(5,6) Inductance n Measuring Instruments
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
What is inductance?
Property of conductor to induce voltages that oppose change in current
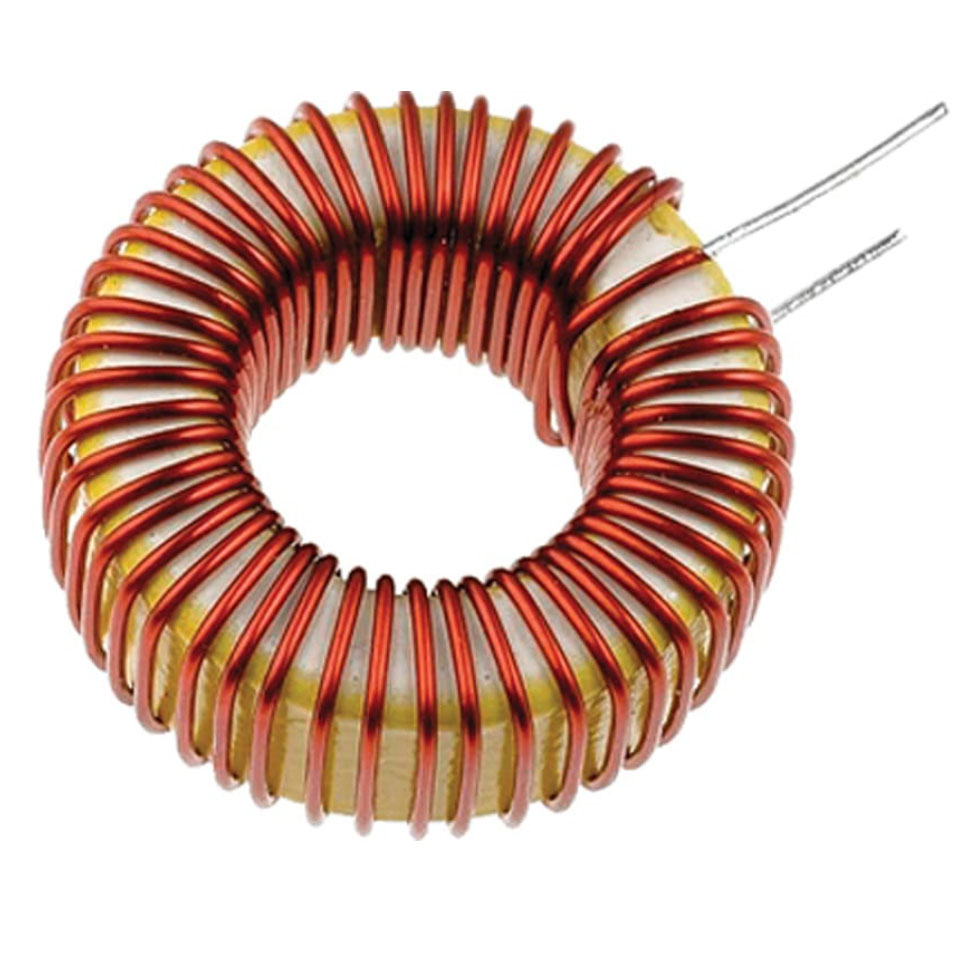

What is an inductor?
