AP Biology ALL UNITS AP Exam Review
1/477
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
478 Terms
Carbohydrate Examples
glucose, fructose, sucrose, starch, glycogen, cellulose, monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
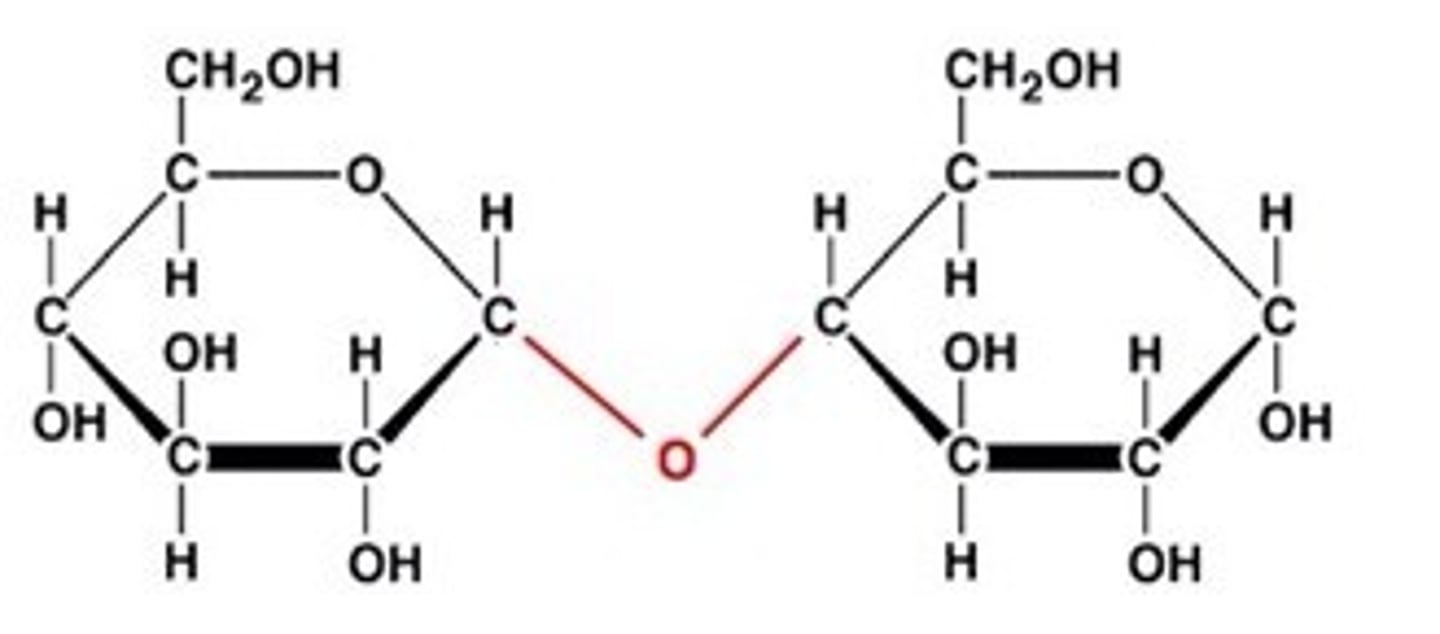
Disaccharide
A double sugar, consisting of two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis.
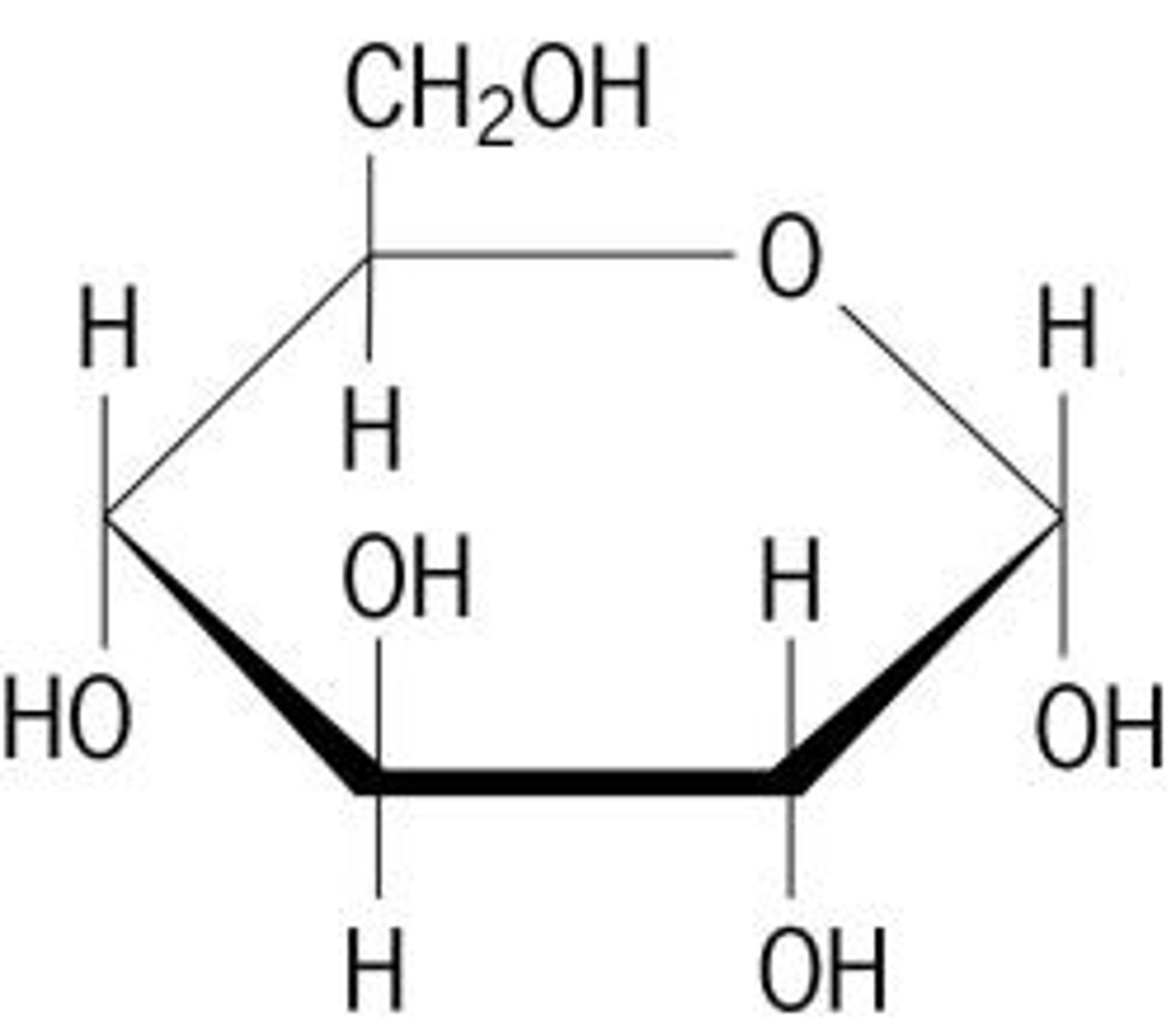
Monosaccharide
A single sugar molecule such as glucose or fructose, the simplest type of sugar.
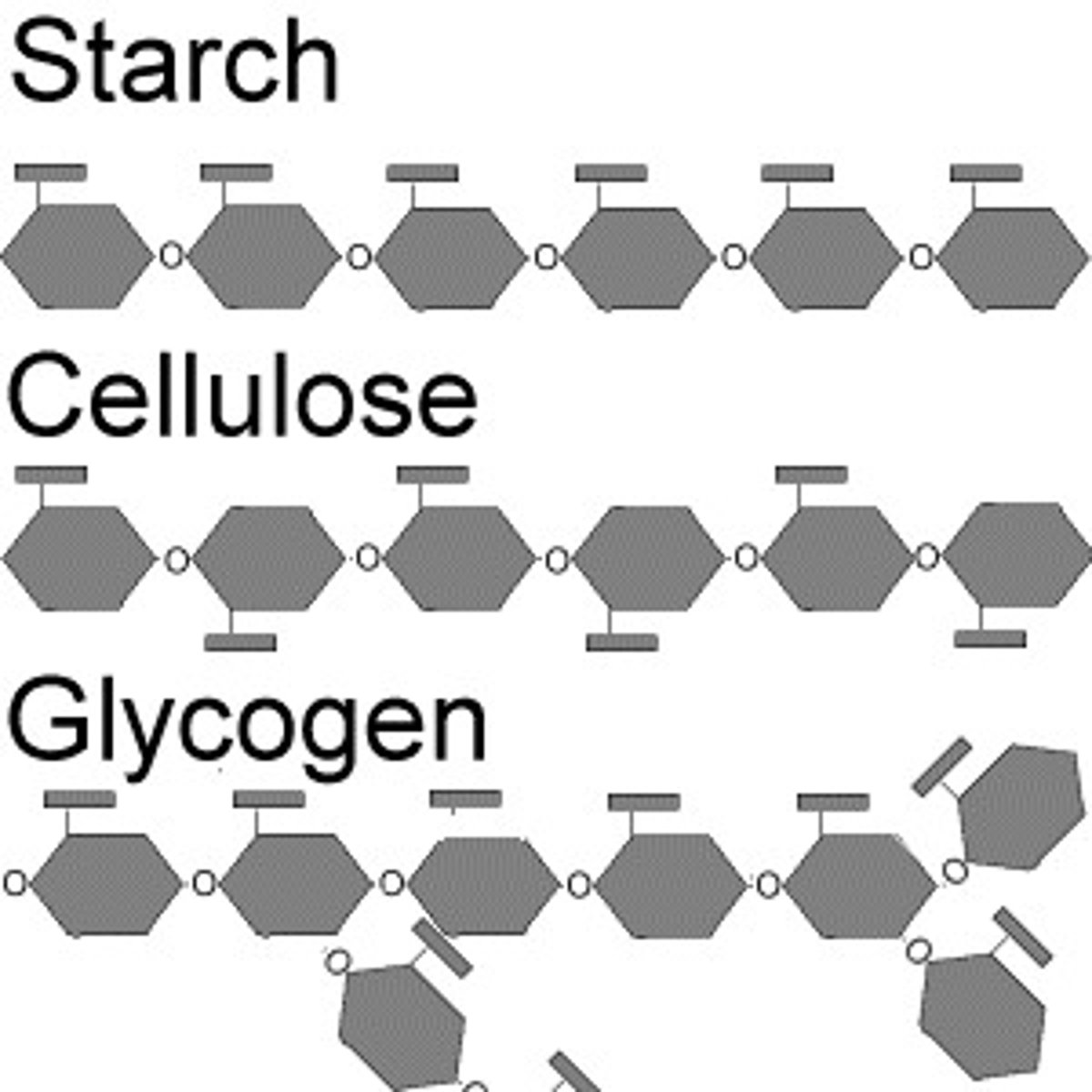
Polysaccharide
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides
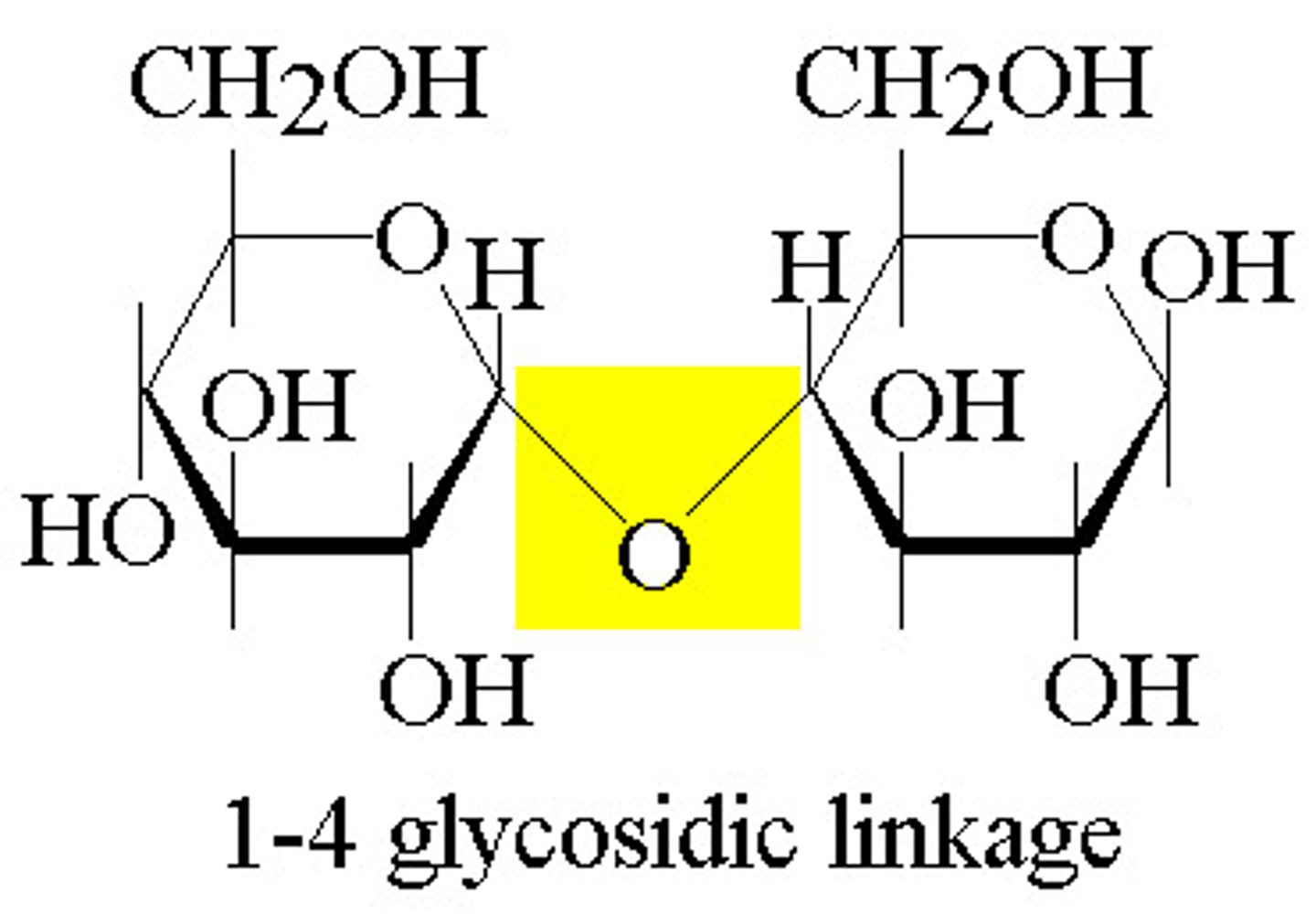
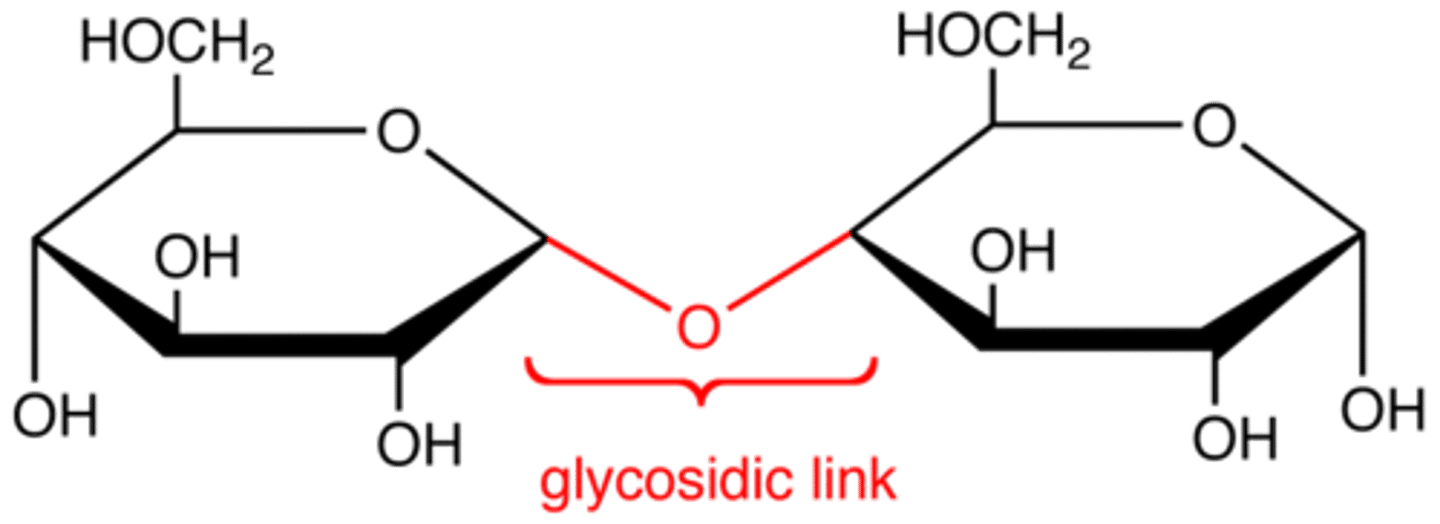
Glycosidic Linkage
A covalent bond formed between two monosaccharides by a dehydration reaction.
