MEDCHEM 14 - carboxylic acids, fatty acids, prostaglandins
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/5
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
1
New cards

for carboxylic acids we wanna know abt properties and occurence
their reactions (acidity)
and the synthesis of carboxylic acids
their reactions (acidity)
and the synthesis of carboxylic acids
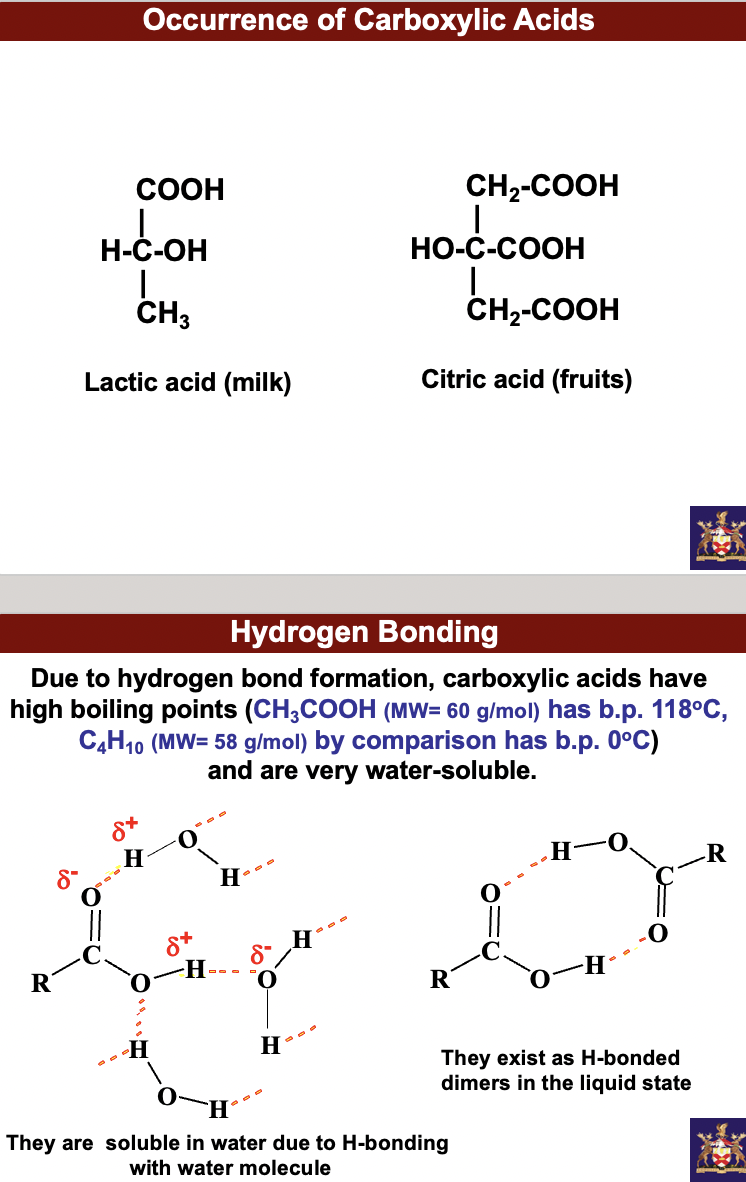
carboxylic acids, RCOOH contain the -COOH (carboxyl) group. it occurs in lactic acid and citric acid. Its a carbon liked to 3 dif atoms, trigonal planar, bond angles \~120 around carboxylic acid carbon. The carboxylic acid carbon, like carbonyl compounds, can be attacked at carbonyl carbon by nucleophiles. The OH like alcohols can be deprotonated.
\
when it comes to solids, liquids and gases, distances between particles increase when intermolecular attractions between particles are disrupted. Energy has to be provided (like temp increase) to disrupt intermolecular attractions between particles.
Due to hydrogen bond formation, carboxylic acids have high boiling points (CH3COOH (MW= 60 g/mol) has b.p. 118oC, C4H10 (MW= 58 g/mol) by comparison has b.p. 0oC) and are very water-soluble. They are soluble in water due to H-bonding with water molecule. They exist as H-bonded dimers in the liquid state
\
when it comes to solids, liquids and gases, distances between particles increase when intermolecular attractions between particles are disrupted. Energy has to be provided (like temp increase) to disrupt intermolecular attractions between particles.
