Understanding Acids, Bases, and Salts
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Arrhenius Theory
A theory explaining the behavior of many acids and bases.
Electrolyte
A substance which, when dissolved in water, forms a solution capable of conducting an electric current.
Concentration of Ions
The amount of ions present in a solution, which affects its ability to conduct electricity.
Properties of Acids
Acids dissolve in water, are electrolytes, taste sour, neutralize bases, react with active metals, and turn blue litmus red.
Properties of Bases
Bases dissolve in water, are electrolytes, taste bitter, neutralize acids, emulsify fats and oils, feel slippery, and have a pH more than 7.
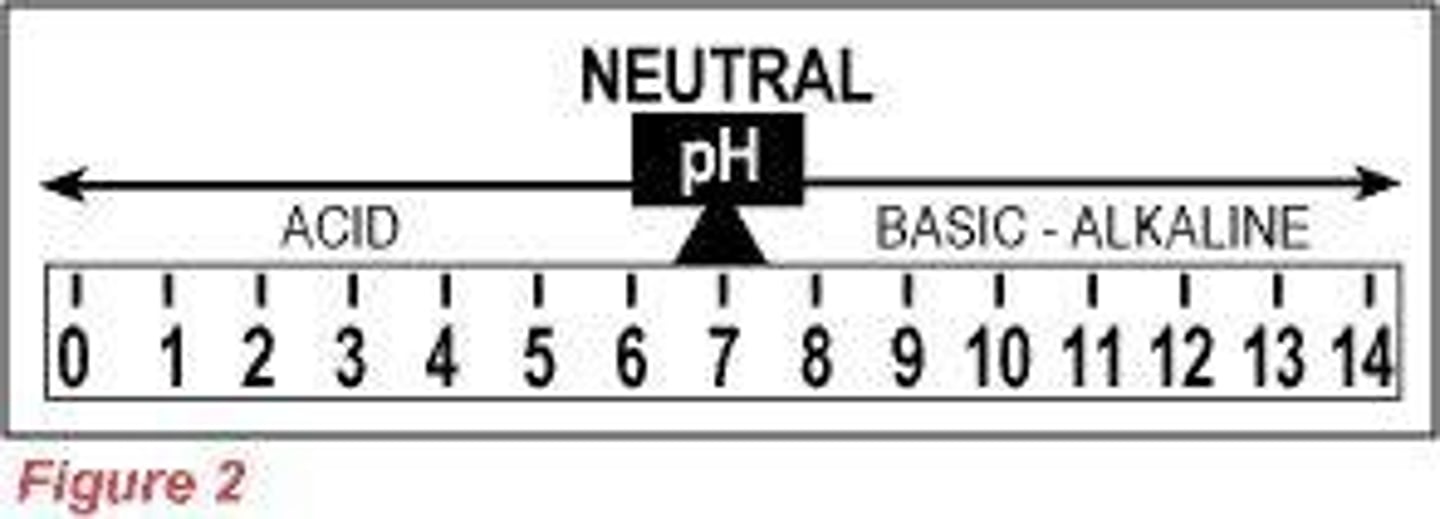
pH of Acids
Acids have a pH less than 7.
pH of Bases
Bases have a pH more than 7.
Hydrochloric Acid
HCl(aq), hydrochloric acid is an electrolyte.

Hydrogen Ion
H+(aq), the only positive ion in an aqueous solution of an Arrhenius acid.
Hydronium Ion
H3O+(aq), a representation of the hydrogen ion in solution.
Arrhenius Bases
Arrhenius bases yield OH-(aq), hydroxide ion as the only negative ion in an aqueous solution.
Neutralization Process
An Arrhenius acid and an Arrhenius base react to form a salt and water.
Salt Formation
The nonmetal from the acid combines with the metal from the base to make a salt.
Water Formation in Neutralization
The H+ from the acid combines with the OH- from the base to make water (HOH = H2O).
Ammonia as a Base
When ammonia (NH3) dissolves in water, it produces hydroxide ions.
Hydroxide Ion
OH-(aq), the only negative ion produced when an Arrhenius base is dissolved in water.
Acetic Acid
An organic chemist would write the formula for acetic acid in a specific way.
Common Acids
Acids start with H, as listed in Table K.
