N4331 - Exam 1 (Peds - UTA Nickols)
1/58
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
Regarding newborn growth and development, discuss the meaning of cephalocaudal and proximodistal patterns
cephalocaudal: learn skills from head to toesproximodistal: learn from trunk to fingers
____ kg = _____ lbs
____ oz = _____ mL____
cm = _____ in____
tsp = ____ mL
1 kg = 2.2 lbs
1 oz = 30 mL
2.54 cm = 1 inch
1 tsp = 5 mL
What is the normal schedule of newborn assessments?
1m
2m
4m
6m
9m
12m
Define hand movement development stages in a newborn
2m: open/close hands
6m: raking grasp
9m: pincer grasp
12m: feed self w/ spoon
Discuss development of fontanelles
posterior: close @ 2-3m
anterior: close @ 12-18m (referred to as " soft spot")
Define strabismusIs this normal in a newborn?
eyes straying in gaze ∵ undeveloped eye muscles
common until 6m of age
How should you inspect the ear of a newborn?Toddler?
infant: pull pinna down and back
toddler: same! down and back
used different method once 3+ years
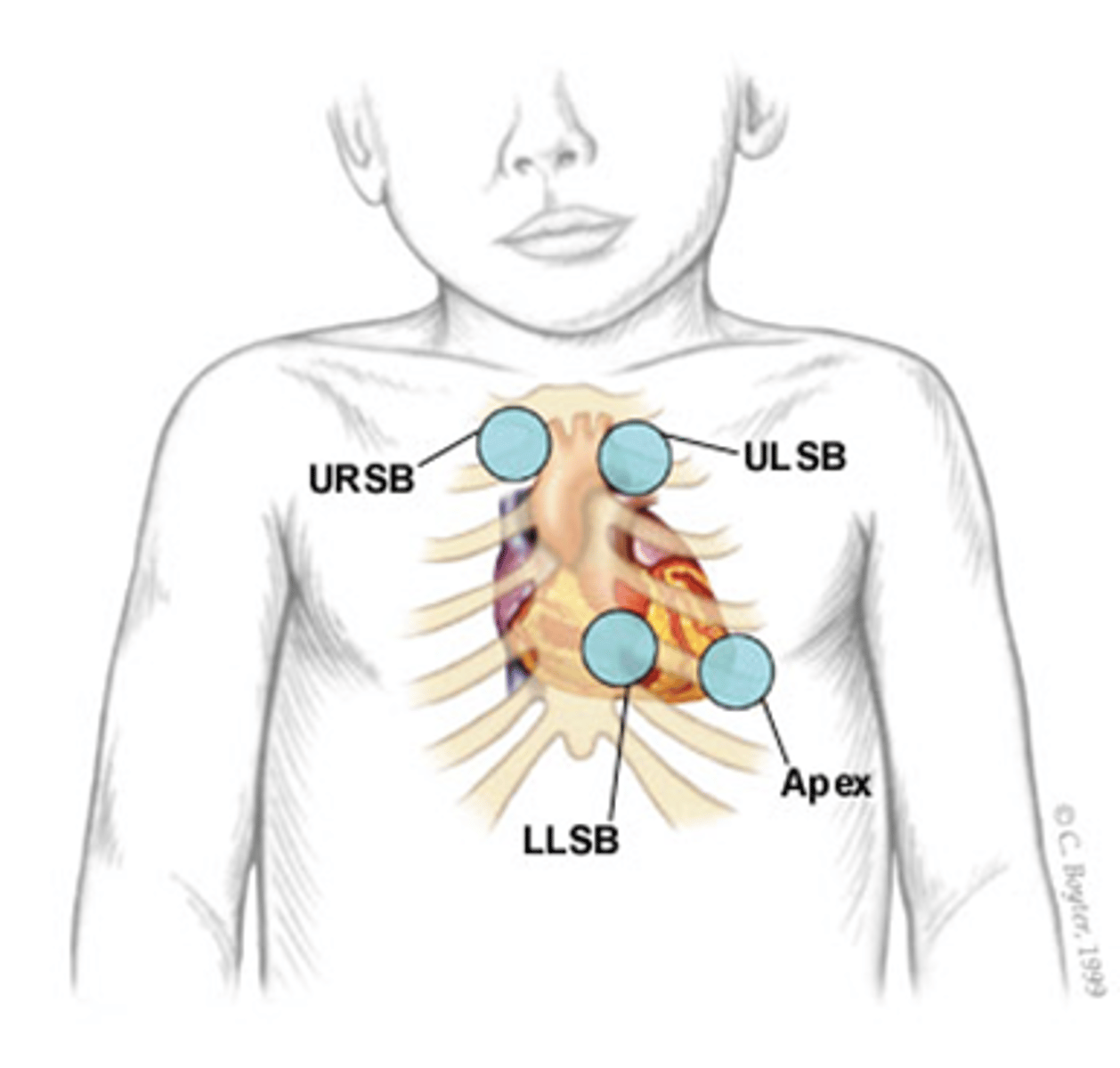
What is the expected pulse range of a newborn?Where should pulse be assessed?How long should pulse be assessed?