Due to hydrogen bond formation, carboxylic acids have high boiling points (CH3COOH (MW= 60 g/mol) has b.p. 118oC, C4H10 (MW= 58 g/mol) by comparison has b.p. 0oC) and are very water-soluble. They are soluble in water due to H-bonding with water molecule. They exist as H-bonded dimers in the liquid state
2
New cards
physiologically important carboxylic acids
* **fatty acids** (unsat vs. sat) and prostaglandins
* long chain carboxylic acids
* lipids
* **fatty acids** (unsat vs. sat) and prostaglandins
* long chain carboxylic acids
* lipids
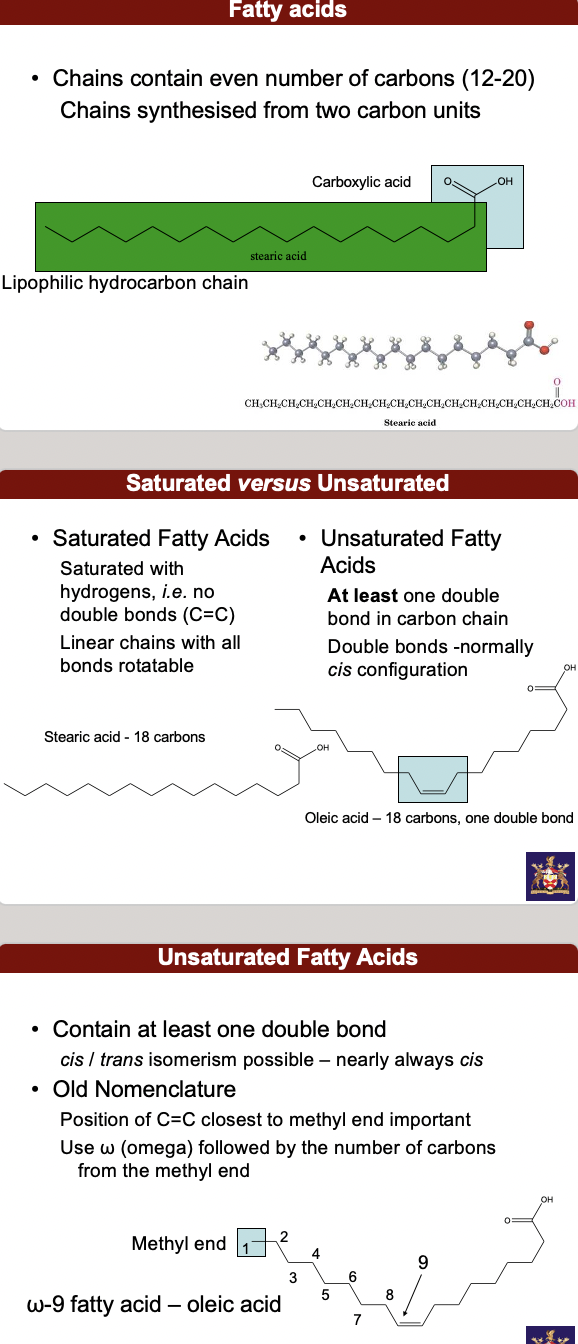
^^**fatty acid**^^ chains contain even number of carbons (12-20) chains synthesized from 2 carbon units: the lipophilic hydrocarbon chain and the carboxylic acid.
