4.1.4 Production, costs & revenue
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is production?
where inputs (FOP) are converted into outputs (goods/services)
production makes use of all factor inputs in producing goods or services
What does productivity mean?
efficiency of production
What are the different forms of productivity?
Labour productivity - output per worker (most common one referred to)
Capital productivity - output per unit of capital
Factor productivity - avg output of all FOP
How do you measure labour productivity?
Total output / number of workers
Example of labour productivity:
In 2014 a firm employing 2 workers produced 80 items per week. The same firm in 2015 employs 5 workers and produces 190 items per week.

What does the productivity gap refer to?
difference in labour productivity between UK & its competitor countries
What is capital productivity?
relationship between capital put into a business and the level of output of interest
What does land productivity refer to?
compare two pieces of farmland: which yields the most wheat per acre per year, for instance
How do you measure capital productivity?
Total output/ total investment
How do you measure land productivity?
Total output/ area of land used
What is short-run production?
ability to produce w/out having to increase fixed FOP
(It may hire more or fewer workers, for instance, but doesn’t have to buy new machinery.)
What is long-run production?
occurs when a firm changes the scale of all its factors of production
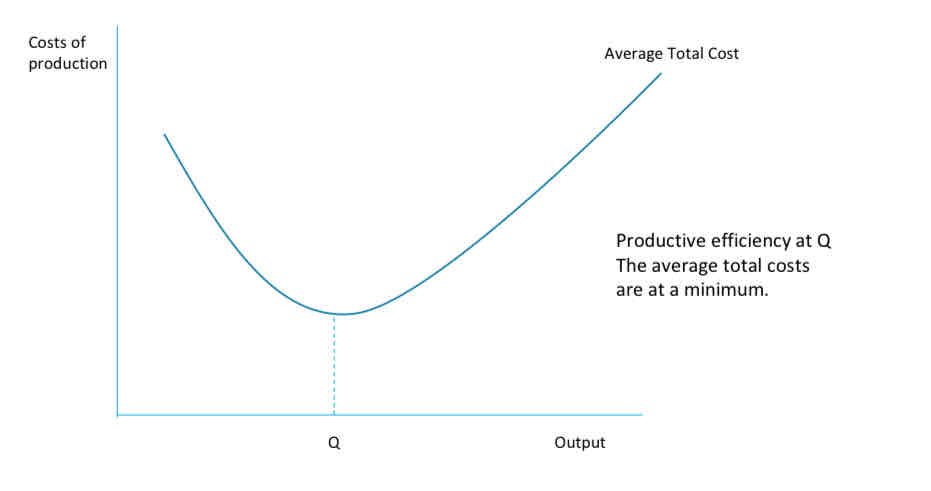
What is productive efficiency?
when an economy uses minimum inputs to produce the maximum output at lowest cost
What is the equation for the average total cost?
Total cost/ output
What can productive efficiency be shown by?
using an average cost curve diagram
What does the term economies of scale refer to?
How decisions of individuals, producers and government can improve resource allocation
What can we see through economies of scale?
productive efficiency is created when:
Purchasing economies lead to a reduction in costs
o Specialisation can lead to a more efficient use of inputs
o Better management can lead to increased output with the same factor inputs
What does the term diseconomies of scale mean?
how decisions of individuals, producers and government can lead to a misallocation of resources
What can we see through diseconomies of scale?
productive inefficiency is created where resources are misallocated:
o Lack of communication between employees
o Lack of coordination by management
o Bureaucracy, occurs when large organisations, particularly government, have overly complex administrative procedures. This increases costs.