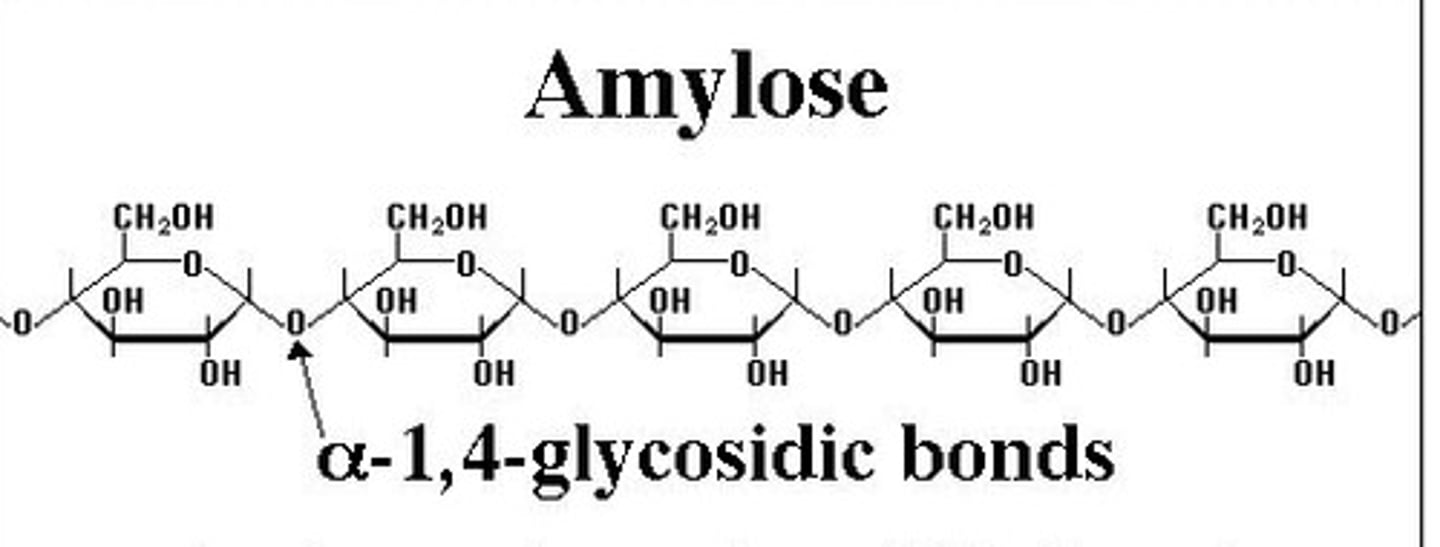
Starch
A storage polysaccharide in plants consisting entirely of glucose.
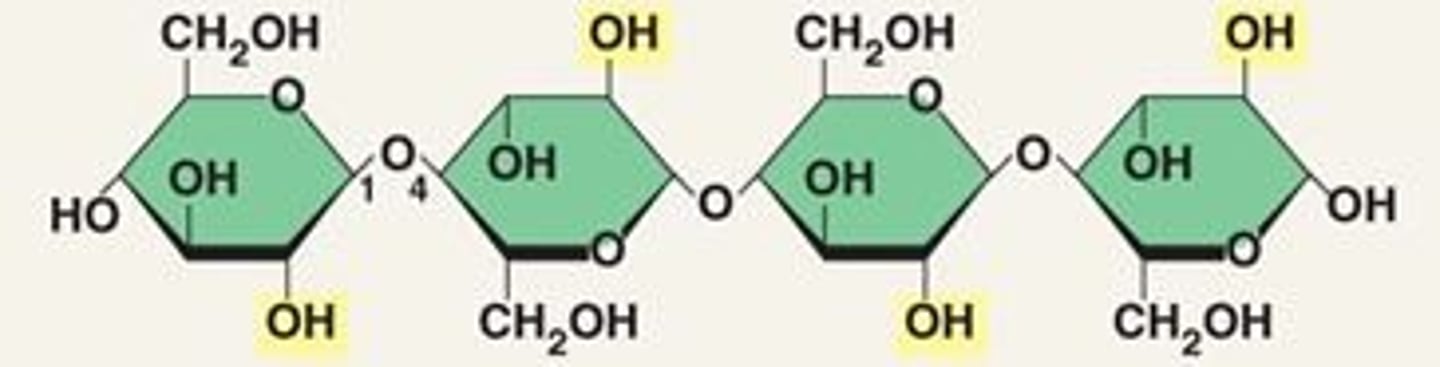
Cellulose
A substance (made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of many organisms
Lipid Examples
fatty acids, fats, saturated fats, unsaturated fats, steroids, phospholipids, cholesterol, triglycerides
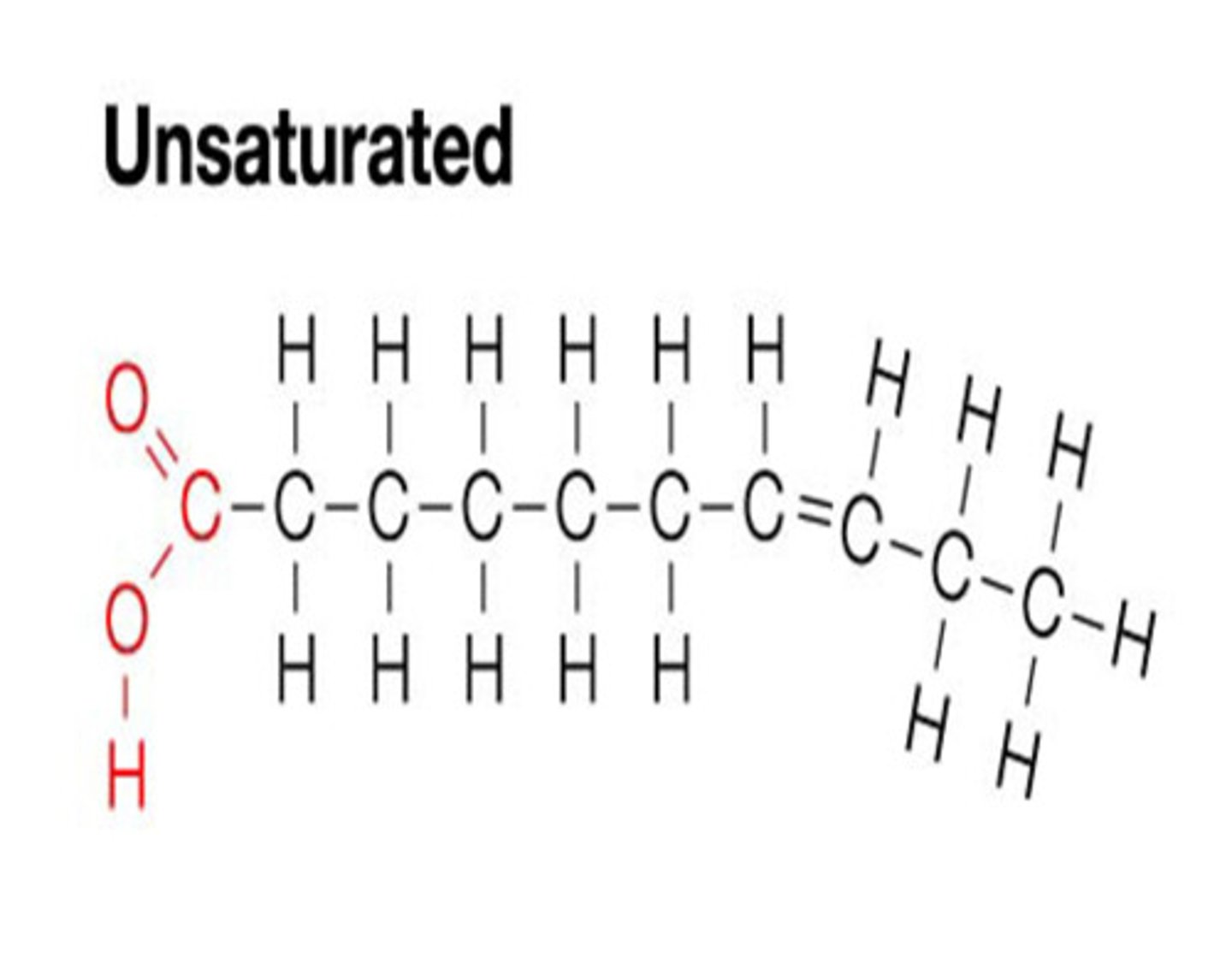
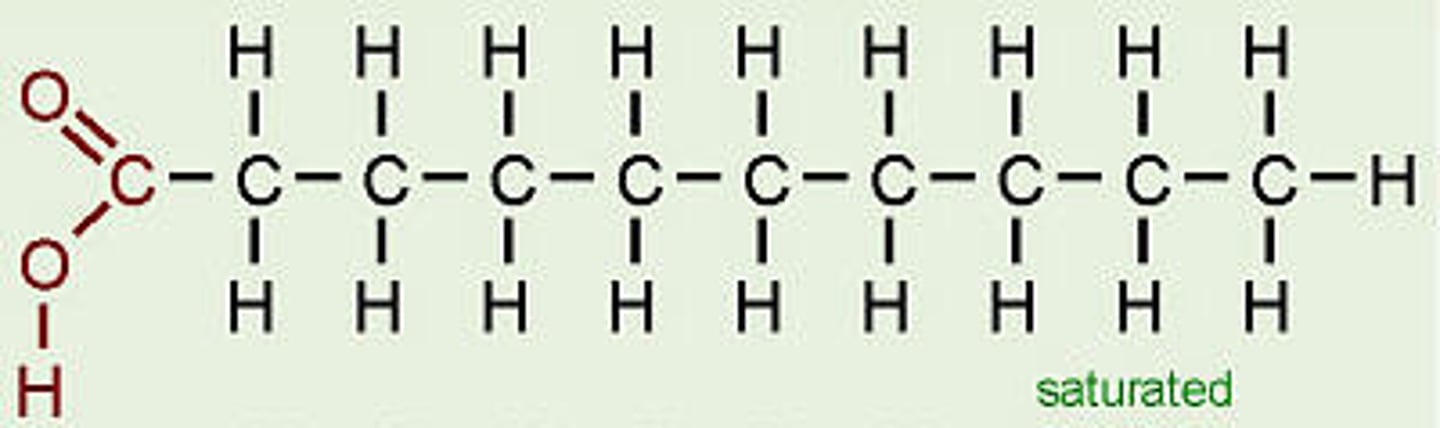
Unsaturated Fat
A lipid made from fatty acids that have at least one double bond between carbon atoms.
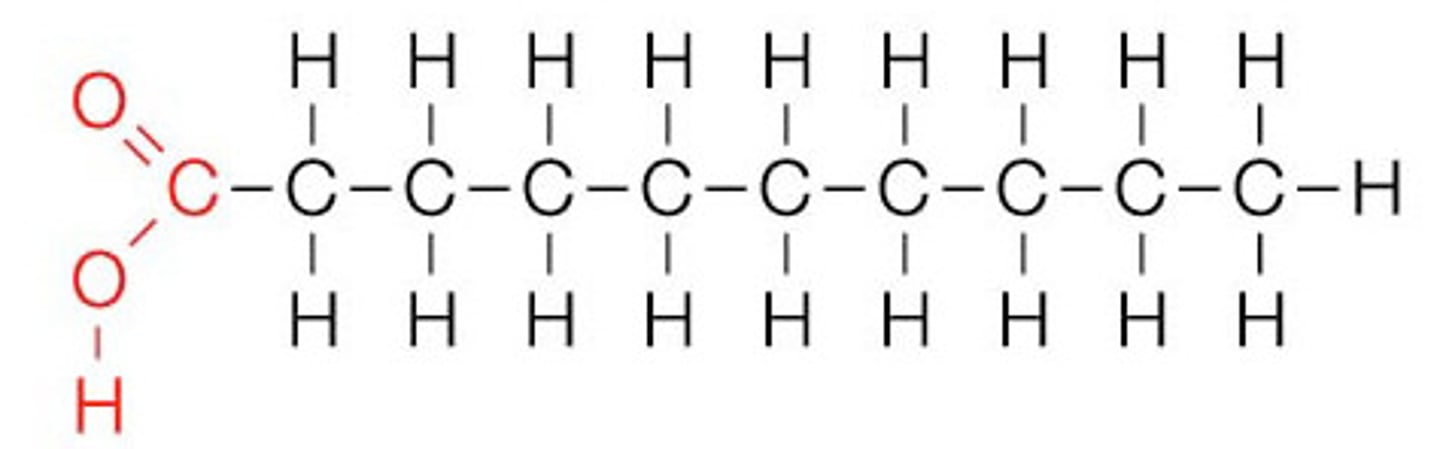
Saturated Fat
A lipid made from fatty acids that have no double bonds between carbon atoms
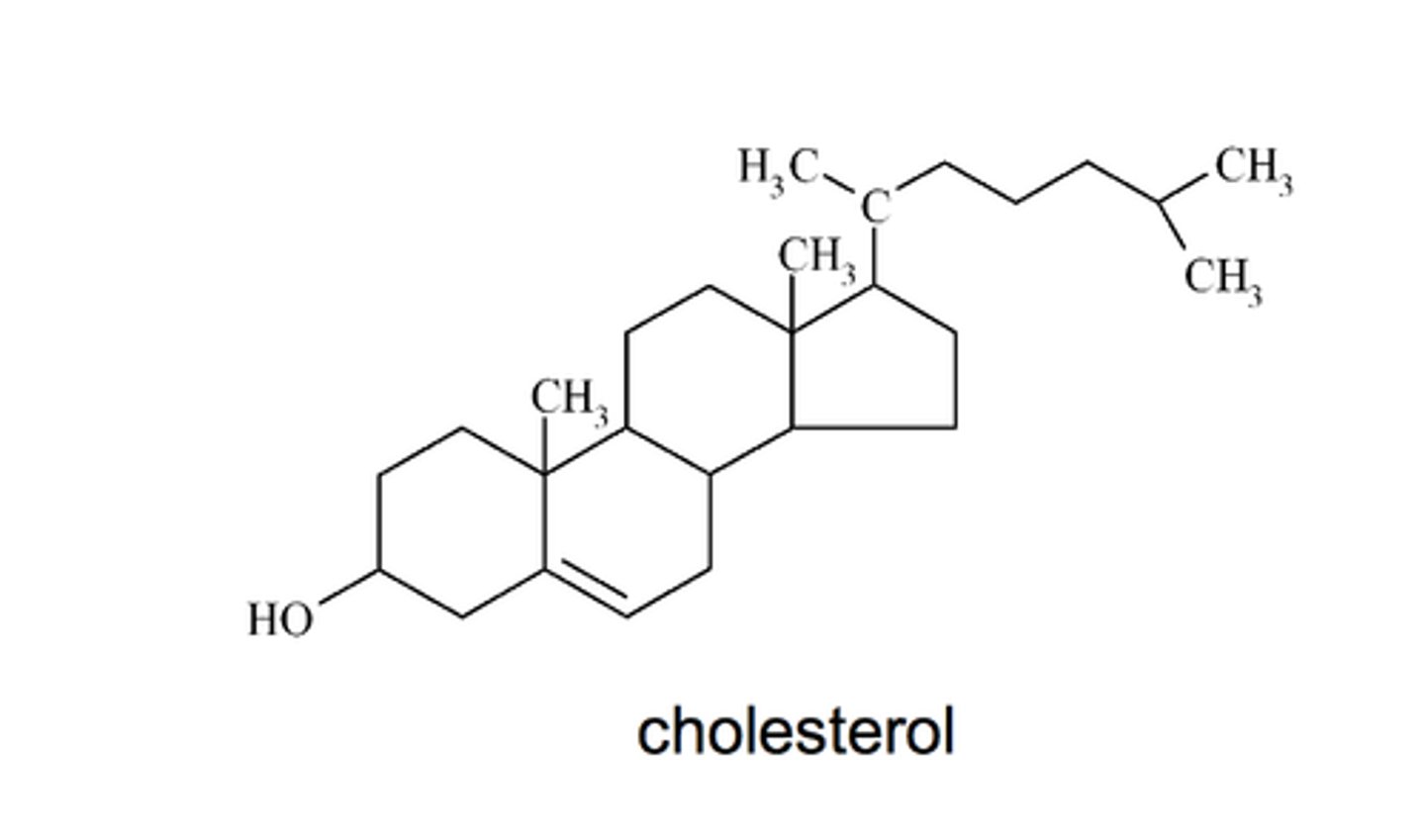