**• Saturated** Fatty Acids Saturated with hydrogens, *i.e.* no double bonds (C=C) Linear chains with all bonds rotatable
**• Unsaturated** Fatty Acids **At least** one double bond in carbon chain Double bonds -normally *cis* configuration. Contain at least one double bond *cis* / *trans* isomerism possible – nearly always *cis*
• Old Nomenclature - Position of C=C closest to methyl end important. Use ω (omega) followed by the number of carbons from the methyl end
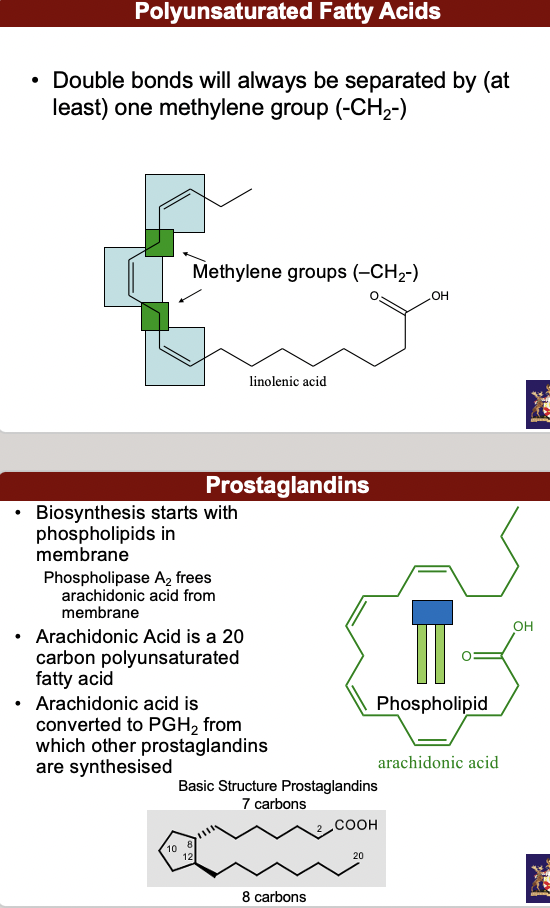
**• Polyunsaturated** fatty acids - Double bonds will always be separated by (at least) one methylene group (-CH2-)
^^**Prostaglandins**^^
• Biosynthesis starts with phospholipids in membrane. Phospholipase A2 frees arachidonic acid from membrane
• Arachidonic Acid is a 20 carbon polyunsaturated fatty acid
• Arachidonic acid is converted to PGH2 from which other prostaglandins are synthesized
**• Saturated** Fatty Acids Saturated with hydrogens, *i.e.* no double bonds (C=C) Linear chains with all bonds rotatable
**• Unsaturated** Fatty Acids **At least** one double bond in carbon chain Double bonds -normally *cis* configuration. Contain at least one double bond *cis* / *trans* isomerism possible – nearly always *cis*
• Old Nomenclature - Position of C=C closest to methyl end important. Use ω (omega) followed by the number of carbons from the methyl end
**• Polyunsaturated** fatty acids - Double bonds will always be separated by (at least) one methylene group (-CH2-)
^^**Prostaglandins**^^
• Biosynthesis starts with phospholipids in membrane. Phospholipase A2 frees arachidonic acid from membrane
• Arachidonic Acid is a 20 carbon polyunsaturated fatty acid
• Arachidonic acid is converted to PGH2 from which other prostaglandins are synthesized
3
New cards
reactions (acidity) - carboxylic acids form salts
dissociation (ionization) of carboxylic acids
Ka and pKa
dissociation (ionization) of carboxylic acids
Ka and pKa
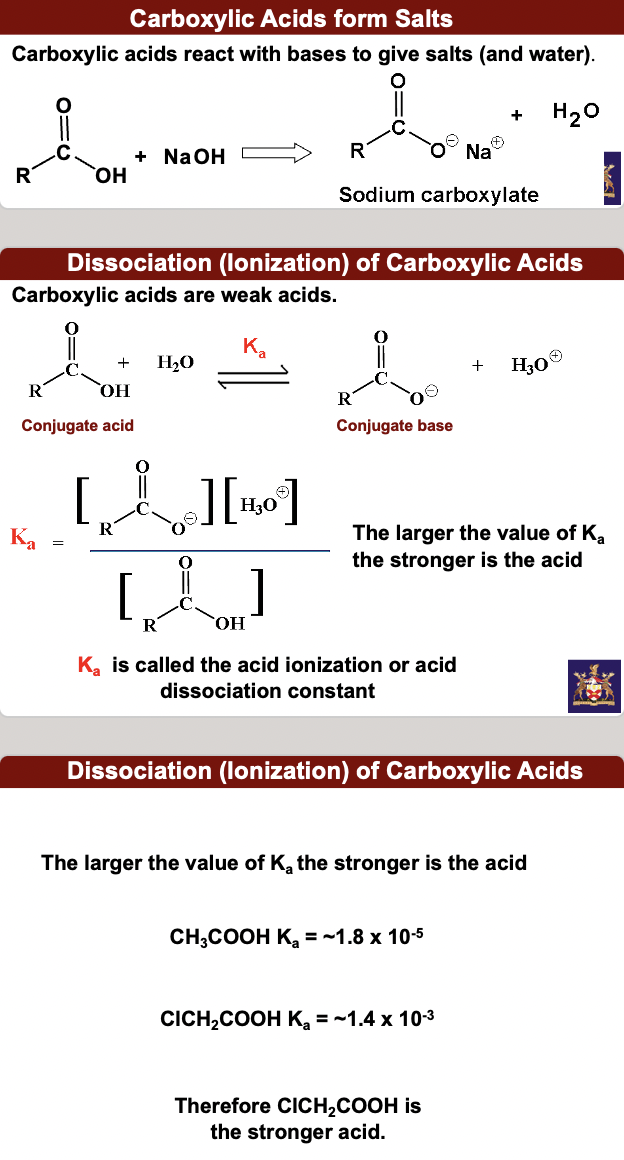
**carboxylic acids react with bases to give salts (and water).**
carboxylic acids (CAs) are weak acids (WAs). The larger the value of Ka the stronger is the acid. Ka is called the acid ionization or acid dissociation constant.