Conductor formed into coil, increases inductive effects compared to straight conductor
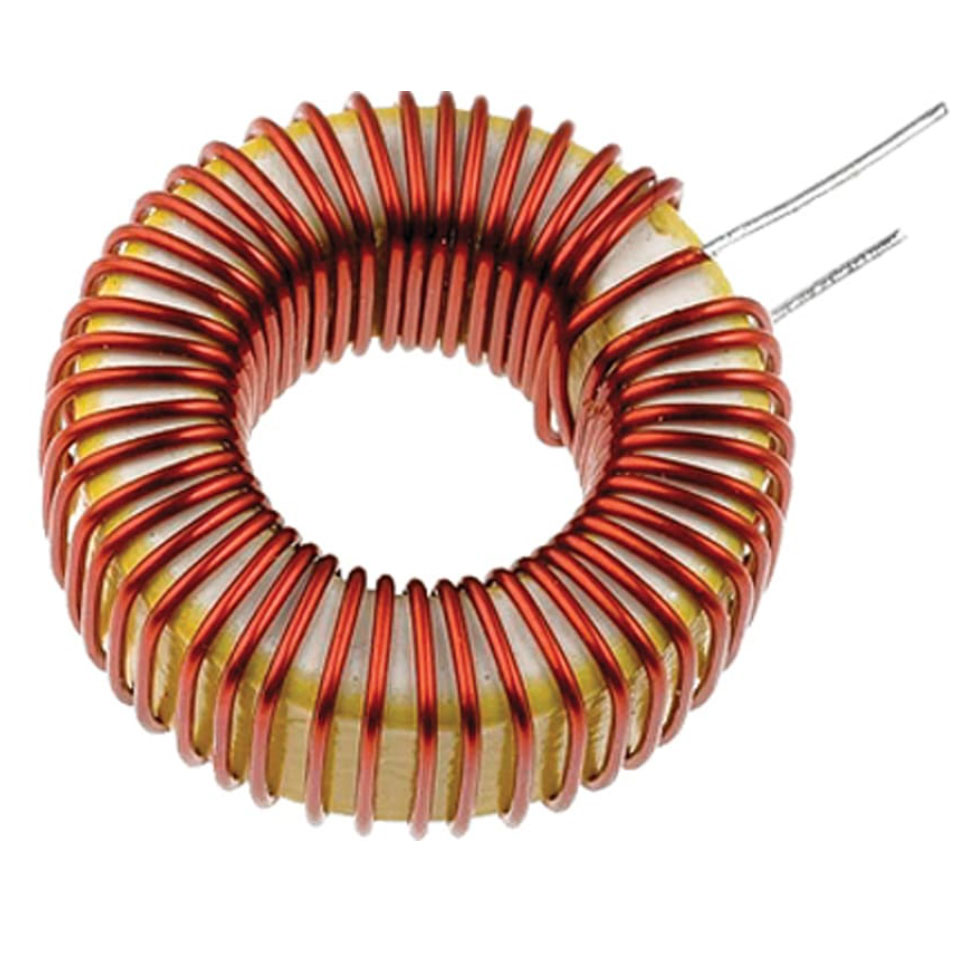


How does inductor store energy? (include pic of inductor for both)
After resistance from establishing magnetic field, holds magnetic energy until current changes or stops