Steroid
lipid molecule with four fused carbon rings
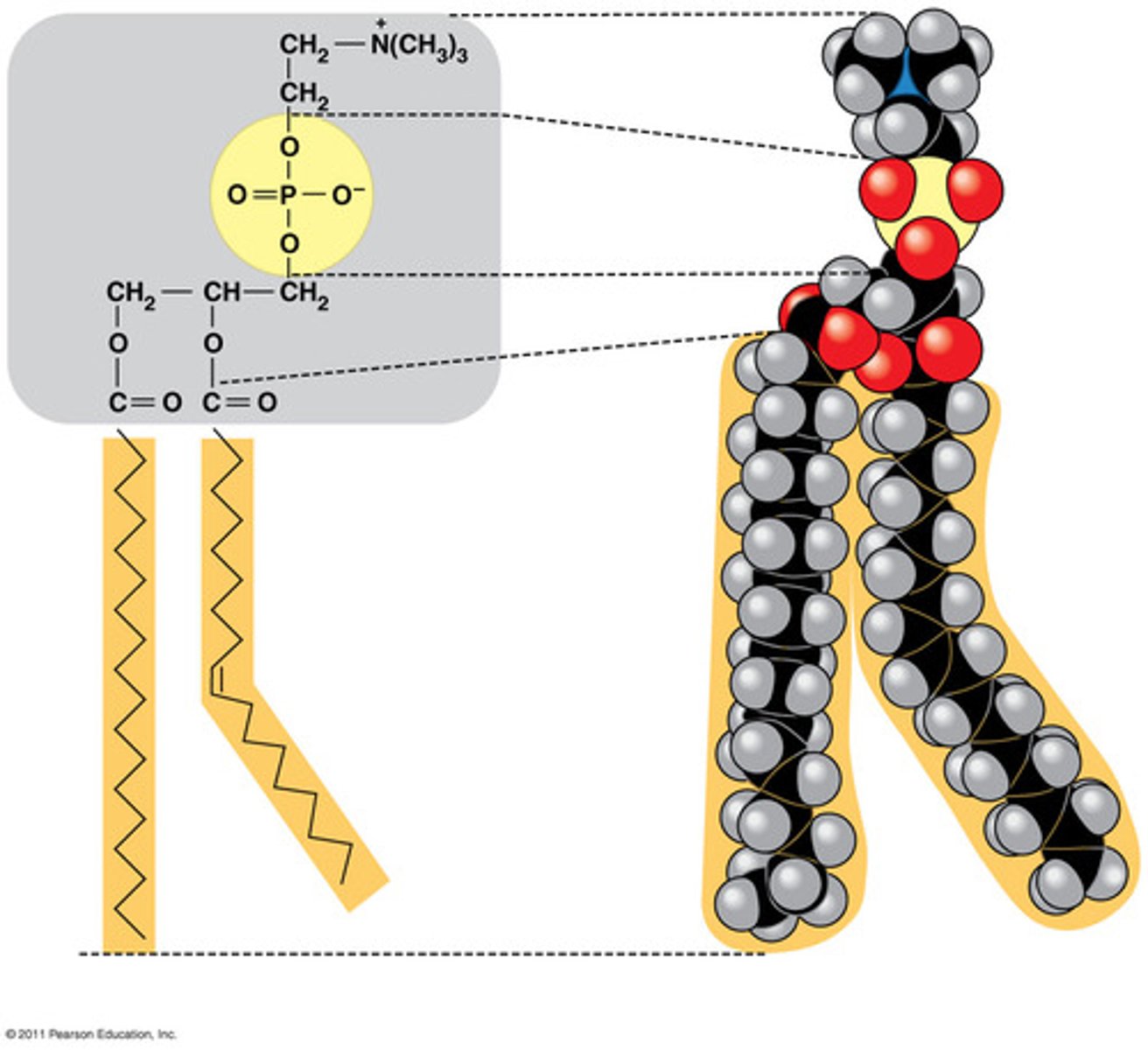
Phospholipid
a lipid that contains phosphorus and that is a structural component in cell membranes
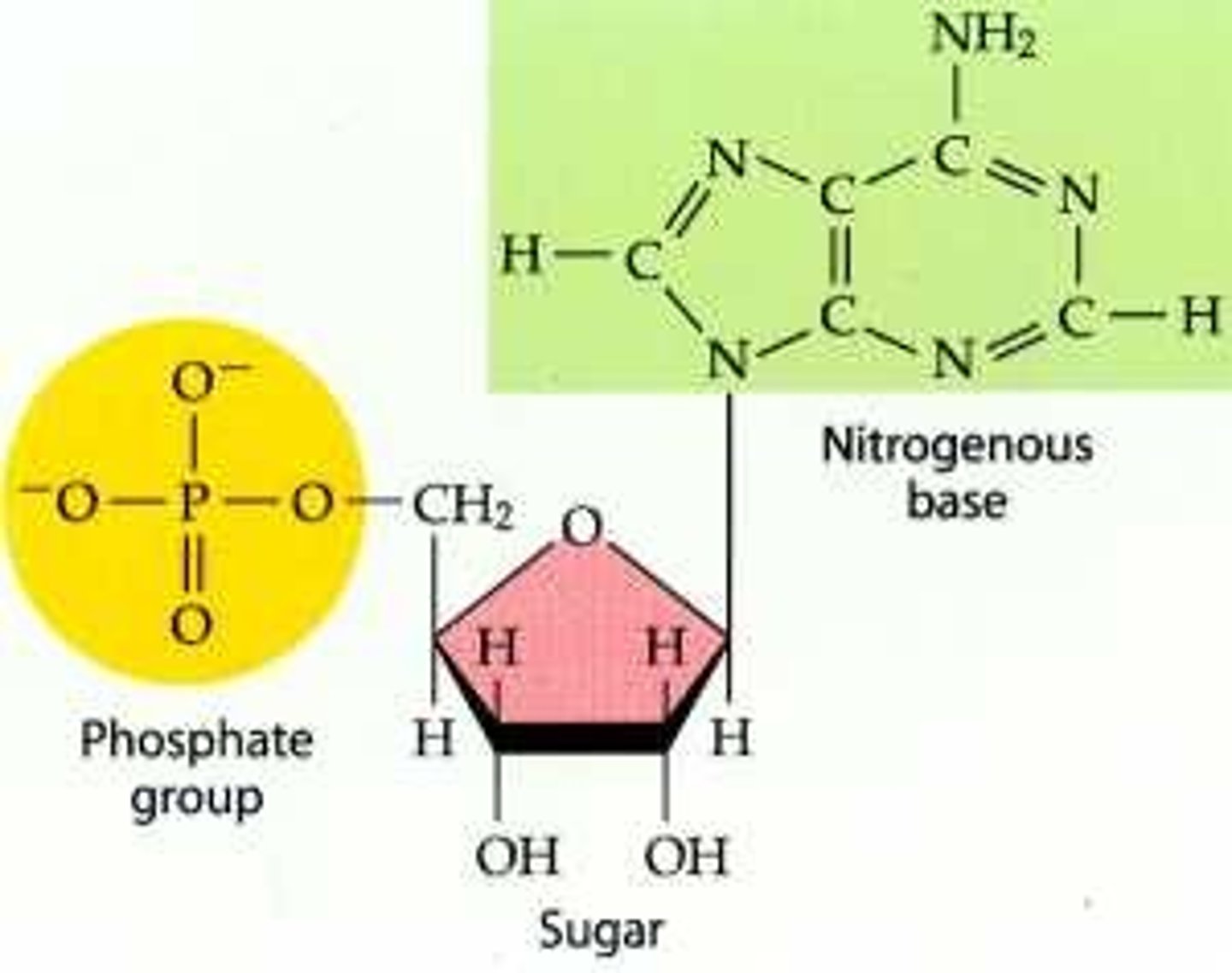
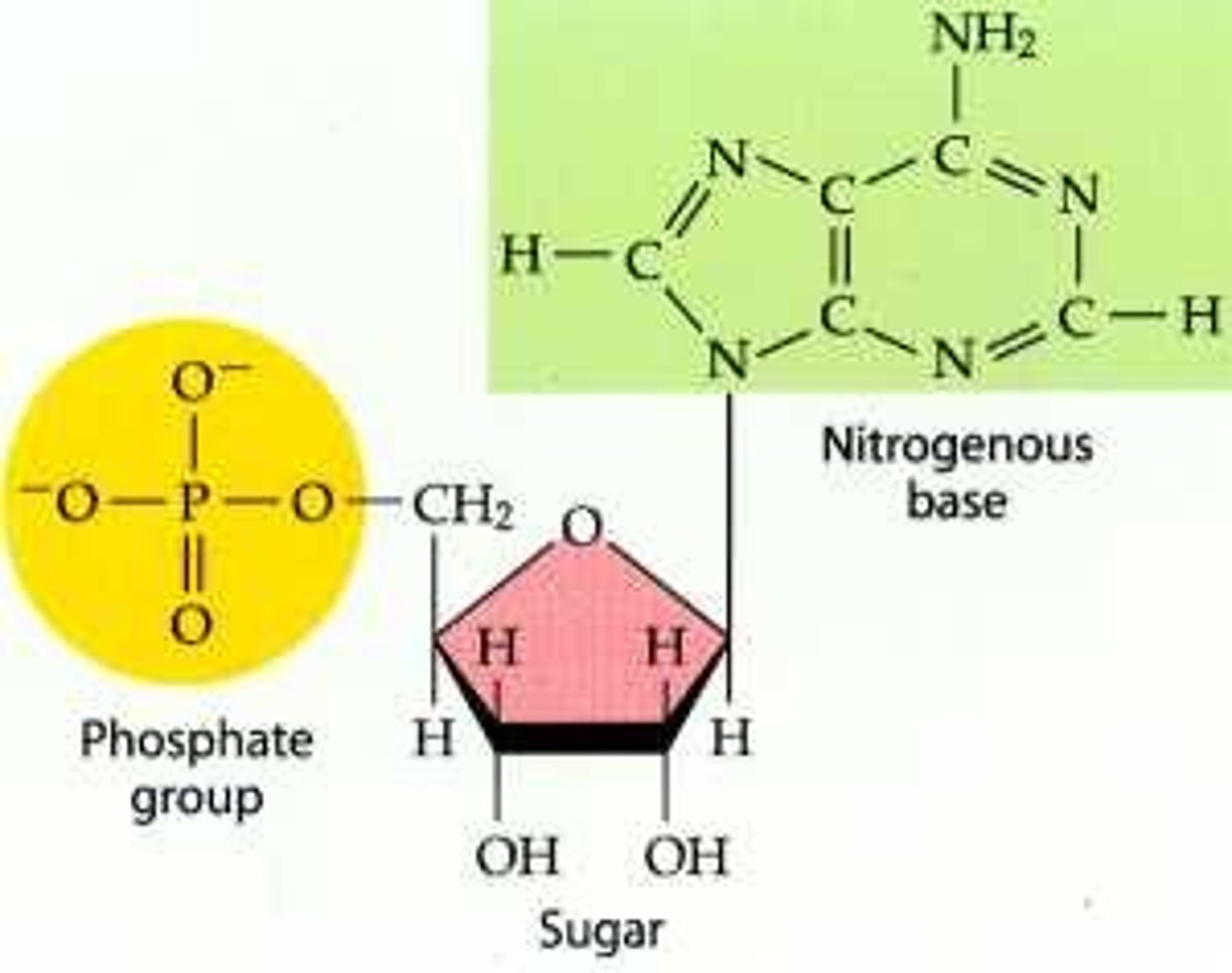
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
Nucleic Acid Examples
DNA, RNA, (ATP and ADP are modified nucleic acids)
Protein Examples
amino acids, primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary structures, collagen, hemoglobin, enzymes
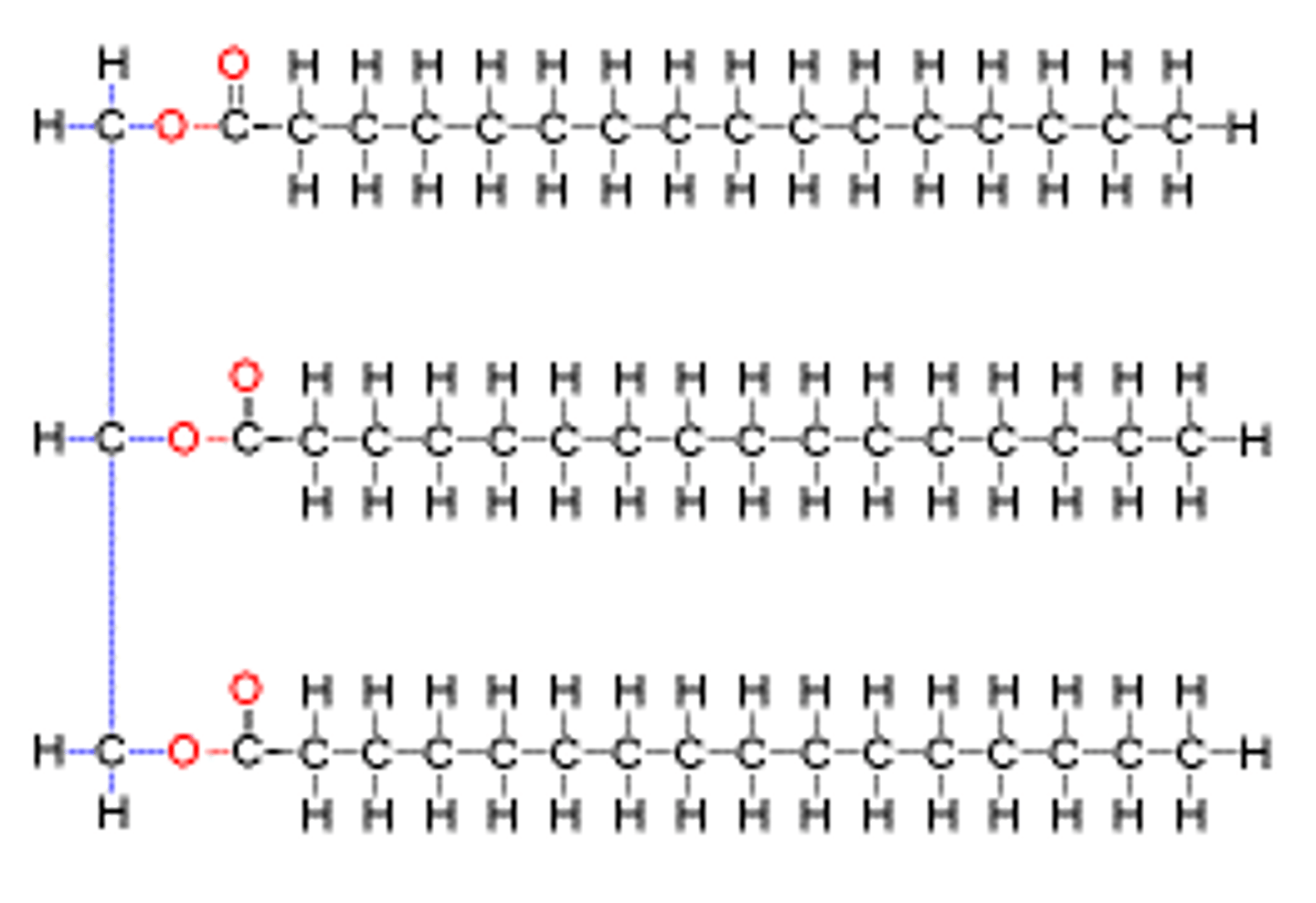
Triglyceride
a lipid made of three fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule
Amino Acid Examples
glutamine, proline, cysteine, lycine, ...
