Apologia Biology (3rd edition) Module 4
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
83 Terms
Cytology
study of cells
Ingestion
ability to take in nutrients

Digestion
Breakdown of food substances into simpler forms that can be absorbed and used
Respiration
The process by which cells break down simple food molecules to release the energy they contain.

Transport
ability to distribute or circulate molecules from one part of a cell to another
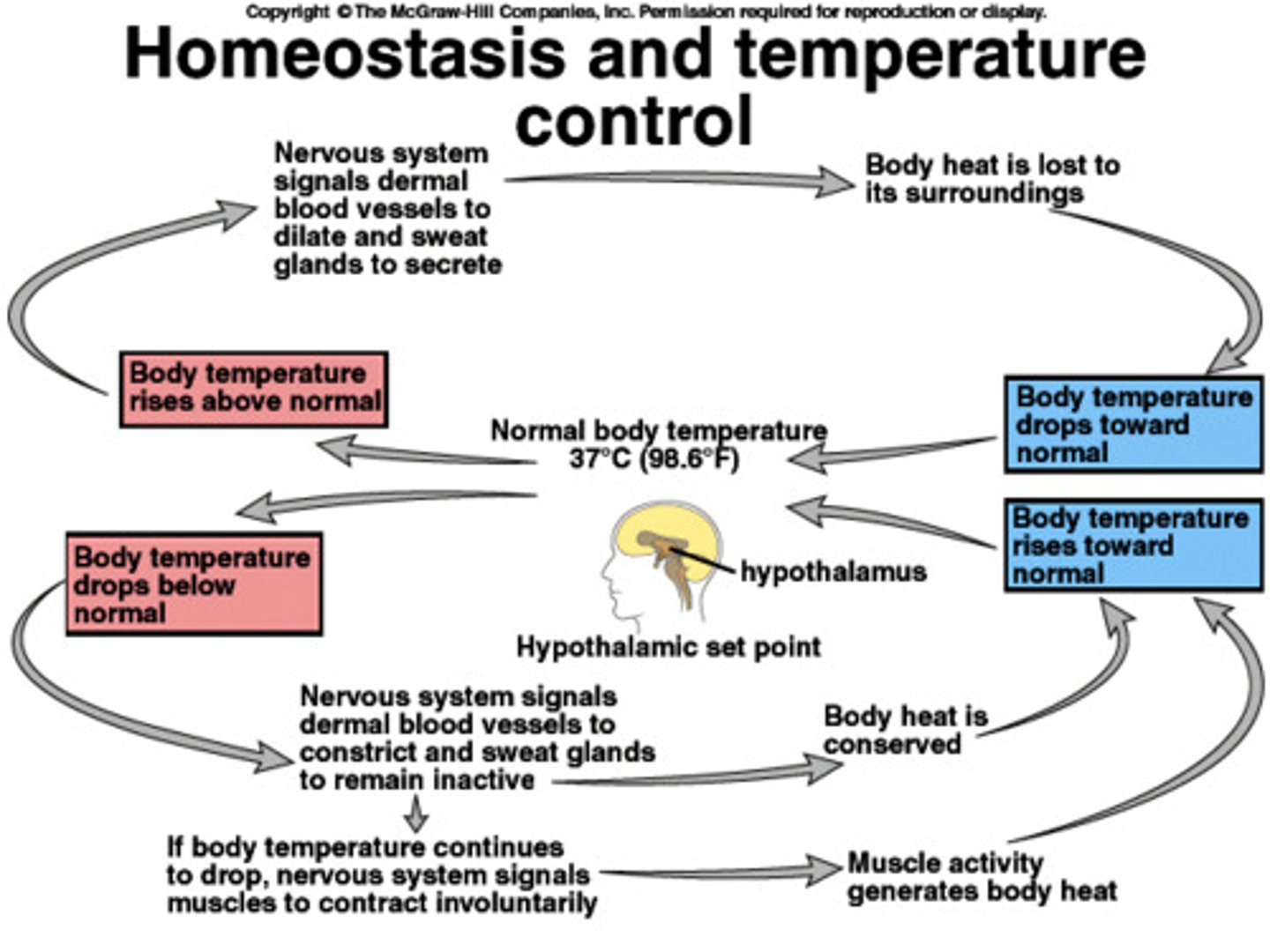
Homeostasis
ability to maintain internal stability
Synthesis
Combine simple compounds into complex molecules
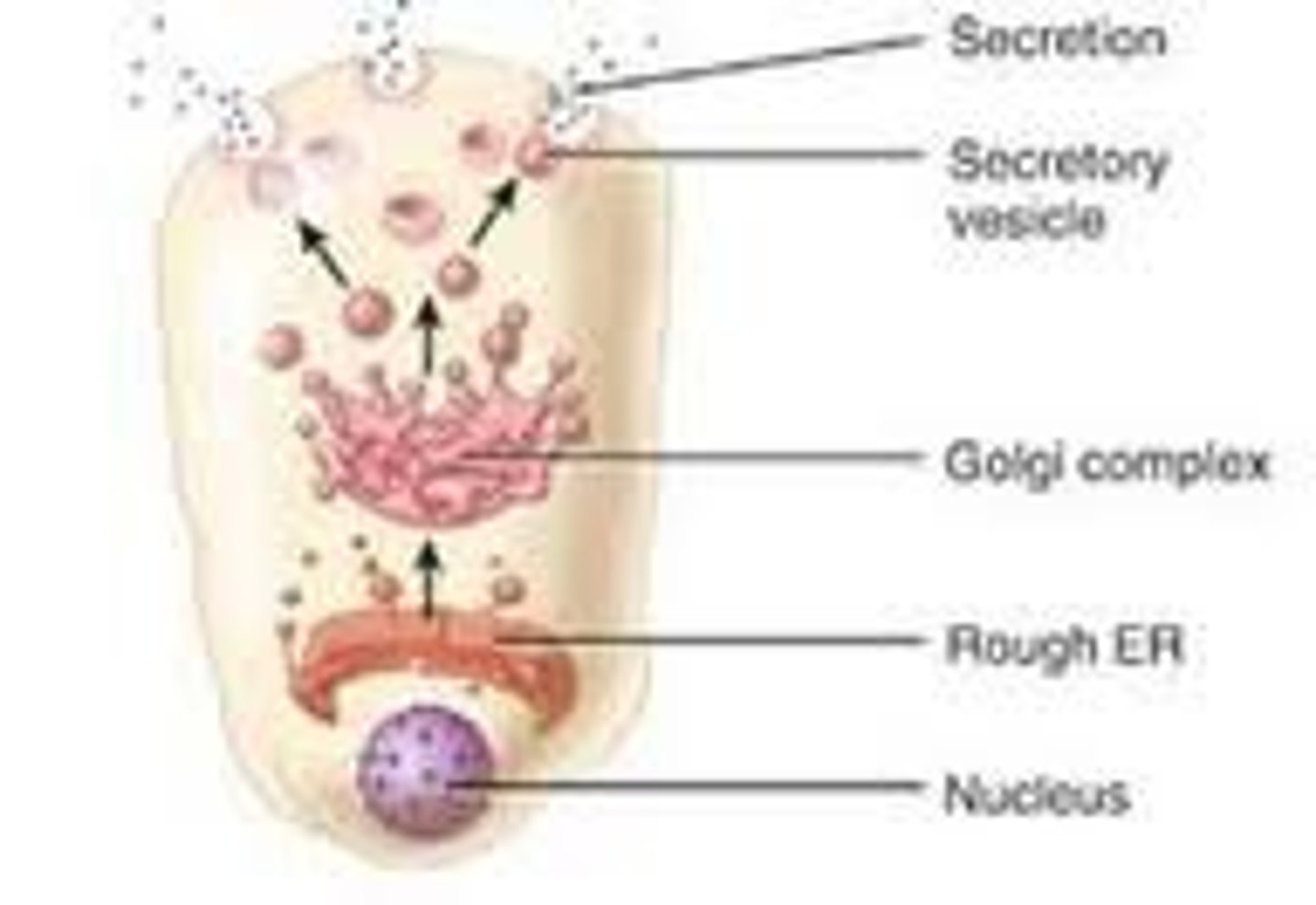
Secretion
The release of biosynthesized substances.