Common Bases
Bases are listed in Table L.
Conductivity of NaOH
NaOH would conduct electricity if it was dissolved in water, not as a solid.
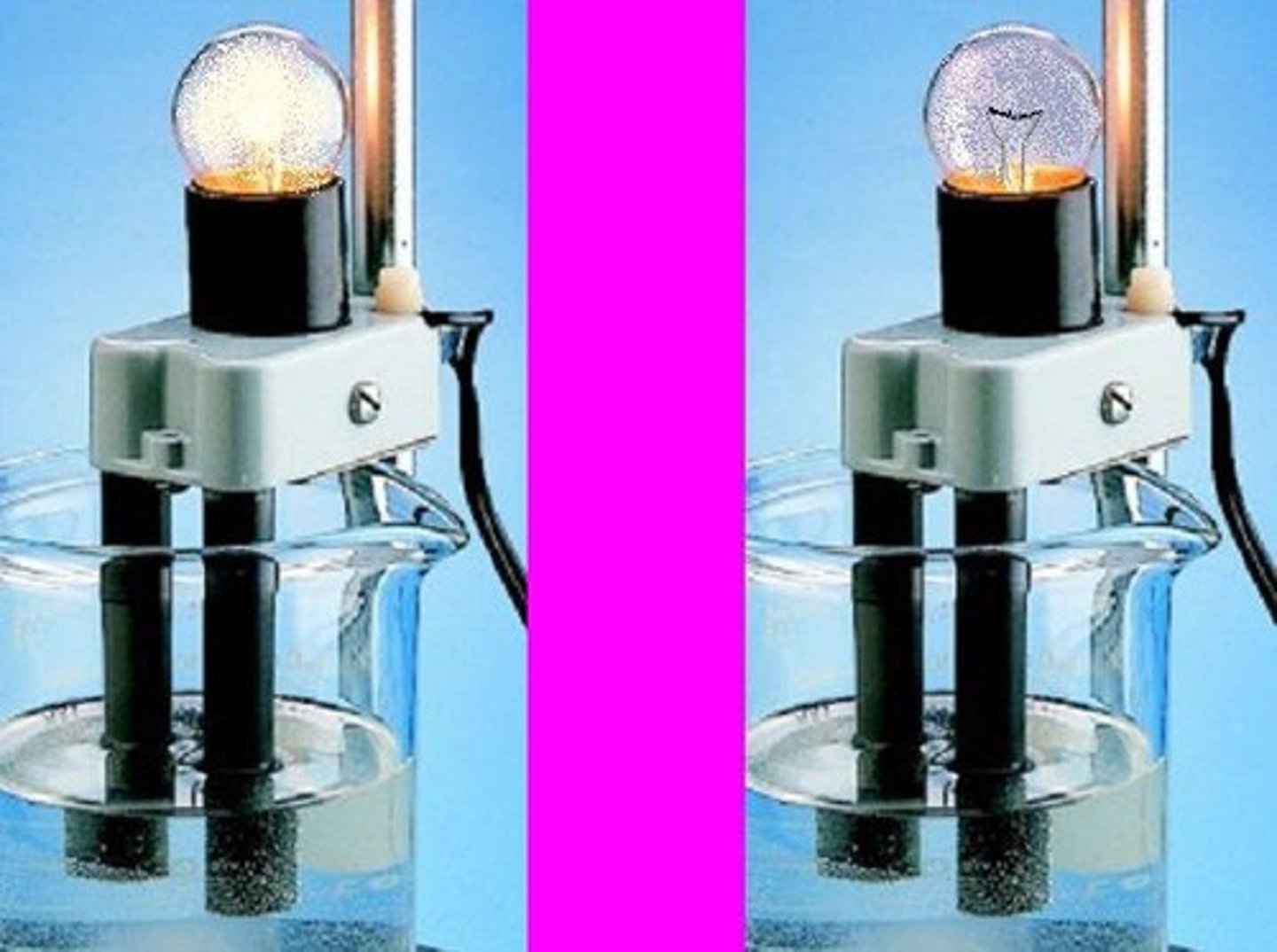
Conductivity of CH3OH
CH3OH is an alcohol, a non-electrolyte.
Conductivity of H2O
Water is a non-electrolyte, even as a liquid.
