reproductive system
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
spermatogenesis
testes
structure of testes
seminiferous tubules lines with spermatogenic cells
interstitial cells
make testosterone
outside seminiferous tubules
formation of sperm cells
within sustentacular cells
all stuff in background
provide comforting and nurturing place for sperm cells
“nurse cells”
primary spermatocytes (diploid)
undergo mitosis
each chromosome has copy
separated homologous pairs
secondary spermatocytes (haploid)
second meiotic division
break up sister pairs
1 chromatid per chromosome
spermatids and sperm (haploid)
physical shape of sperm
male reproductive anatomy
penis
urethra
carries urine and sperm out of the body
corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum
changes in blood flow allow tissue to accumulate causing erection
internal accessory organs
epididymides
store, mature, and transport sperm
ductus deferentia
carry sperm to urethra
inside prostate gland
seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands
secretions into urethra
join together to make semen
secrete fructose
for energy (anaerobic)
as biproduct: lactic acid
secrete buffer for the acid
smooth muscle constricts so during ejaculation urine isnt secreted
hormonal control of male reproductive functions
hypothalamic and pituitary hormones
gonadotropic releasing hormone
tells pituitary gland to release hormones
follicle stimulating hormone
stimulates cells to undergo division to make eggs and sperm
interstitial cell stimulating hormone (males)
in females: luteinizing hormone
testes to make testosterone and androgen
stimulates release of hormones
male sex hormones
testosterone and dihydrotesterone
androgens
testosterone
primary
development of male reproductive organs and characteristics
dihydrotesterone
more potent
male genitalia during fetal development
secondary sexual characteristic during puberty
inhibin
controls FSH
secrete less
testes and ovaries make
regulation of male sex hormones
feedback loop with brain, pituitary gland, and testes
SRY- sex determining region of Y
encodes for transcription factor
genes that promote development of male features are now activated
y is smaller than x
what if SRY region is damaged
chromosomally have Y
dont show characteristics
male structures not developed during fetal stages but do respond during adult puberty
fetal testosterone is problem
called intersex
what if receptors arent sensitive
never develop external genitalia
not even during adult puberty
always look like female
called intersex
nondisjunction
multiple X chromosomes
look male but isnt
ex) XXY: extra x chromosome inhibited
also called intersex
Oogenesis and follicle development
Oogenesis- female
primary oocyte (diploid) suspended in prophase I
at birth female born with all primary Oocytes she will have
will not continue to next phase until puberty
