psych unit 4
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
person perception
forming impressions of people using:
social comparison (compare urself to others)
attribution theory (explain causes of behaviors)
actor-observer bias & fundamental attribution error
external causes → our actions
internal traits → others’ actions
FAE: underestimate impact of situation
just world phenomenon
the world is just → people get what they deserve
explicit vs implicit bias
explicit: conscious preference, expressed openly
ms bryant liking tall guys or wtv
implicit: unconscious, automatic
ms bryant’s bias against “fat ppl”
ingroup & outgroup
ingroup: ppl we share a common identity
outgroup: ppl different from our ingroup
foot-in-the-door phenomenon
agree to a small request = tendency to agree to a larger request later
cognitive dissonance
we reduce discomfort when two of our cognitions are inconsistent by changing one opinion/behavior or justifying it
peripheral route vs central route persuasion
peripheral: attention-getting cues to trigger quick emotion based judgments
celebrity endorsements
central: evidence & arguments to trigger careful thinking
normative vs informational social influence
conforms to group behavior bc:
normative: person desires to gain approval
informational: person’s willing to accept others’ opinions
social facilitation, loafing, contagion
facilitation: people perform better in the presence of others
actually strengthens “LIKELY” performance
loafing: ppl exert less effort when working w a group
contagion: unconscious imitation of others’ behaviors
deindividuation
loss of self restraint when anonymous in group situations
group polarization
enhancement of preexisting inclinations after group discussion
zimbardo stanford prison experiment
ordinary ppl will conform to expectations of a social role (even if it leads to drastic change in behavior)
festinger cognitive dissonance
ppl only given $1 to lie about a boring task experienced more cognitive dissonance (rated it more enjoyable) than those given $20 to lie (justification was solely monetary)
asch conformity
individuals yielded to a majority group’s “wrong” opinion when answering “obvious” questions about line length
milgram obedience to authority
“teachers” delivered electrical shocks to fake “students” at the instruction of an authority figure
tight vs loose cultures
tight: ppl often obey social norms
little PDA, punctuality
loose: ppl expect variability
jaywalking, littering
frustration aggression principle
frustration (attempt to achieve smth was blocked) → anger → aggression
mere exposure effect
repeated exposure to novel stimuli → preference
self disclosure
revealing intimate details about ourselves
bystander effect
bystanders are less likely to give aid if others are present
social exchange theory
social behavior depends on weighing of costs & benefits
reciprocity norm & social responsibility norm
reciprocity: we should help those who have helped us
social responsibility: we should help those who need help
social trap
two parties pursuing self-interest are caught in mutual destructiveness
mirror image perceptions
“i’m moral and peaceful, the enemies are evil and aggressive!!”
superordinate goals
shared goals only achievable thru cooperation
“opposing” group of boys had to work tgt
psychoanalysis → psychodynamic theories of personality
freud’s theories that thoughts/action come from unconscious motives
free association
person relaxes and says whatever comes to mind
id, ego, superego
id: irrational, illogical, impulsive
ego: rational
superego: moralistic, perfectionist
defense mechanisms
ego protects itself using these tactics to distort reality
