Basic Info
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Know the role of the vascular system
carries blood, oxygen, nutrients, and lymph fluid
removes waste
Know what makes up the vascular system
heart, blood, and blood vessels
Be able to identify all components of the vascular system
heart, arteries, capillaries, veins, blood
Know the function of the arteries
carry blood away from the heart
Know the function of the veins
return blood to the heart
Know the function of the capillaries
connects the smallest arteries to the smallest veins, facilitating exchange between blood and tissues
What tunica intima layer is composed of
smooth endothelium
What tunica media layer is composed of
smooth muscle and elastic tissue
What tunica externa layer is composed of
fibrous connective tissue
Know the anatomy of blood vessels
tunica intima, tunica media, tunica externa and the lumen
Function of the tunica intima
produces chemicals, causes blood vessels to dilate and contract
Function of the tunica media
allows vessel to change diameter
Function of the tunica externa
supports and protects the vessel
Function of the lumen
greater size allows for greater volume of blood to flow at a lower pressure
Know what the lumen of a blood vessel refers to
hollow passageway where blood flows
The anatomical differences of arteries
thicker walls, smaller lumens, higher pressure
The anatomical differences of veins
thinner walls, bigger lumens, lower pressure
Know how the size of the lumen has an effect on blood flow and blood pressure
greater size, greater volume, decreased pressure
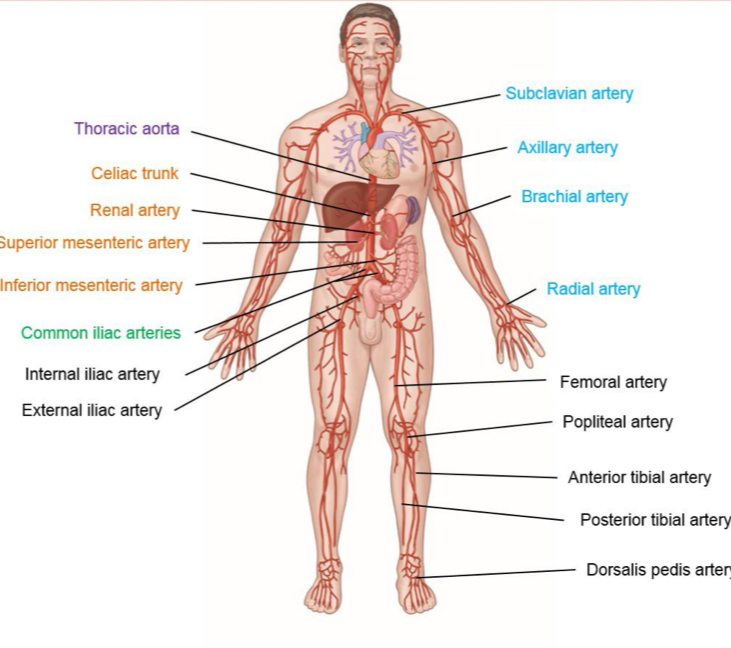
Be able to identify the arteries listed on slide 10
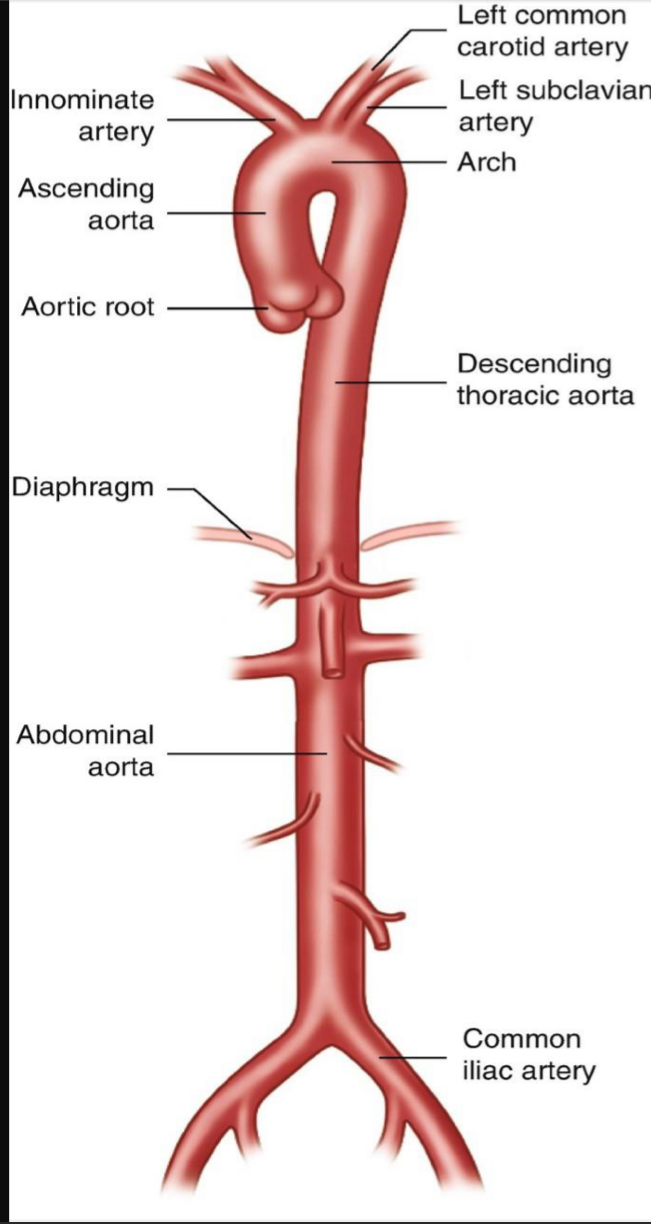
Be able to identify all portions of the aorta including the branches
Ascending aorta
coronary arteries branch off, supplying heart
Aortic arch
connects with descending aorta
Descending (thoracic) aorta
from aortic arch to diaphragm portion of abdomen
Abdominal aorta
from diaphragm to above the pelvis
Branches of the descending aorta
thoracic and abdominal aorta
Thoracic aorta supplies
muscles of the chest and upper abdomen
Abdominal aorta supplies
celiac trunk, digestive system
