sequencing, precision medicine
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
what is a contig
consensus sequence partially reconstructed sequence
what makes a quality/trustworhty sequence assembly?
high fold coverage - 50Cx or more
why would dna sequencing fail
error with extraction
With medication development in what order do we do the three major stages and why
culture study, animal research, human trials - make sure its safe/ no bad side effects
what is precision medicine
using a persons DNA sequnce to see if drug will work for them
what is microarray and how does it measure protein
analyzes protein expression on a large scale by detecting presence and quantity of specific molecules
what is the structure/ parts of an amino acid
R gorup, Amine group, carboxyl group, Hydrogen, conneteed to central/ a carbon
what bond connects amino acid together and what does it prodcue
peptide bond N of amine - C of carboxyl - makes H2O
what makes something hydrophobic
non polar
what make something hydrophilic
polar
what does aliphatic mean
organic compound with open chain structure
what does amphipathic mean
molecule has both hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
what is an alpha helix and beta sheet
A - coils B - forms a sheet
what is the function of a chaperonin protein
assists in folding of proteins, puts in lowest energy state
what is a disulfide bond and wha tis their purpose in protien folding
2 S, put secondary structures together
what amino acid forms disulfide bonds
cytosine
what is a primary protien structure
amino acid chain
what is a secondary protien structure
folding of polypeptide chain into a helix or B sheet
what is a tertiary protien structure
1 complete protein
what is a quatrenary protien structure
2 or more proteins together
what is a domain
independently folidng distinct structual and funciton unit within a protein
what is a subunit
individual polypeptide chain that assembles with other chains to form a larger protein complex
why is the rotation of R-groups important in protien folding
flexibility, interactions, stability, function
What si the difference between a parallel and antiparallel beta sheet
p - same direciton ap - oposite direction , H bodnings, more common/ stable
put yes
yes

what is this called
helix turn helix

what is this called
four helix bundle

what is this called
coiled coil

what is this called
B hairpin

what is this called
antiparallel B sheet

what is this called
B barrel
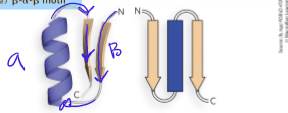
what is this called
B a B motif
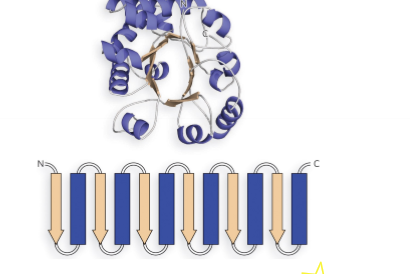
what is this called
a/B barrel domain

what is this called
greek key motif
what determines tertiary structure
domain and domain orientation
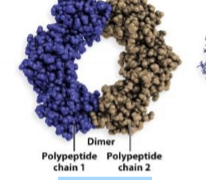
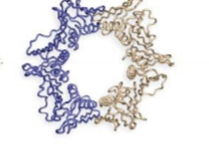
what is this showing, what does it represent
van der waals surface - forces

what is this showing, what does it represent
sticks - bonds of atoms
what is this showing, what does it represent
a - carbon trace - carbons
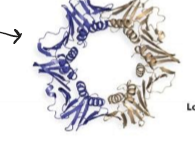
what is this showing, what does it represent
ribon diagram - a helix vs. b sheets

what is this showing, what does it represent
electrostatic surface representation basic vs. acid, + vs -