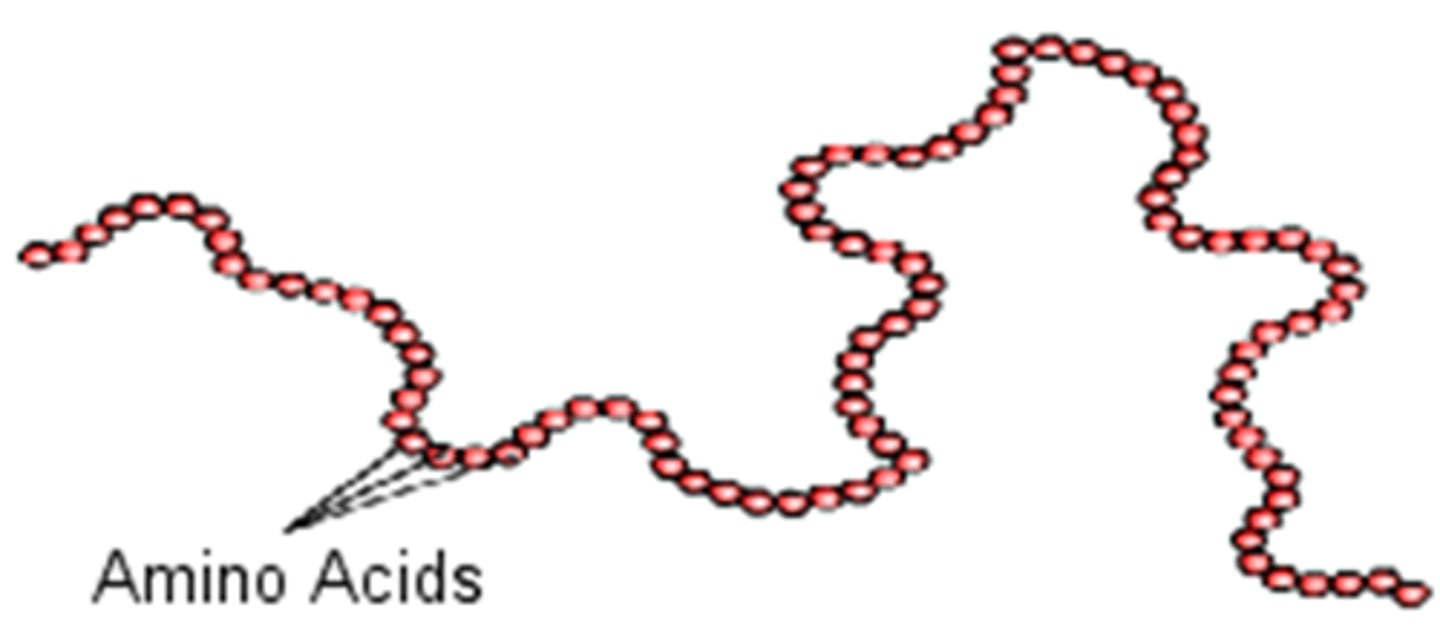
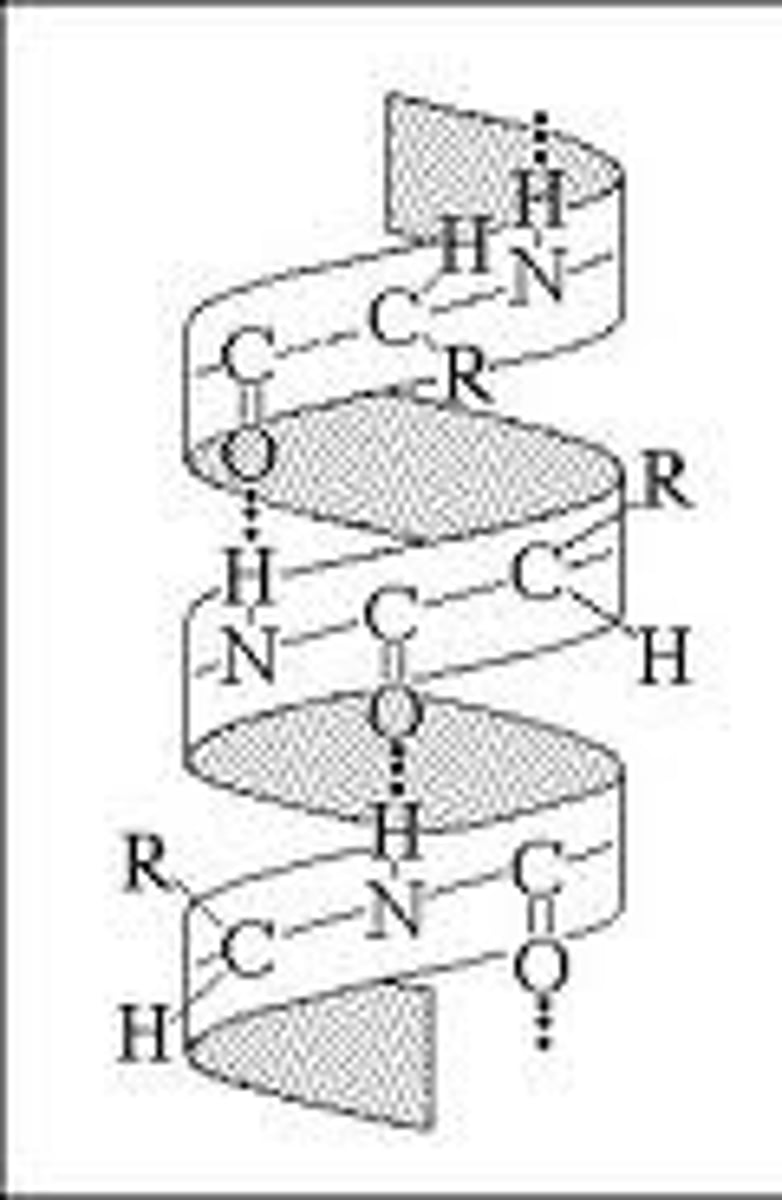
Primary Structure of a Protein
sequence of amino acids

Secondary Structure of a Protein
protein structure is formed by folding and twisting of amino acid chain
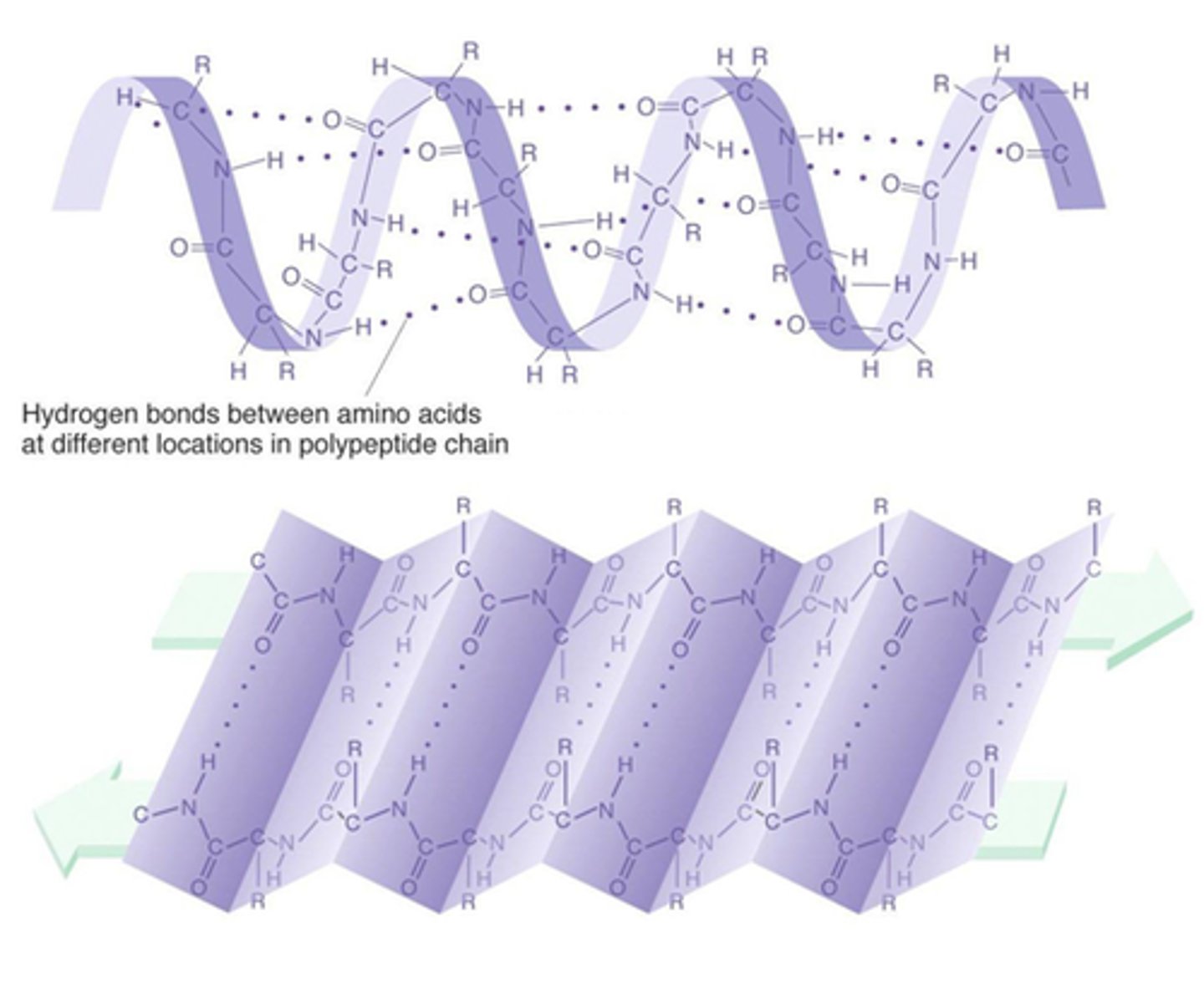
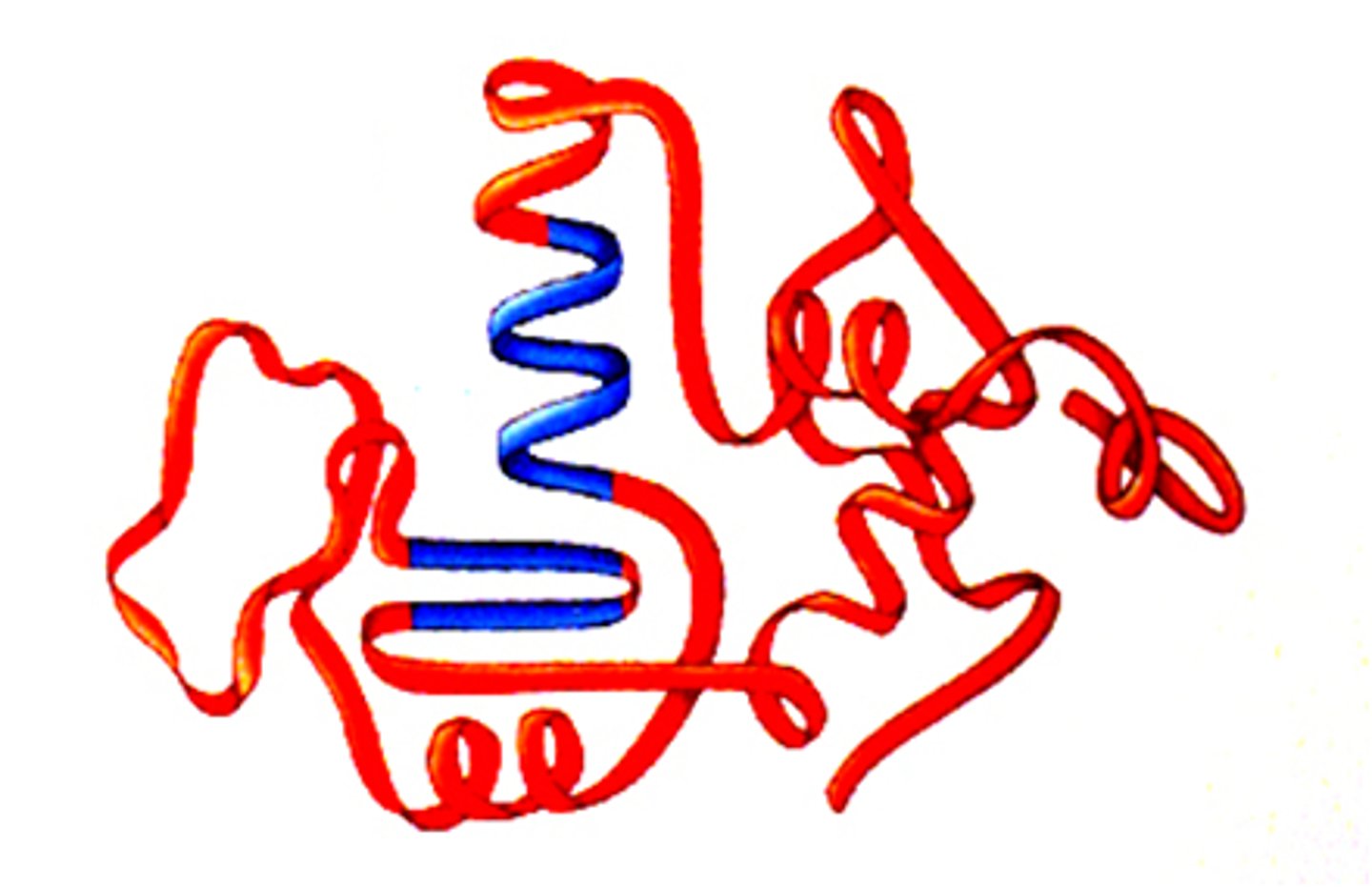
Tertiary Structure of a Protein
protein structure is formed when the twists and folds of the secondary structure fold again to from a larger 3D structure
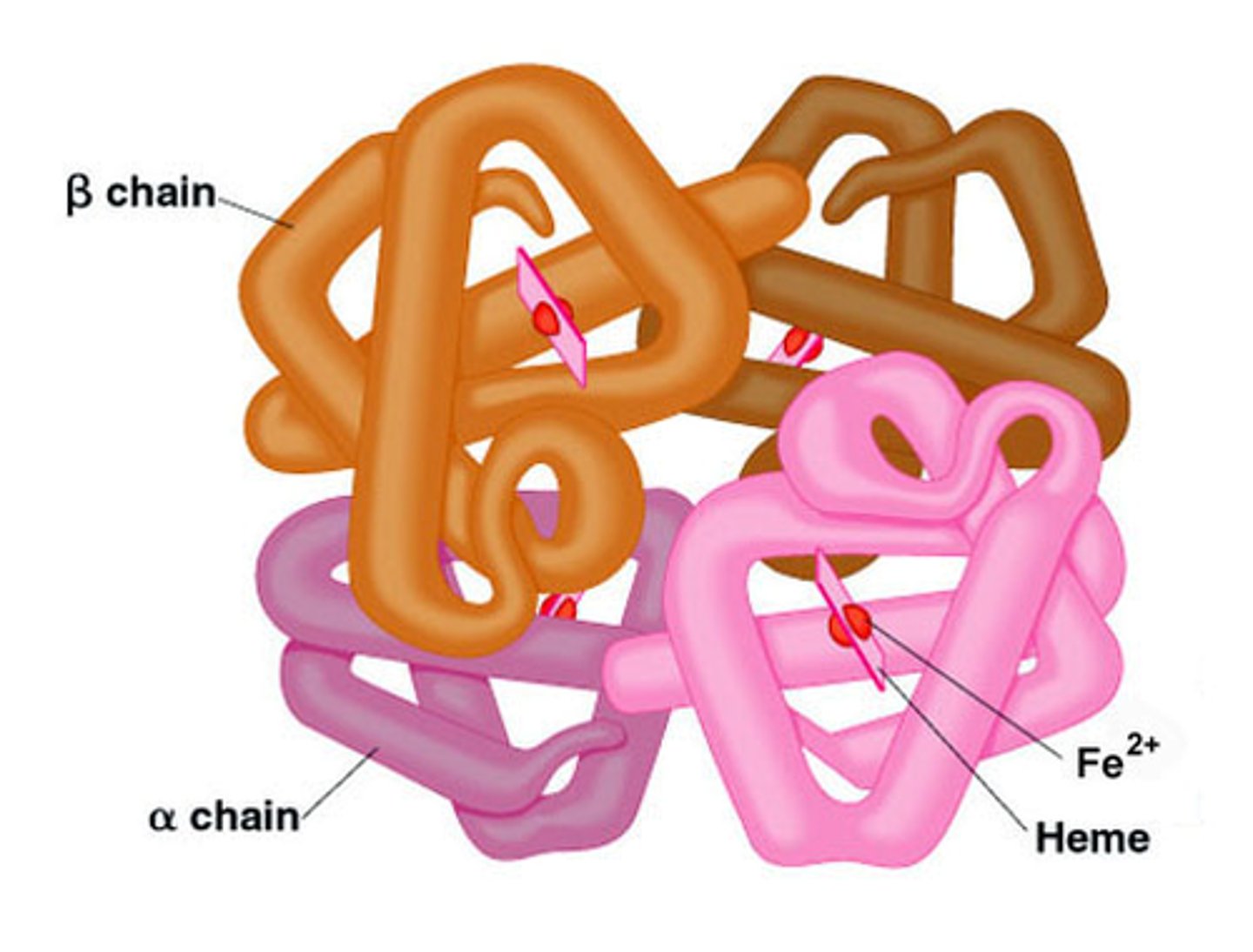
Quaternary Structure of a Protein
protein structure is a protein consisting of more than one folded amino acid chain
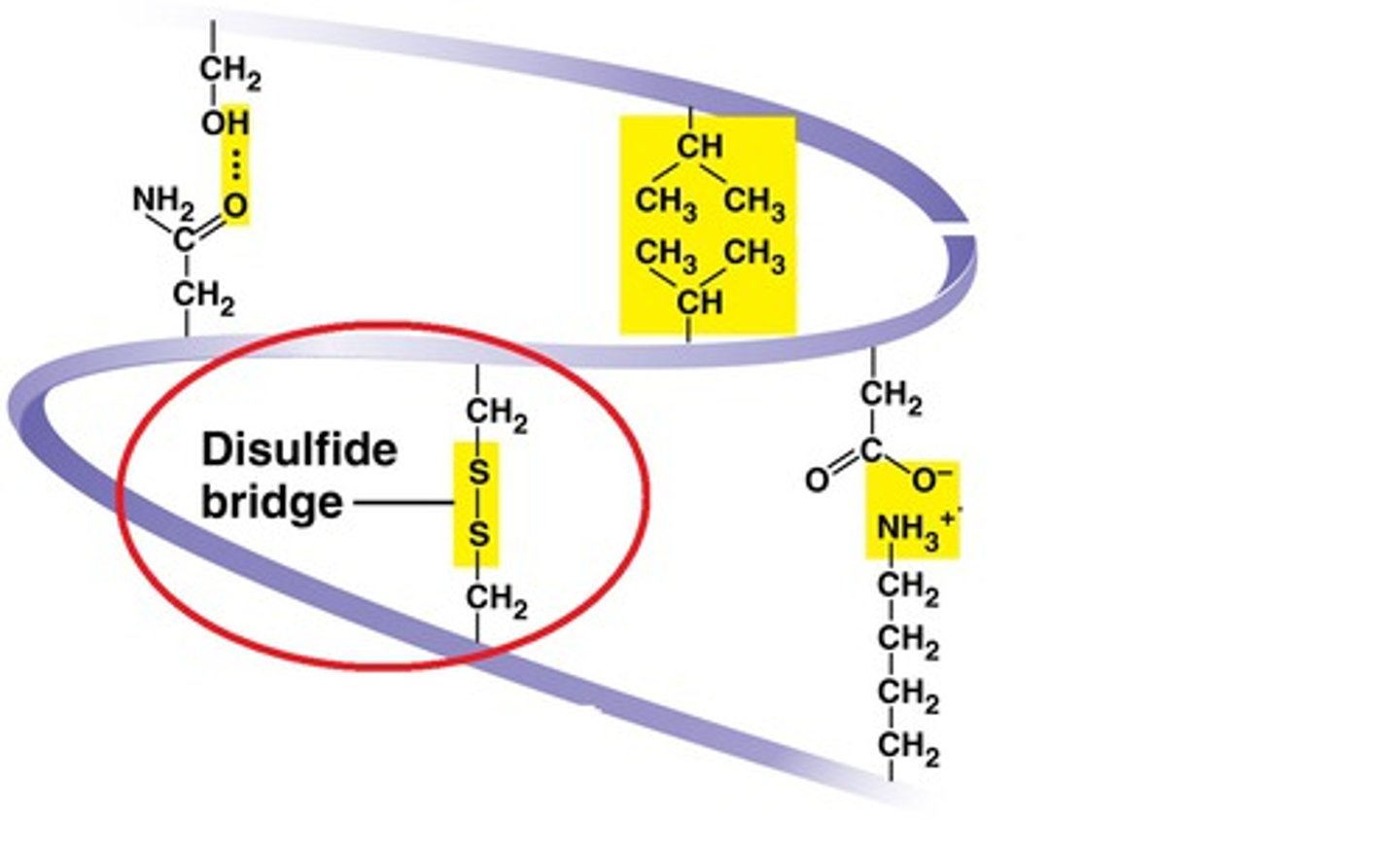
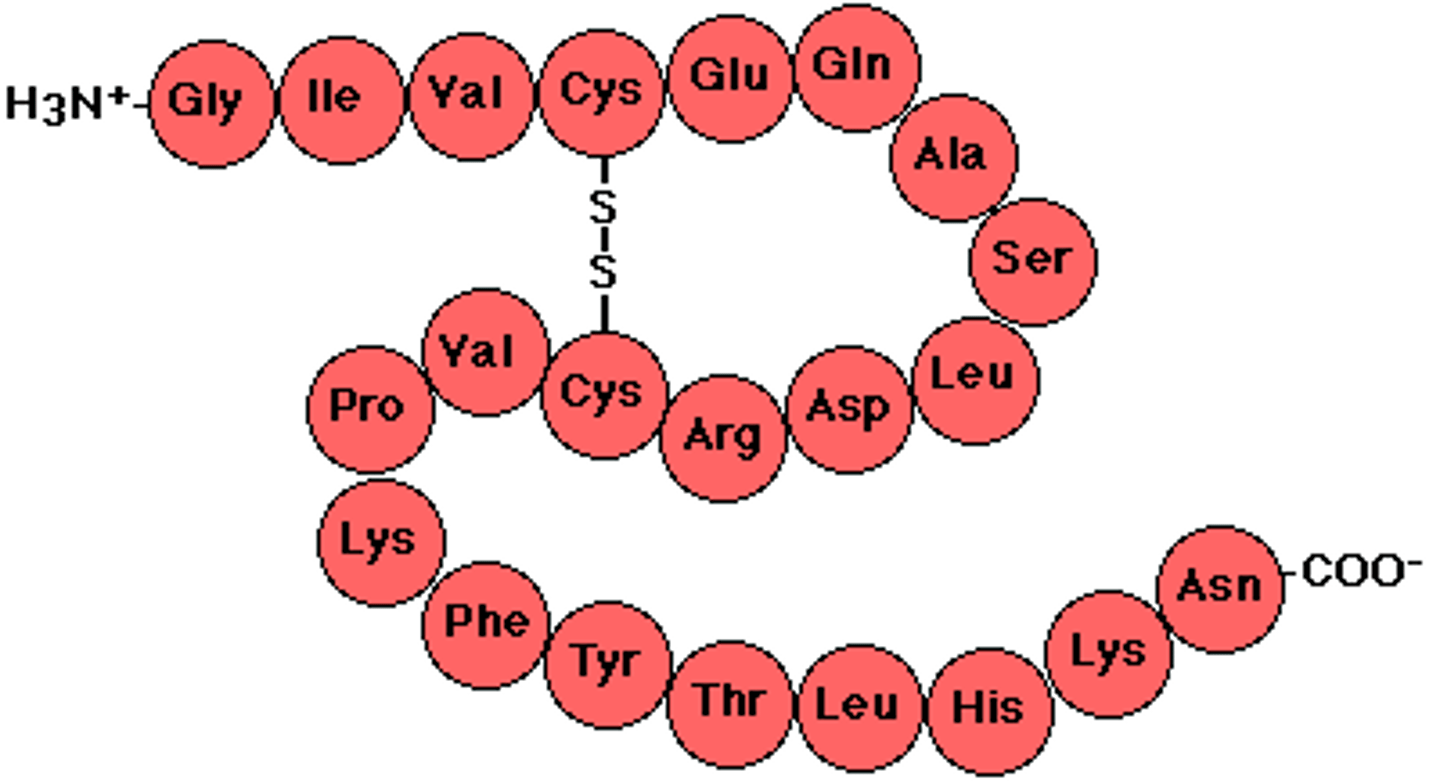
Disulfide Bridge
The covalent bond between two sulfur atoms (-S—S-) linking two molecules or remote parts of the same molecule.
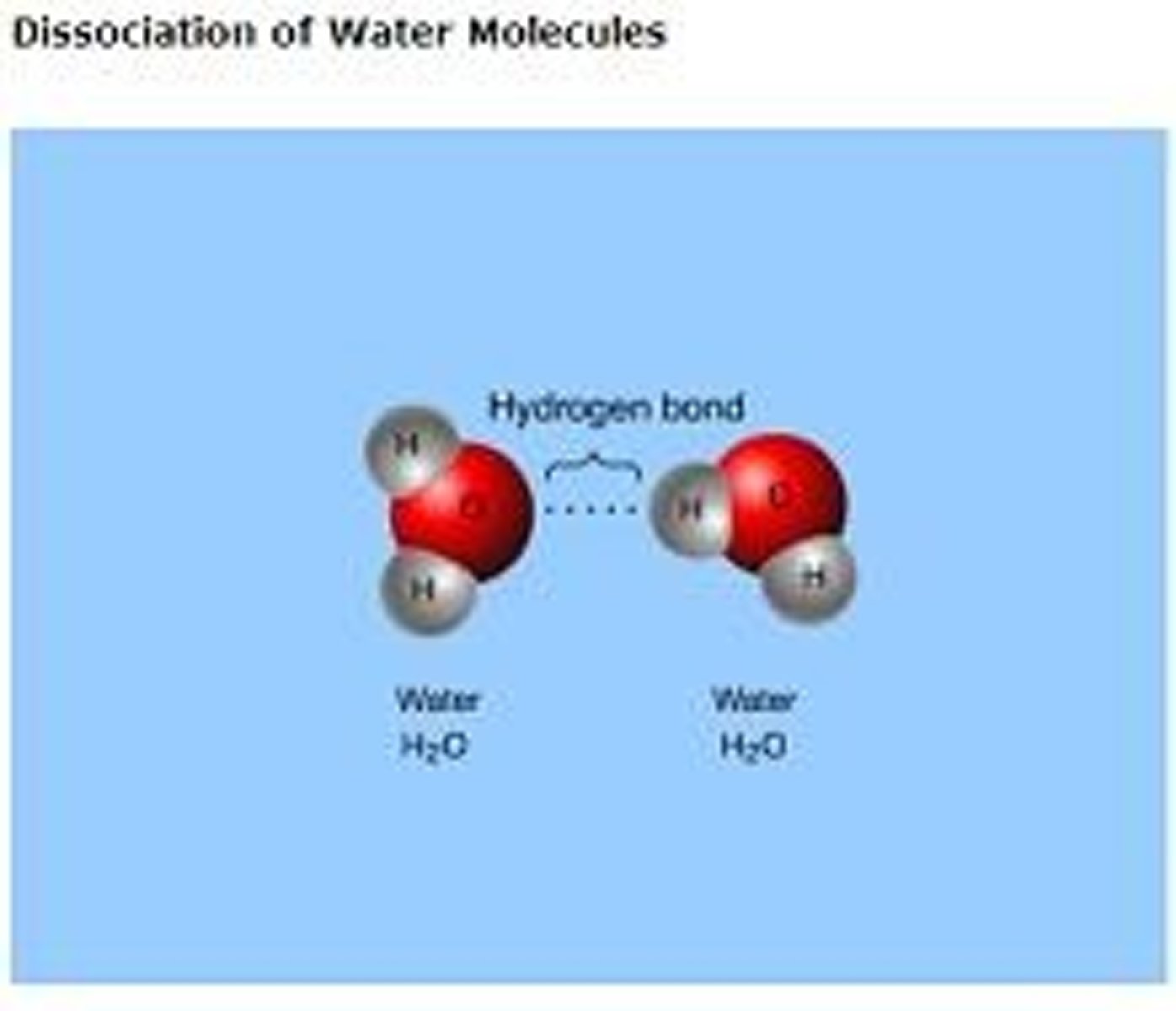
Hydrogen Bonds
Very weak bonds; occurs when a hydrogen atom in one molecule is attracted to the electrostatic atom in another molecule
nucleic acid
kind of macromolecule that stores, transfers, and expresses genetic information
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Nitrogen (CHOPN)
elements that make up a nucleic acid
nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base
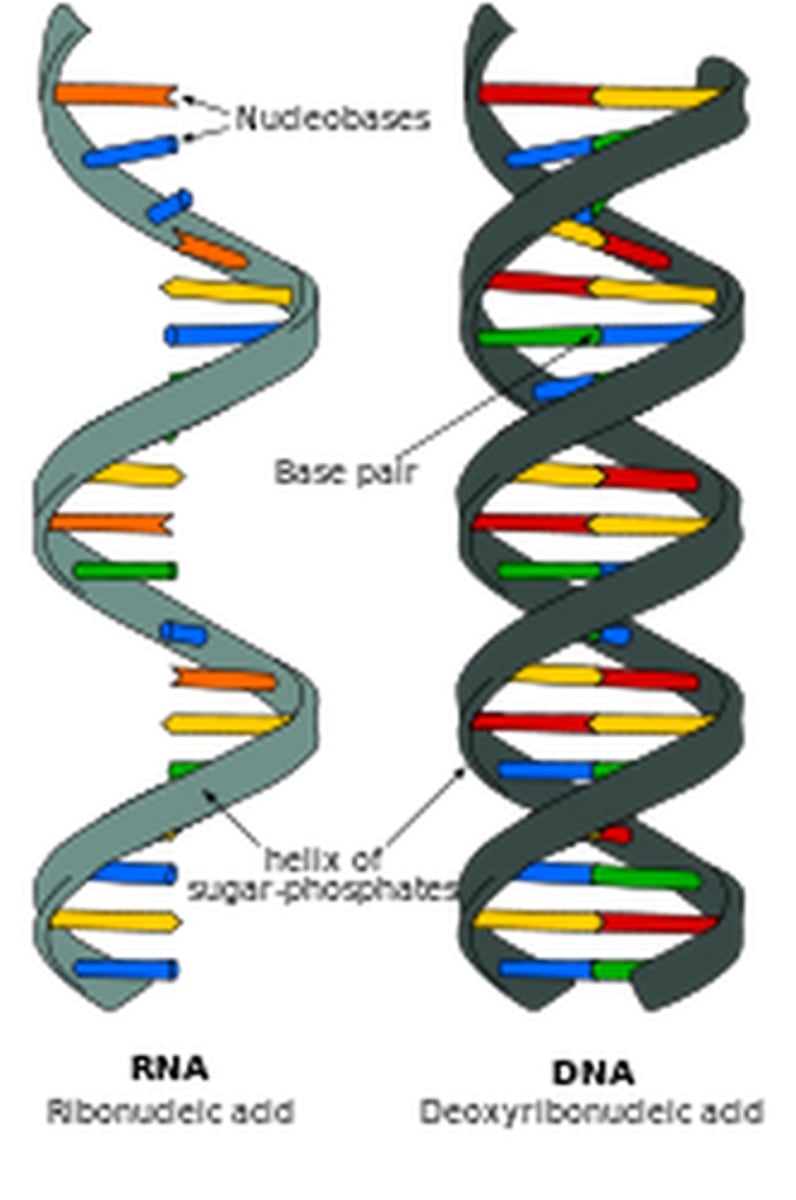
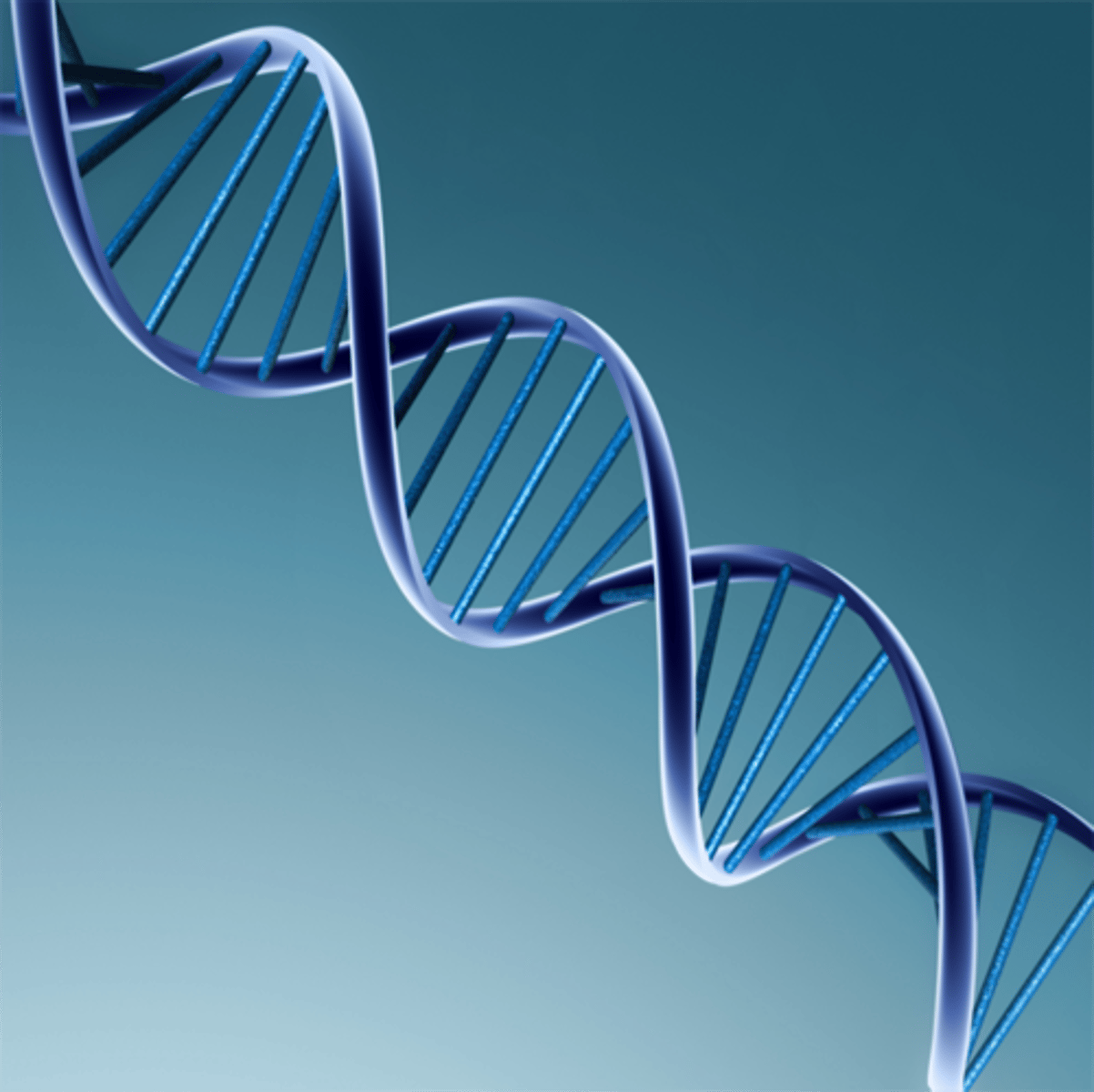
double helix
term used to describe the arrangement of a DNA strand

RNA
ribonucleic acid; a polymer of nucleotides that transfers genetic information
how RNA differs from DNA
the sugar in RNA is ribose; Uracil bonds with Adenine; RNA is single-stranded
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen (CHON)