Neutralization Reaction
A reaction between an acid and a base that produces a salt and water.
Titration
A laboratory process in which a volume of solution of known concentration is used to determine the concentration of another solution.
MaxVa = MbxVb
Formula used in titration where Ma is the molarity of the acid, Mb is the molarity of the base, Va is the volume of the acid, and Vb is the volume of the base.
Equivalence Point
The point in a titration where the moles of H+ equals the moles of OH-.
HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq)
The reaction produces NaCl(aq) + HOH.
H2SO4(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq)
The reaction produces CaSO4(aq) + 2H2O.
Regents Question: 06/02 #25
Given the reaction HCl(aq) + LiOH(aq) produces HOH(l) + LiCl(aq), the reaction is best described as neutralization.
Regents Question: 06/03 #30
Which equation represents a neutralization reaction? (4) H2SO4 + Mg(OH)2 produces MgSO4 + 2 H2O.
Concentration of HNO3
When 50. milliliters of an HNO3 solution is exactly neutralized by 150 milliliters of a 0.50 M solution of KOH, the concentration of HNO3 is 1.0 M.
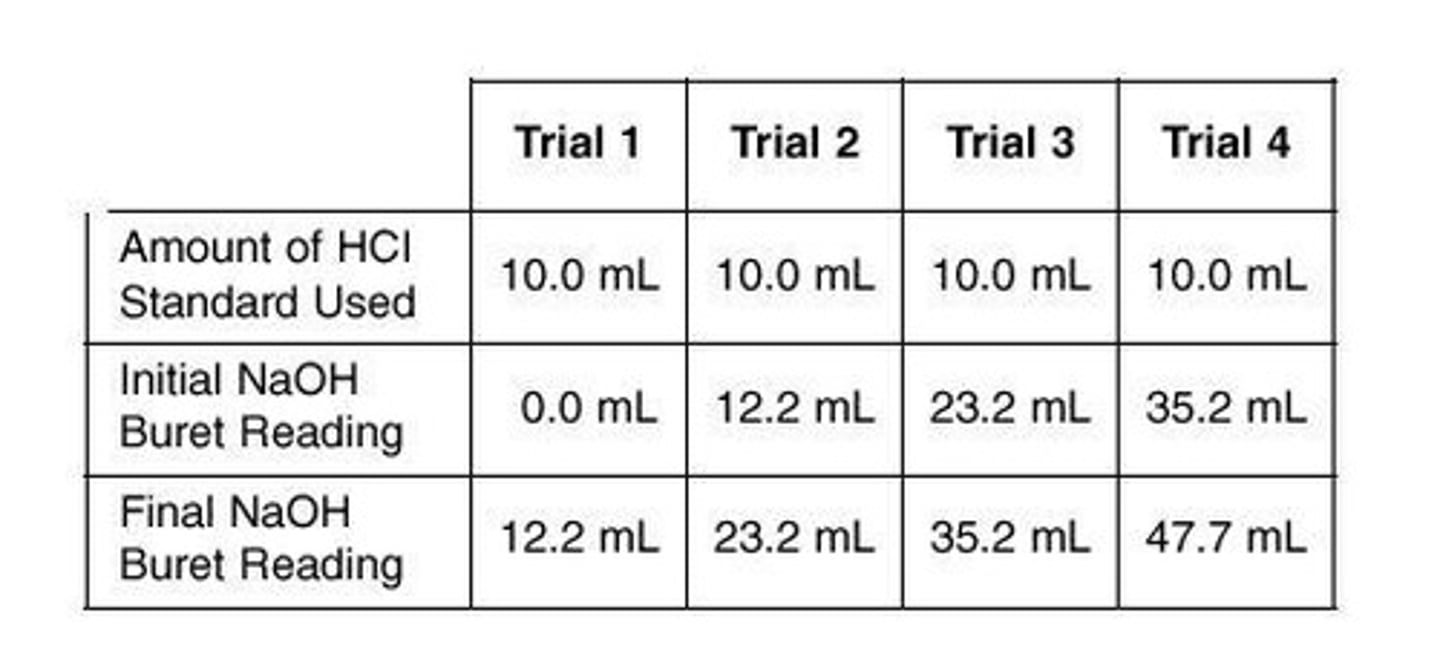
Volume of NaOH solution
To neutralize 10.0 mL of the standard HCl solution in trial 3, the volume of NaOH solution used is calculated based on the titration data.