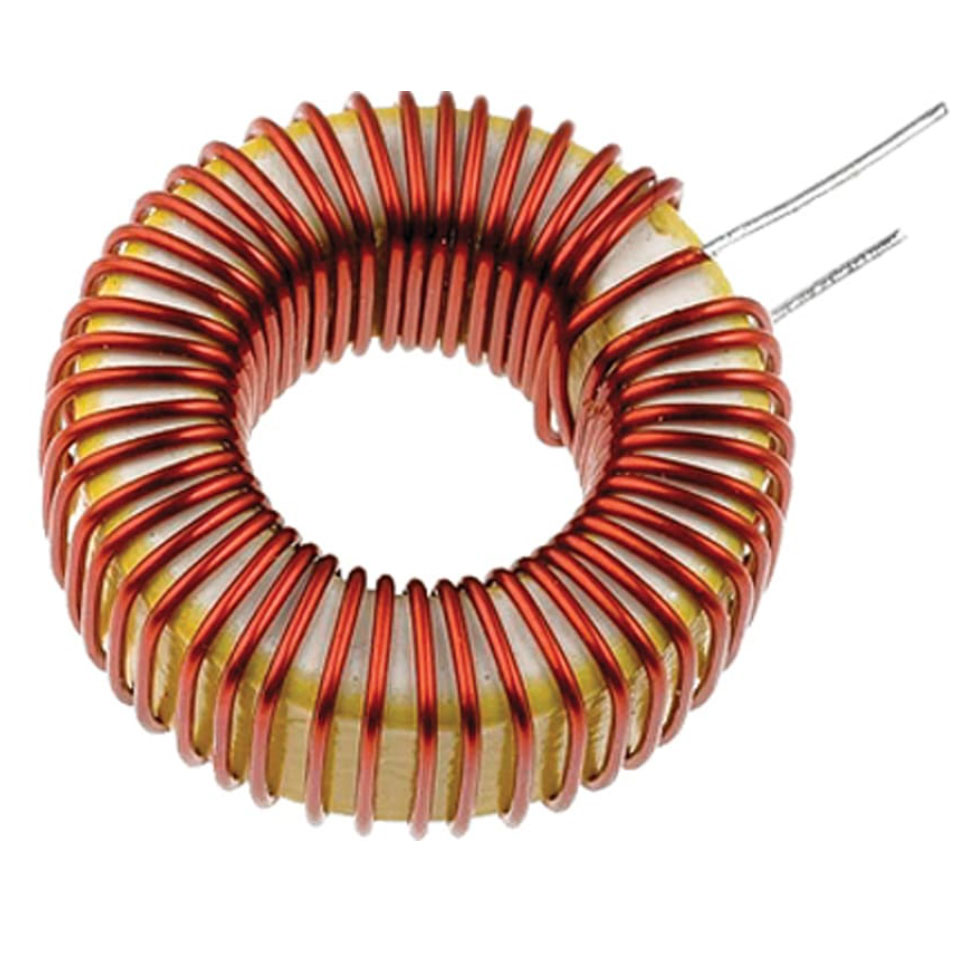

Other names for inductor?
Choke, ballast
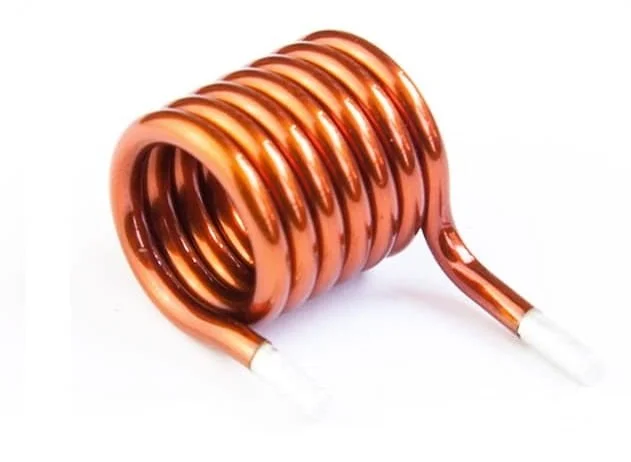

How are air-cored inductors made?
Conductor coiled around hollow former, core is open space
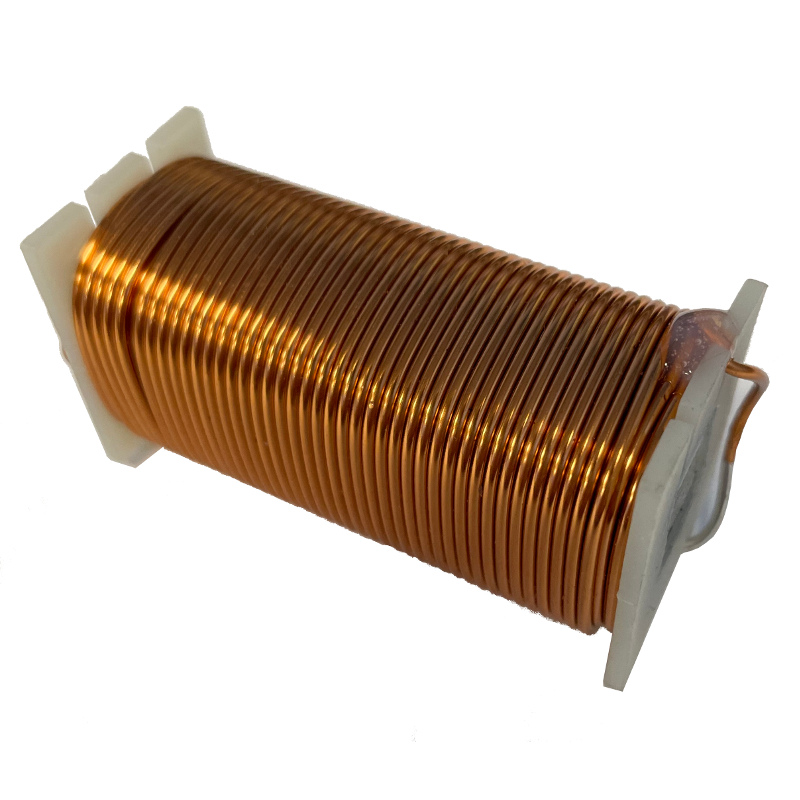

How are iron-cored inductors made?