elements that make up a protein
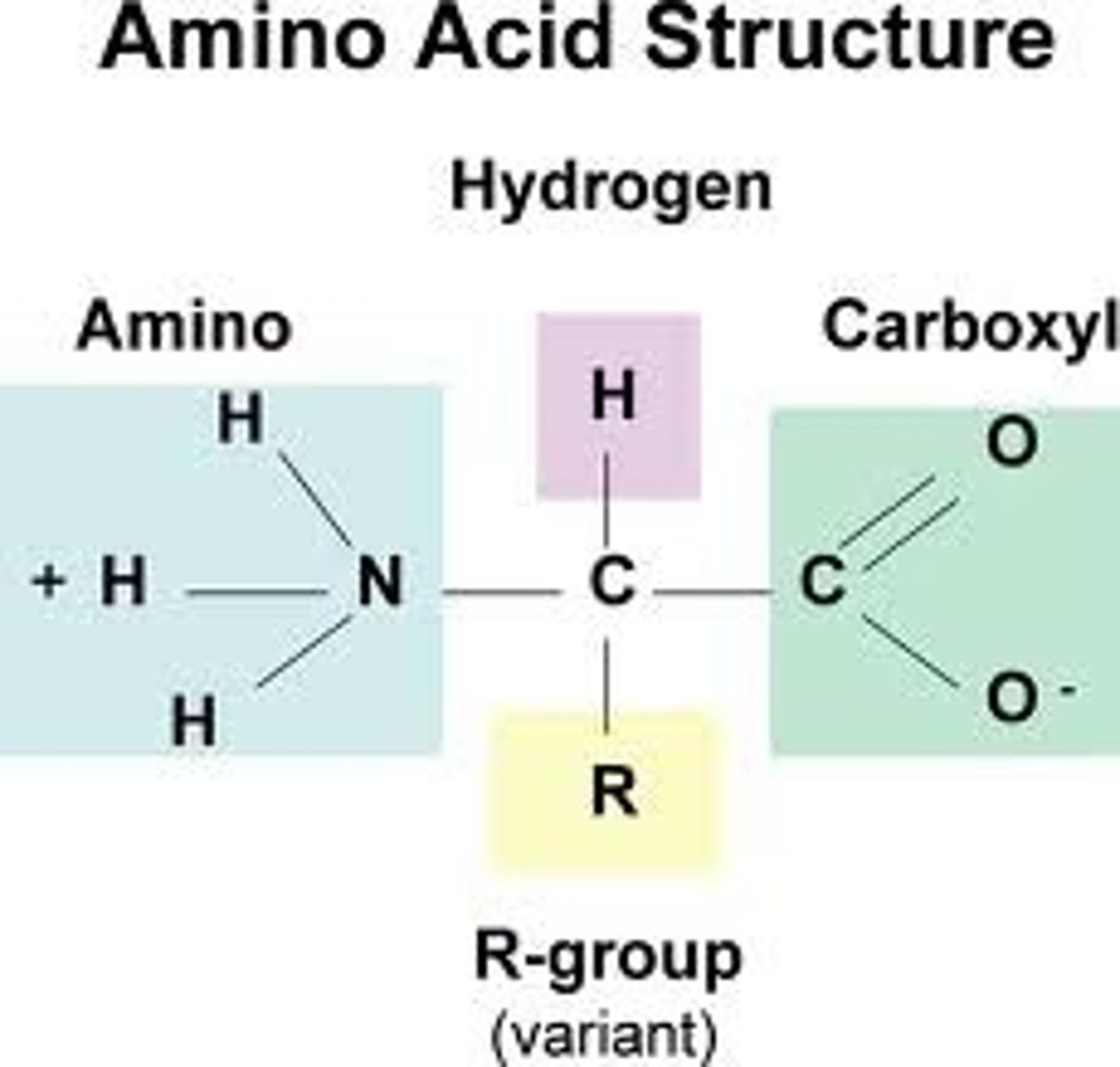
amino acid
building block (monomer) of proteins, composed of an amino group and a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and an R-group
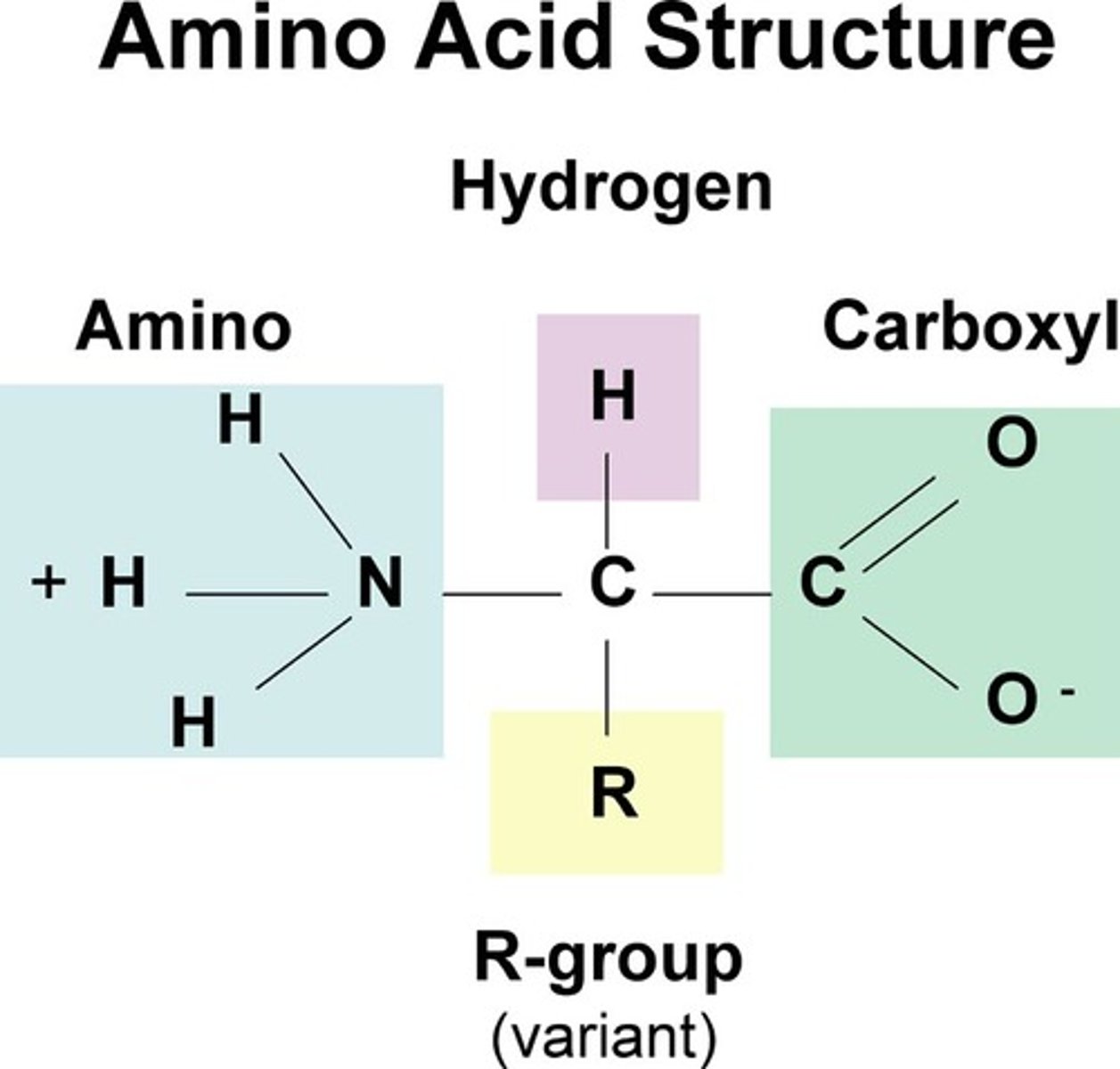
structure of an amino acid
a carboxyl group, an amino group, a central Carbon, a Hydrogen, and an R-group
peptide bond
covalent bond formed between amino acids
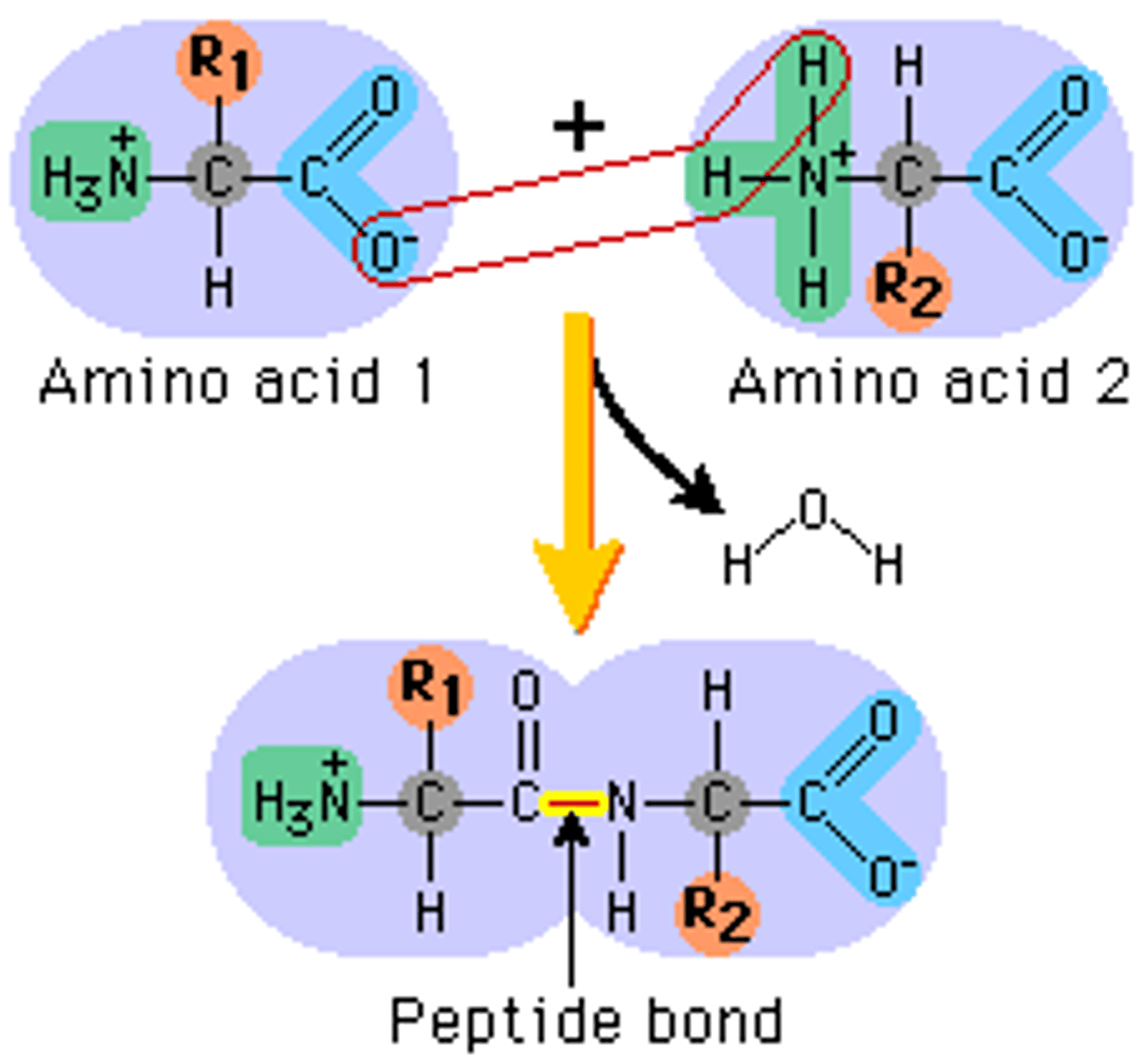
polypeptide chain
a long line of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds
R-group
stands for the rest of the compound, different for each kind of amino acid, giving the amino acid its properties
properties the R-group may give the amino acid
hydrophilic or hydrophobic, polar or nonpolar, acidic or basic
four levels of a proteins structure
primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, quaternary structure
hydrophobic R-groups
move together to the interior of a protein, away from water
lipids
macromolecule made of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen (CHO) that is mostly nonpolar not soluble in water;
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen (CHO)
elements that makeup both Carbohydrates and Lipids
fatty acid
building block of a lipid made of a hydrocarbon chain and a carboxyl group
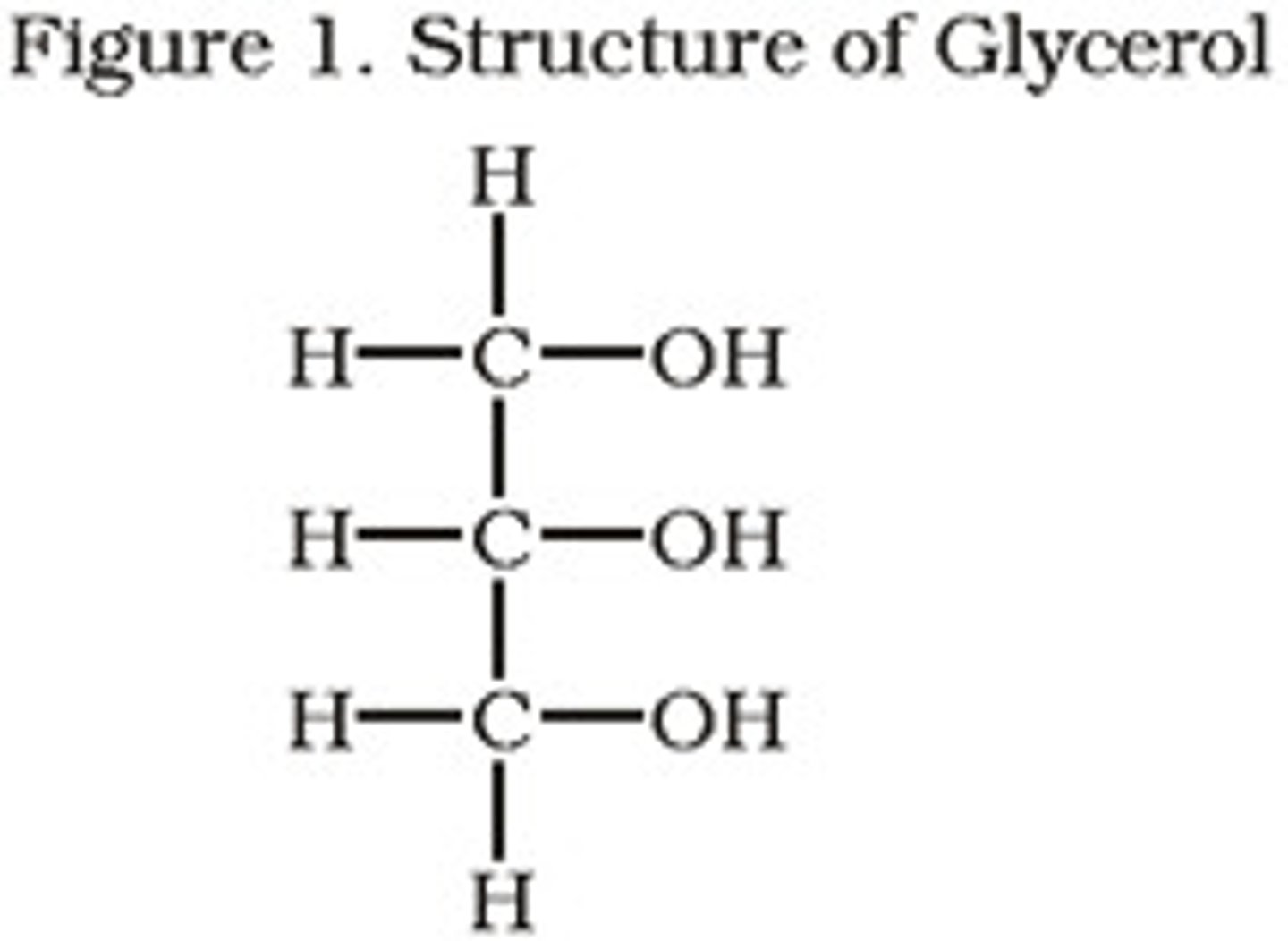
glycerol
a carbon alcohol that is hydrophilic
functions of lipids
long-term energy storage, insulation, part of the cell membrane, chemical messenger, waterproofing
phospholipid
lipid made of two hydrocarbon chains, glycerol, and a phosphate group
