Histology II
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Mesenchymal Cells
embryonic connective tissue; gives rise to all other connective tissue types

Areolar Loose Connective Tissue
spread out string projections; provides cushion to organs
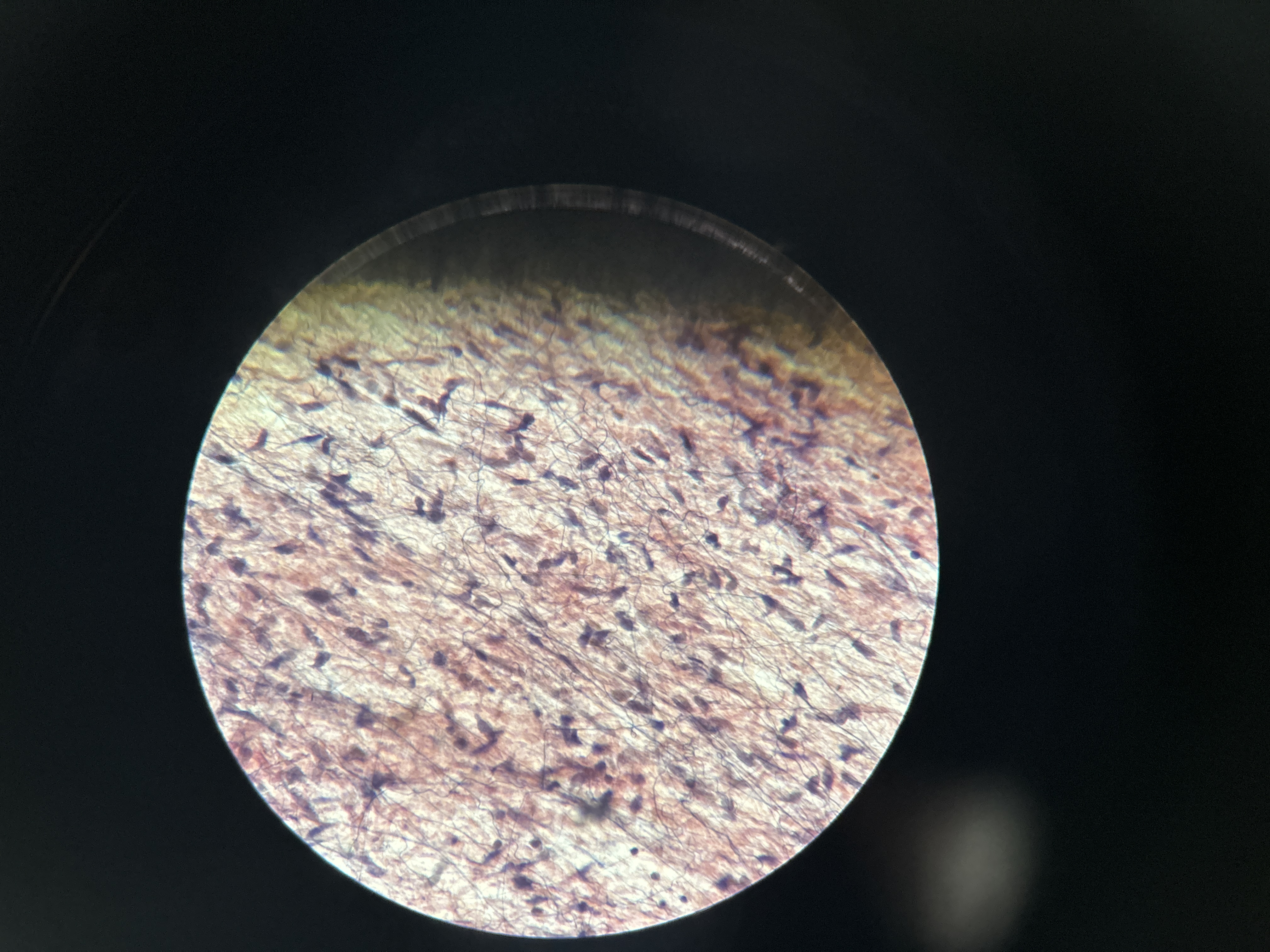
Reticular Loose Connective Tissue

Adipose Loose Connective Tissue
in breast, under skin, around eyeballs and kidneys
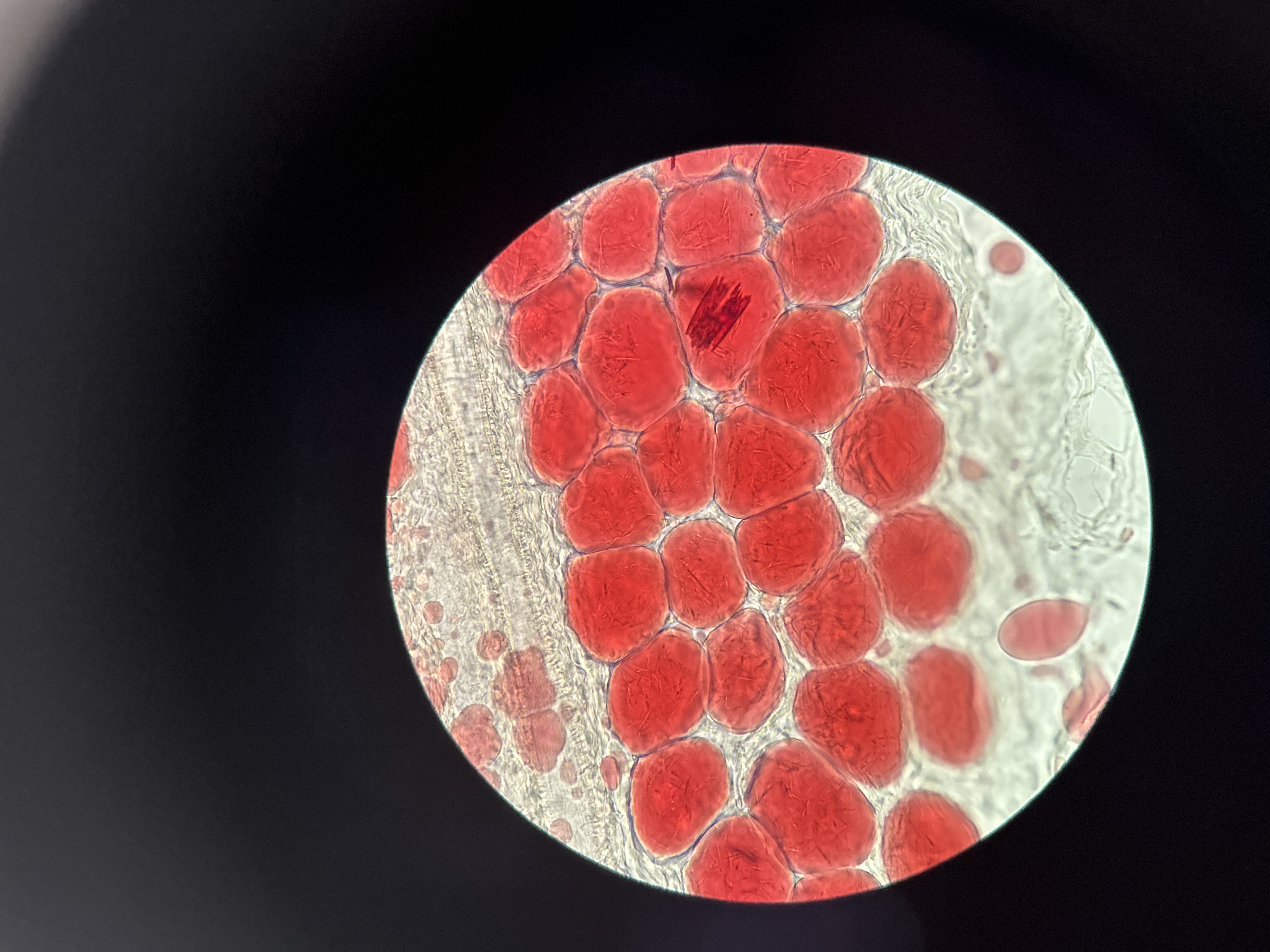