Conductor coiled around iron former
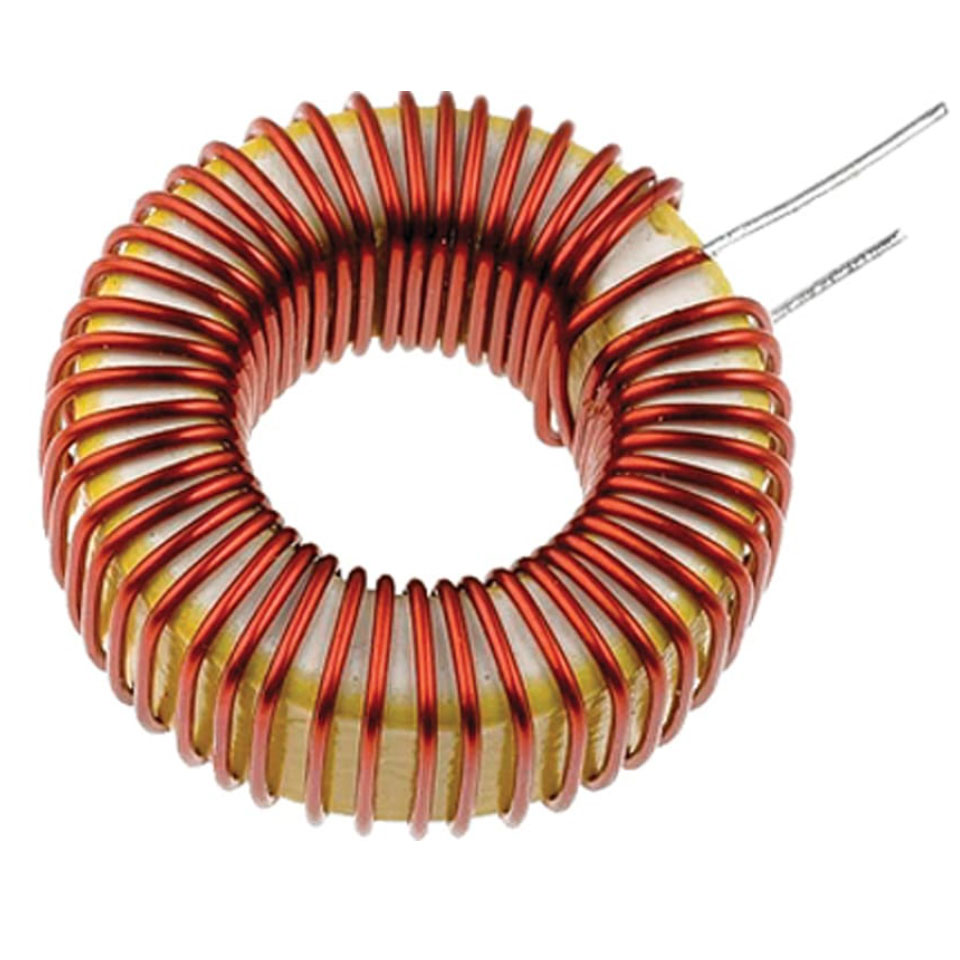

How are ferrite-cored inductors made?
Blend of ferric oxide and trace metals

What inductor symbol is this?
Air Core Inductor

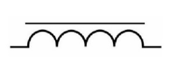
What inductor symbol is this?
Iron Core Inductor
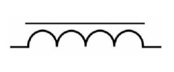
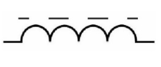
What inductor symbol is this?
Ferrite Core Inductor
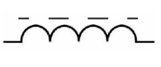
Where are air core inductors used?
