Selling and Sales Management - Chapter 4: Strategic sales management and analytics
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Activity
Filling time with tasks
e.g. Just talking to people
Productivity
Doing important tasks with time
e.g. Making a plan to get people closer to purchasing
Customer pipeline
A way of breaking down the consumer journey from the salesperson’s perspective
Managing the consumer pipeline
Figuring out the next step that’ll move the consumer toward a sale
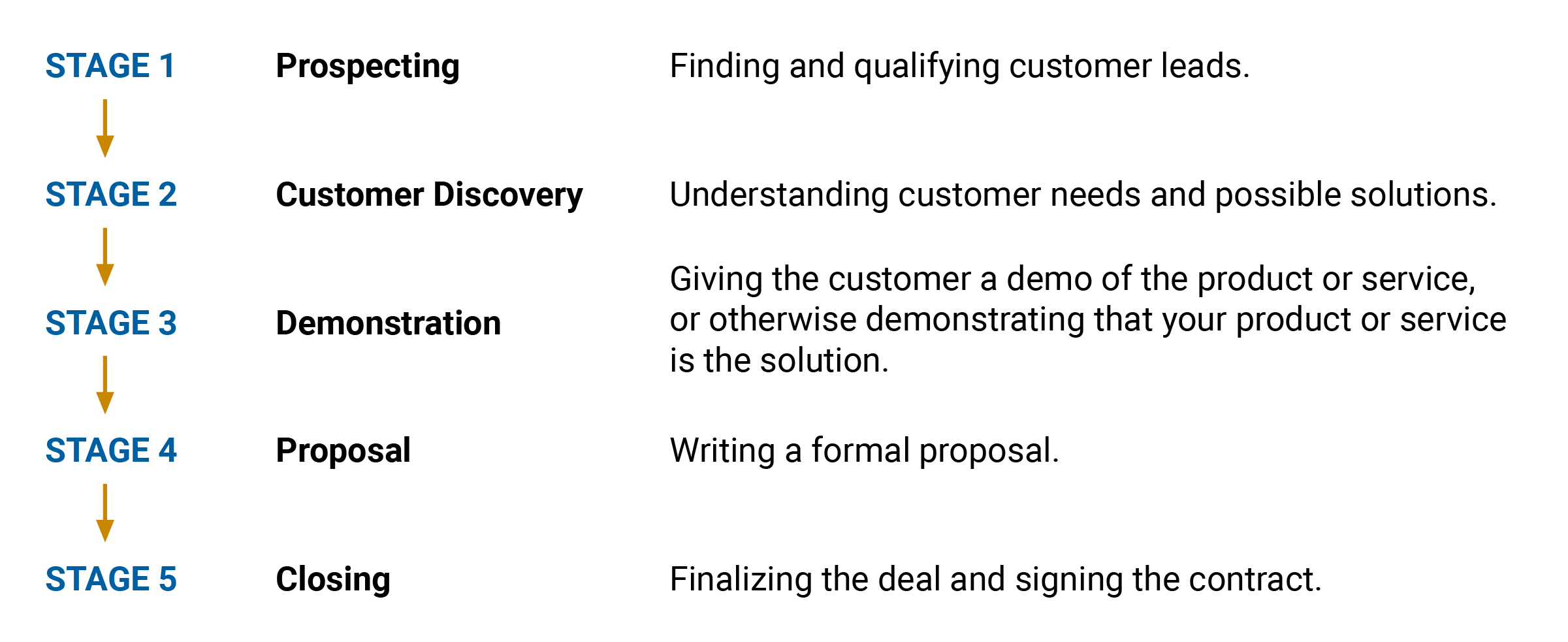
Prospecting stage
Things done to find potential customers, as well as lead qualification and initial conversations
e.g. Cold outreach, inbound/outbound sales
Customer discovery stage
Understanding customer needs and possible solutions
Needs assessment
Identifying a consumer’s needs and wants
BANT
B - Budget
A - Authority (the decision maker)
N - Needs
T - Time
How much talking should be done?
Customer should do 60% - 70%
Salespeople should do 30% - 40%
What questions should the seller ask?
Effective discovery questions to find out the consumer’s problems
Demonstration stage
Overview of the offering that conveys how it can solve the customer’s problem
e.g. A live demo of computer software and how it works
Demonstration stage (con’t)
If an offering can’t be demoed easily, then other ways must be found to demonstrate how it can solve the problem
Proposal
An overview of the offering’s features that also contains an explanation of how it can solve the consumer’s issue, pricing, and post-purchase offerings
Proposal (con’t)
The client gets a document which can be shared with others
Closing
The customer agrees to buy the product and signs a contract; the salesperson stays in close contact with the customer and works with the legal team and sales operations to make sure they won’t change their mind
When does most of the negotiation happen?