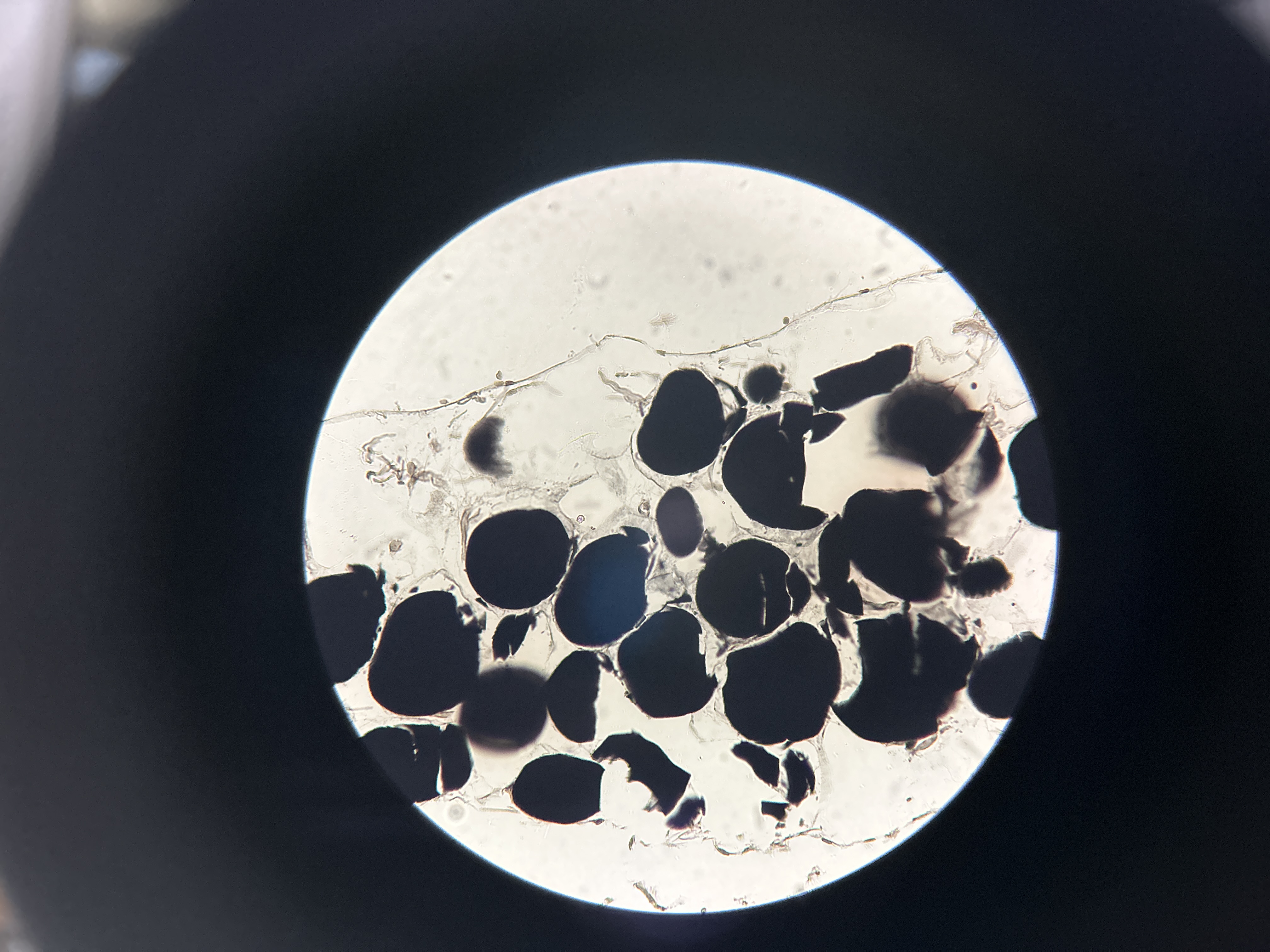
Adipose in Osmic Acid
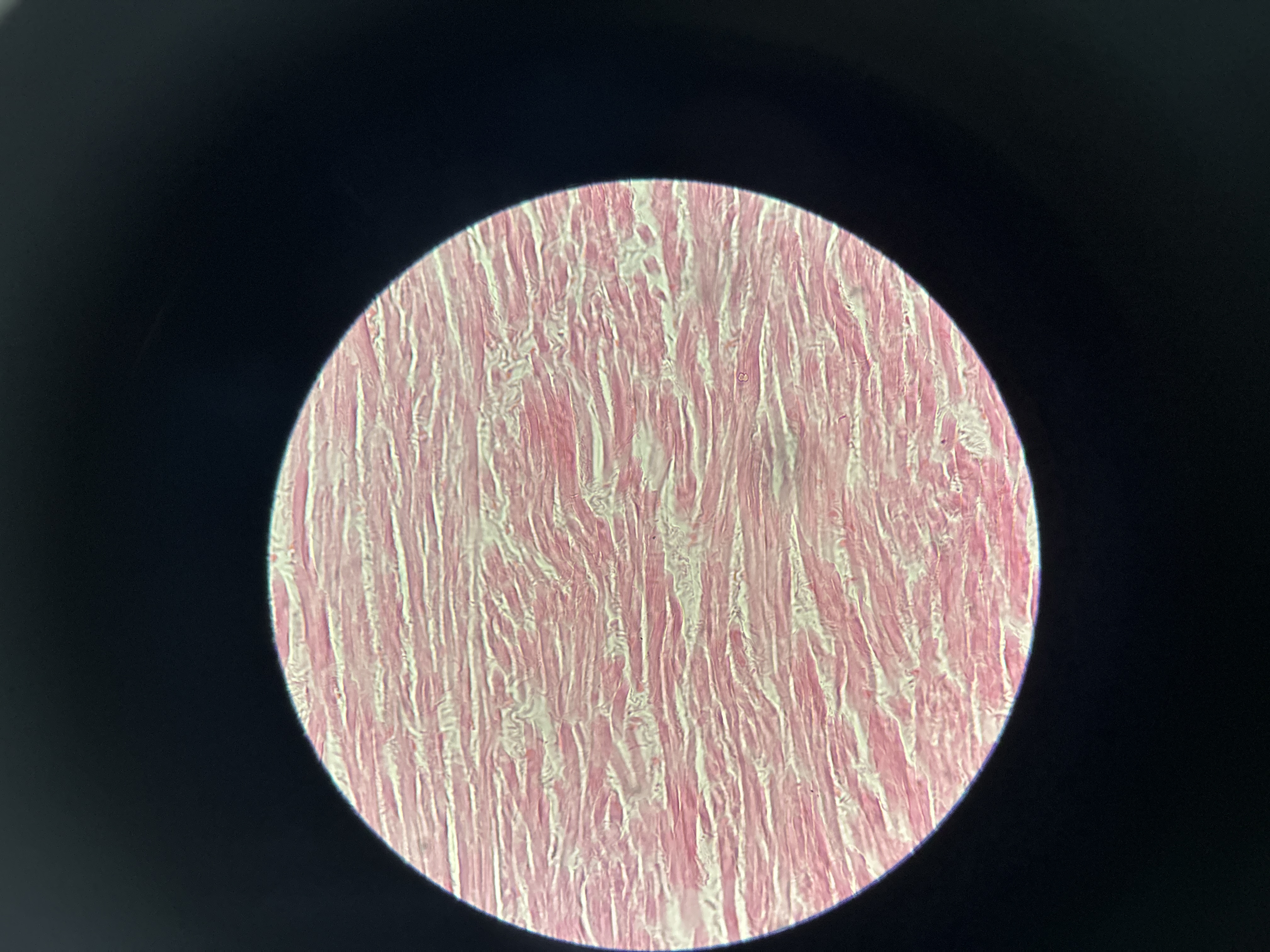
Regular Dense Connective Tissue
in tendons and most ligaments; major cell type is fibroblasts
Elastic Cartilage