High frequency applications (air has no eddy currents)
Where are ferrite core inductors used, how can inductance of inductor be varied?
High-Med frequency applications i.e. electronic filters, tuning circuits. Methods to vary inductance include air gap, withdrawing core from cylindrical inductor
What core types (not material) are usually used?
Laminar plates of silicon steel, Toroidal cores (continuous strip of thin steel). Cores differ as per required heat dissipation and mounting situation
What are some applications for iron core conductors?
Power supply frequency, lamp ballasts, filtering for VSD (variable speed drives), radio frequency filtering, high voltage ignition systems (i.e. spark plugs)
How is laminated iron core inductor made?
Electrically insulated sheets of silicon steel (helps reduce hysteresis, eddy current losses)
In straight/coiled conductor, how does current increase induce self inductance?
Current increases, field expands inducing voltage in conductor, which opposes current increase. Expanding flux lines cut conductor material inducing EMF in conductor. Fleming Right Hand Rule shows induced EMF opposes current change
In straight/coiled conductor, how does current decrease reduce self inductance?
As current decreases, field starts collapsing as flux lines induce voltage in conductor which supplies stored current
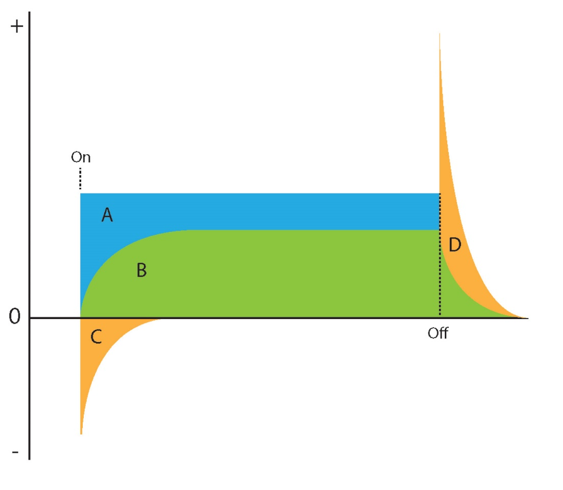
Identify following regions: Supply voltage, current, induced voltage switch on, induced voltage switch off
A: Supply voltage, B: Current, C: Induced voltage at switch on, D: Induced voltage at switch off
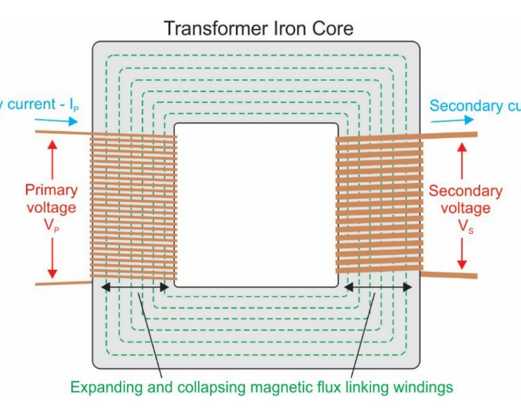
How does mutual inductance between two coils work?
Occurs when magnetic field in one coil induces EMF in adjacent coil
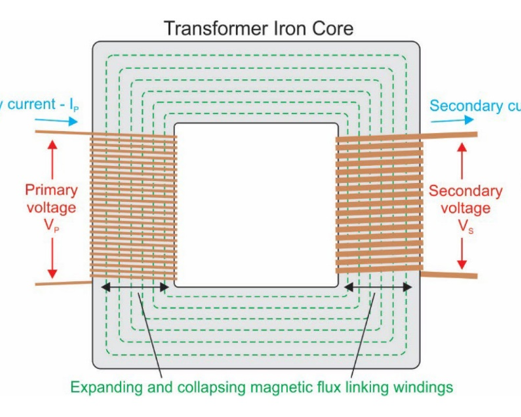
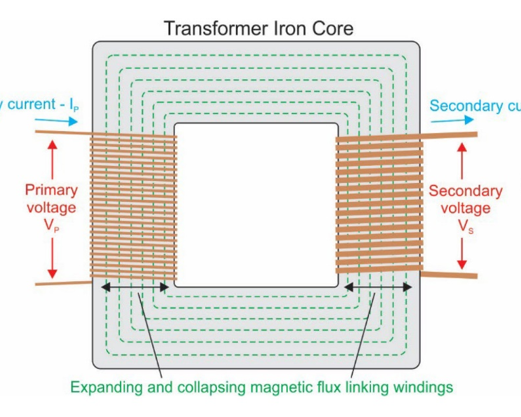
In transformer, what do the primary and secondary windings do?