The larger the value of Ka the stronger is the acid
CH3COOH Ka = \~1.8 x 10’-5
ClCH2COOH Ka = \~1.4 x 10’-3
Therefore ClCH2COOH is the stronger acid.
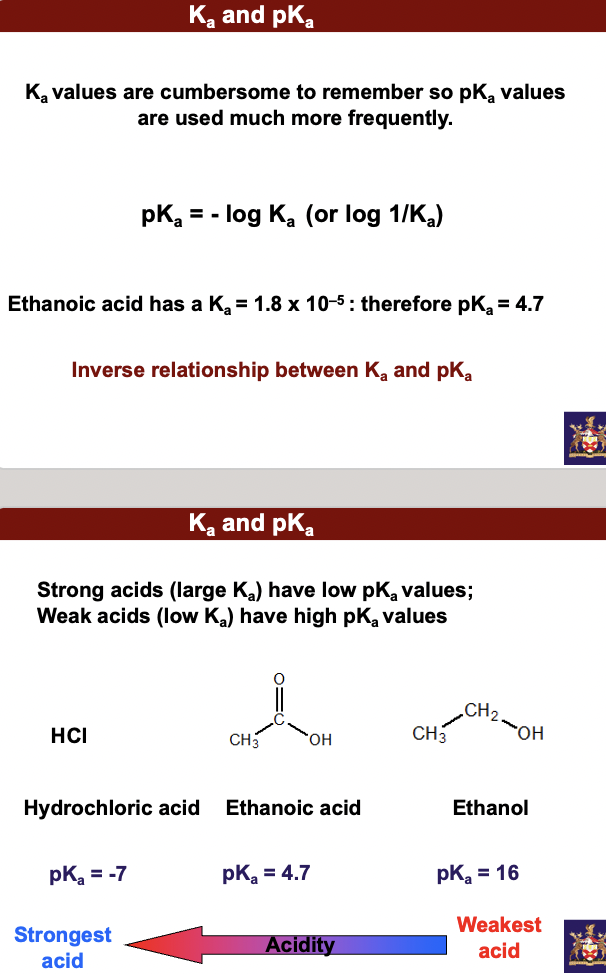
**Ka values are cumbersome to remember so pKa values are used much more frequently.**
**pKa = - log Ka (or log 1/Ka)**
Ethanoic acid has a Ka = 1.8 x 10–5 : therefore pKa= 4.7
Inverse relationship between Ka and pKa
**Strong acids (large Ka) have low pKa values; Weak acids (low Ka) have high pKa values**
carboxylic acids (CAs) are weak acids (WAs). The larger the value of Ka the stronger is the acid. Ka is called the acid ionization or acid dissociation constant.
The larger the value of Ka the stronger is the acid
CH3COOH Ka = \~1.8 x 10’-5
ClCH2COOH Ka = \~1.4 x 10’-3
Therefore ClCH2COOH is the stronger acid.