Know where each part of the aorta and its branches supply blood to (which part/region of the body). This includes the thoracic aorta, descending aorta (and its branches), and the abdominal aorta and the branches of the abdominal aorta
Be able to identify the carotid arteries and know their function
supplies blood to the neck, part of the face, and the brain
Also know what happens if there is blockage in the carotids
carotid artery stenosis, increases the risk of stroke
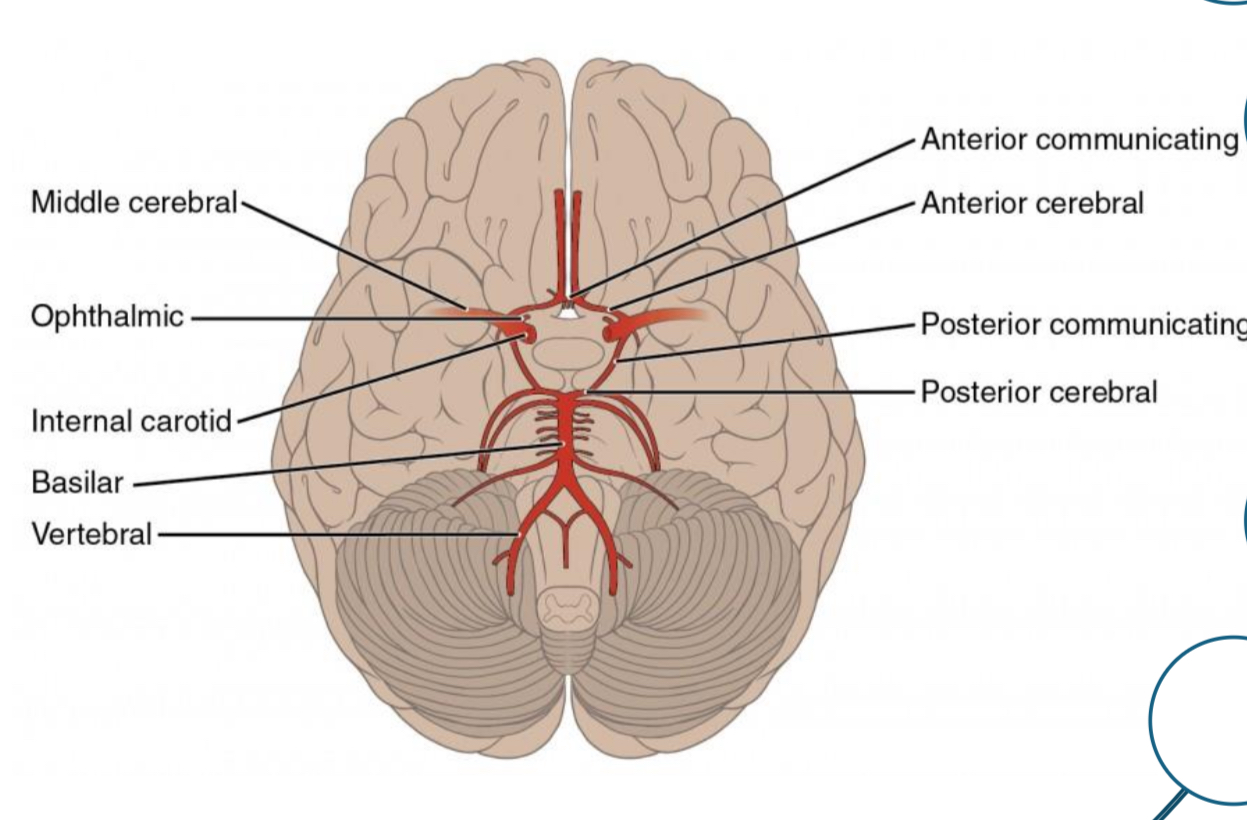
Be able to identify the Circle of Willis and its function
blood supply to the brain, backup or collateral supply
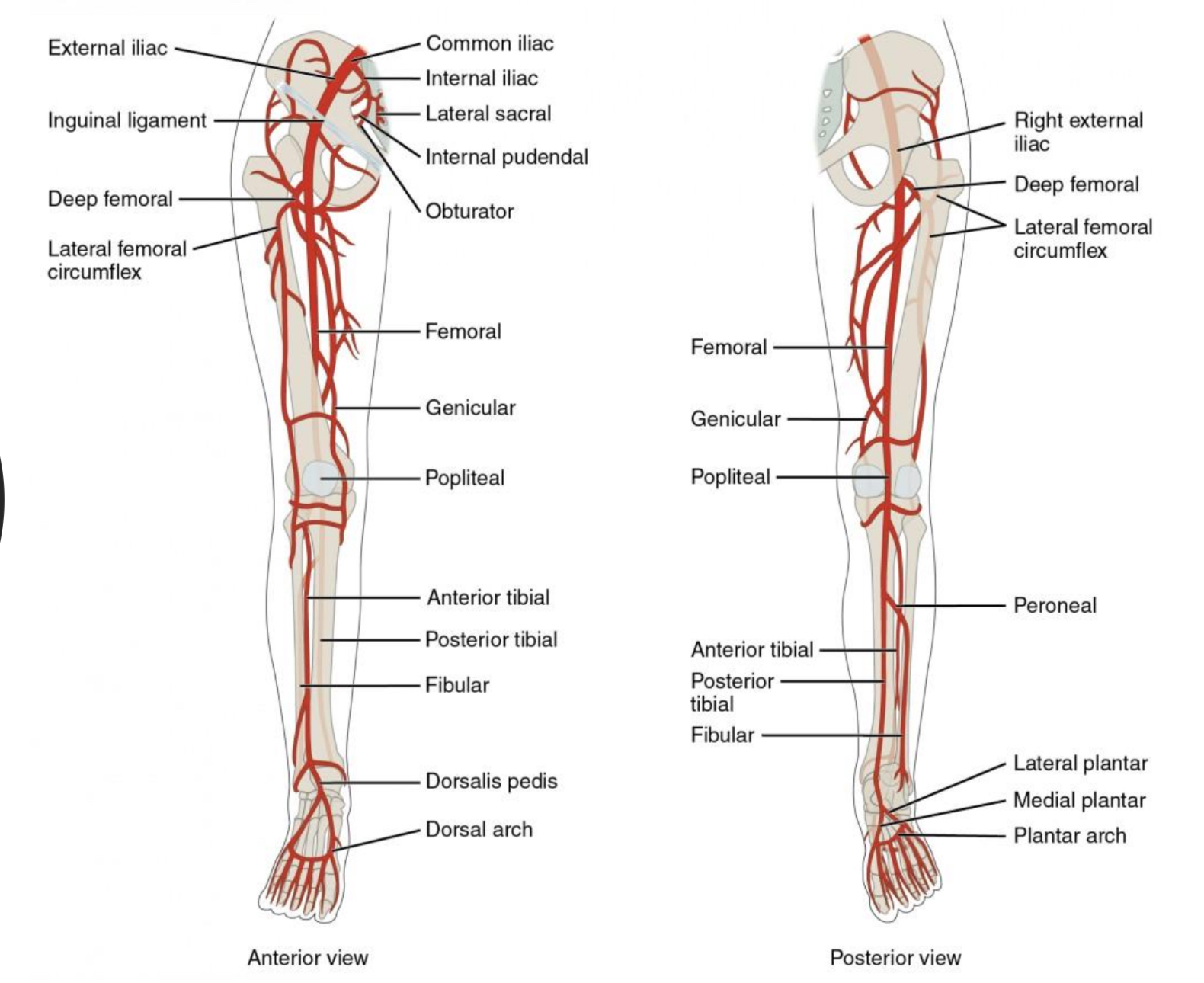
What are the arteries of the arm extensions of
subclavian arteries
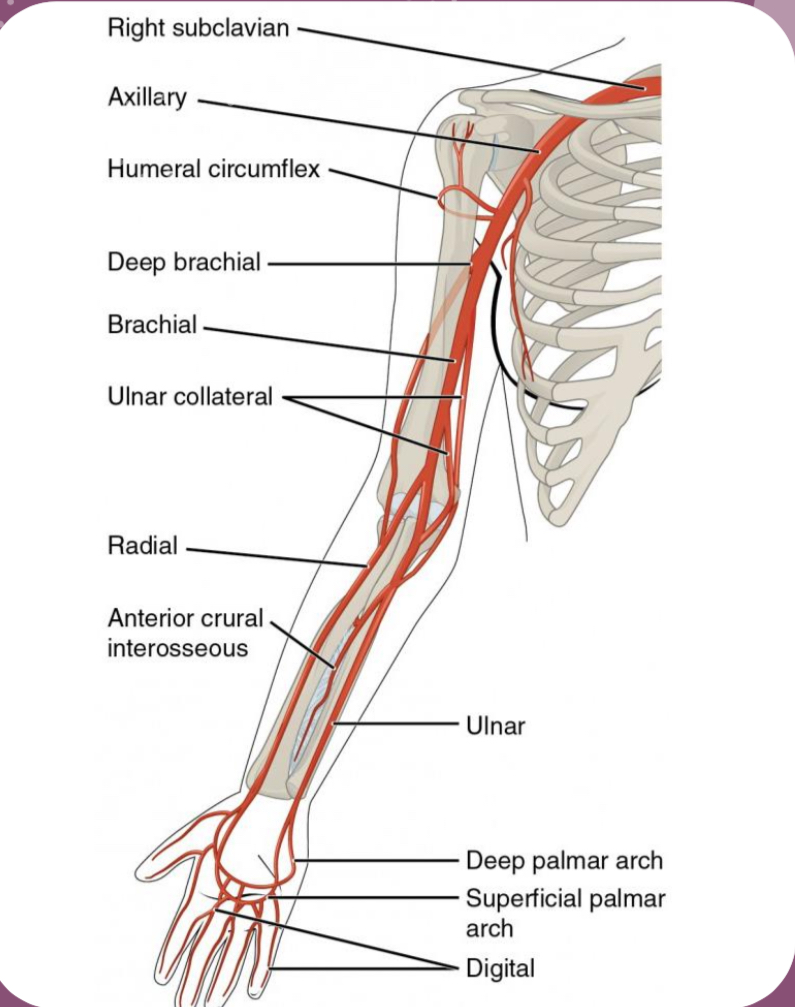
Be able to identify the arteries of the arm and leg
Be able to identify the Vena Cava and know its function
largest vein in the body, carries oxygen poor blood from the body to the right atrium
Functionality of superior vena cava
takes blood from neck, head, arms, and chest back to the heart
Functionality of inferior vena cava
brings blood from legs, feet, abdomen and pelvis back to the heart
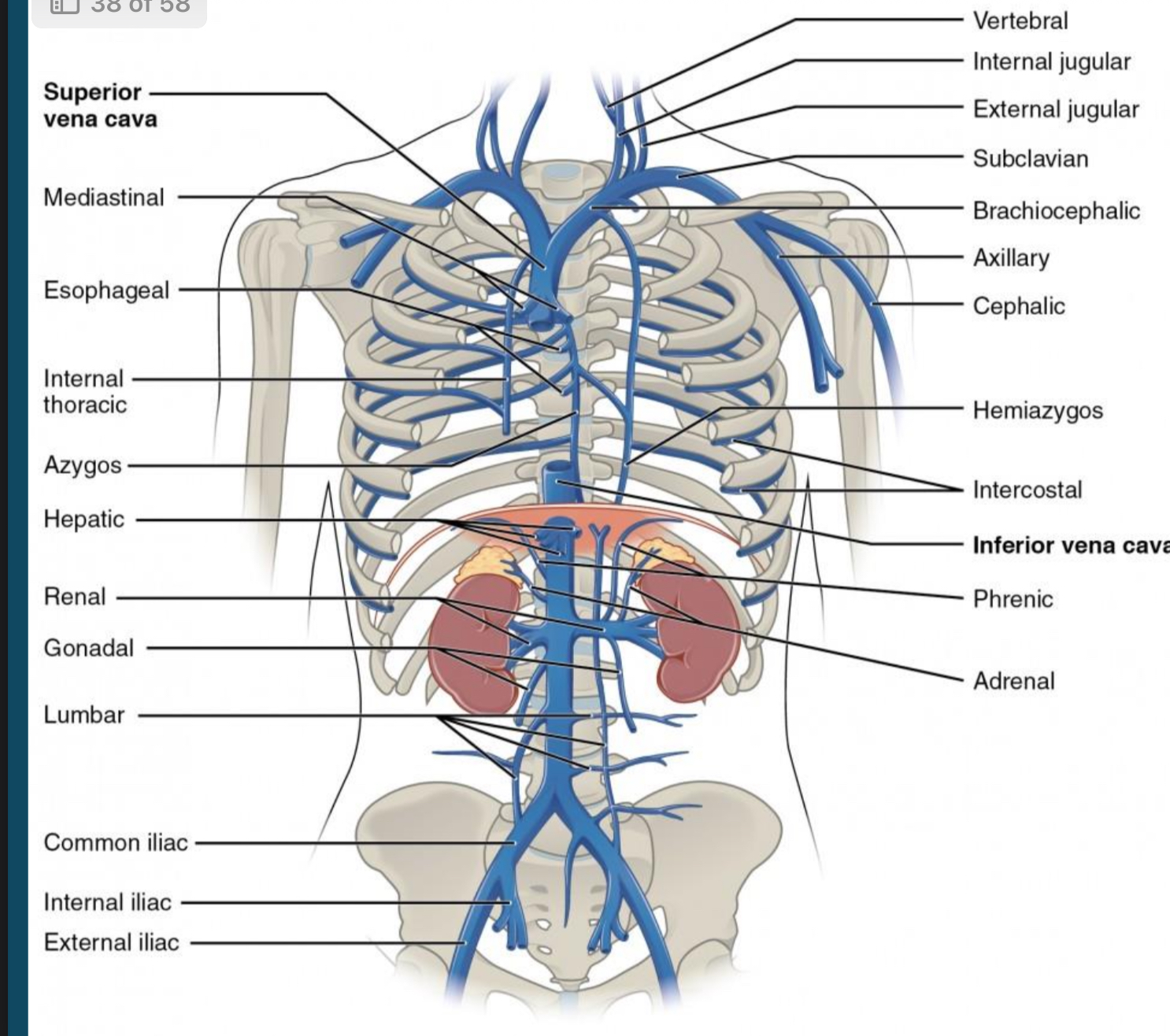
Be able to identify the veins of the thorax and abdomen.
