervous system, but not quite
important landmark in evolution of nervous systems
in medusae, nerve net and nerve ring function like a central nervous system, but not quite
important landmark in evolution of nervous systems
27
New cards
nerve ring
ring of nerves near the end of the bell
28
New cards
Class Hydrozoa
mostly marine, colonial (freshwater forms do exist!)
has polyp and medusa forms
typical hyzroid colonies look like:
* base, stalk, one or more terminal zooids
* hydranths
* gonangia
may have perisarc
has polyp and medusa forms
typical hyzroid colonies look like:
* base, stalk, one or more terminal zooids
* hydranths
* gonangia
may have perisarc
29
New cards
zooids
individual polyps found in hydroid colonies
30
New cards
hydranths
feeding zooids that capture prey in a hydroid colony
31
New cards
gonangia
reproductive polyps that form medusa buds in hydroid colonies
32
New cards
perisarc
non-living chitinous covering found “shrink-wrapped” around hydroids
33
New cards
hydroid medusae
small (mm or cm across)
velum
gastrovascular cavity - continuous from mouth to tentacles
bell margin has:
* many sensory cells (detecting light and other things)
* nerve rings
velum
gastrovascular cavity - continuous from mouth to tentacles
bell margin has:
* many sensory cells (detecting light and other things)
* nerve rings
34
New cards
velum
shelf-like lip in the medusa form of hydroids
helps with trapping water in order to propel itself farther
helps with trapping water in order to propel itself farther
35
New cards
freshwater hydras
solitary polyps
can flop around and move
no medusa stage
nematocysts capture prey
some species with symbiotic algae
sexual and asexual reproduction
can flop around and move
no medusa stage
nematocysts capture prey
some species with symbiotic algae
sexual and asexual reproduction
36
New cards
other examples of hydrozoans
*Physalia* (Portuguese man-of-war)
polymorphic colonies with both polyps and medusae
acts as one individual
mutualistic relationship with some fish
polymorphic colonies with both polyps and medusae