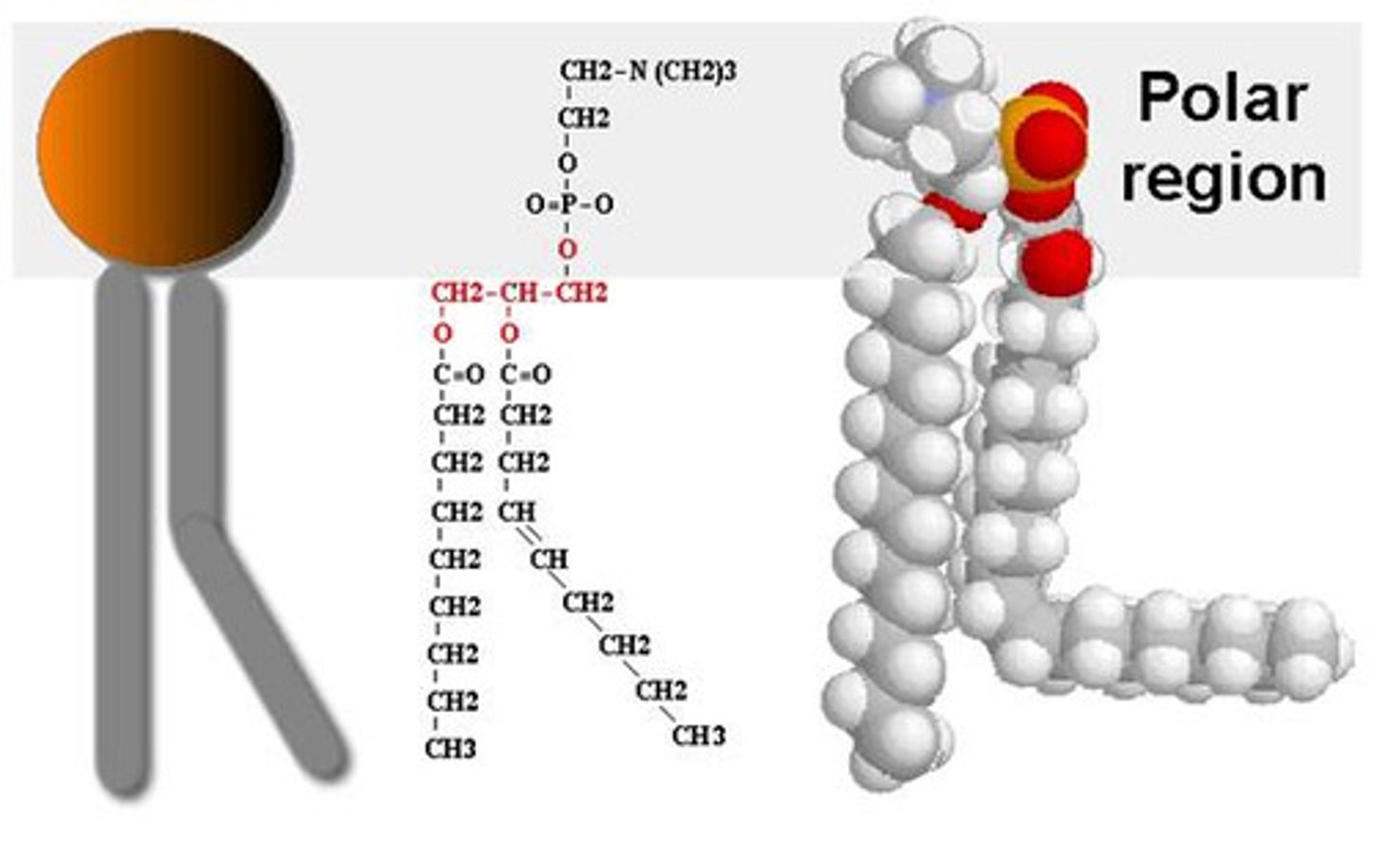
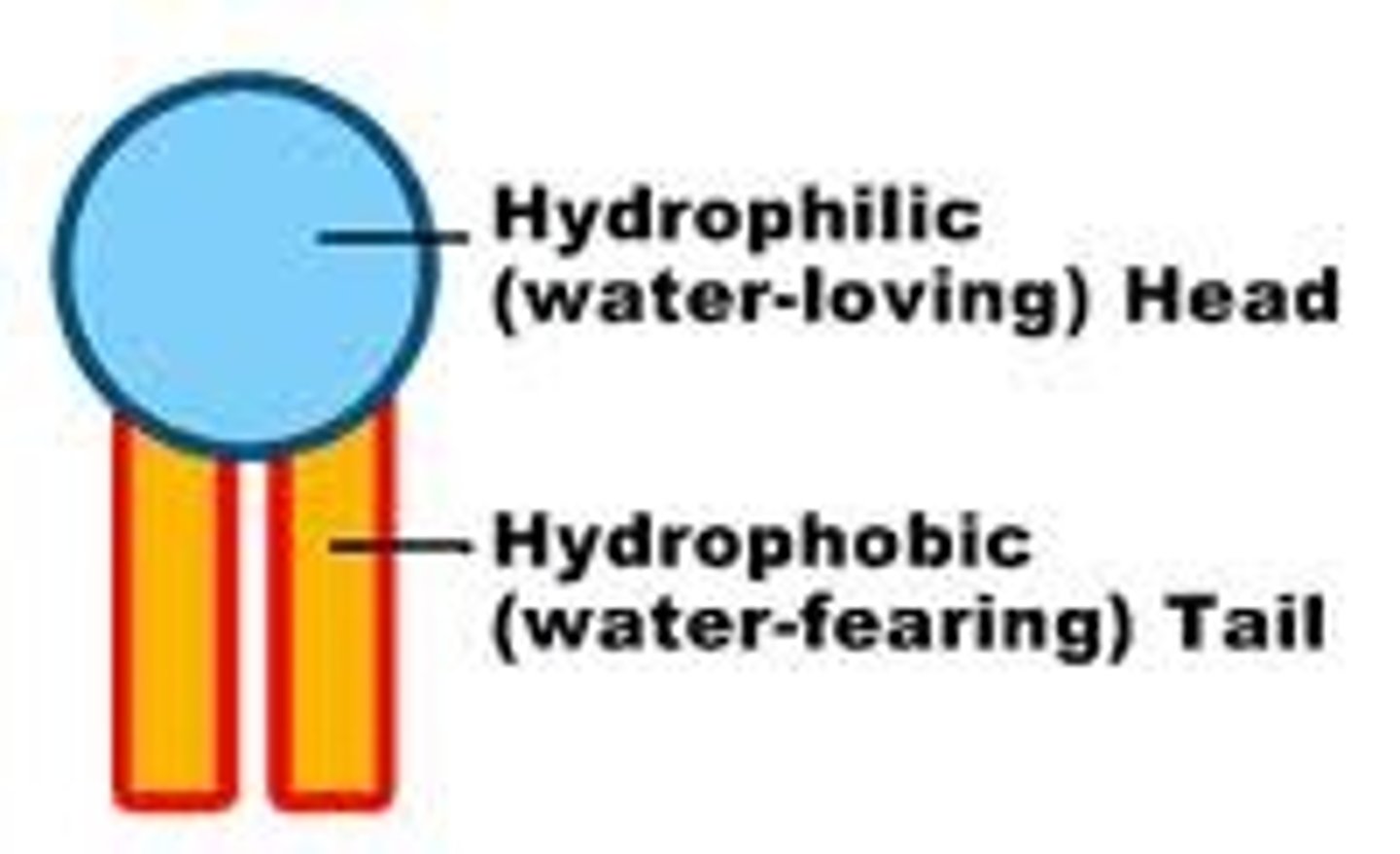
hydrophobic tail
another name for the hydrocarbon chain in a phospholipid
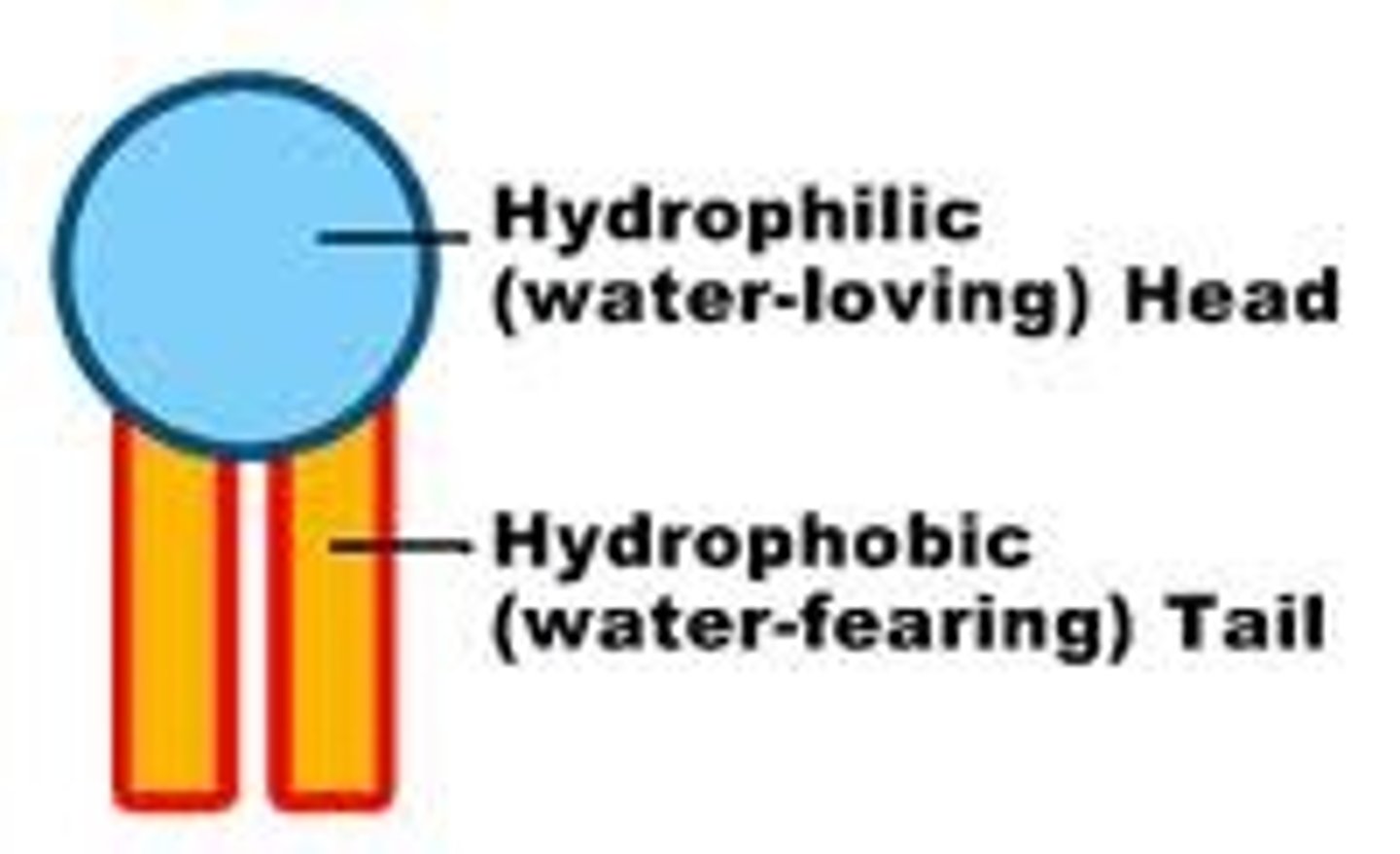
hydrophobic head
another name for the phosphate group in a phospholipid
-ose
suffix carbohydrates usually end in (gluc-ose, fruct-ose)
glycosidic linkage
covalent bond that forms between a monosaccharide and another molecule (like another monosaccharide)
macromolecules
large organic molecules
four
number of covalent bonds carbon can form with other elements
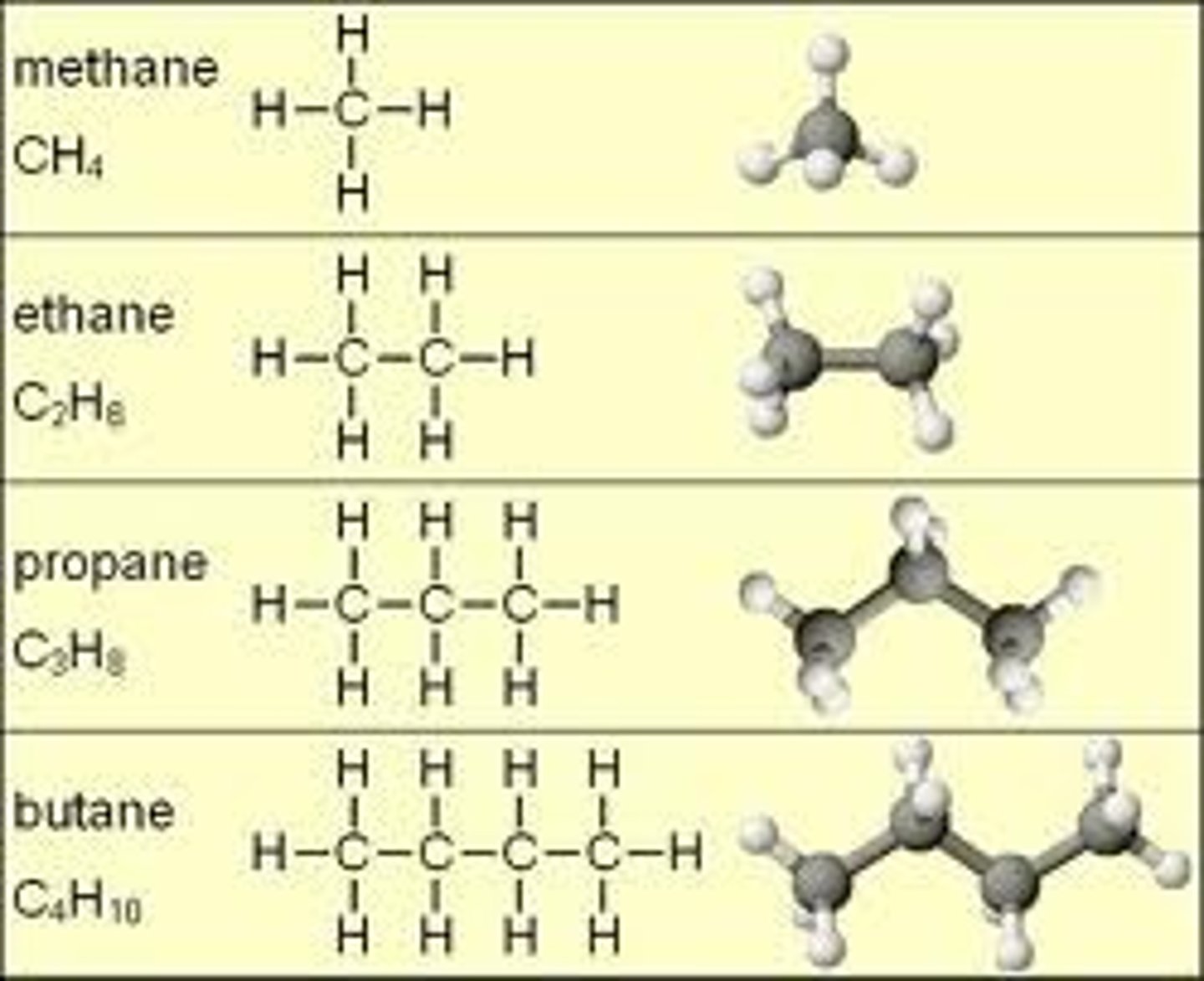
hydrocarbons
carbon and hydrogen atoms that are covalently bonded that make them stable and nonpolar
nonpolar
No partial charges. Not soluble in water
polar
Has partial charges. Soluble in water
polymer
molecules that consist of many repeated monomers
monomer
molecules that consist of a single unit
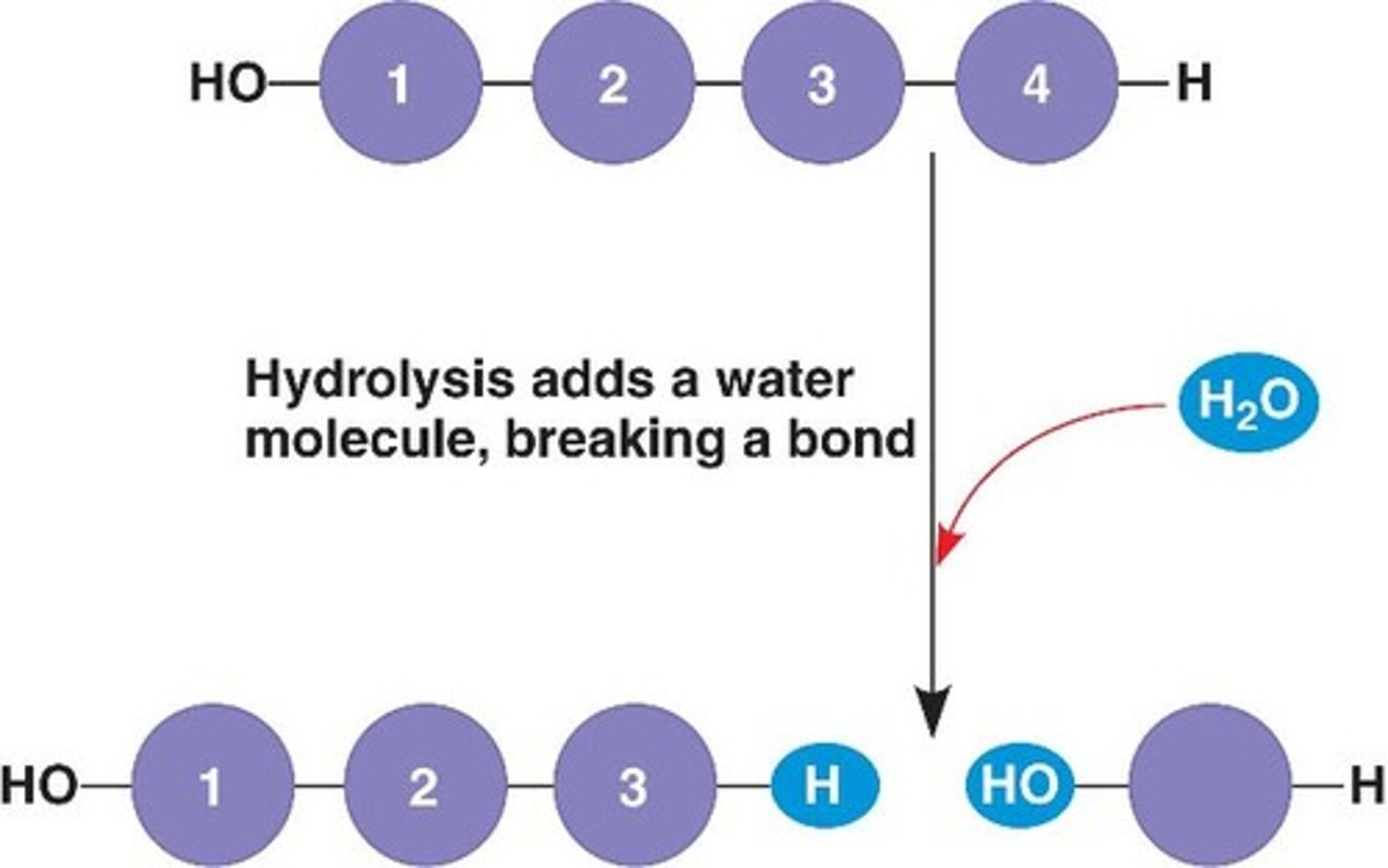
dehydration synthesis
reaction that links monomer molecules together, releasing a molecule of water for each bond formed
hydrolysis
the process of adding a water molecule to break a polymer into monomers
functional groups
parts of organic molecules that are involved in chemical reactions
charge of the oxygen atom in a water molecule
slightly negative
charge of the hydrogen atoms in a water molecule
slightly positive
hydrophilic
Term for substances that dissolve in water.
hydrophobic
Term for substances that do not dissolve in water.
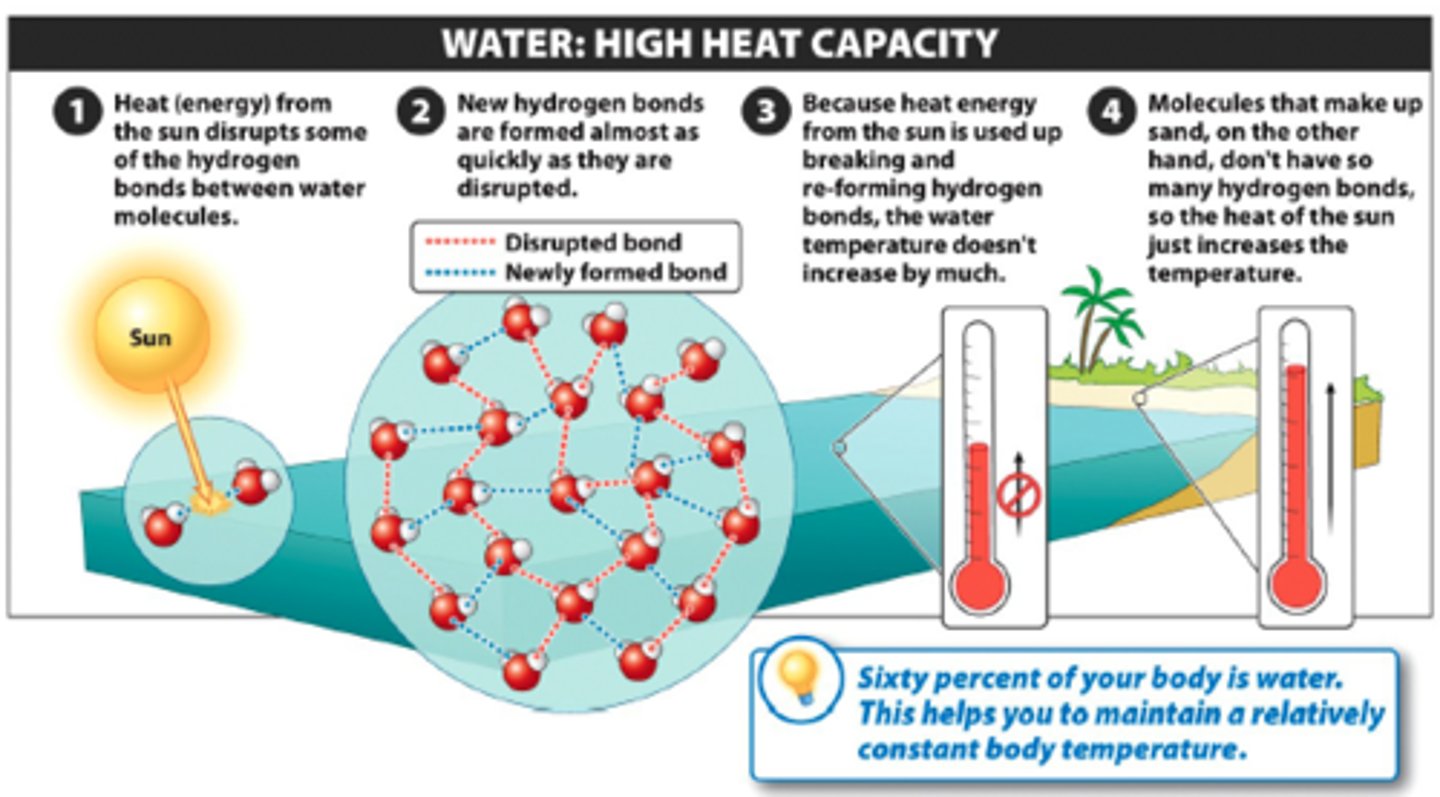
high specific heat
property of water in which water changes temperature very slowly with changes in heat due to hydrogen bonding
evaporative cooling