Know the veins of the thorax and abdomen that parallel the arteries.
Be able to identify the veins of the neck, arms and legs.
Know the make-up of the capillaries
only composed of tunica intima and simple squamous endothelial cells, smallest lumen
Explain the process of diffusion
oxygen, nutrients, and waste moves in capillaries through blood and tissue
Know the three types of capillaries
continuous, fenestrated, sinusoidal
Where in the body continuous capillaries are primarily located
muscle tissue, skin, lungs, CNS
Where in the body fenestrated capillaries are primarily located
kidneys, small intestine, endocrine glands
Where in the body sinusoidal capillaries are primarily located
liver, spleen, bone marrow, lymphoid tissues
Know the functions of the arterioles
carries blood from heart to tissues and organs, connects arteries and capillaries, controls blood flow, manage and control force of blood, regulate amount of blood to tissues
Know the functions of the venules
receive blood from capillaries to direct to larger veins
Be able to explain where hepatic portal circulation is found
gastrointestinal tract
The components involved in hepatic portal circulation
from gi tract, spleen, and pancreas to the liver before general circulation
The function of hepatic portal circulation
to filter toxins in blood using the liver before general circulation
Be able to explain how pressure differences within the vascular system drives blood flow
arteries have the highest pressure, then capillaries, then veins, as blood travels from the heart and aorta to the body
Be able to explain blood viscosity effect on blood flow and blood pressure
how easily blood flows, greater viscosity, slower flow
Vasoconstriction
narrowing of the blood vessels
Vasodilation
widening of the blood vessels
Know where blood velocity is the greatest
aorta
Know where blood velocity is the weakest
capillaries
Be able to explain how skeletal muscle within the calf contributes to proper blood flow and increase circulation
contraction pushes blood to the heart, valves in veins ensure no backflow
Varicose veins
calf blood backflow
Explain the role of the diaphragm in aiding circulation
regulates pressure in thorax and abdominal cavity
Atherosclerosis
a buildup of plaque in arterial walls