Bromthymol Blue
An indicator that changes color at a neutral pH (7), appropriate for determining the end point of a titration.
Phenolphthalein
An indicator that changes color right after being neutral, used in titrations.
Average Molarity of NaOH
Calculated as (1.0 + 1.1 + 1.0 + 0.96)/4 = 1.015, rounded to 1.0 M.
Acid-Base Theories
One theory states that an acid is an H+ (proton) donor and a base is an H+ (proton) acceptor.
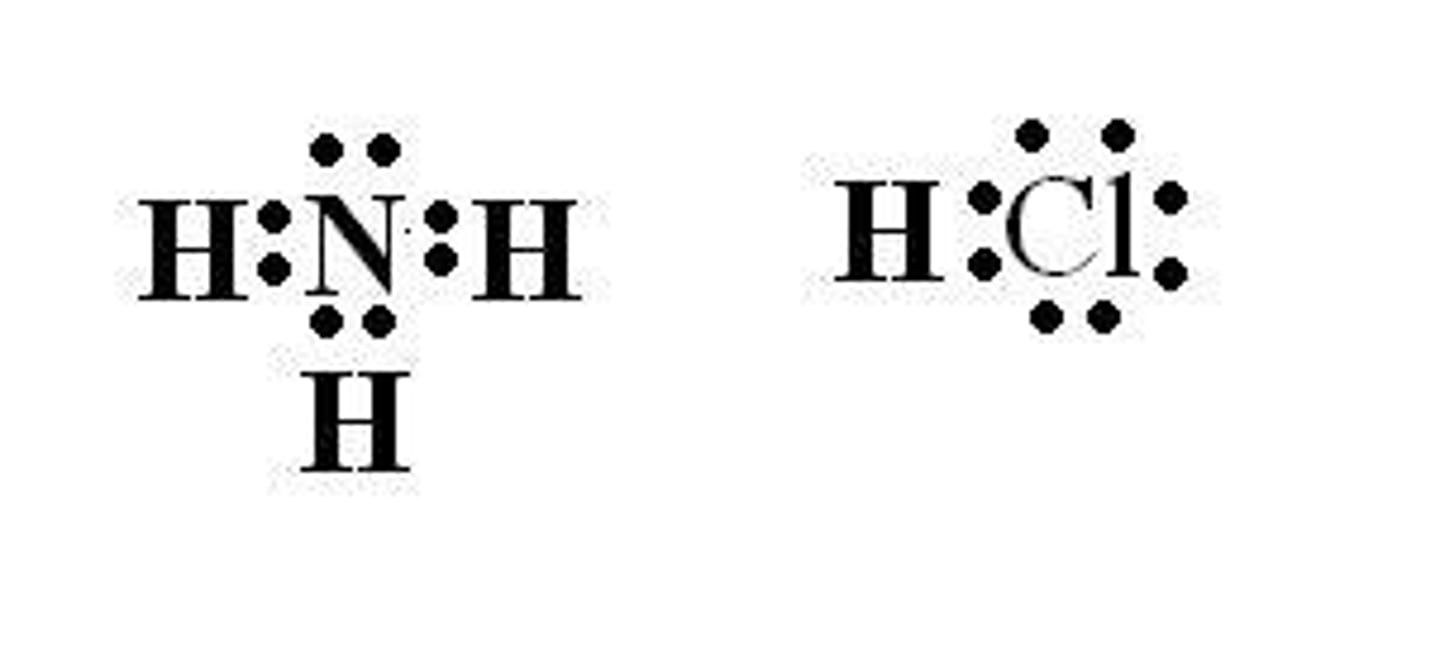
pH Value
The acidity or alkalinity of a solution can be measured by its pH value.
Indicators
Substances used to show the relative level of acidity or alkalinity of a solution.
HCl donates a proton
In the reaction between NH3 and HCl, HCl acts as the proton donor.