auricle of the ear; maintains shape but allows flexibility
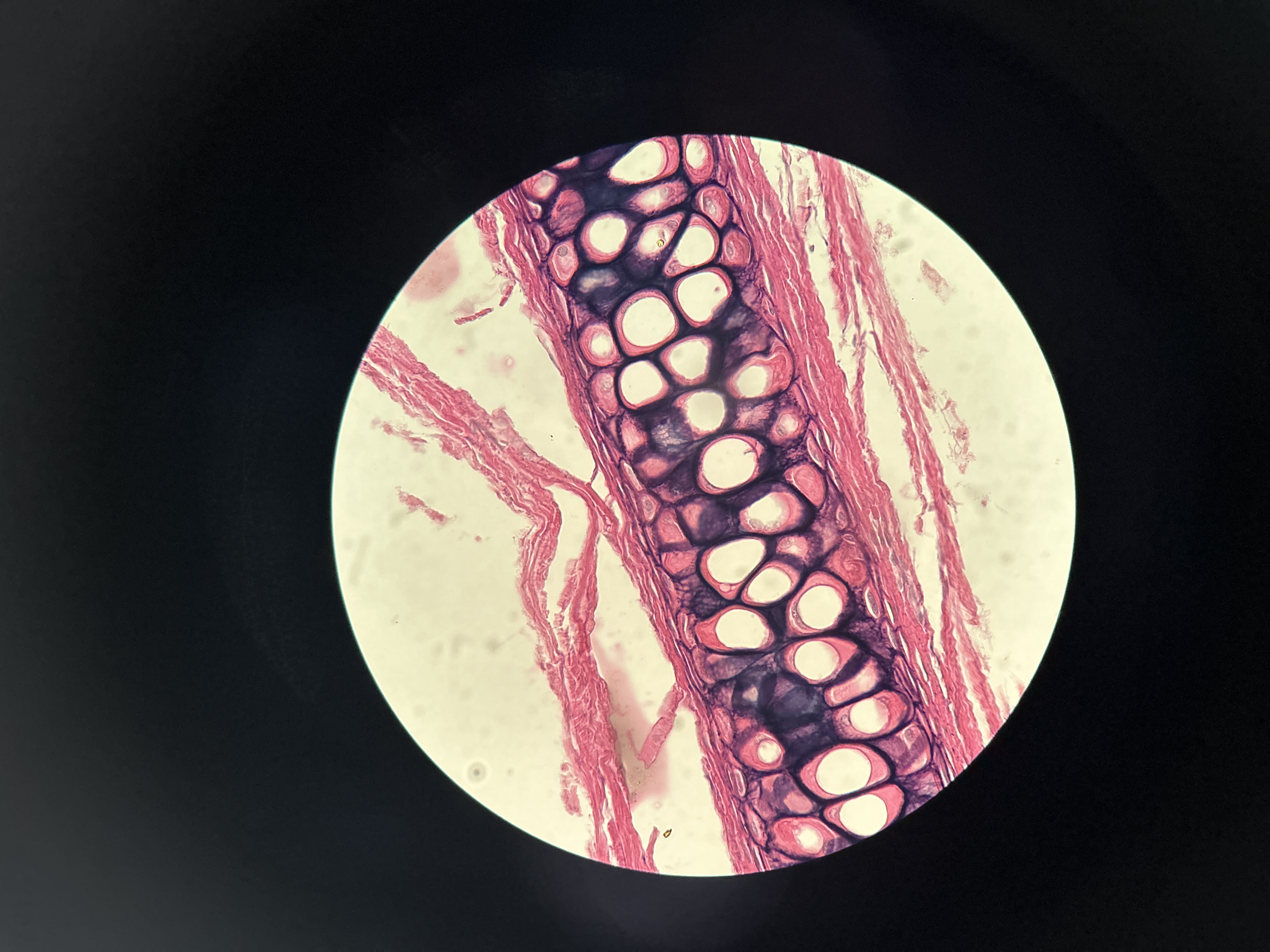
Elastic Dense Connective Tissue
in walls of large arteries and the brachial tubes

Irregular Dense Connective Tissue