acts as one individual
mutualistic relationship with some fish
37
New cards
Class Scyphozoa
most of the larger jellyfish in this class
mostly in open sea
bells vary in shape and size
most less than 1/2 m across
scalloped margin
mostly in open sea
bells vary in shape and size
most less than 1/2 m across
scalloped margin

38
New cards
true jelly body plan
no velum
many nematocysts
thick layer of mesoglea
dioecious
internal fertilization
many nematocysts
thick layer of mesoglea
dioecious
internal fertilization
39
New cards
examples of true jellies
moon jellies
* cosmopolitan distribution
upside down jellyfish
* tissues have symbiotic dinoflagellates
* acts like a polyp so the dinoflagellates make sugar
* uses bell to suction cup itself to the bottom
* cosmopolitan distribution
upside down jellyfish
* tissues have symbiotic dinoflagellates
* acts like a polyp so the dinoflagellates make sugar
* uses bell to suction cup itself to the bottom
40
New cards
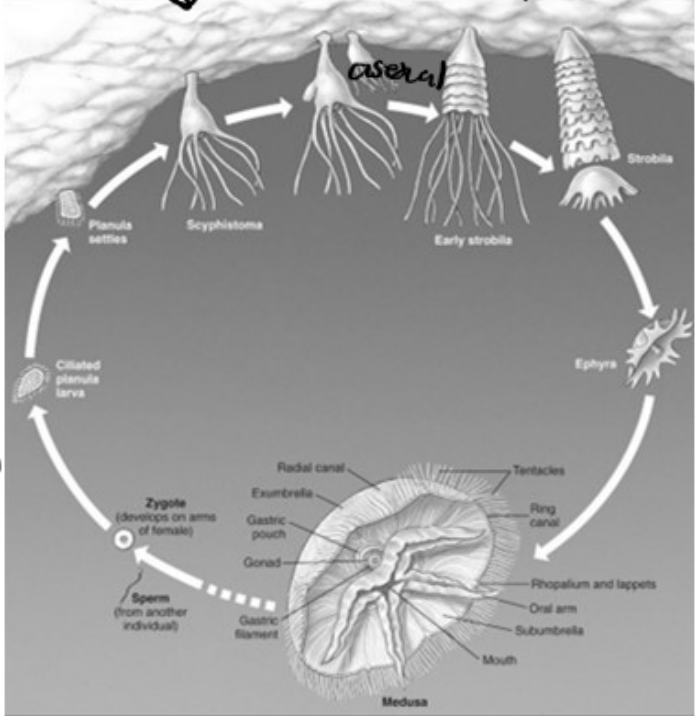
Scyphozoa life cycle
zygote → cilicated planula larva → planula attaches to form scyphistoma → scyphistoma under goes strobilation → strobila forms ephyrae → break loose to form
41
New cards
scyphistoma
the name of strobilating polyps in class Scyphozoa
42
New cards
strobilation
the asexual reproduction of medusae
43
New cards
Class Staurozoa
no medusa stage
solitary polyp on a stalk
polyp top resembled a medusa
reproduce sexually
very few species
not much is known about this class
solitary polyp on a stalk
polyp top resembled a medusa
reproduce sexually
very few species
not much is known about this class

44
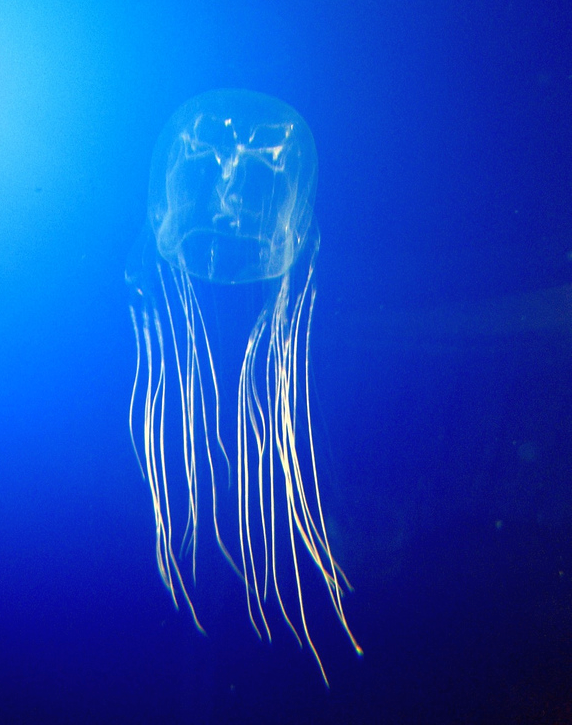
New cards
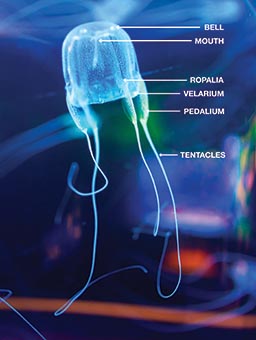
Class Cubozoa
box jellyfish, sea wasps
dominant medusa form
* polyp form inconspicuous or unknown
voracious predators
dominant medusa form
* polyp form inconspicuous or unknown
voracious predators

45
New cards
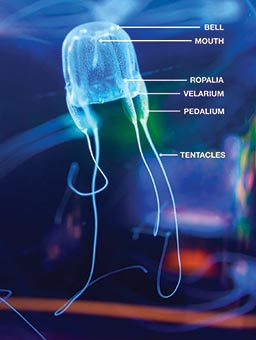
box jelly body plan
mostly small (2-3 cm)
umbrella square, tentacles at the corners