**Ka values are cumbersome to remember so pKa values are used much more frequently.**
**pKa = - log Ka (or log 1/Ka)**
Ethanoic acid has a Ka = 1.8 x 10–5 : therefore pKa= 4.7
Inverse relationship between Ka and pKa
**Strong acids (large Ka) have low pKa values; Weak acids (low Ka) have high pKa values**
4
New cards
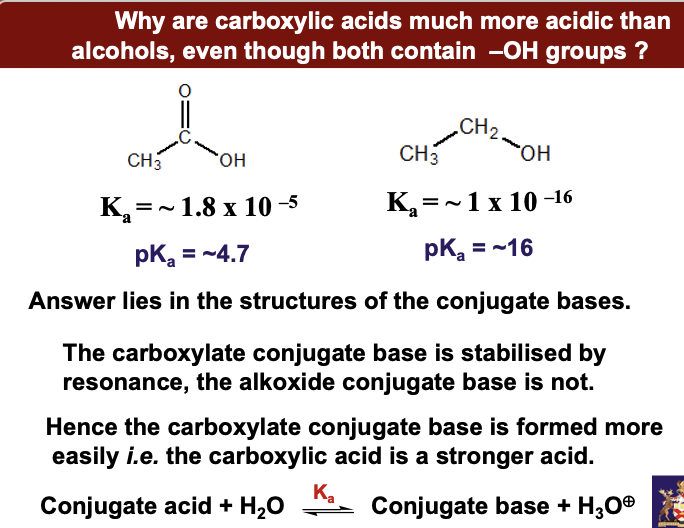
**Why are carboxylic acids much more acidic than alcohols, even though both contain –OH groups ?**
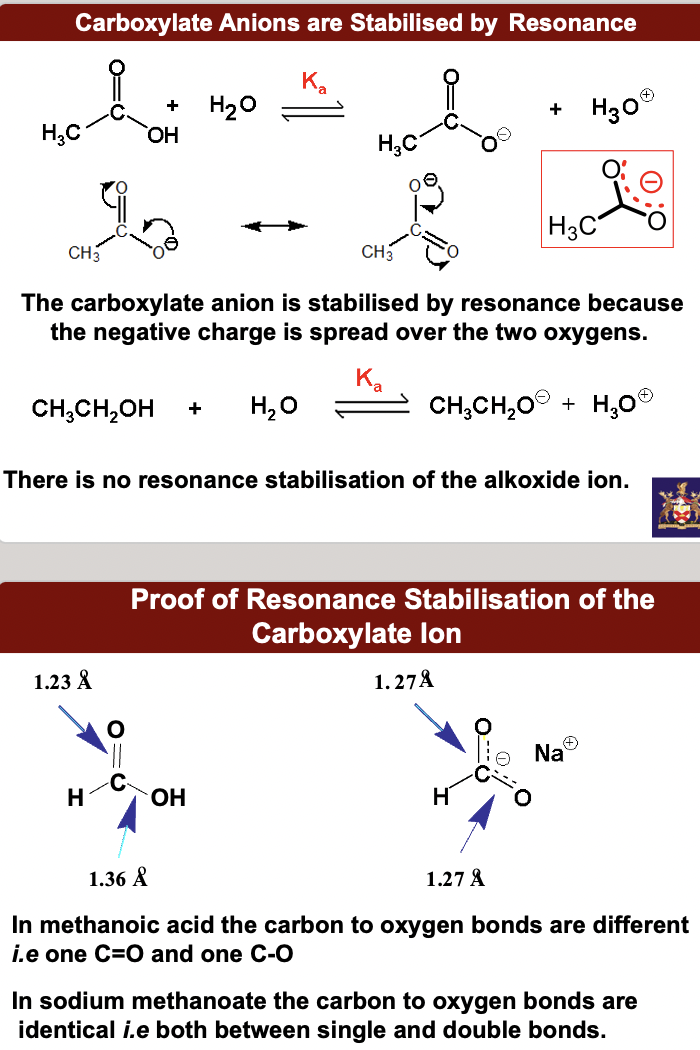
Carboxylate Anions are Stabilised by Resonance
Proof of Resonance Stabilisation of the Carboxylate Ion
Carboxylate Anions are Stabilised by Resonance
Proof of Resonance Stabilisation of the Carboxylate Ion
Answer lies in the structures of the conjugate bases. **The carboxylate conjugate base is stabilised by resonance, the alkoxide conjugate base is not. Hence the carboxylate conjugate base is formed more easily** ***i.e.*** **the carboxylic acid is a stronger acid.**
Conjugate acid + H2O