Excretion
the process by which wastes are removed from the cell

Egestion
The removal of nonsoluble waste materials.

irritability
ability to respond to stimuli

Movement
ability to move
Reproduction
ability to produce more cells

Organelle
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell

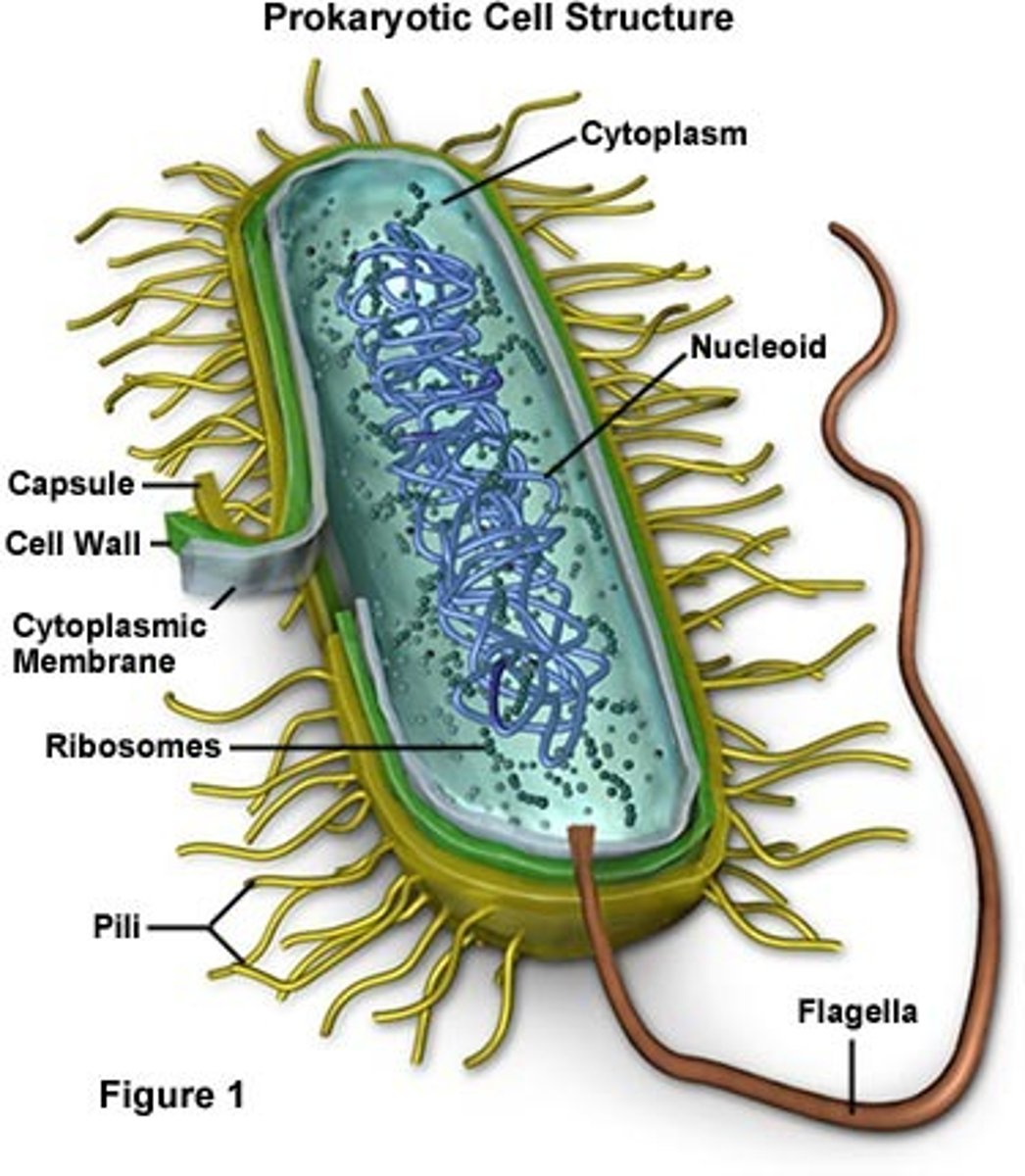
Prokaryotic
cells that do not have a nucleus
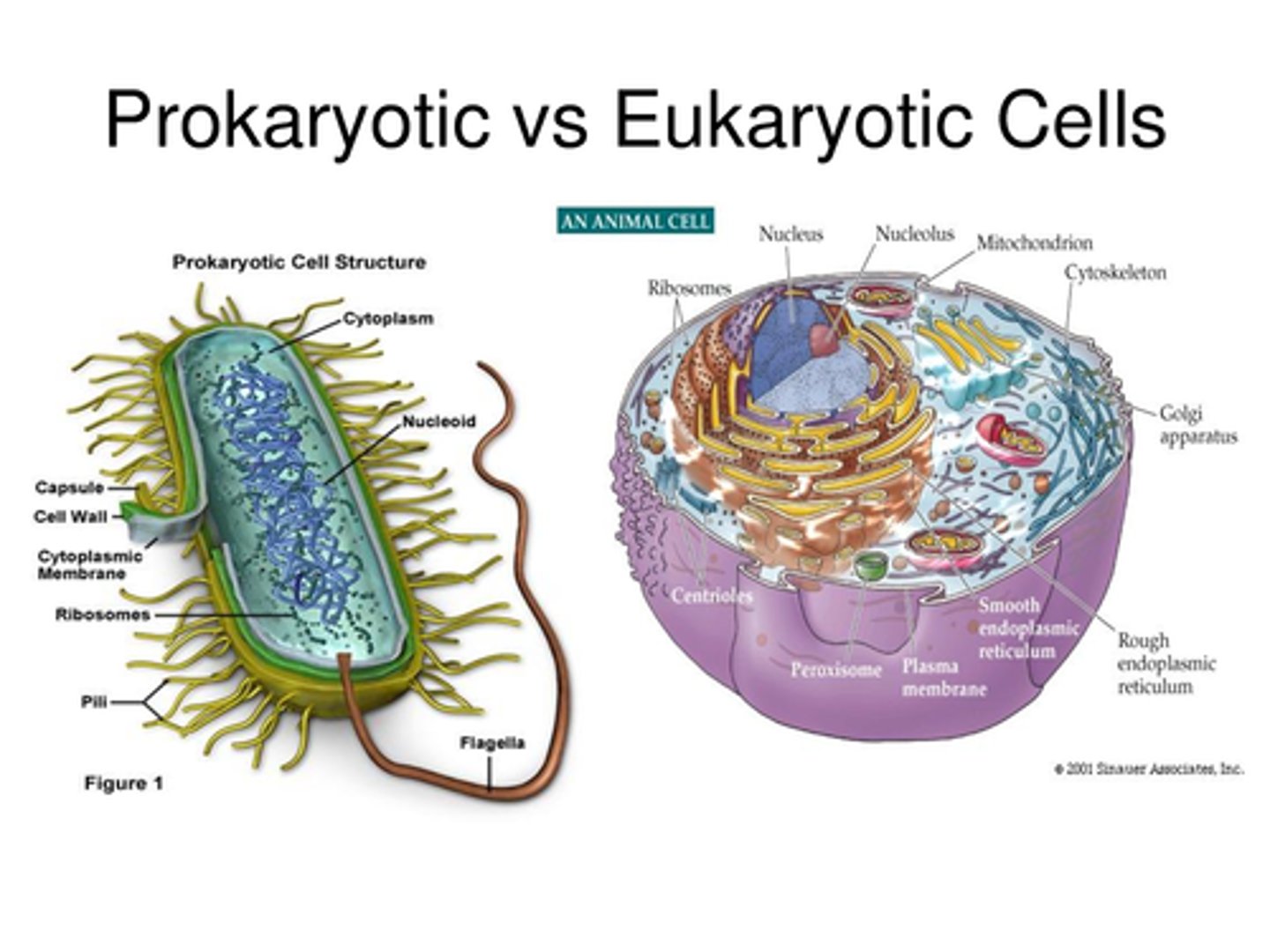
Eukaryotic
Cell with a nucleus (surrounded by its own membrane) and other internal organelles.