During the proposal and closing stages
Potential consumer pool
The group of potential consumers working towards a purchase
Dividing the potential consumer pool
Allows for assessment of the pool’s health when the pool is divided
Dividing the potential consumer pool example
You have 50 consumers, and after dividing them into different stages of the pipeline, there are 40 in the prospecting stage and 10 in the discovery stage
Based on the findings, you’ll need to advance the consumers to the later stages by taking the appropriate steps
Consumer pipeline conversion funnel
Measures conversion rates during the sales process
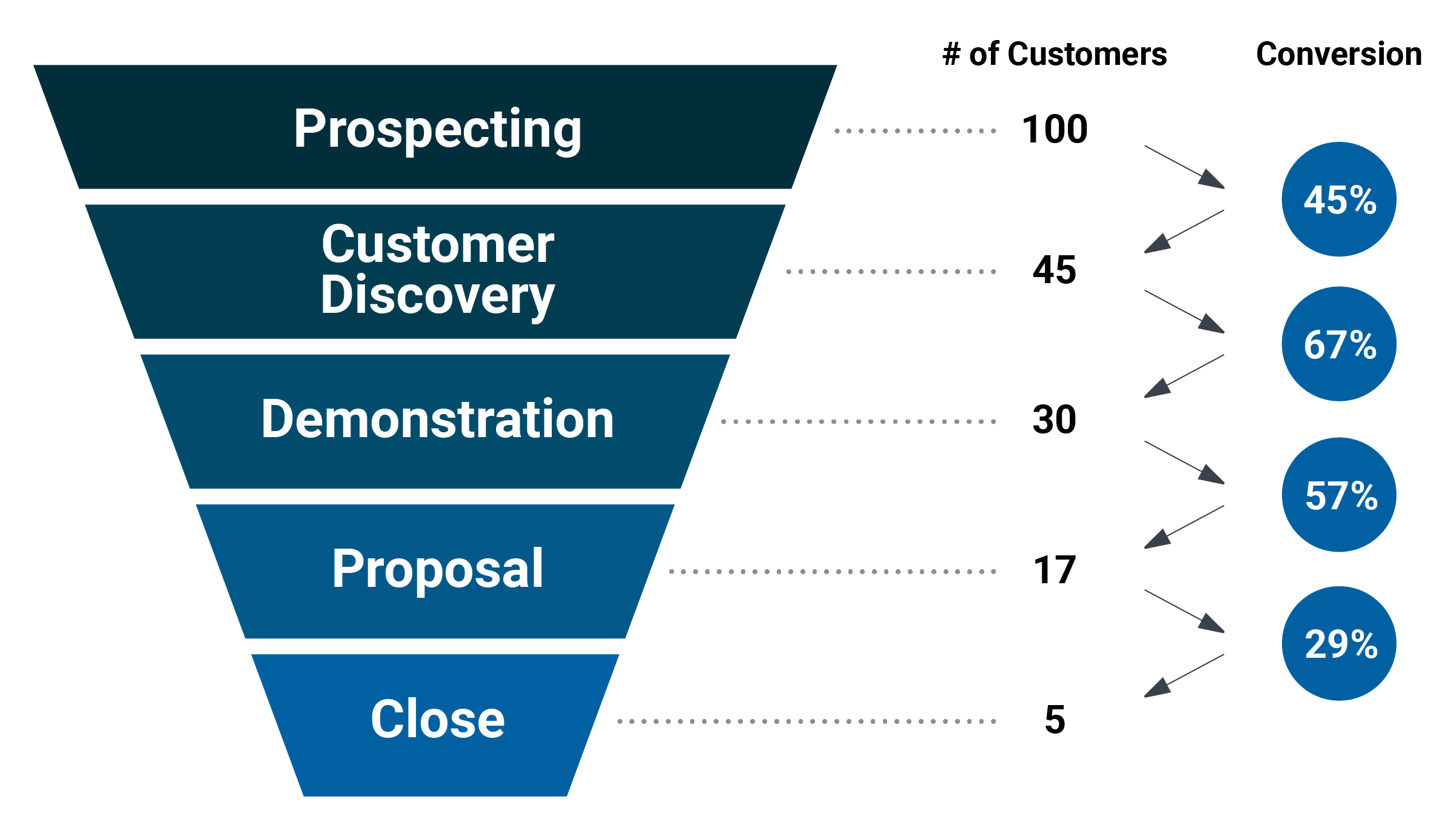
What does the sales pipeline reflect?
Reflects what a seller does during the sales process
How to manage a salespipeline
Follow up with leads
Get rid of dead leads
Monitor metrics
Give the pipeline more content
Selling analytics
Metrics and other data used to measure a salesperson’s performance and optimize selling opportunities
Customer relationship management (CRM)
Focuses on customer and deal management and enhanced lead tracking, and makes it easier for salespeople to move opportunities along the stages
How do CRMs help with organization
Preventing critical tasks from being overlooked
Ensuring leads are contacted effectively
Keeping track of leads and their contact info
Scorecard
A spreadsheet in which KPIs are emailed out to sales teams
At what point do metrics become valuable?
When sellers have something to compare them to
e.g. Dashboards show how one’s metrics compare to company averages or their goals/quotas
Time trend analytics
Patterns of data that aim to understand trends over time
Year-over-year analytics (YoY)
Compares one period of time in the current year to the same time period from the previous year; is very popular in industries where sales fluctuate seasonaly
Month-over-month (Mom)
Compares the current month to the previous month
Customer analytics
A measurement of the value and condition of a salesperson’s customers; can be measured individually or in a group
Customer analytics examples
Total revenue per customer, average order size, customer revenue growth, and acquisition cost
Market analytics
The market’s current value and future opportunities
What can a “market” be to a salesperson?