Conjugate acid + H2O
5
New cards
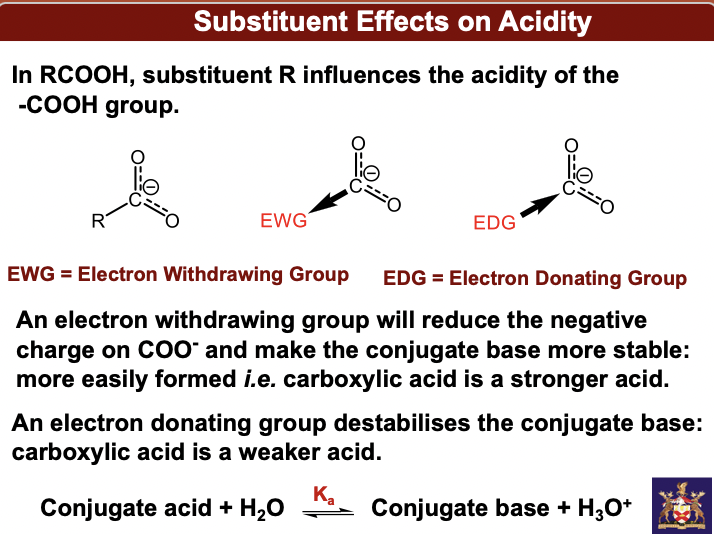
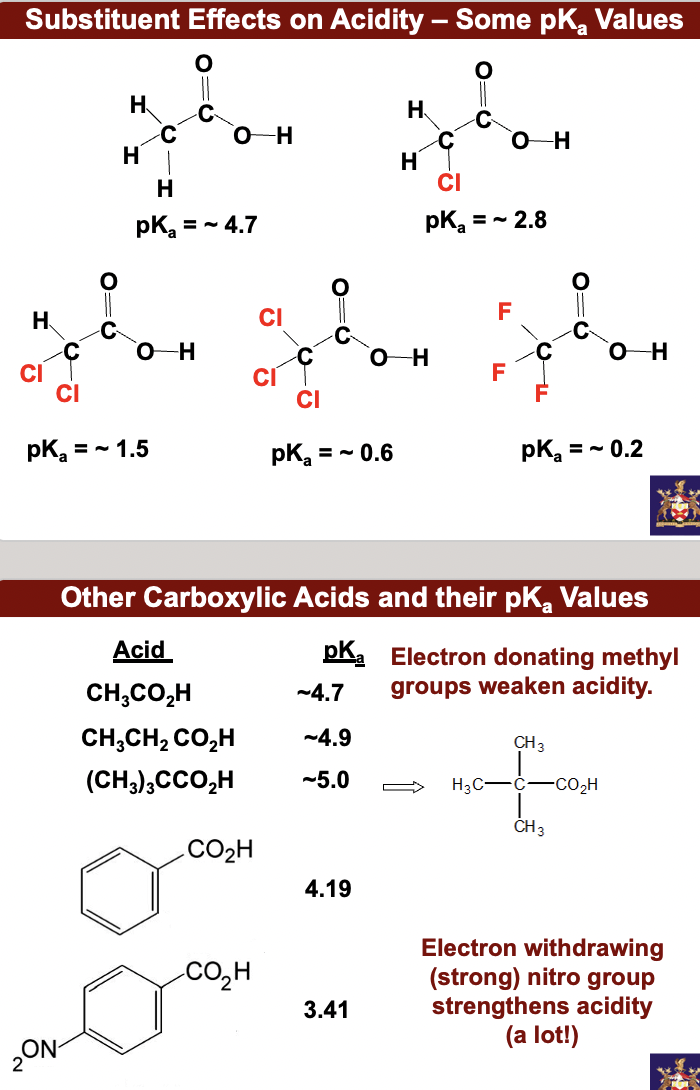
Substituent effects on acidity
other carboxylic acids and their pKa values
other carboxylic acids and their pKa values
**In RCOOH, substituent R influences the acidity of the -COOH group.\**
EWG = Electron Withdrawing Group
EDG = Electron Donating Group
An electron withdrawing group will reduce the negative charge on COO- and make the conjugate base more stable: more easily formed *i.e.* carboxylic acid is a stronger acid. An electron donating group destabilises the conjugate base: carboxylic acid is a weaker acid.
Conjugate acid + H2O
EWG = Electron Withdrawing Group
EDG = Electron Donating Group
An electron withdrawing group will reduce the negative charge on COO- and make the conjugate base more stable: more easily formed *i.e.* carboxylic acid is a stronger acid. An electron donating group destabilises the conjugate base: carboxylic acid is a weaker acid.