in fibrous capsules of organs and joints and skin’s dermis
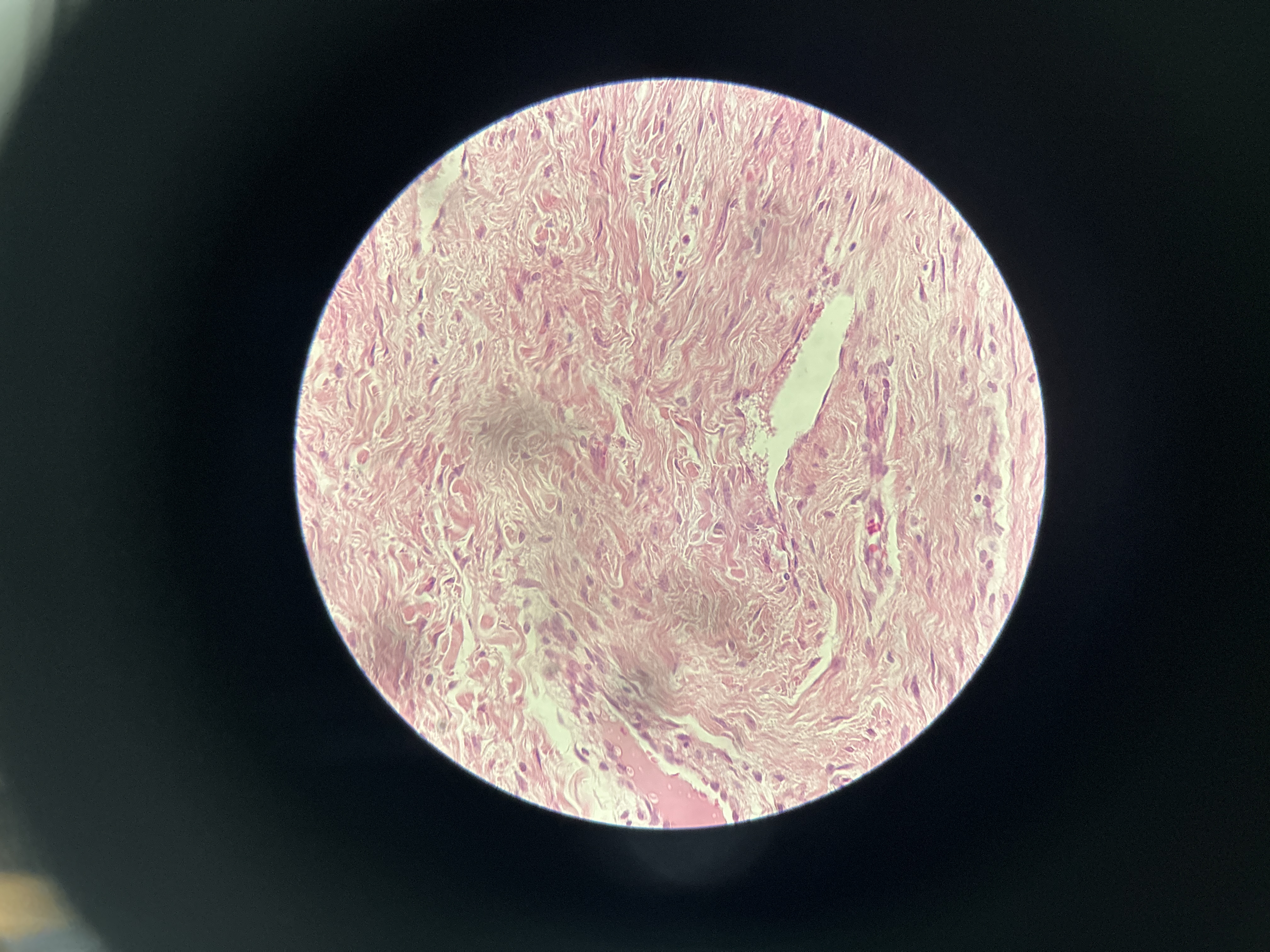
Hyaline Cartilage
tough and flexible tissue that covers joints, supports respiratory tract, and support to the nose, trachea, and larynx.