membrane
thin layer of tissue covering a structure or cavity
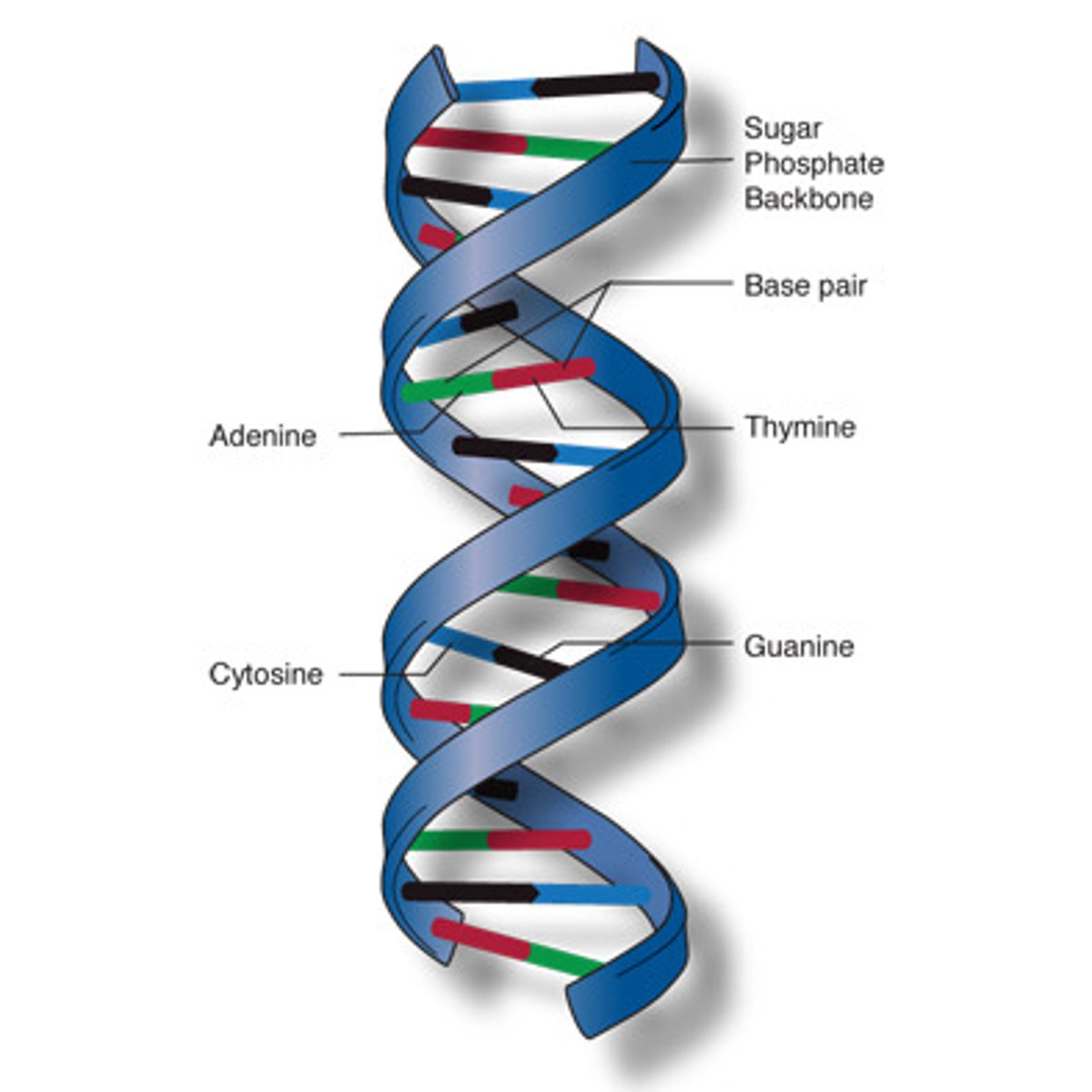
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