Conjugate acid + H2O
6
New cards
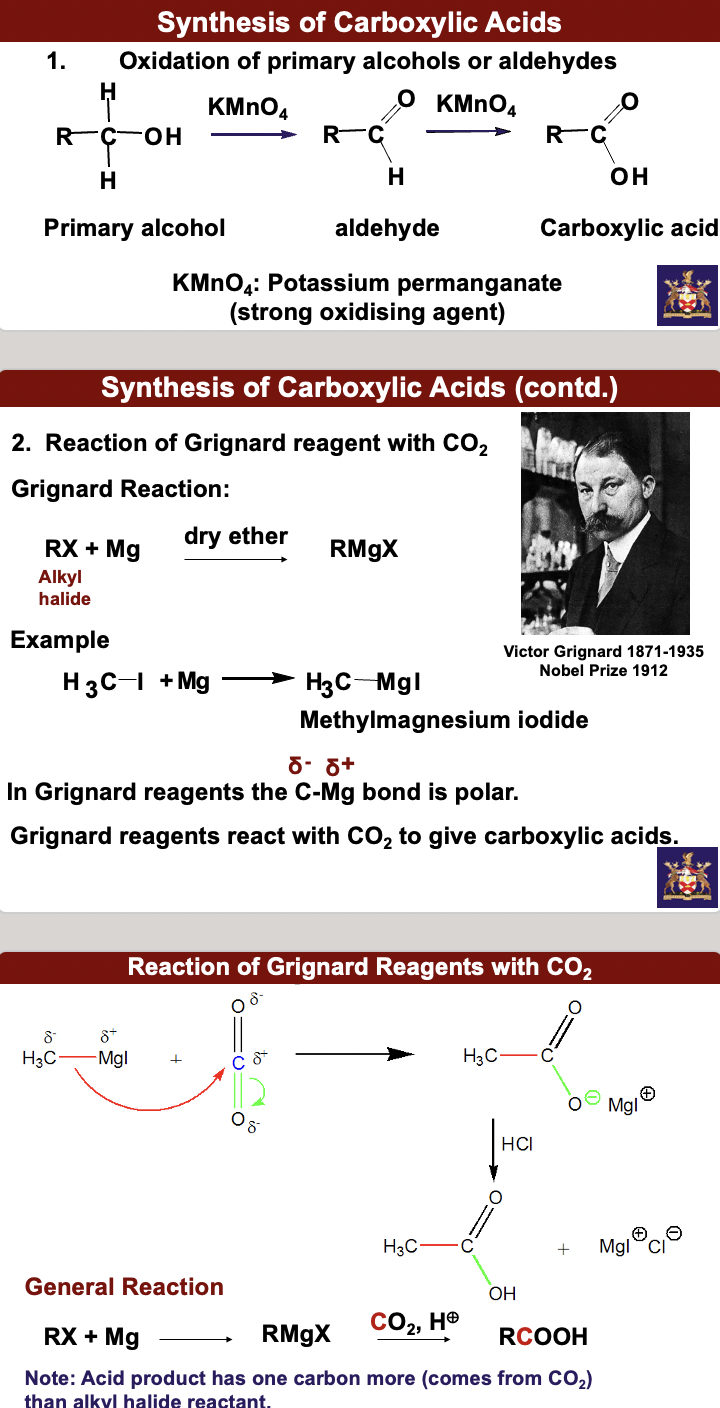
synthesis of carboxylic acids
synthesis of benzoic acids and oxidation of alkybenzene side chains
synthesis of benzoic acids and oxidation of alkybenzene side chains
1. oxidation of primary alcohols or aldehydes : primary alcohol → aldehyde → carboxylic acid by way of KMnO4: Potassium permanganate (strong oxidizing agent)
2. Reaction of Gringnard reagent w CO2. Grignard Reaction:
Rx(alkyl halide) + Mg -dry ether→ RMgX
Example: H3C-l + Mg → H3C-MgI (methlymagnesium iodide)
In Gringnard reagents the C-Mg bond is polar (delta minus C and delta+ Mg). Grignard reagents react w CO2 to give carboxylic acids.
3. Oxidation of an alkylbenzene w KMnO4 gives a benzoic acid. Alkylbenzene: methyl, primary and secondary, but not tertiary alkyl groups are oxidized.