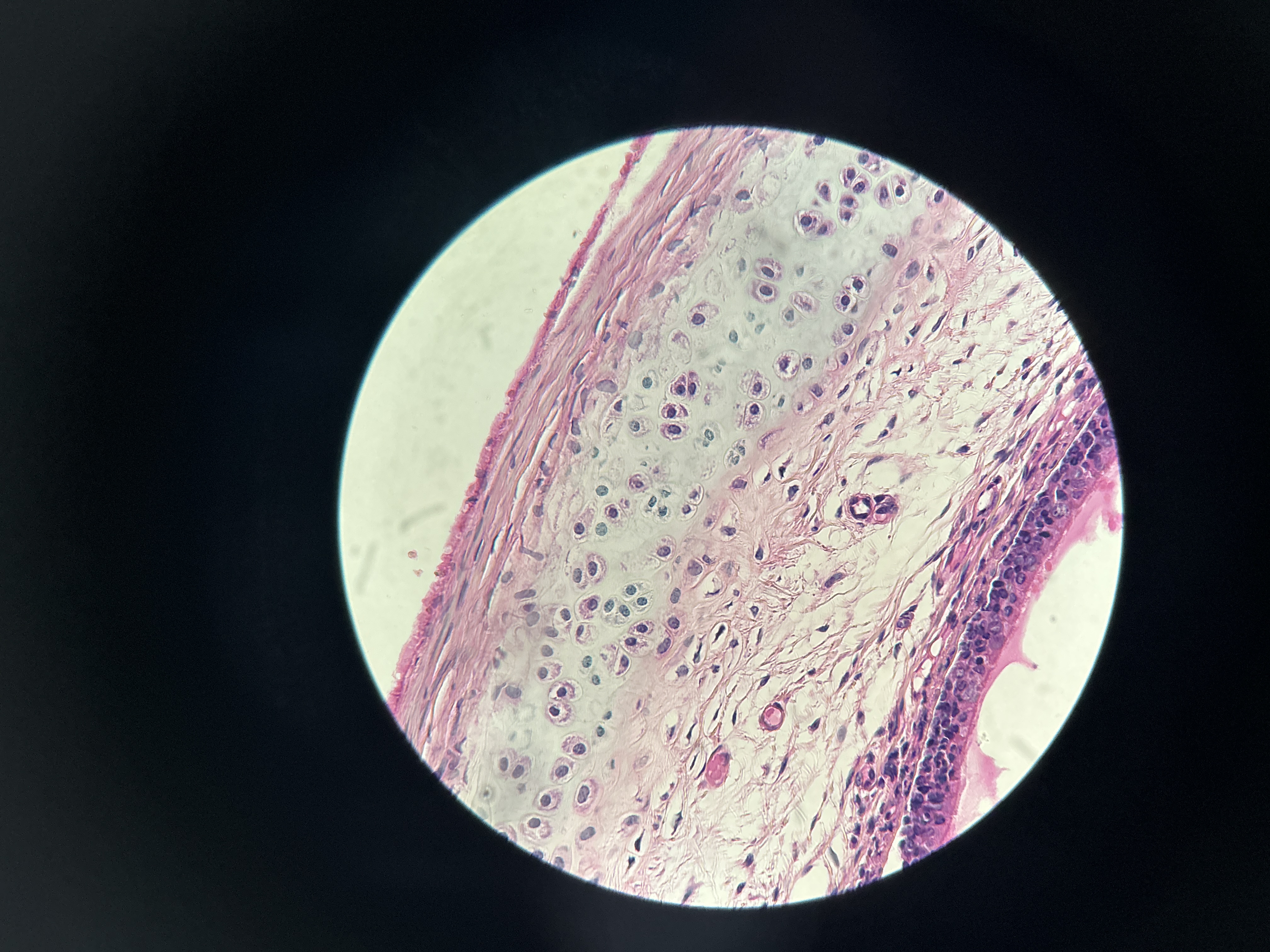
Fibrocartilage
intervertebral discs and pubic symphysis, and discs of knee joint

Neutrophil
phagocytise bacteria; multi-lobed nucleus

Lymphocyte
immune response cells

Monocyte
