MCAT General Chemistry - Compounds and Stoichiometry
1/35
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
compounds
pure substances composed of two or more elements in a fixed proportion; can be broken down by chemical means to produce their constituent elements or other compounds; characterized by describing their physical and chemical properties
molecule
combination of two or more atoms (same or different) held together by covalent bonds; smallest units of compounds that display their identifying properties
formula unit
represents the empirical formula of an ionic compound
formula weight
represents the molecular weight of an ionic compound; found by adding up the atomic weights of the constituent ions according to its empirical formula; units are amu per molecule.
atomic weight
a weighted average of the masses of the naturally occurring isotopes of an element
molecular weight
the sum of the atomic weights of all the atoms in a molecule; atomic mass units (amu) per molecule
mole
a quantity of any substance equal to the number of particles that are found in 12 grams of carbon-12; defined as Avogadro’s number
Avogadro’s number (NA)
6.022 × 1023 mol–1.
molar mass
mass of one mole of a compound; expressed in g/mol
equivalents
how many moles of product one mole of a given starting material will produce
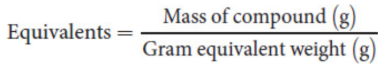
gram equivalent weight
This amount of a compound, measured in grams, that produces one equivalent of the product of interest
where n is the number of particles of interest produced or consumed per molecule of the compound in the reaction
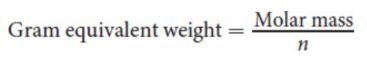
Normality (N)
measure of concentration, given in the units equivalents/L; not equivalent to molarity
where n is the number of particles of interest produced or consumed per molecule of the compound in the reaction
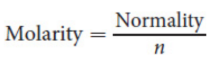
structural formulas
skeletal representations of compounds that show the various bonds between the constituent atoms of a compound
law of constant composition
any pure sample of a given compound will contain the same elements in an identical mass ratio
ex. every sample of water will contain two hydrogen atoms for every one oxygen atom, or—in terms of mass—for every one gram of hydrogen, there will be eight grams of oxygen
empirical formula
simplest whole-number ratio of the elements in the compound
molecular formula
exact number of atoms of each element in the compound and is a multiple of the empirical formula
ex. An empirical formula of CH2O is indicative of a monosaccharide (glucose, fructose, galactose)
percent composition
the percent of a specific compound that is made up of a given element by mass
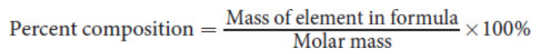
combination reaction
two or more reactants forming one product; more reactants than products:
ex. formation of water by burning hydrogen gas in air
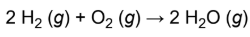
decomposition
a single reactant breaks down into two or more products, usually as a result of heating, high-frequency radiation, or electrolysis; more products than reactants
ex. breakdown of mercury(II) oxide
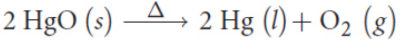
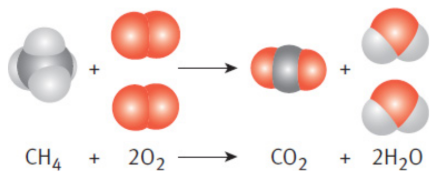
combustion reaction
involves a fuel (usually a hydrocarbon, but can be sulfur or sugars) and an oxidant (normally oxygen) to form the two products of carbon dioxide and water
ex. methane
single-displacement reaction
an atom or ion in a compound is replaced by an atom or ion of another element; often redox
ex. solid copper metal will displace silver ions in a clear solution of silver nitrate to form a blue copper nitrate solution and solid silver metal
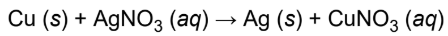
double-displacement/metathesis reactions
elements from two different compounds swap places with each other to form two new compounds
ex. solutions of calcium chloride and silver nitrate are combined, insoluble silver chloride forms in a solution of calcium nitrate
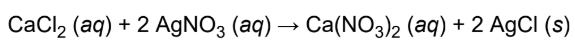
Neutralization reactions
specific type of double-displacement reaction in which an acid reacts with a base to produce a salt (and, usually, water)
ex. hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide will react to form sodium chloride and water
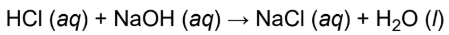
law of conservation of mass
The mass of the reactants consumed must equal the mass of products generated; the number of atoms of each element on the reactant side equals the number of atoms of that element on the product side
law of conservation of charge
the total electric charge in an isolated system never changes; the net quantity of electric charge, the amount of positive charge minus the amount of negative charge in the universe, is always conserved
Stoichiometric coefficients
the numbers placed in front of each compound, are used to indicate the relative number of moles of a given species involved in the reaction
limiting reagent/reactant
reactant that will be used up or consumed completely
excess reagent/reactants
reactants that remain after all the limiting reagent is used up
theoretical yield
the amount of product predicted; maximum amount of product that can be generated as predicted from the balanced equation, assuming that all of the limiting reactant is consumed, no side reactions have occurred, and the entire product has been collected
raw or actual yield
the amount of product actually obtained during a reaction
percent yield
The ratio of the actual yield to the theoretical yield, multiplied by 100 percent
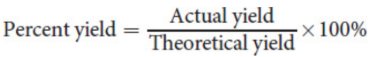
oxyanions
polyatomic ions containing oxygen
most oxygen per-
more oxygen -ate
less oxygen -ite
least oxygen hypo-
oxidation states,
elements can even have several different charges
ex. transition metals
ionicity
the degree to which a compound exhibits ionic character, meaning the extent to which it contains ions and their behavior in terms of electrical conductivity and solubility
electrolytes
solutes that enable solutions to carry currents
strong - dissociates completely into its constituent ions
weak - ionizes or hydrolyzes incompletely in aqueous solution, and only some of the solute is dissolved into its ionic constituents
solvate
dissolve