Geographic-level (location) or product-level (different product categories)
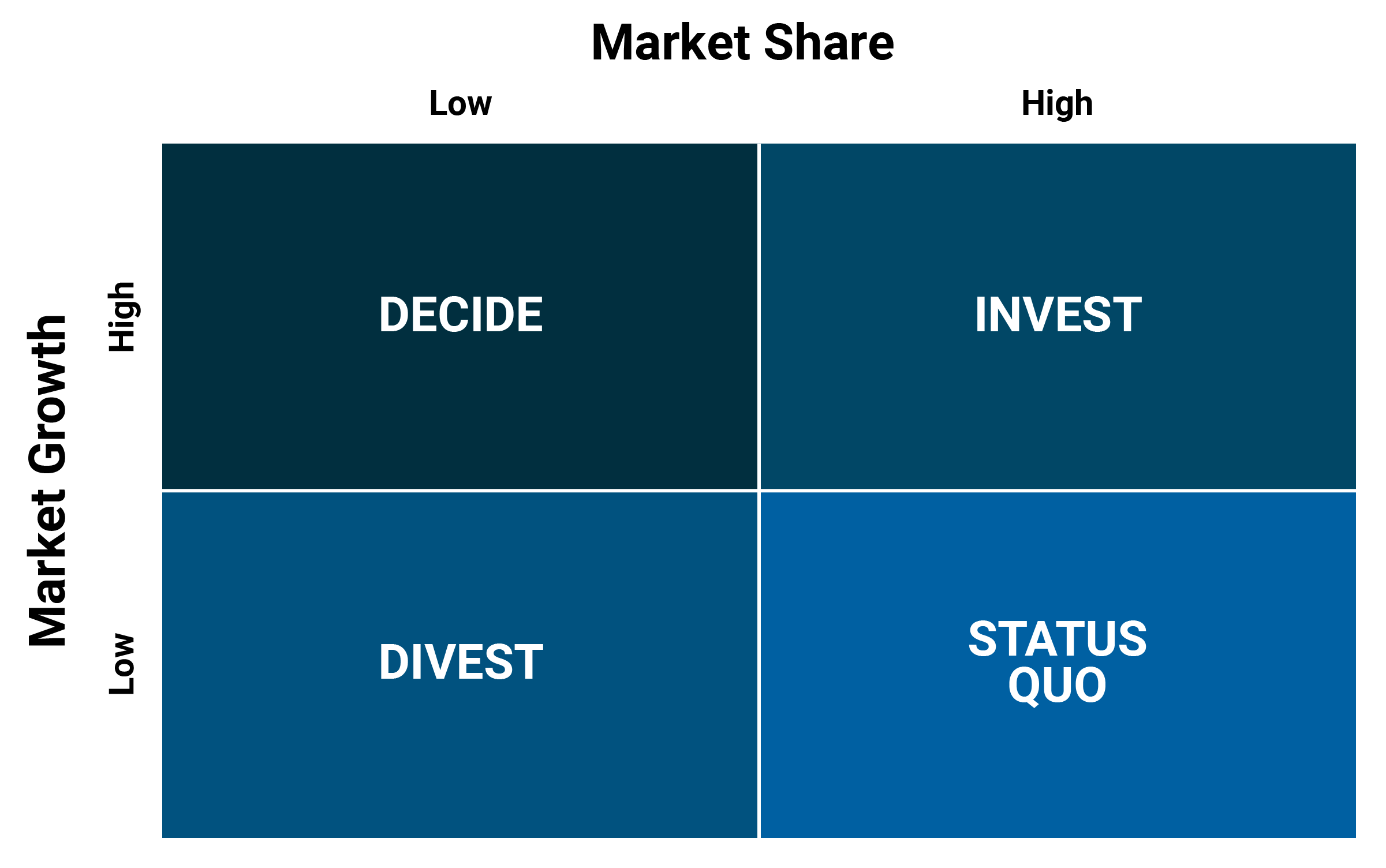
Market share
A market’s total value captured by the specific company
e.g. John Deere’s farming equipment sales is worth $15 million, and you’ve sold $5 million worth of equipment, then the market share is 33% (5 divided by 15)
Market growth
The rate at which a market is growing; is the market is growing fast, then consider increasing market share in that area
Market growth (con’t)
Is measured by year-by-year or month-by-month analytics
e.g. If the market is $15 this year and $13 last year, then the growth would be 15.38% ([15-13]/13)
Investing
Supplying more time, resources, and budget to increase sales in the market
Formula for calculating sales quota process
total revenue earned/sales revenue quota
Formula for calculating renewal rate
Total customers renewed/total customers up for renewal
Formula for calculating average order size
total revenue/total unique orders
Formula for calculating customer revenue growth
Revenue from this month - last month from customer divided by revenue last month from customer
Formula for calculating acquisition cost
Sum of all expenses used to aquire the customer