then only a few per month will travel to next phase
unequal cytokinesis in meiosis I
fertilized egg has to go on multiple day journey
takes all its nutrients it’ll need
reduce chromosome number
doesn’t happen unless egg is fertilized
secondary Oocyte (haploid)
gets most of mass
to survive journey
first polar body (haploid, degenerates)
reduce number of chromosomes
wont develop
get rid of genetic material
medically, can harvest and see if bad gene is located here, if it is than secondary Oocyte doesn’t have it
assures wont pass gene onto next generation
Meiosis II at fertilization
zygote
second polar body (degenerates)
follicle maturation
primordial follicle
thin single layer of cells (squamous)
suspended at birth
primary follicle
thin layer now more cuboidal
follicle changing
size of oocyte never really changes
20-25 start to develop
290 days from start to ovulation
pre antral (secondary) follicle
a lot of transitions
start forming fluid filled cavity
antrum
very small
mature antral follicle
large antrum
increase in pressure
makes oocyte rupture through wall
zona pellucida
immediately surrounding oocyte
non cellular material
takes many sperm to break through
corpus alabans
pregnancy not achieved
corpus luteum dies off and reabsorped
corpus luteum
remnant of follicle
emits hormones
maintain pregnancy
female internal accessory organs
uterine tubes (fallopian tubes)
transport eggs from ovaries to uterus
uterus
superior to urinary bladder
proximal 1/3 is the cervix that dilates close to delivery
receives fertilized egg and protects fetus during development
vagina
pathway for menstruation
birth canal
hormonal control of female reproductive functions
hypothalamic and anterior pituitary hormones
gonadotropic-releasing hormone
travels through infundibulum
stimulates pituitary gland to secrete FSH and LH
follicle stimulating hormone
promotes developmeny of gametes
1st meiotic division
development of eggs
luteinizing hormone
men: intertsitial cell stimulating hormone
stimulates release of sex hormones- 2 weeks pattern in feedback
estrogens- secondary sex characteristics
progesterone
androgens
female sex hormones
estrogens and progesterone
estrogen: thicken uterine lining
progesterone: prepare uterus for potential implantation
androgens
inhibin
inhibit follicle stimulating hormone
homologous anatomical structures
testes and ovaries
penis and clitoris
scrotum and labia
same innervation
same blood flow
female reproductive cycles
ovarian activity
follicular phase
day 1-14
developing antral follicle → mature antral follicle
ovulation
surges of LH and FSH
14-21
oocyte breaking through
corpus luteum
luteal phase
21-28
degenerating corpus luteum
corpus albicans
uterine activity
menstrual phase
blood vessels constrict
lining of uterus dies off and sheds
28-5
proliferative phase
estrogens increase number of cells