80-160 bpm
apical pulse @ 3-4 rib to left (medial) to midclavicular line
monitor for full 60 sec
When does hand preference appear in a child?
2-3 yrs
Are murmurs common in newborns
yes, S3 very common
murmurs often asymptomatic but should always be inspected by MD
When does myelination of the spinal cord occur?
birth to 24m
that's why reflexes are developing and changing
Discuss the timing of primitive vs protective reflexes
primitive: during 1st year of life, exception=Babinski (until 24m)
protective: develop after primitive disappear
What would you expect for stools of breastfed newborns?Formula fed?
BF: thinner, seedy & yellow
FF: pastier, darker in color
_____ is not a sign of constipation
Gruntingmeans retraction or respiratory distress
Regarding stools, importance is on ______ not _______. However (type of stool) is of concern.
consistency not quantity
small, hard stools = concern
What pain scale is used in pediatrics?Define the acronymDescribe scoring
FLACC (for infants and toddlers)
face/legs/activity/cry/consolability
each category scored on level 0-2, overall scores range 0-10 (10 being highest)
Define expected weight milestones for newborns
lose 10% first week of life but regain by 2nd wk
1st month: gain 20-30g/day
4-6m: weight doubles
12m: weight triples
When should baby teeth be present? How many are there?
by 3 years; 20 teeth total
What age is considered the toddler stage?
12m - 3y (36m)
What happens to a toddlers BP and HR as they develop?
↑BP : (86-106) / (42-63)
↓HR: 98-140
What age is a "potbelly" appearance considered normal?
toddler age (12m-3y)
When assessing newborn reflexes, it is important to assess for ________
symmetry
asymmetry can indicate neuro or ortho problem
List the primitive reflexes and when they disappearWhat age are they seen?
seen until ~12m, except for Babinski=24m
Moro reflex: disappears @ 2m, startle reflex
Rooting reflex: disappears @ 4m
Tonic neck: disappears @ 5-7m, fencer reflex
Palmar reflex: disappears @ 5-6m
Plantar reflex: disappears @ 9-12m
Babinski reflex: disappears @ 24m
Describe how to test the moro reflex
When does it disappear?
