thoracic spine & ribs
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
facet joints are in what plane
frontal
most spinous process in thoracic spine align with
the body of the segment below
T1, T11, and T12 have [full costal facets/demifacets]
full costal facets (ribs articulate with 1 vertebral body)
what are the 6 main ligaments in the spine
- anterior longitudinal ligament
- posterior longitudinal ligament
- ligamentum flavum
- interspinous ligament
- intertransverse ligament
- supraspinous ligament
what are the joints for posterior articulation of the ribs?
- costotransverse
- costovertebral
T-spine: if rotation is the primary motion, sidebending is in the [same/opposite] direction
same - ipsilateral coupling
T-spine: if sidebending is the primary motion, rotation is in the [same/opposite] direction
opposite - contralateral coupling
thoracic/rib movement during flexion
facet: upglide/opening - superior and anterior
rib: anterior rotation
CT: superior glide
thoracic/rib movement during R sidebending
- coupling: L rotation
- facet: R anteroinferior/L posterosuperior
- rib: R anteroinferior/L posterosuperior
- CT: R superior glide/L inferior glide
thoracic/rib movement during R rotation
- coupling: R sidebending
- facet: R posteroinferior/L anterosuperior
- rib: R posteroinferior/L anterosuperior
- CT: R inferior glide/L superior glide
each typical thoracic vertebra has __ costal articular surfaces
6
- 2 demifacets on each side
- 1 on TP on each side
typical costovertebral joints are on ribs __-__
2-9
on what VB demifacets does rib 6 articulate?
T5 and T6
T1-T6: ___ costal tubercles on ___ costal facets
convex on cocave (opposite)
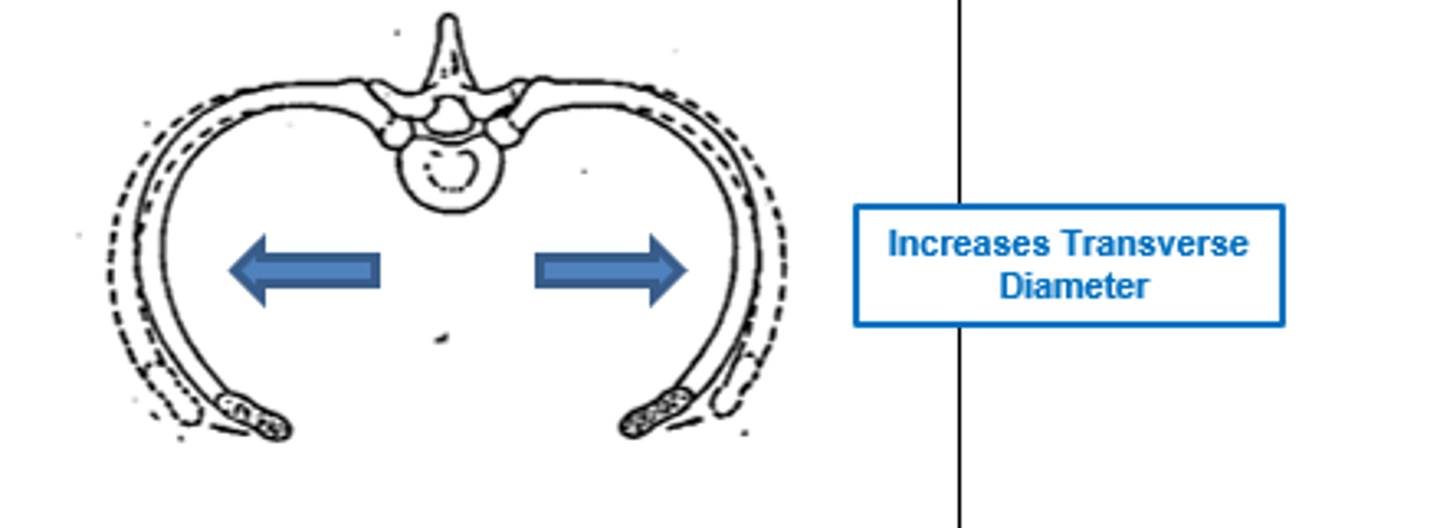
motion of ribs 1-6
pump handle - anterior/posterior rotation
motion of ribs 7-10
bucket handle - elevation and depression
motion of ribs 11-12
caliper - transverse plane motion
pain from thoracic spine inflammation can mimic serious conditions such as
- cardiac/pulmonary issues
- renal disease
- fx or tumors
- AAA
most common cause of thoracic pain
postural syndromes
screening questions for systemic involvement in t-spine
- bowel/bladder dysfunction