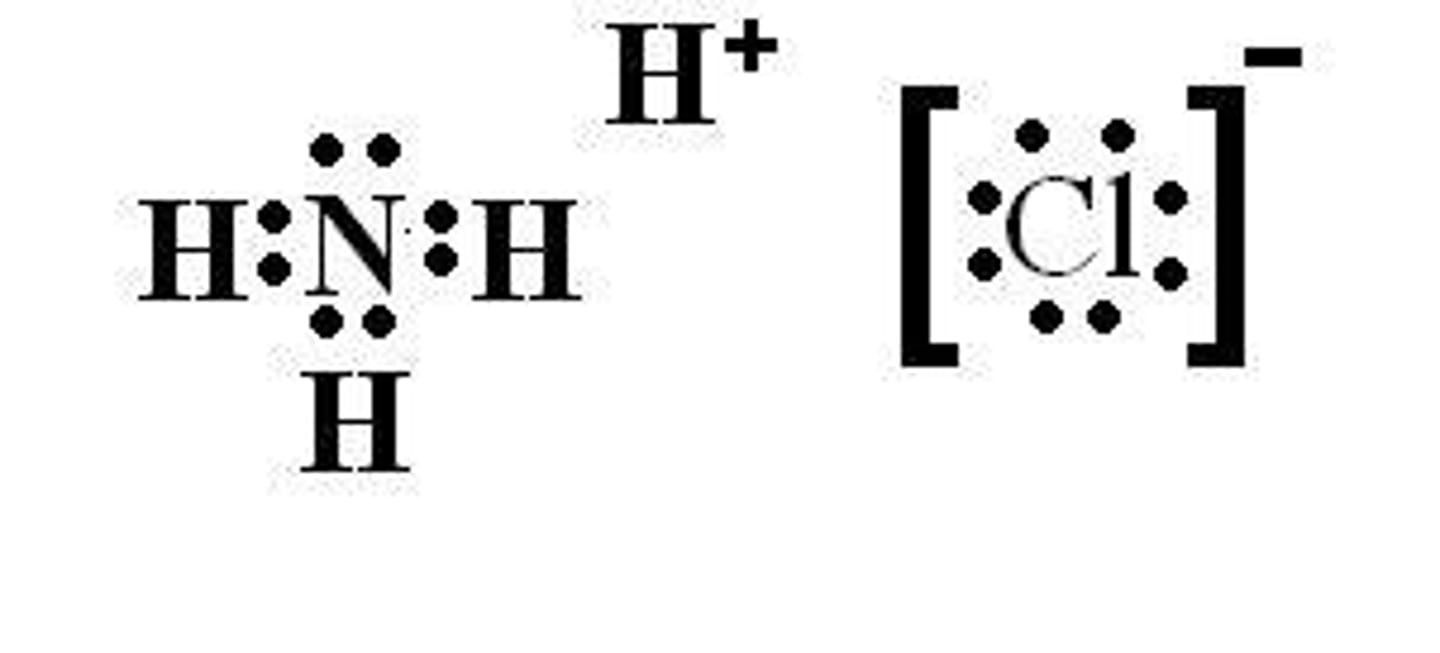
NH3 accepts a proton
In the reaction between NH3 and HCl, NH3 acts as the proton acceptor.
Molarity of OH-
In titration, Mb represents the molarity of the hydroxide ion.
Volume of Acid
In titration, Va represents the volume of the acid solution used.
Volume of Base
In titration, Vb represents the volume of the base solution used.