pedalium at base of each tentacle
has velarium at edge of umbrella
has potent toxins: can kill a human in a couple of minutes
umbrella square, tentacles at the corners
pedalium at base of each tentacle
has velarium at edge of umbrella
has potent toxins: can kill a human in a couple of minutes
46
New cards
pedallium
flat blade at the base of each tentacle in class Cubozoa
47
New cards
velarium
umbrella edge turns in in class Cubozoa
increases swimming efficiency
like the velum in hydrozoa
increases swimming efficiency
like the velum in hydrozoa
48
New cards
Class Myxozoa
newer class in Cnidarians
obligate parasites
structurally, are highly reduced cnidarians
* extremely small genome for an animal
obligate parasites
structurally, are highly reduced cnidarians
* extremely small genome for an animal
49
New cards
Class Myxozoa body plan
tiny - just a couple of cells big
has polar capsules
has polar capsules
50
New cards
Class Myxozoa examples
those that cause whirling disease
annelid worms
annelid worms
51
New cards
polar capsules
found in class Myxozoa
homologous to nematocysts
homologous to nematocysts
52
New cards
Class Anthozoa
no medusa stage
all marine
large gastrovascular cavity and divided into different parts
has three subclasses
all marine
large gastrovascular cavity and divided into different parts
has three subclasses

53
New cards
Anthozoa subclasses
Hexacorallia
Ceriantipatharia
Octocorallia
Ceriantipatharia
Octocorallia
54
New cards
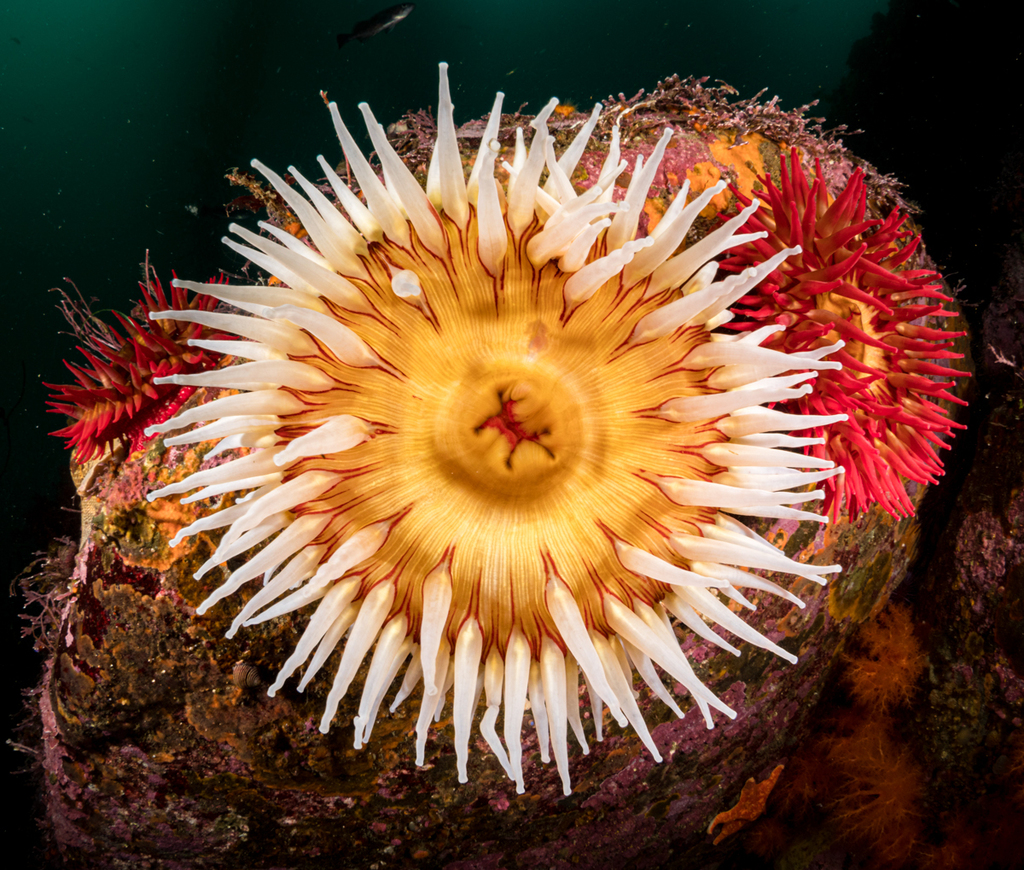
subclass Hexacorallia
part of class Anthozoa
sea anemones, hard corals
hexamerous (6) body plan
polyps larger, heavier than hydrozoan polyps
resides in costal areas
glide on pedal discs
oral discs
carniverous
some can swim
sea anemones, hard corals
hexamerous (6) body plan
polyps larger, heavier than hydrozoan polyps
resides in costal areas
glide on pedal discs
oral discs
carniverous
some can swim

55
New cards
pedal disk
found in subclass Hexacorallia
lets it attach to shells, rocks, etc.
lets it attach to shells, rocks, etc.