Hold infant in hands & lift few cm off surface, gently drop head into other hand, this should illicit startle reflex
head will throw back, hands open & arms extend out to sides then retract in
disappears @ 2m
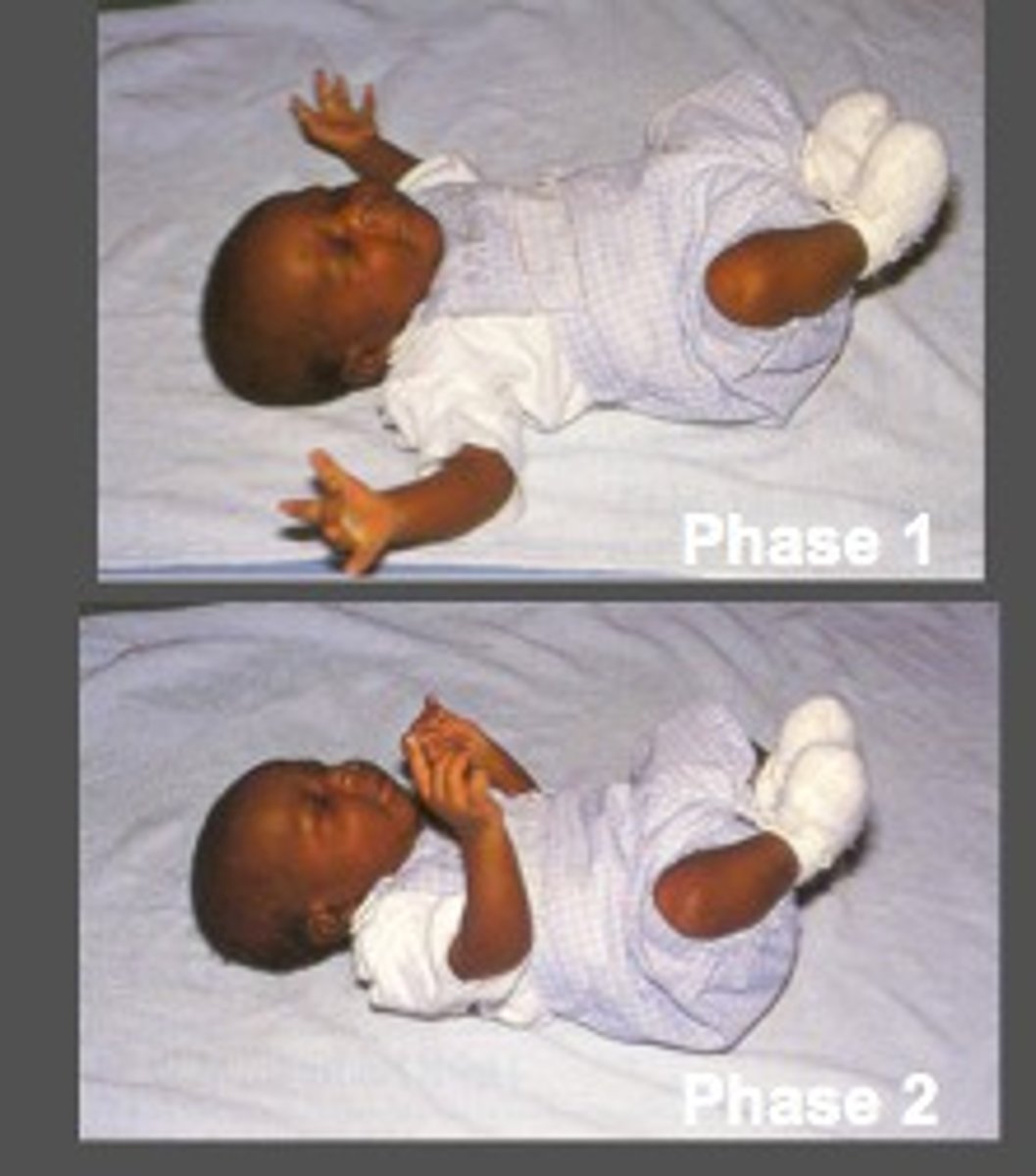
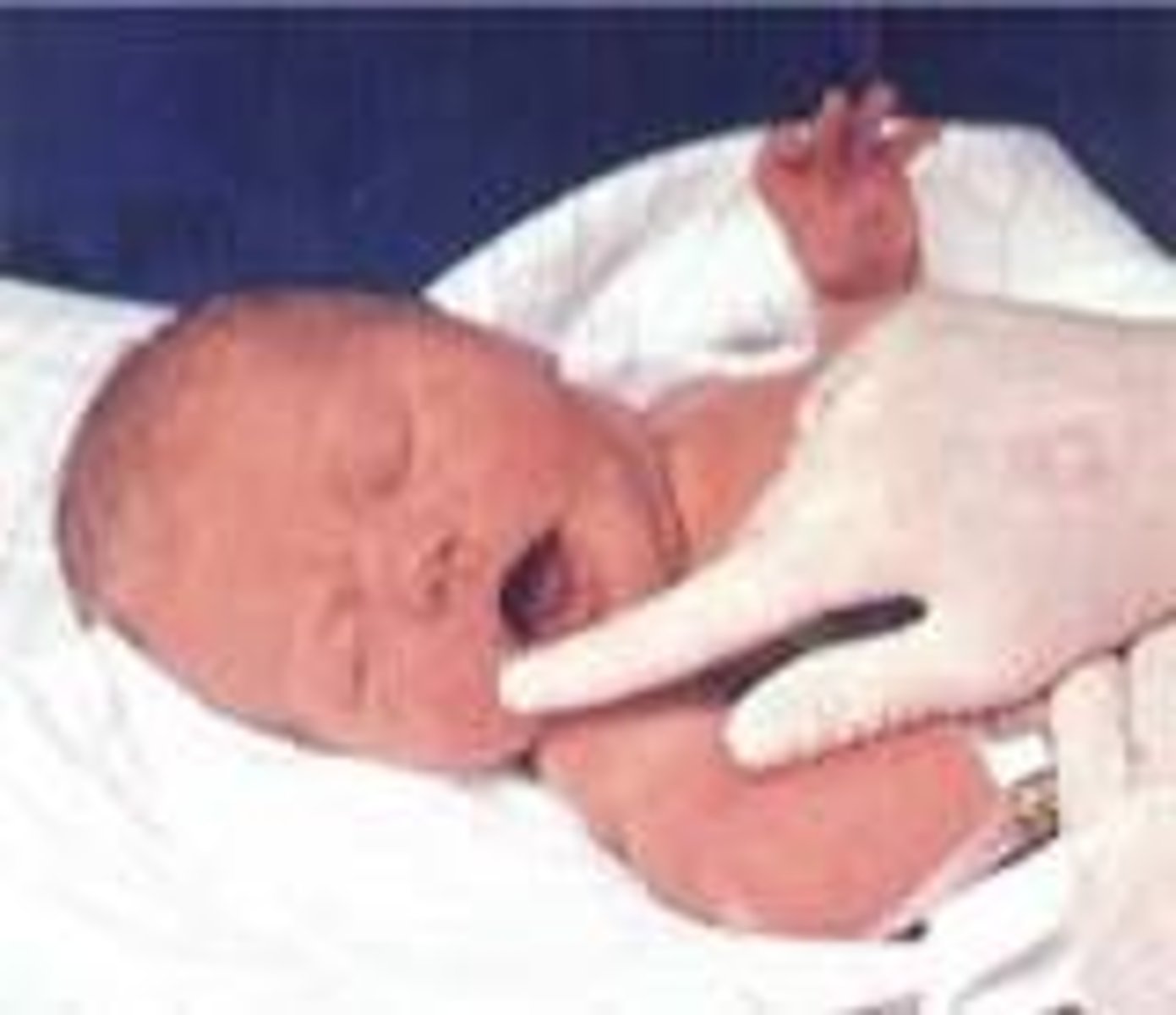
Describe how to test the rooting reflexWhen does it disappear?
stroke infant's cheek
turns head and starts suckling
disappears @ 4m
(note: feeding solid foods @ 6 months)
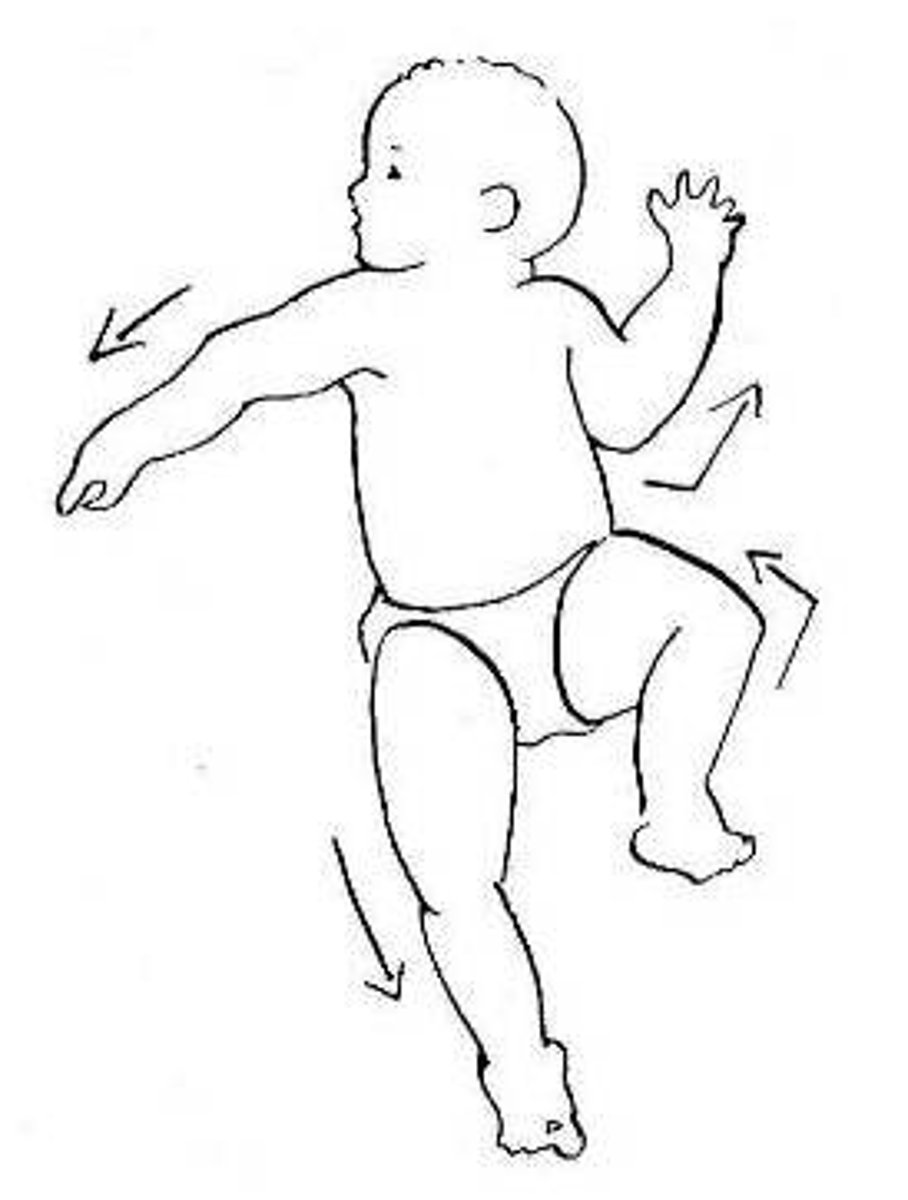
Describe how to test the tonic neck reflex
When does it disappear?
turn infant's head to one side
extends extremities (arm and leg) of side turned head towards and retracts opposite side extremities
disappears @ 5-7m