freud says this was indirect & unconscious
repression
exclusion of anxiety producing feelings, thoughts
can only remember vague details abt traumatic event
displacement
impulses are redirected to substitute person/object
annoyed at school, short tempered w mom
sublimation
sexual urges are re channeled into productivity
rationalization
justifying actions/feelings w alternative explanations (rather than acknowledging true desires)
gaslighting
projection
attribution of ones unacceptable urges to others
married woman attracted to coworker thinks he’s hitting on her
reaction formation
thinking/behaving in a way that’s extreme opposite of their impulse
attracted to a girl → bully her
denial
failure to recognize existence of anxiety provoking info
alcoholic fails to acknowledge his addiction
undoing
atoning for an unacceptable action with another action
cheats on taxes, makes large donation to church
regression
retreating to behavior pattern of earlier stage of development
after bitter divorce, child crawls into bed w mother
collective unconscious
we’re impacted by common reservoir of memory/images (archetypes)
experience can leave epigenetic marks impacting gene expression
terror management theory (TMT)
awareness of our mortality → anxiety → following cultural beliefs/attempting to achieve high self esteem
thematic apperception test (a projective test)
given ambiguous pictures → make up stories
rorschach inkblot test
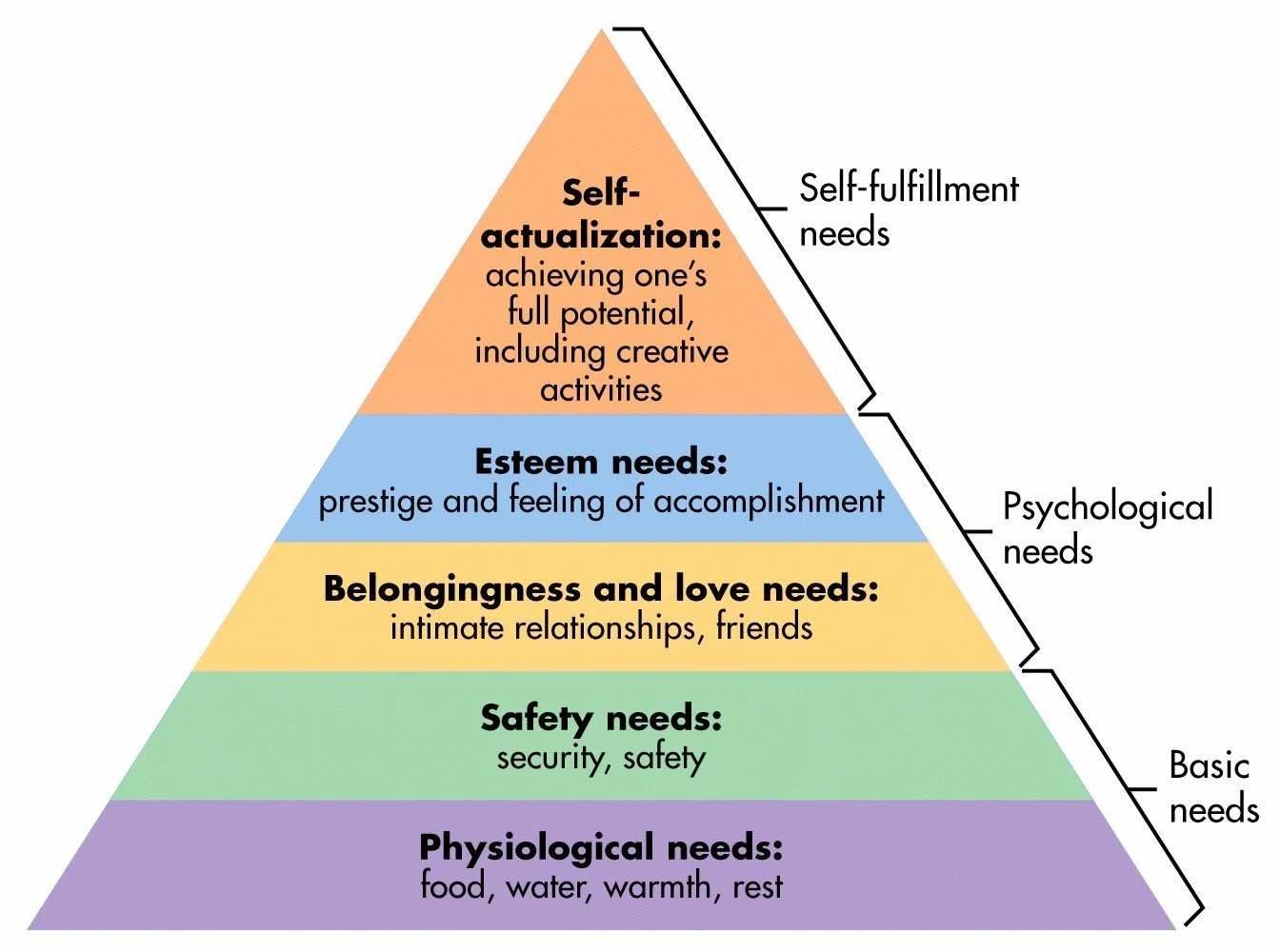
hierarchy of needs
self transcendence & self actualization
esteem
belongingness/love
safety
physiological
personality inventory
long questionnaires that assess several traits at once
minnesota multiphasic personality inventory (empirically derived)
developed to identify emotional disorders (and assess personality)
empirically derived (selecting from a pool of items) and scored objectively
big 5 factors (OCEAN)
openness: imaginative, independent
conscientiousness: organized, careful
extraversion: sociable, affectionate
agreeableness: trusting, soft-hearted
neuroticism: anxious, insecure
social cognitive perspective vs behavioral approach
social-cog: interaction btwn individuals and their situations → personality
behavioral: learning → personality
reciprocal determinism
person-environment interaction
behavior, internal cognition, environment
spotlight effect
overestimating how much ppl notice about you
self esteem, self efficacy, self serving bias
esteem: self worth
efficacy: competence
self serving: favorable self perception
dunning kruger effect
ppl are most overconfident when they’re most incompetent
drive reduction theory
when a physiological need increases (food/water), so does our physiological drive to reduce it
maintains homeostasis
arousal theory & yerkes dodson law
performance increases w arousal only up to a point (beyond that, it decreases)
affiliation need
need to build relationships & feel belonging
self determination theory
we feel motivated to satisfy need for CAR:
competence
autonomy
belonging
intrinsically vs extrinsically motivated behaviors
intrinsically: inherently satisfying (enhance feelings of CAR)
extrinsically: external rewards/pressures (loses sense of control)
achievement motivation
internal desire for accomplishment (REGARDLESS OF EXTERNAL AWARDS)
glucose
sugar that’s source of energy
low glucose levels = hunger
set point
allows for humans to hover around a stable weight
basal metabolic rate
body’s resting rate of energy output
polygraph
lie detection device
facial feedback effect
facial states trigger corresponding feelings
smiling → happier, frowning → sadder, etc.
behavior feedback effect
behavior influences feelings/mood
downcast eyes, shuffling steps → unenergetic mood