56
New cards
oral disk
found in subclass Hexacorallia
surrounds the open mouth and where the tentacles attach to
surrounds the open mouth and where the tentacles attach to
57
New cards
sea anemone behavior
can contact and withdraw tenacles into their oral disk
mutualistic relationships:
* many harbor symbiotic dinoflagellates (algae)
* some live on crab shells
* some provide shelter for anemone fish
mutualistic relationships:
* many harbor symbiotic dinoflagellates (algae)
* some live on crab shells
* some provide shelter for anemone fish
58
New cards
sea anemone reproduction
sexual reproduction:
* some dioecious, some monoecious
* monoecious species are protandrous
asexual reproduction:
* occurs via pedal laceration
* occurs via longitudinal fission, but also transverse fission and budding
* some dioecious, some monoecious
* monoecious species are protandrous
asexual reproduction:
* occurs via pedal laceration
* occurs via longitudinal fission, but also transverse fission and budding
59
New cards
protandrous
produce sperm first, then eggs later
found in sea anemones
found in sea anemones
60
New cards
pedal laceration
type of asexual reprduction
pieces of pedal disk break off and regenerate
found in sea anemones
pieces of pedal disk break off and regenerate
found in sea anemones
61
New cards
true (stony) corals
looks like tiny sea anemones in calcareous cups
secretes exoskeleton
in colonies, exoskeleton can becomes massive, but the living coral forms thin layer over that exoskeleton
secretes exoskeleton
in colonies, exoskeleton can becomes massive, but the living coral forms thin layer over that exoskeleton

62
New cards
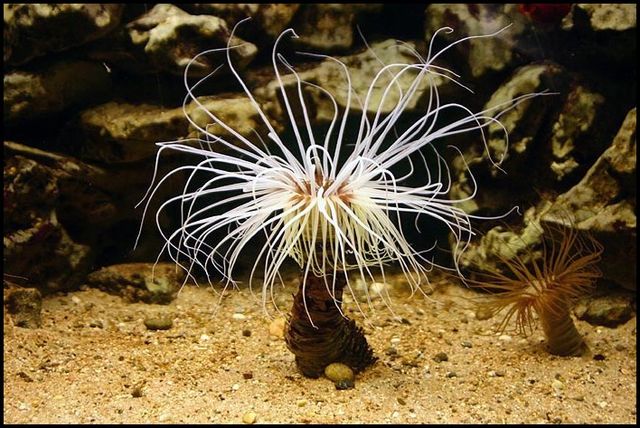
subclass Ceriantipatharia
part of class Anthozoa
few species
tube anemones
* solitary, buried in soft sediments
thorny corals
* colonial, attach to form substrates
* tough, spiny exoskeleton
hexamerous (6) body plan
few species
tube anemones
* solitary, buried in soft sediments
thorny corals
* colonial, attach to form substrates
* tough, spiny exoskeleton
hexamerous (6) body plan

63
New cards
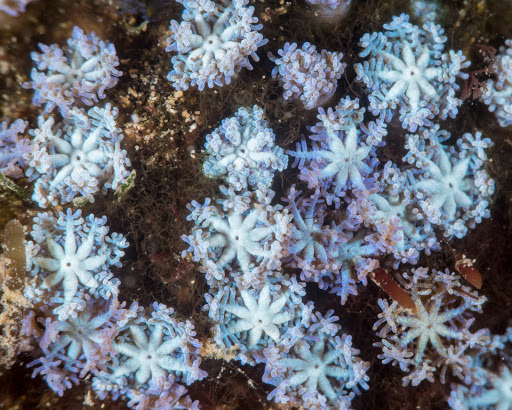
subclass Octocorallia
part of class Anthozoa
soft and horny corals (sea fans, sea pens, sea pansies, etc.)
octomerous (8) body plan
* eight pinnate tentacles
* eight complete septa
all are colonial, with some varied forms
soft and horny corals (sea fans, sea pens, sea pansies, etc.)