Describe how to test the palmar grasp reflex
When does it disappear?
place finger into infant's hand
automatically grasps your finger
disappears @ 5-6m
Describe how to test the plantar grasp reflex
When does it disappear?
stroke bottom side of infant's foot (ball of foot)
toes should flex
disappears @ 9-12m
Describe how to test the Babinski reflex
When does this disappear?
stroke infant's foot up from heel to toe
toes should splay out
disappears @ 24m
KNOW STAGES Define the Erikson vs Piaget development stage of a newborn:
name of stage
stage domain
definition
- Erikson: trust vs mistrust / psychosocial stage / infants rely on caregivers so basic needs met
- Piaget: sensorimotor / cognitive / learning about world through sensation
Define the Erikson vs Piaget development stage of a toddler:
name of stage
stage domain
definition
E: autonomy vs shame & doubt / psychosocial / learning to do things on their own & make choices
P: sensorimotor until age 2 → preoperational begins @ 2y / learning to manipulate objects, begins to imitate, symbolic thinking @ 2y
What age would the following be observed?
1. drinking from a cup
2. jumping up/down
3. crawling up stairs
4. walking independently
5. pedals
6. walks up/down stairs
7. jumps forward
8. runs
9. climbs objects
10. kicks ball
remember either 15/18/24/36
1. 15m
2. 24m
3. 15m
4. 18m
5. 36m
6. 36m
7. 36m
8. 24m
9. 24m
10. 24m
What age should child be in rear-facing car seat?