cells increase in size
5-19
secretory phase
progesterone make lining thick and spongy
perfect for implantation (day 21)
19-28
if fertilization does occur
corpus luteum remains functional
estrogen, progesterone levels remain elevated
menstruation prevented, cycle interrupted
promotes corpus luteum for 3 months
maintain lining of uterus
prevent developing of more follicles
if fertilization doe not occur
corpus luteum degenerates into corpus albicans
estrogen and progesterone levels drop
menstruation occurs, cycle begins anew
lining sheds
corpus luteum dies
development of more follicles
menopause (female climacteric)
unique to few members of mammals (humans, whale, etc)
2ish year period where lose period
fertilization and pregnancy
transport of sex cells
oocyte move through fallopian tube
down toward uterus
importance of semen composition
fructose and protoglandins
seminal vesicles
citrate and prostate specific antigen
prostate gland
important to detect prostate cancer
lubricant and buffer
bulborethral glands
buffer for the acidic sperm and eggs
fertilization to form a zygote
fertilization in ovary
only begins 2nd meiotic division if sperm breaks through corona radiata/ zona pellucida and then reach cell membrane
opening then needs to close so no more sperm can penetrate- zona pellucida stays closed for about 4 days before dissolving
acromosome containing enzyme helps dissolve pellucida
early embryonic development and implantation
cleavage by mitosis to form morula
day 1-5
right away
collection of cells
identical
morula
don’t gain size
no resources- still in fallopian tubes
increase cell number
day 6
cell differentiation
hollow structure with cell mass inside
inside- develop into child (embryonic cells)
outside- extra embryonic cells- placenta, etc
cant implan by itself
cant go back
implantation of blastocyst- come in contact with uterine wall
embryoblast (inner cell mass)
develop child
embryonic cells
does not produce umbilical cord/placenta
trophoblast
attaches to uterine wall
extra embryonic cells
beginning of placenta (implantation)
placenta
embryonic and maternal portions
everything in brown
fetus and mother blood never come in contact
exchange across placental membrane
nutrient from mother → fetus
waste from fetus → mother
fetal circulation
gas exchange at placenta, not lungs
blood returning to heart well oxygenated
ductus venosus
to shunt blood (detour)
in liver
blood being delivered to liver and instead of going through luver get put into inferior vena cava
we don’t need the liver as fetuses
bc we don’t have food by mouth
becomes a ligament as an adult
foramen ovale
shunt blood
opening between right and left atrium
no need to go to lungs
when take first breath, flap of tissue sealed it off
ductus arteriosus
shunt blood
pulmonary trunk→ aorta
blood from right vetricle goes into pulmonary trunk and right into aorta