Red Litmus
Turns Blue in Base
Blue Litmus
Turns Red in Acid
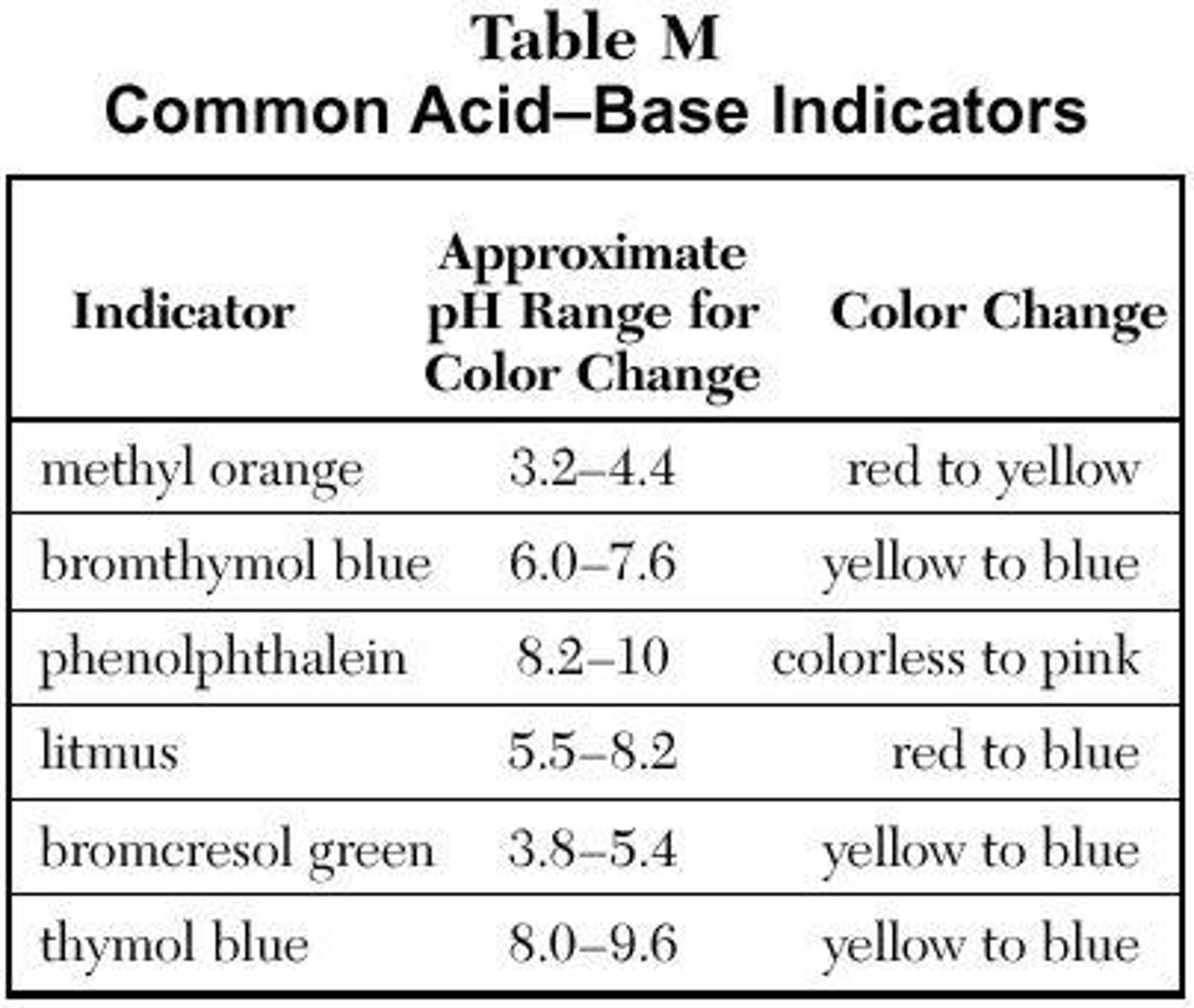
Methyl Orange at pH 3
Red
Methyl Orange at pH 5
Yellow
Methyl Orange at pH 7
Yellow
Methyl Orange at pH 9
Yellow
Bromthymol Blue at pH 3
Yellow
Bromthymol Blue at pH 5
Yellow
Bromthymol Blue at pH 7
Green
Bromthymol Blue at pH 9
Blue
Bromcresol Green at pH 3
Yellow
Bromcresol Green at pH 5
Green
Bromcresol Green at pH 7
Blue
Bromcresol Green at pH 9
Blue
Thymol Blue at pH 3
Blue
Thymol Blue at pH 5
Yellow
Thymol Blue at pH 7
Yellow
Thymol Blue at pH 9
Yellow
Thymol Blue at pH 10
Green
[H3O+] Formula
[H3O+] = 1 x 10^-pH
Hydronium Ion Concentration
An acid with a pH of 2 has 10x the [H3O+] concentration as an acid with a pH of 3.
Base Hydronium Ion Concentration
A base with a pH of 10 has 100x the [H3O+] concentration as a base with a pH of 12.
pH Scale
Each decrease of one unit of pH represents a tenfold increase in hydronium ion concentration.