octomerous (8) body plan
* eight pinnate tentacles
* eight complete septa
all are colonial, with some varied forms

64
New cards
soft & horny coral body plan
gastrovascular cavities communicate through solenia
have coenenchyme
skeleton secreted within the coenenchyme
have coenenchyme
skeleton secreted within the coenenchyme
65
New cards
solenia
tubes found connecting gastrovascular cavities in soft and horny corals
66
New cards
coenenchyme
tissue consisting of mesoglea and solenia, connecting cavities together
found in soft and horny coral
found in soft and horny coral
67
New cards
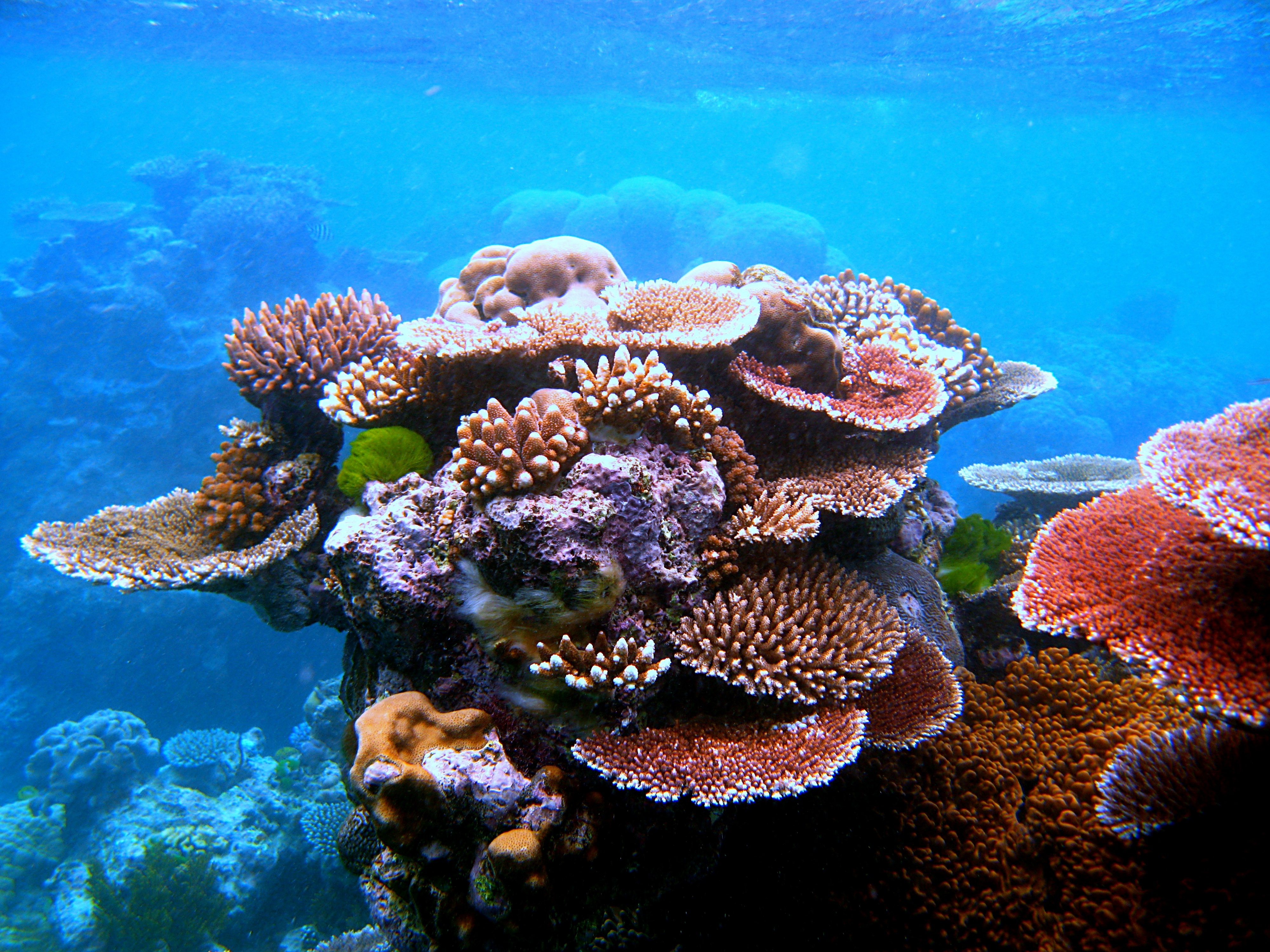
coral reefs
productive, diverse ecosystems
limestone deposited over 1000s of years
* living plants and animals limited to the top layer
limestone deposited over 1000s of years
* living plants and animals limited to the top layer
68
New cards
Coral reefs need _________________ corals for reef formation, but other species may be involved.