when take first breath constricts and wont work anymore
umbilical vessels
red= umbilical vein
blue= umbilical artery
goes away from heart
circulatory changes at birth
decreased vascular resistance
increased pulmonary blood flow
closure of fetal circulatory shunts
hormonal changes during pregnancy
human chorionic gonadotrophin
trophoblast cells make
tells to implant
tell corpus luteum to persist
continue to secrete estrogen and progesterone to promote uterine wall and placenta
only 3 months
FSH and LH
FSH: inhibin prevents FSH
LH: less important
don’t have ovulation
role of corpus luteum in first trimester
make estrogen and progesterone
placental estrogen, progesterone, and lactogen
lactogen: stimulating mammary glands to develop
estrogen: uterine lining development, enlarge reproductive organs, inhibit FSH and LH
progesterone: uterine lining development, inhibit uterine contractions, inhibit FSH and LH
binds to spots on uterus that oxytocin binds to- prevents contractions
from placenta
relaxin
in childbirth
relax cervix and symphysis joint (more flexible)
aldosterone
conserve Na, water follows
larger body mass
need to conserve fluid
need more volume
parathyroid hormone
raises blood levels of calcium
helps develop fetus skeleton
birth (parturition)
hormonal changes
progesterone
binds to same spot on uterus that oxytocin does
prevents contractions
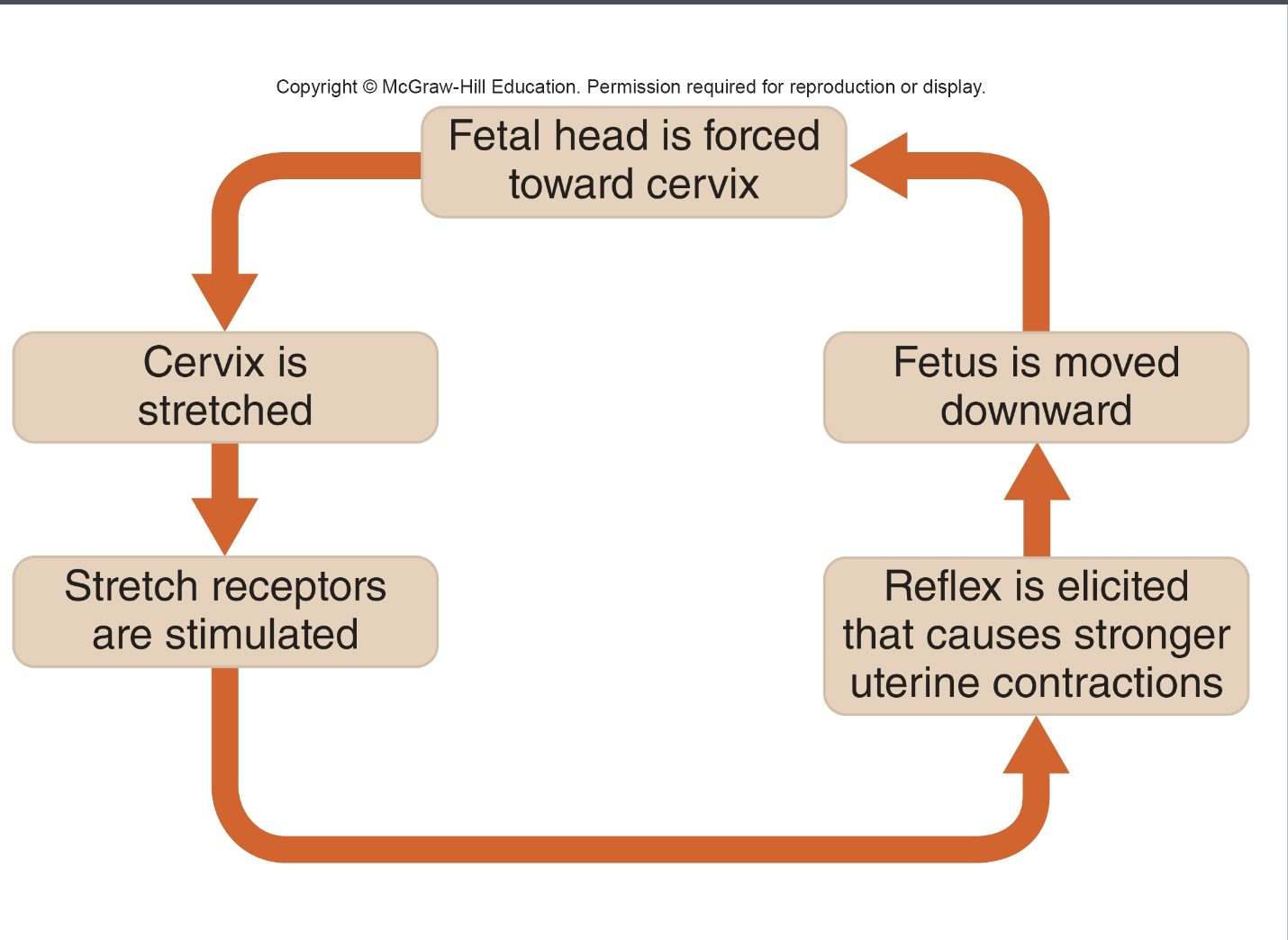
oxytocin
stimulates uterine contraction
role of positive feedback
make sure your answer on the exam is a loop
response continues trend
afterbirth
amniotic sac ruptures
“water breaks”
birth under way
need to deliver placenta at end of birth
“afterbirth”
less estrogen and androgens promotes delivery
if not all delivered can become sick with sepsis due to dead tissue in body
involution
uterus shrink back to prepregnancy size
positive feedback birth
mammary glands
breast changes during pregnancy
placental estrogens, progesterone, lactogen
estrogens: ductal growth
progesterone: increase size and number of milk producing glands
lactogen: modified sweat gland, stimulate mammary glands
increase in size= increase in breast size
lactigen goes away after birth
prepares breast
prolactin
cause sweat glands to produce milk
begina after delivery
milk production and secretion
prolactin
cause glands to produce milk
begin after delivery
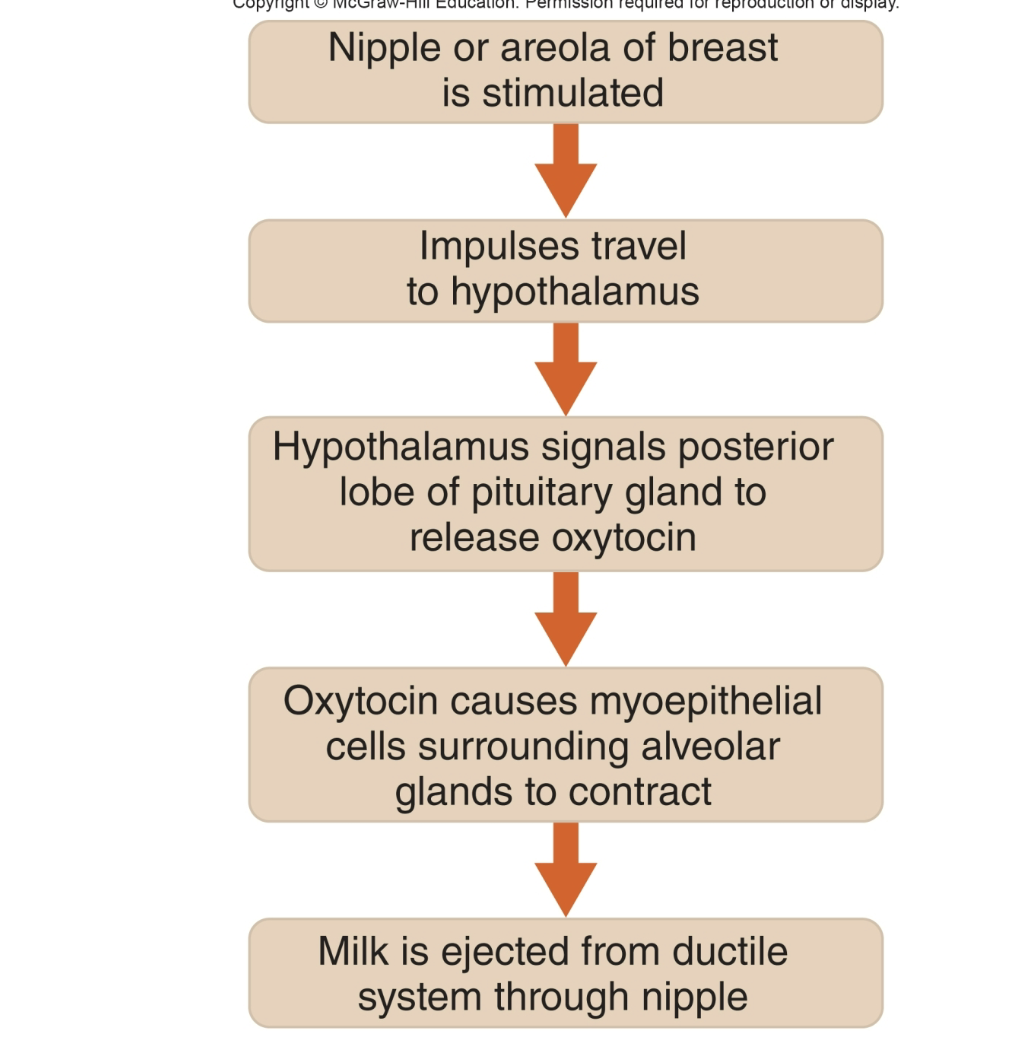
oxytocin
helps ejection of milk using the neuroendocrine reflex
stimulate myoepithelial cells to contract
myoepethelial cells surround alveolar glands
colostrum and breast milk
first milk produces
lack fats and carbohydrates
primarily proteins and antibodies
babies born without antibodies
rely on mom for immunity (the first 6 months most important)
still protected after 6 months if mom stops reast feeding due to passive immunity
neuroendocrine reflex