develop into macrophages; phagocytosis

Eosinophil
kill parasites, role in histamine response
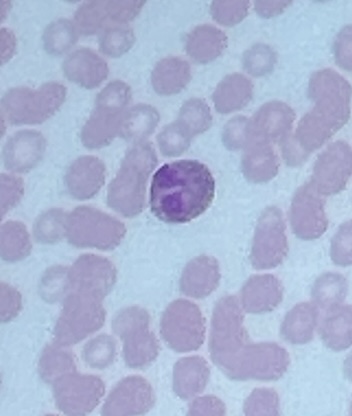
Compact Bone
calcified bone
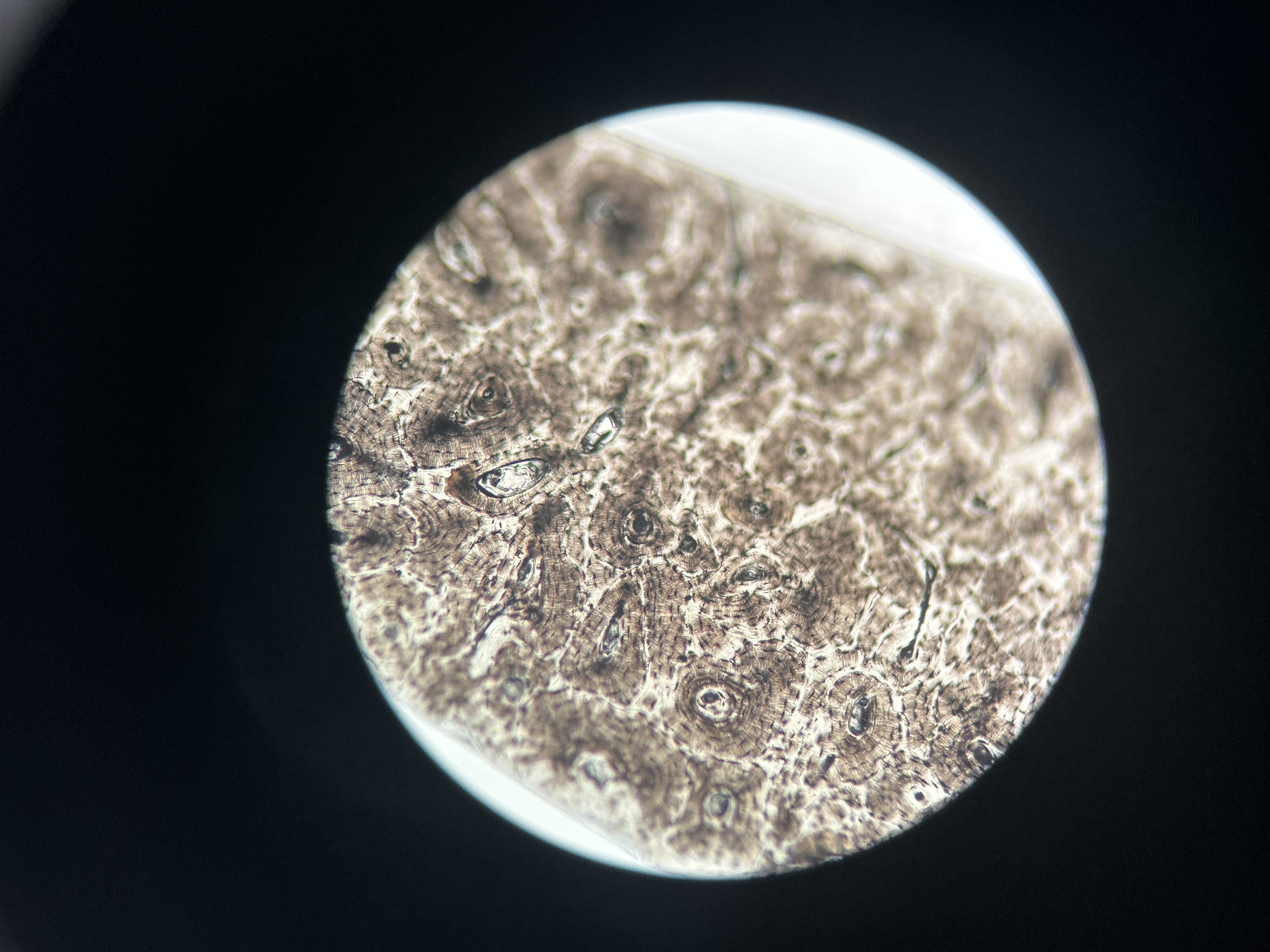
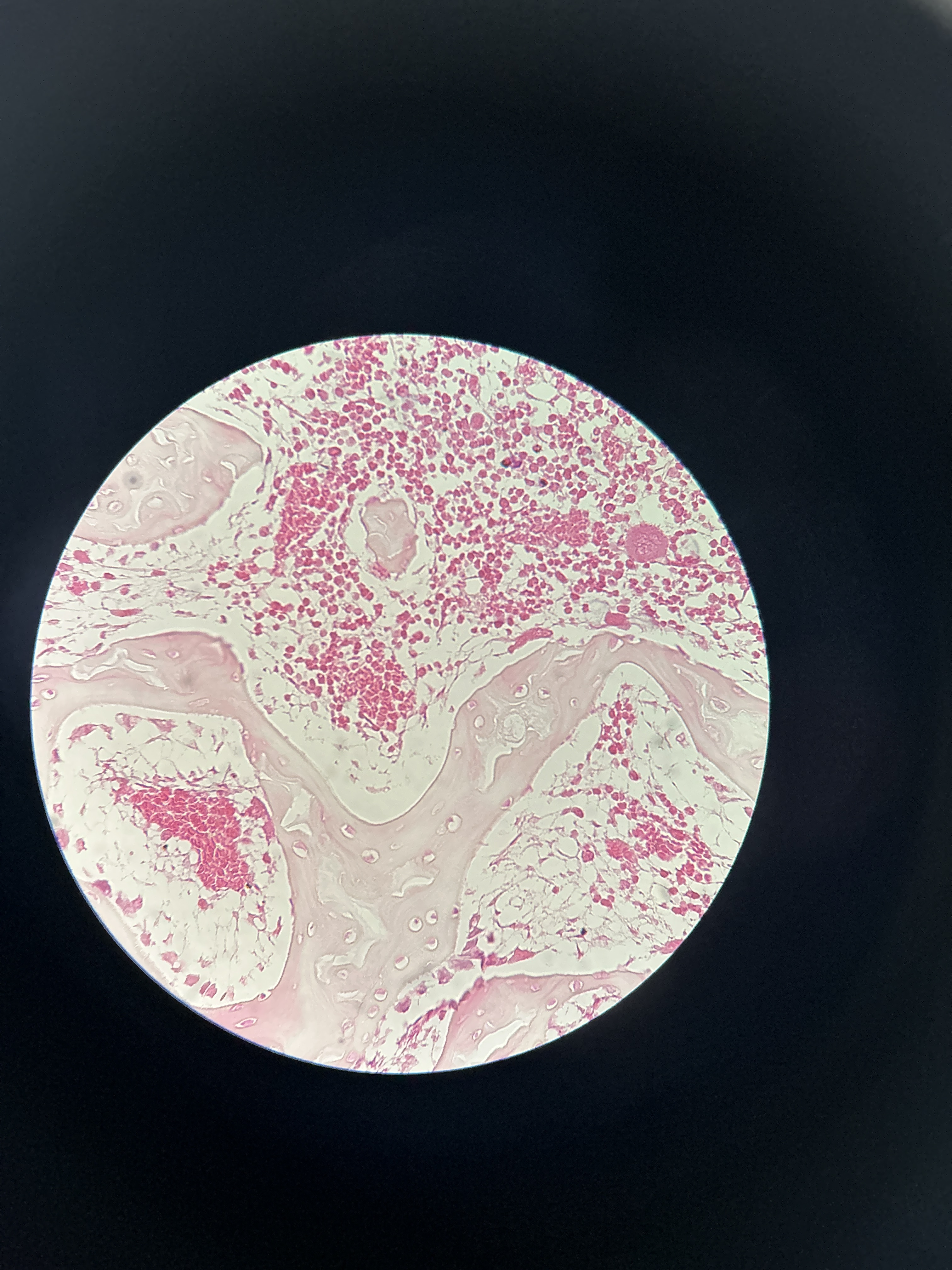