Primary supplies EMF, secondary has EMF of mutual induction induced into it
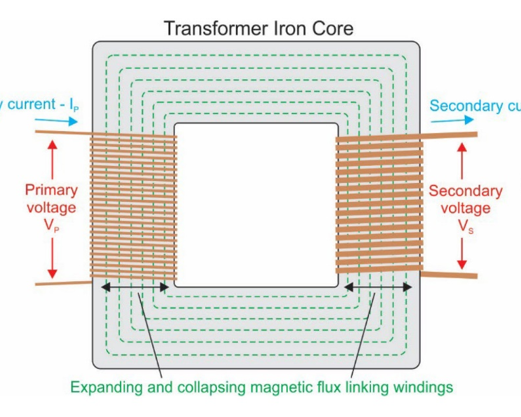
What might happen to telephone cables if power cables are ran alongside them?
Voltages may be induced in phone line, may interrupt phone operation or even damage equipment
How many time constants does it take for current in an inductor to reach steady state conditions?
5
Why does current running through an inductor increase at a specific rate (time constant)
Due to induced voltage limiting initial current flow
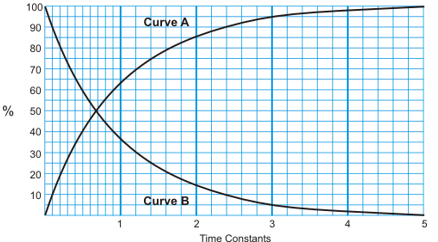
What is this called and how is it used? (universal time curve)
Universal Time Curve, shows rate current is allowed to build up at switch on (A)/ decay at switch off (B)
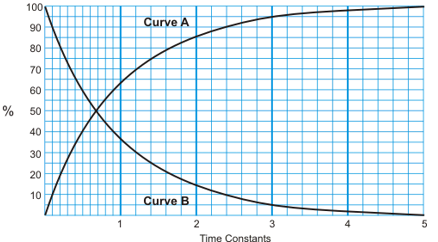
How are continuity, insulation resistance and value of inductance tests done?
Cont: Uses ohmmeter, ensures coil one continuous length. Low ohms ideal
IR: Tests coil hasnt shorted to earth. Infinity ohms ideal, >1MΩ indicates faulty inductor
Val. of Ind.: Specialised tools measures inductance
What advantageous difference does an analogue meter have over a digital meter?
Analogue pointer and scales can be easier to read than digital numerical display
What typical quantities analogue meters are used for?
Insulation, resistance, earth continuity, motor start/run currents
Three common types of analogue meter movement?
Moving coil, moving iron, galvanometer
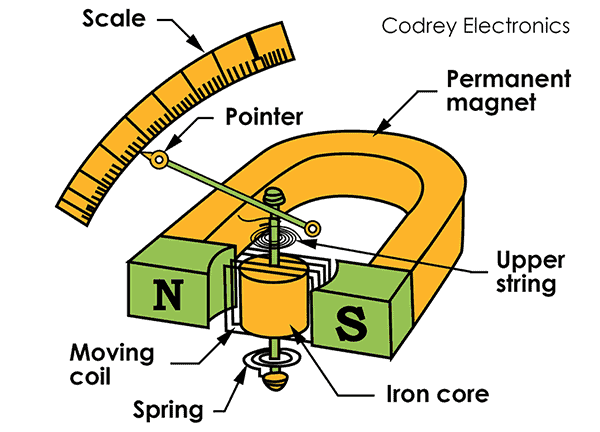
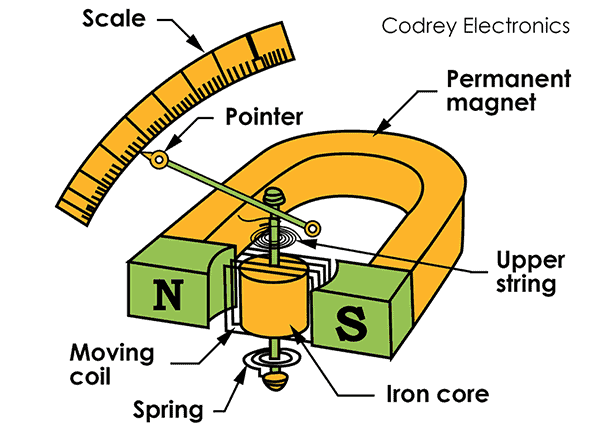
How does a moving coil meter work, and why doesn’t it work on AC?