hermatypic (hard)
(class Hexacorallia)
(class Hexacorallia)
69
New cards
coral reef requirements
warmth, light, salinity of undiluted sea water (basically can’t be next to a river mouth or other body of fresh water)
limited to shallow waters between 30 N and 30 S
limited to shallow waters between 30 N and 30 S
70
New cards
relationship of zooxanthellae and coral tissues
\
zooxanthellae live inside the cells of coral, and gives food to coral during the day
coral gives zooxanthellae a place to live, and the zooxanthellae can take in phosphorous and nitrogen excreted by the coral
zooxanthellae live inside the cells of coral, and gives food to coral during the day
coral gives zooxanthellae a place to live, and the zooxanthellae can take in phosphorous and nitrogen excreted by the coral
71
New cards
threats to coral reefs
nutrients from fertilizer and sewage → excessive algae growth
overfishing of herbivorous fishes → excessive algae growth
pollution (pesticides, oil, sediment, etc.)
global warming → warm water causing coral bleaching
higher atmospheric CO2 → acidifies oceans water, making precipitation of CaCO3 by corals more difficult
overfishing of herbivorous fishes → excessive algae growth
pollution (pesticides, oil, sediment, etc.)
global warming → warm water causing coral bleaching
higher atmospheric CO2 → acidifies oceans water, making precipitation of CaCO3 by corals more difficult
72
New cards
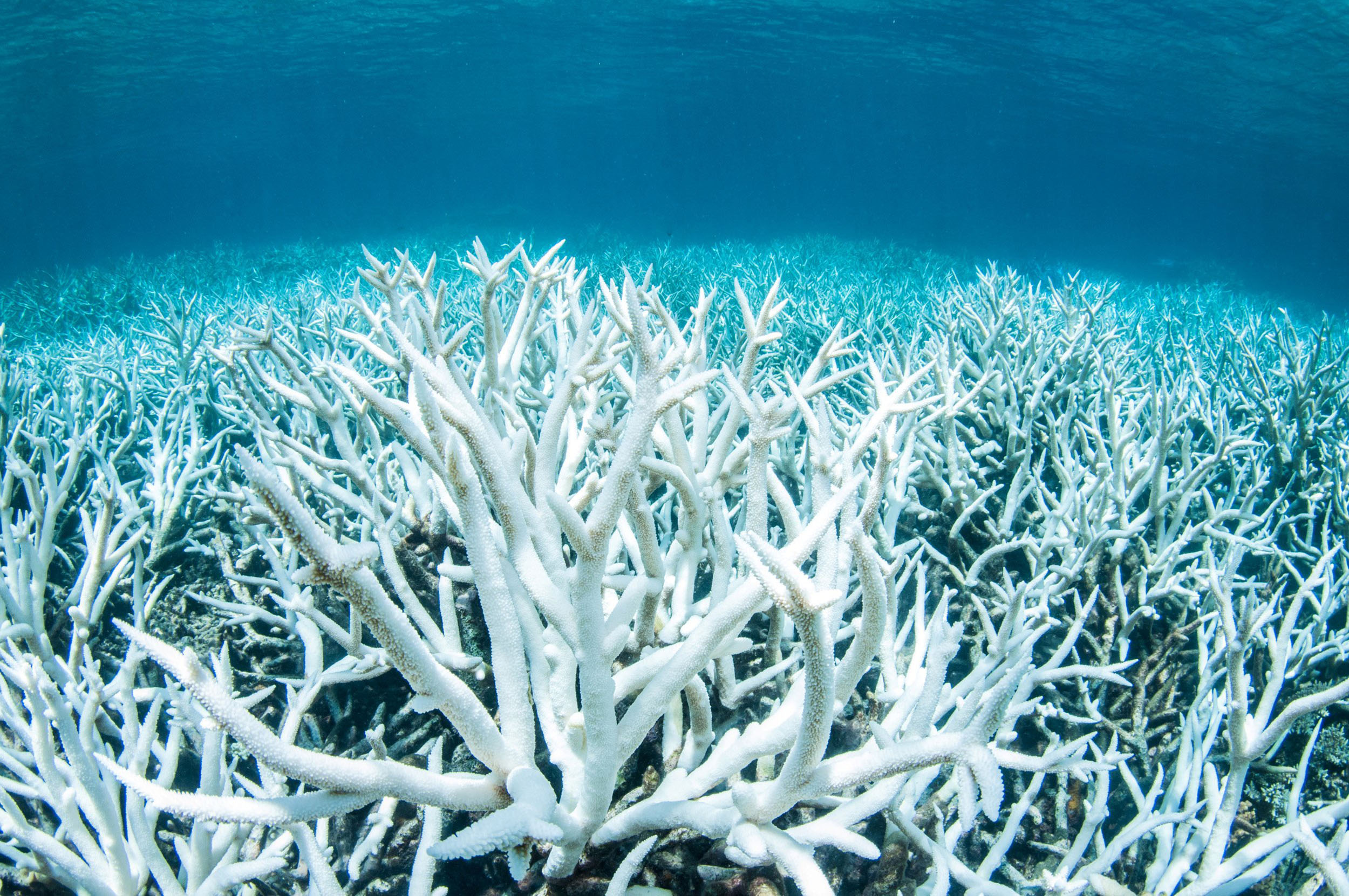
coral bleaching
caused by global warming
coral expels zooxanthellae, causing the coral to turn white
usually results in the death of the coral
coral expels zooxanthellae, causing the coral to turn white