water carries the heat it absorbs away in sweat due to its high specific heat
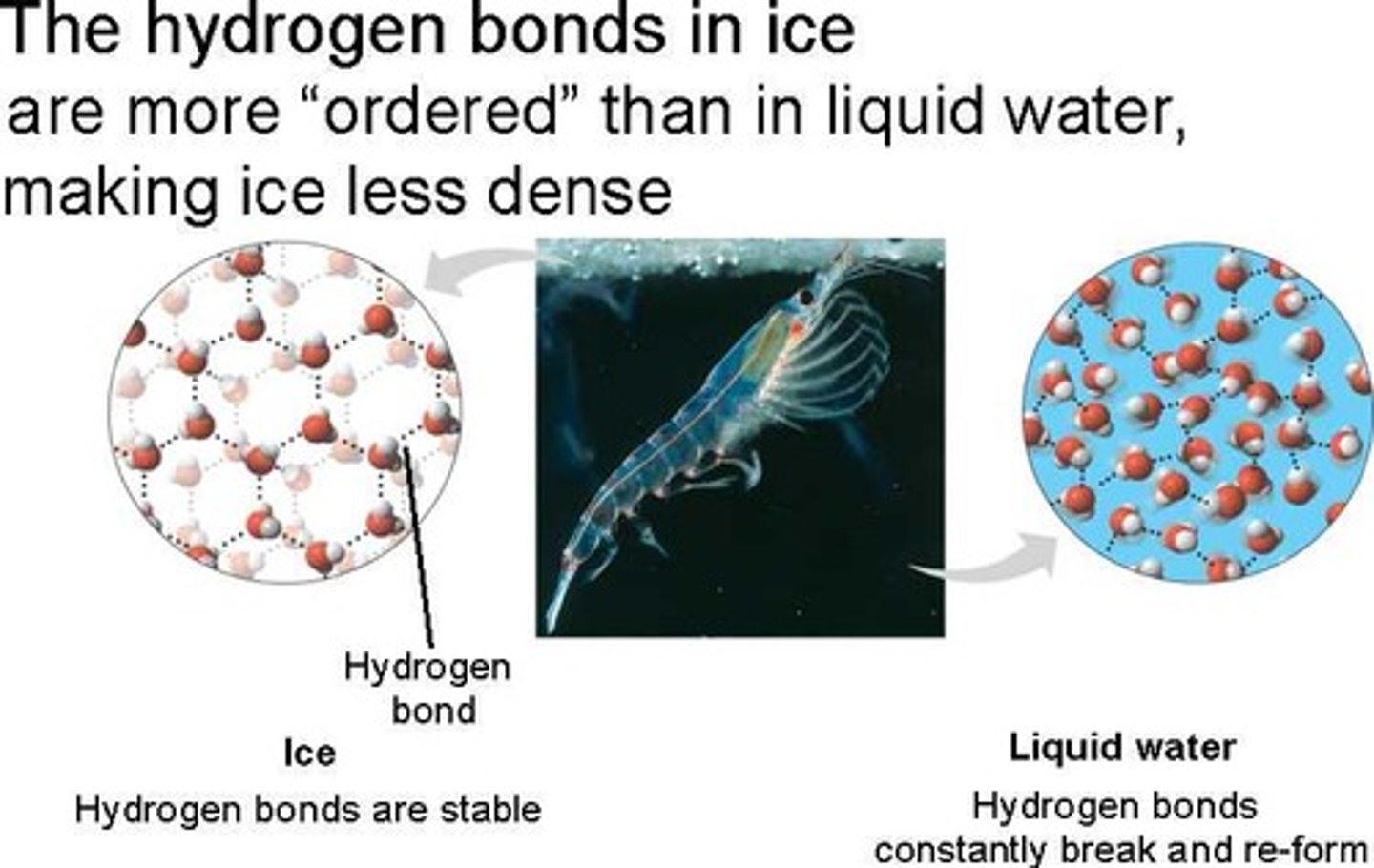
the reason ice floats in liquid water
less dense as a solid; hydrogen bonds form crystalline structure that keeps the water molecules separate
cohesion
the attraction of like substances; water molecules are attracted to other water molecules; this is due to the hydrogen bonding between water molecules
adhesion
the attraction of unlike molecules; water molecules are attracted to other polar surfaces

atom
Smallest form of an element that still displays its particular properties; consisting of a positively charged nucleus and a negatively charged electron cloud.
protons
Atomic particles with a positive charge (+) found in the nucleus of an atom.
neutrons
Atomic particles with a neutral (o) charge found in the nucleus of an atom.
electrons
Atomic particles with a negative charge (-) found outside the nucleus of an atom.
ion
atom becomes charged when it gains or loses an electron
chemical bond
attraction between two atoms by transferring or sharing electrons to attain a stable electron configuration
nonpolar covalent bond
Bond that forms when electrons are shared equally.
covalent bond
Bond that forms when electrons between atoms are shared.
polar covalent bond
Bond that forms when electrons are shared unequally; like that between the oxygen atom and hydrogen atoms in a water molecule
heredity
transmission of traits from one generation to the next
somatic cells
all cells besides gametes
asexual reproduction
single individual is the sole parent and passes copies of its genes to offspring
gene
hereditary unit