Current measured flows through 2 hair springs in and out of coil, coil current flow produces magnetic field. Coil assembly adjacent to permanent magnet. AC must be rectified or meter will keep fluctuating
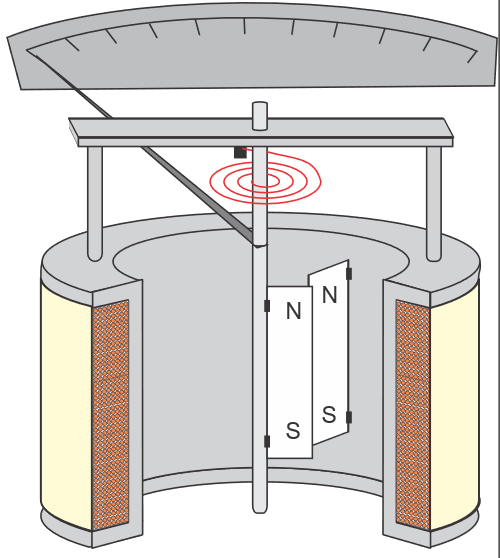
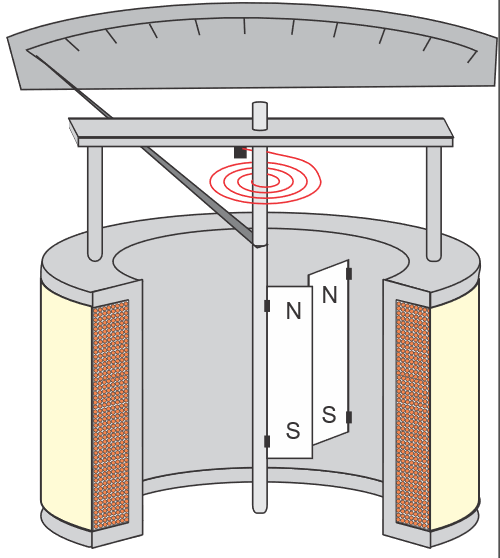
How does a moving iron meter work and what difference in scale calibration (compared to moving coil meter) does it have?
Current flow in through hair spring, iron cores turn into electromagnets, fixed + free vanes repelled (same polarity), moving vane moves pointer. Scale is non-linear.
How does electrodynamometer measure power?
Voltage and current coils in meter multiplied together
How is multiplier resistor used to extend range of moving coil meter movement for measuring higher voltages?
From order of millivolts, multiplier resistor placed in series with meter coil which provides voltage drop required for voltage drop across meter movement + limit FSD current
4 causes of electrical meter damage during use + how to prevent?
Incorrect connection, over-ranging, physical damage, incorrect storage. Prevented by regular condition/operation checks, correct ranges/category
What is minimum required category for meter to take voltage measurements at incoming mains (before service fuse) + domestic switchboard?
Cat IV for mains, Cat III for board
What is parallax error? And can meters be used at any angle?
When analogue meter viewed from side; meter reading should be read from front. Analogue meter on non-normal angle may have accuracy affected by gravity
When using analogue meters, range should put reading at upper end of scale. Why?
Meter accuracy explained as Full Scale Deflection (FSD) value. Meter accuracy of 1% means error of +/-1% on every reading so more sensitive readings reduce this