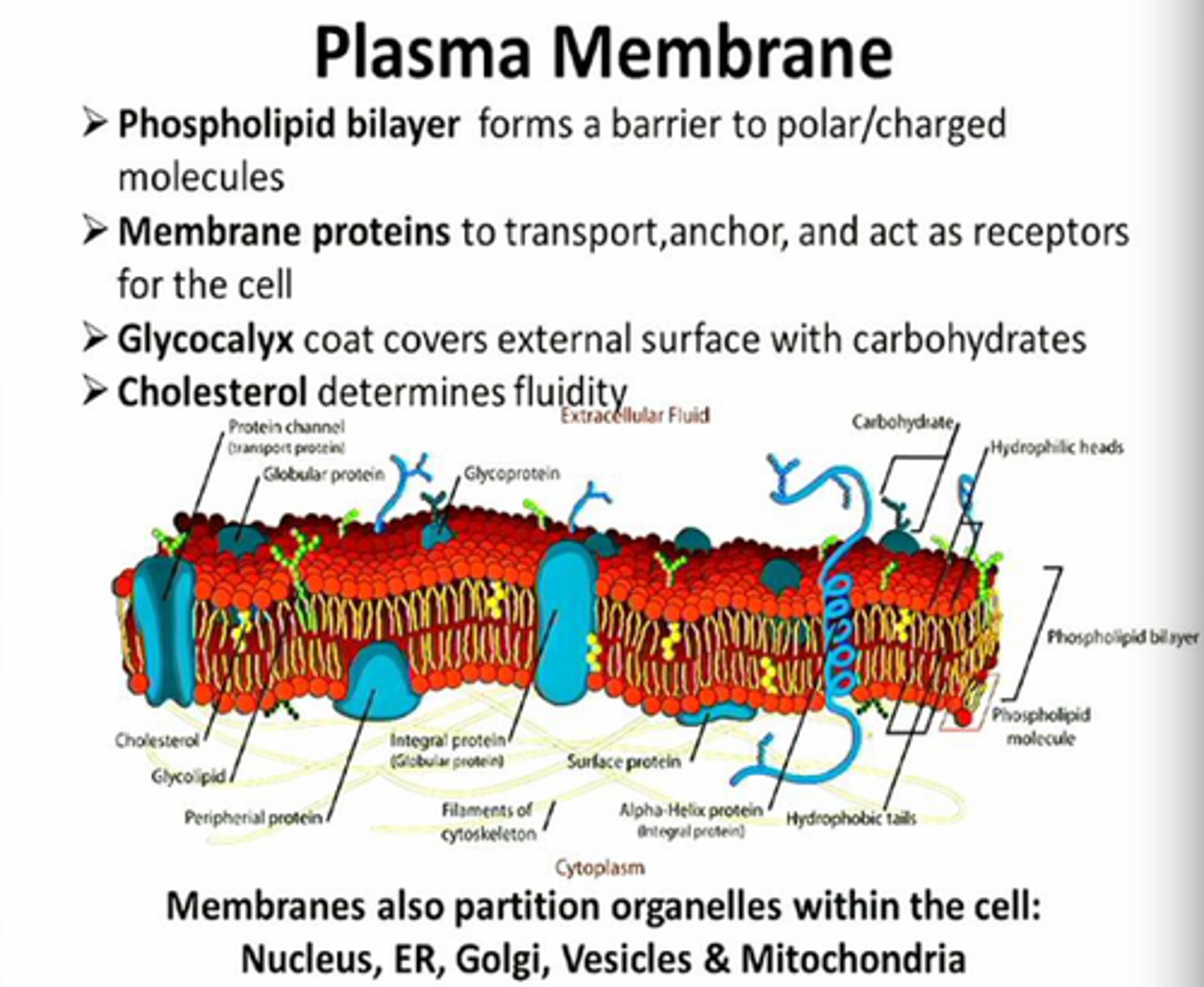
plasma membrane (cell membrane)
Flexible, selectively permeable (having pores or openings) boundary that helps control what enters and leave the cell.