Cancellous Bone
spongy bone
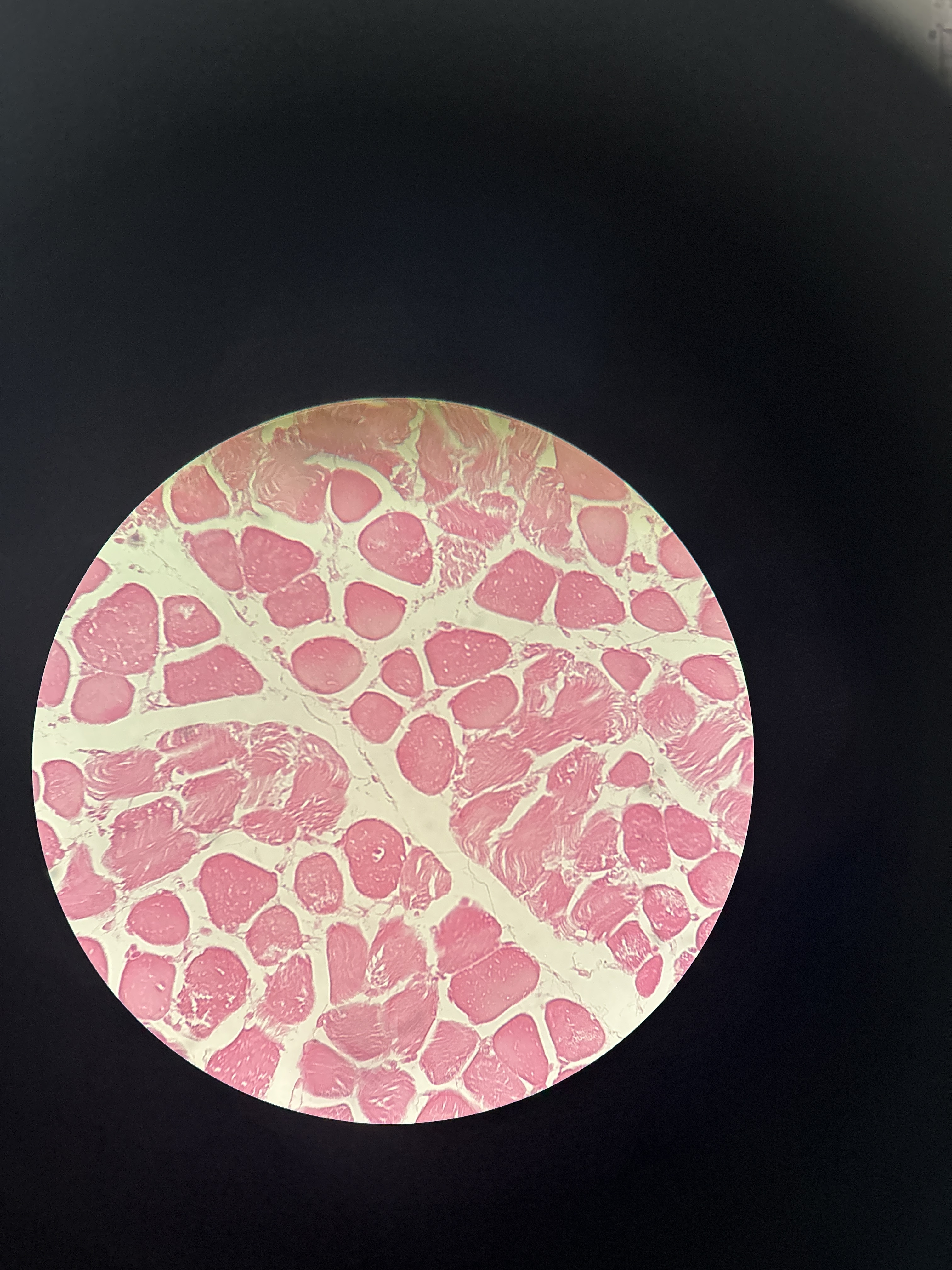
Cancellous Bone
Dense Connective Tissue
regular, elastic, and irregular
Loose Connective Tissue
areolar, reticular, and adipose
Cartilage
hyaline, fibrocartilage, and elastic