- numbness, tingling, or weakness in extremities
- visual or balance disturbances
- nausea/vomiting
- pain unchanged with movement or positions
indicators of ankylosing spondylitis
- difficulty lying prone
- morning sitffness >30 mins
- night pain
- pain improves with exercise, not rest
digestive-relate sxs may refer to T- to T-
T4-T6 (pain immediately after eating)
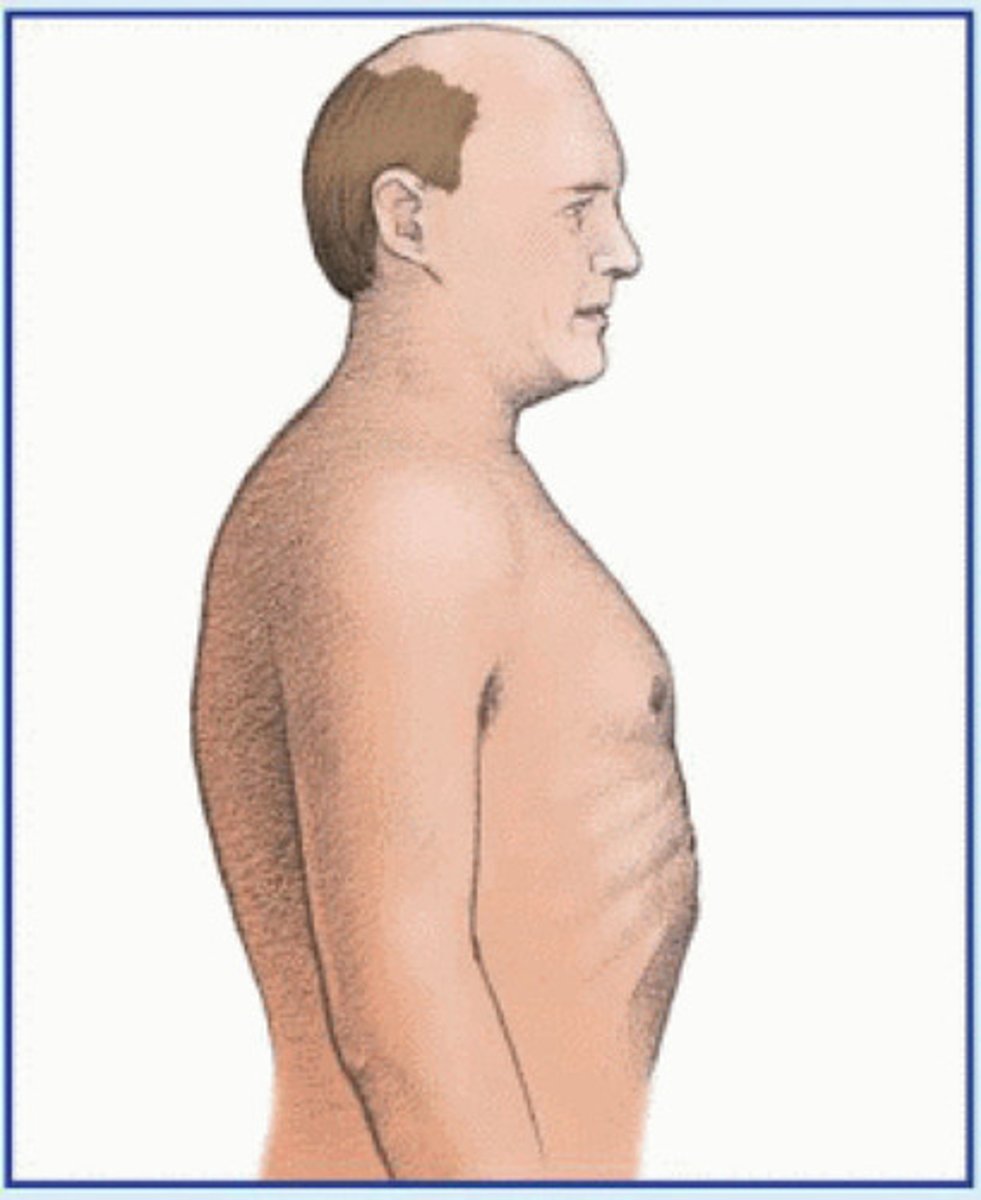
Thoracic spine observation
- flat areas --> loss of flexion
- increased curvature --> loss of extension
- scoliosis --> lateral curve
- shoulder ht --> dominant may be lower
- degree of kyphosis --> affected my lumbar lordosis or FHP
if someone has lateral curve to the R with scoliosis then theres SB to the ____ and therefore rotation to the ____
- left
- right
shingles may present with
characteristic dermatomal lesions
barrel chest
Ant/post diameter > med/lat diameter
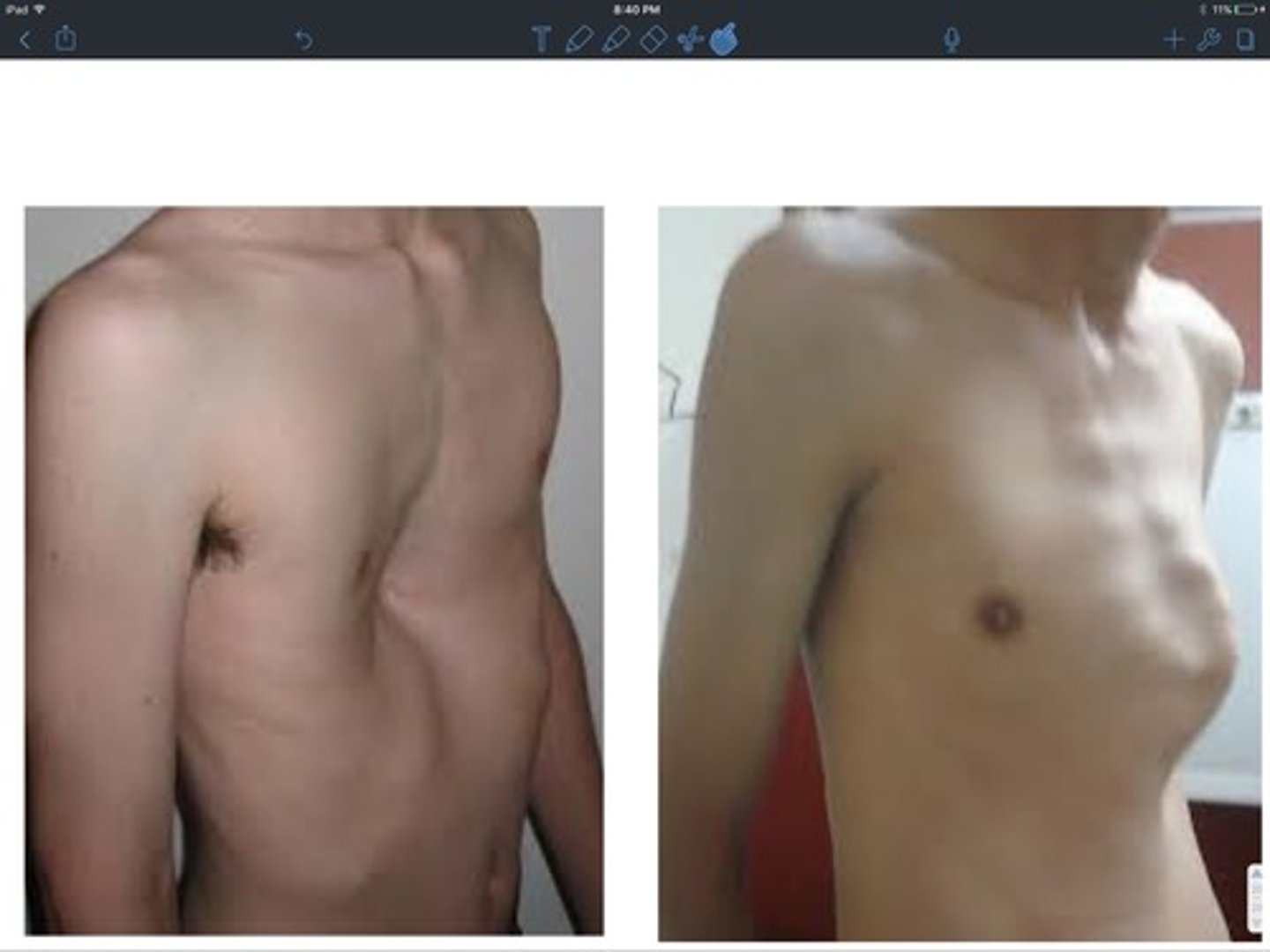
pigeon chest vs funnel chest
- pigeon: sternum and ribs protrude anterior
- funnel: project posterior
are you more likely to do an UQS or LQS for t-spine?