usually results in the death of the coral

73
New cards
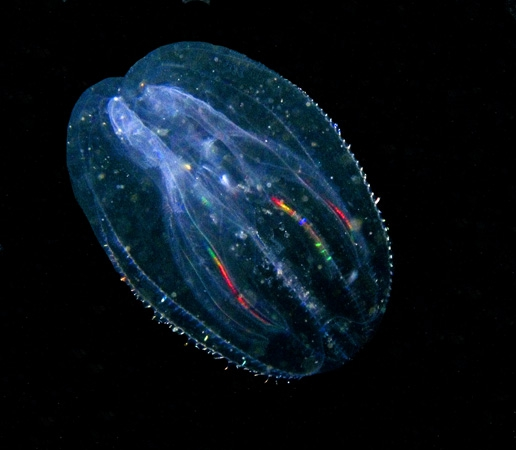
phylum Ctenophora
comb jellies
about 150 species
all marine, mostly preferring warm waters
8 rows of comb-like plates for locomotion
nearly all free-swimming
biradial symmetry
about 150 species
all marine, mostly preferring warm waters
8 rows of comb-like plates for locomotion
nearly all free-swimming
biradial symmetry

74
New cards
comb jelly body plan
some relatively large (1 m)
no definite head, but do have oral and aboral ends
translucent body with gelatinous layer
most have two extendable tentacles
no definite head, but do have oral and aboral ends
translucent body with gelatinous layer
most have two extendable tentacles
75
New cards
comb jelly behavior
some feed on cnidarians, incorporating cnidocytes as defensive mechanisms
bioluminescent
bioluminescent
76
New cards
comb jelly reproduction
monoecious in most species
cydippid larva somewhat resembles adult
medusae and polyp are both monoecious, not different like other cnidarians
cydippid larva somewhat resembles adult
medusae and polyp are both monoecious, not different like other cnidarians
77
New cards
cydippid larva
comb jelly larva
78
New cards
phylogeny of the diploblasts
ctenophores and cnidarians have typical diploblastic characteristics,
but the cells within the gelatinous layer are problematic…
are they really triploblastic organisms?
in short - diploblastic with some added features (from what we know)
but the cells within the gelatinous layer are problematic…
are they really triploblastic organisms?
in short - diploblastic with some added features (from what we know)