variation
any difference between individuals of the same species
sexual reproduction
two parents give rise to offspring that have unique combinations of genes
gametes
cells that transmit genes from one generation to the next
meiosis
cell division that results in haploid gametes (sperm and egg)
haploid cells
cells with single sets of chromosomes (n)
diploid cells
cells with two sets of chromosomes (2n)
homologous chromosomes
pair of chromosomes that are the same size, same appearance and have the same genes
meiosis I
cell division in which a diploid cell with duplicated chromosomes becomes haploid cells with duplicated chromosomes
meiosis II
cell division in which haploid cells with duplicated chromosomes become haploid cells with unduplicated chromosomes
independent assortment
each pair of homologous chromosomes in metaphase I sorts its maternal and paternal homologs independently of every other pair
crossing over
process in which DNA molecules of nonsister chromatids are broken and rejoined to each other
recombinant chromosomes
individual chromosomes that carry genes from two different parents
genetics
study of heredity and inherited variation
character
heritable feature that varies among individuals
trait
variant for a character
P generation
parental generation, the first two individuals that mate in a genetic cross
true-breeding
term used to describe organisms that produce offspring identical to themselves if allowed to self-pollinate
F1 generation
the first generation of offspring obtained from an experimental cross of two organisms
F2 generation
offspring of the F1 generation
allele
alternative version of a gene