LQS
t-spine capsular pattern
SB = rotation > extension > flexion
muscle length tests to consider in thoracic spine
- pec major and minor
- lats
- upper trap
- levator scap
- SCM
- scalenes
breathing assessment
- anterior/posterior upper ribs
- posterior upper ribd
- inferior border of scapula
- posterior lower ribs
what MMTs may you assess if a pt has postural sxs
scapular
what MMTs may you assess if a pt does a lot of standing or repetitive lower limb activities
hip/trunk muscle control
T-spine PAIVM
- pt prone with pillow support
- anterior glide
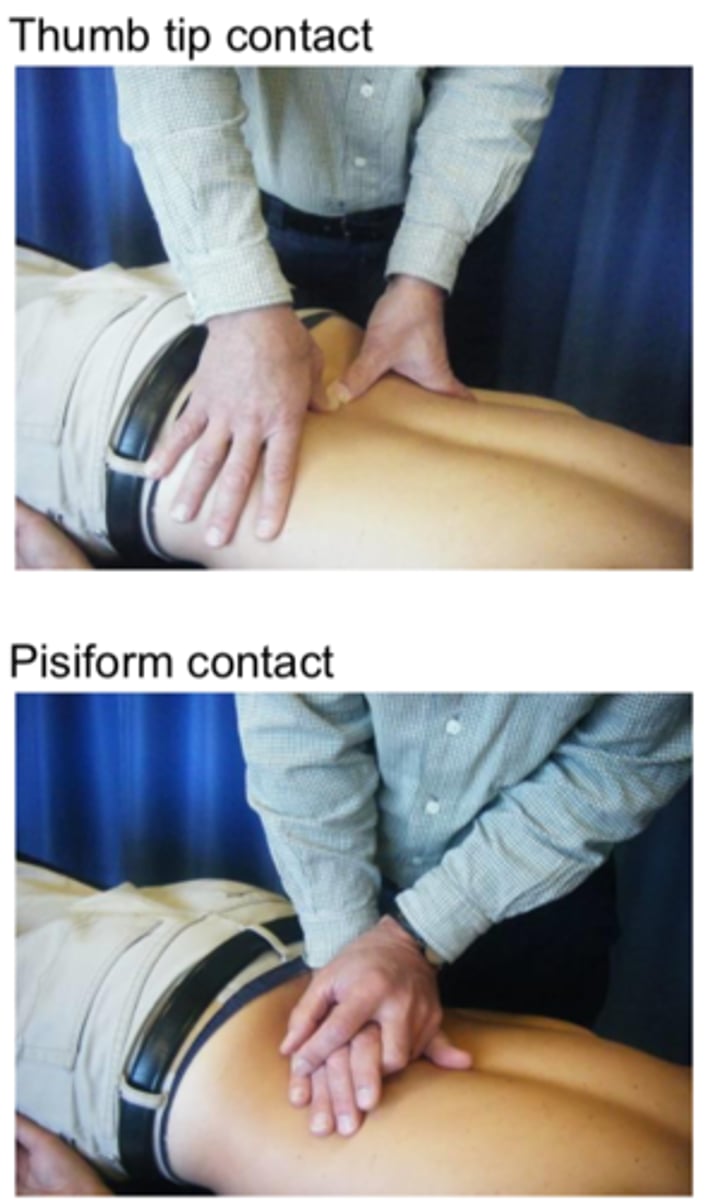
Rotation PAIVM
- fingertip contact staggered on adjacent levels
- ex: T6 TP on L, T7 TP on R (right rotation)
- apply anterior glide
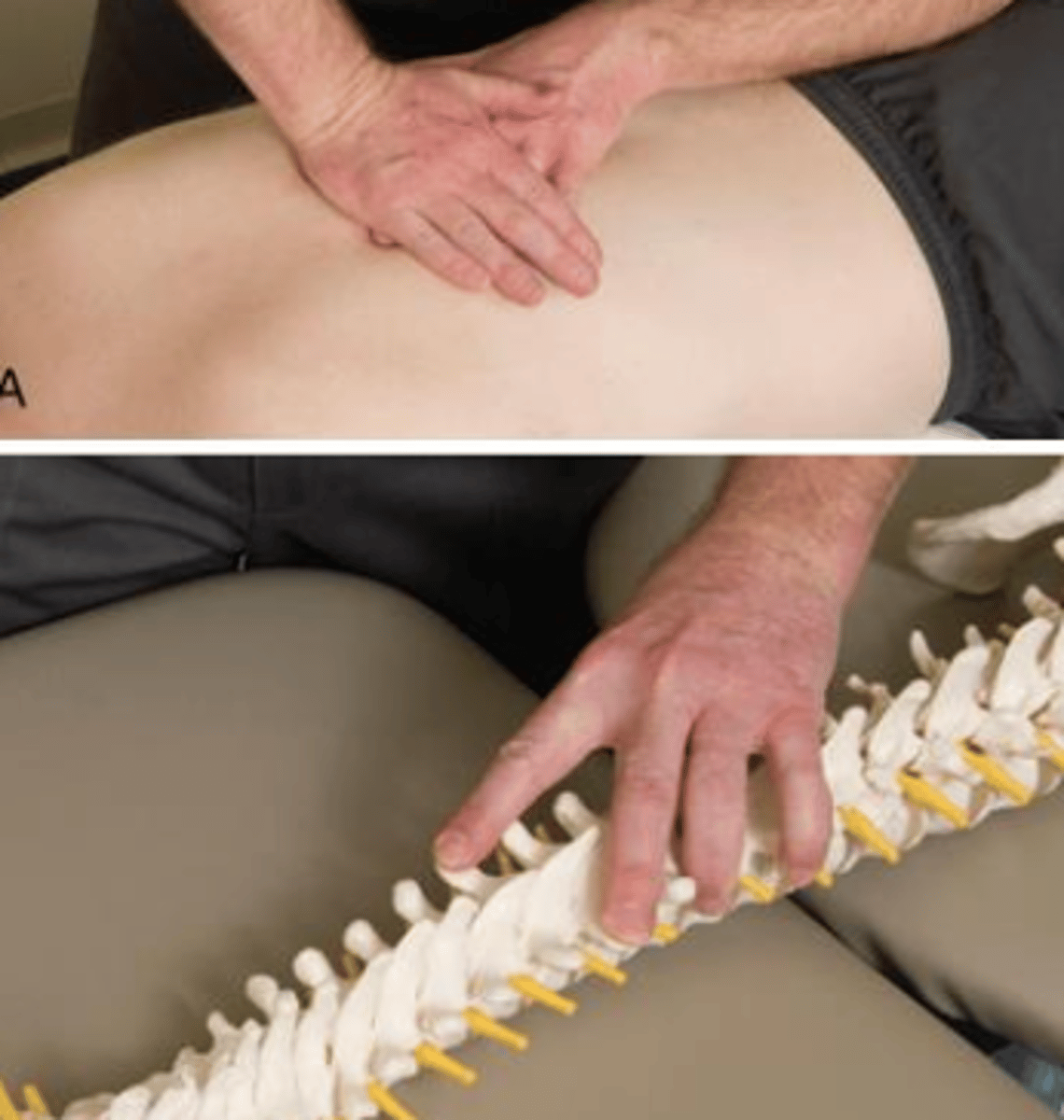
rib spring test
- pt prone with pillow support
- apply anterior force to rib while blocking at SP on same side
- emphasize inhalation with inferior glide
- emphasize exhalation with superior glide
PAIVM in flexion
- pt sitting with arms folded across chest
- PT rests hand on contralateral shoulder
- push SP anterosuperior
PAIVM in extension
- pt hands interlocked behind the neck
- PT brings pt in extension
- push SP anteroinferior
PAIVM in rotation
push on side of SP laterally
- rotate R, push SP L
thoracic scoop mob
- improves general thoracic extension mobility for upper thoracic
- PT in stride stance and arms threaded through pts crossed arms
- apply anterior force through finger contacts while using patient's arms as counterpressure into extension