Front-facing car seat?
rear: ↓2 y.o
front: 2-4 y
What is echolalia? When does it disappear?
repeating words toddler has heard
ends at 3y or red flag
KNOW What is animism? When does it develop?
believing inanimate objects have feelings/are alive (like stuffed animals)
develops in preoperational stage (Piaget) at 2y
Discuss the gross motor skills expected during stages of newborn life
1m: move arms and legs
2m: lift head
4m: rolls from stomach to back, supports self on elbows while on stomach
6m: sits up
9m: crawling
12m: stand/walks
Discuss the fine motor skills expected during stages of newborn life
1m: opens fingers
2m: brings hands together
4m: grasps objects
6m: raking grasp, bangs objects on surfaces
9m: feeds self, lets go of objects on purpose, bangs objects together
12m: pincer grasp, feeds self with spoon and cup
Discuss expected communication during newborn stages
1m: crying @ different pitches
2m: cooing, gurgling
4m: turns to voices
6m: babbling, expresses sounds of joy/displeasure
9m: copies sounds, mama/dada unspecifically, understands "no"
12m: few words, uses simple gestures, mama/dada specifically
If child not babbling or imitating sounds by age ______, they have delay in language development and should seek MD.
7 months
What common childhood condition is associated with speech delay?
recurrent ear infections due to fluid in ear
What are the recommendations for newborns concerning carseats? (4 points)
A rear-facing car seat with 5-point harness for 0-12m AND <20lbs
(in other words, if <20lbs AND aged 0-12m, put in rear-facing seat w/ 5pt harness)
KNOW SIDS prevention points (4)
provide skin-to-skin immediately after birth for 1h
place on back to sleep
share room, but not bed, until 6m of age
offer pacifier at naptime and bedtime
What toys are most appropriate for young infants? Older infants?
young: toys that can be kicked/batted, contrasting colors, unbreakable mirror
older: toys that make noise, light up, soft dolls, teething rings, board books, large blocks?
How long should room sharing last for a newborn?
until at least 6 months
reduces risk of SIDS
What are the hunger cues?
rooting
suckling
crying
opening mouth
hands to mouth
Weaning an infant from breast or bottle can begin when infant can readily use a cup. What age is this?
12 months
What age do you typically start introducing solid foods? What milestone must occur first?
6 months disappearance of tongue extrusion reflex (otherwise just spits food out)
When introducing solid foods; what order should they be introduced? How frequently should new foods be introduced and why?
start at 6m
iron fortified cereals → pureed veggies → fruits
one new food every 3 days to detect allergies
KNOW What are the live attenuated vaccines? Knowing this is important why?
MMR and varicella
(contraindicated for immunocompromised)
What are the contraindications for vaccines?
1. no live attenuated (MMR & varicella) if immunocompromised
2. if previous vacc reaction (most common DTaP, still rare but serious)
3. egg allergy, no longer contraindicated!!!
What are the vaccines during first year of life?Route? Viral/bacterial?
Hep B: IM / V (given @ hospital after birth)
Rotavirus: Oral / V (severe diarrhea)
DTaP: IM / B
Hib: IM / B
PCV (pneumococcal conjugate): IM / B
IPV (polio): IM or SubQ / V
influenza: IM / V
MMR: SubQ / V
Varicella SubQ / V
Vaccines for toddler stage of life? Thing to remember about 2 of these vaccines?
MMR
varicella
Hep A
know: MMR & varicella are live attenuated, may see normal s/e of rash/vesicles
What are the classifications of dehydration?
Identify the following for each classification:
RR
pulse/HR
BP
LOC
urine output
fontanels
tears
mild/mod/severe
- fontanels: soft/sunken/very sunken
- tears: present/decreased/absent
KNOW WHEN TO CALL DOC Common side effects of immunizations (4)
fever up to 102° (call MD if 105°)
↑fussiness 24h after
↑sleep 24h after
redness/swelling at site
What temperature is considered a fever in infants?Best way to measure?Can you give antipyretic?Common s/s associated with fever (3)
>100.4°
rectal temperature
antipyretic: no, not unless extremely irritable
s/s: tachypnic, tachycardic, irritable
What is the normal RR for newborn vs 1y?Tachypnea for newborn?
normal: NB=30-55 vs 1y=25-40
tachypnea: NB=60
You should not feed a newborn if RR is ________. Why?
≥60
tachypneic and risk for aspiration
KNOW What are the compensatory mechanisms used during respiratory _______ (distress/failure)? (5)
Describe what each mechanism does
for respiratory distress
grunting: keeps alveoli open @ end of expiration
retractions: assists w/ ventilation
head bobbing: assists w/ ventilation
nasal flaring: increases diameter of airways
hyperextension of head&neck: opens airways
What vaccine has been helpful in preventing ______, a type of croup?
Hib vaccine for epiglottitis
remember, can't get Hib until 2 months