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
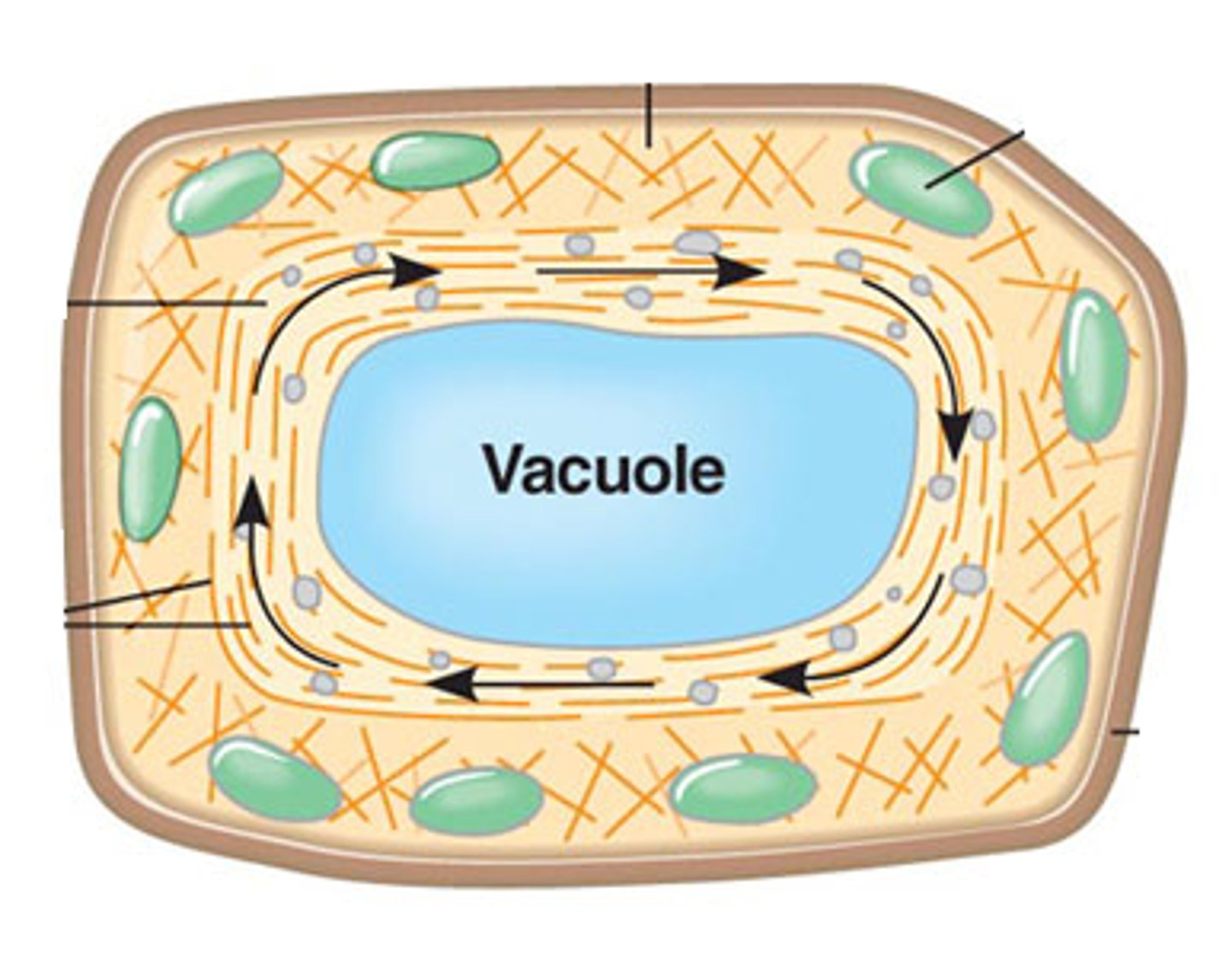
cytoplasmic streaming
The motion of cytoplasm in a cell that results in a coordinated movement of the cell's contents.
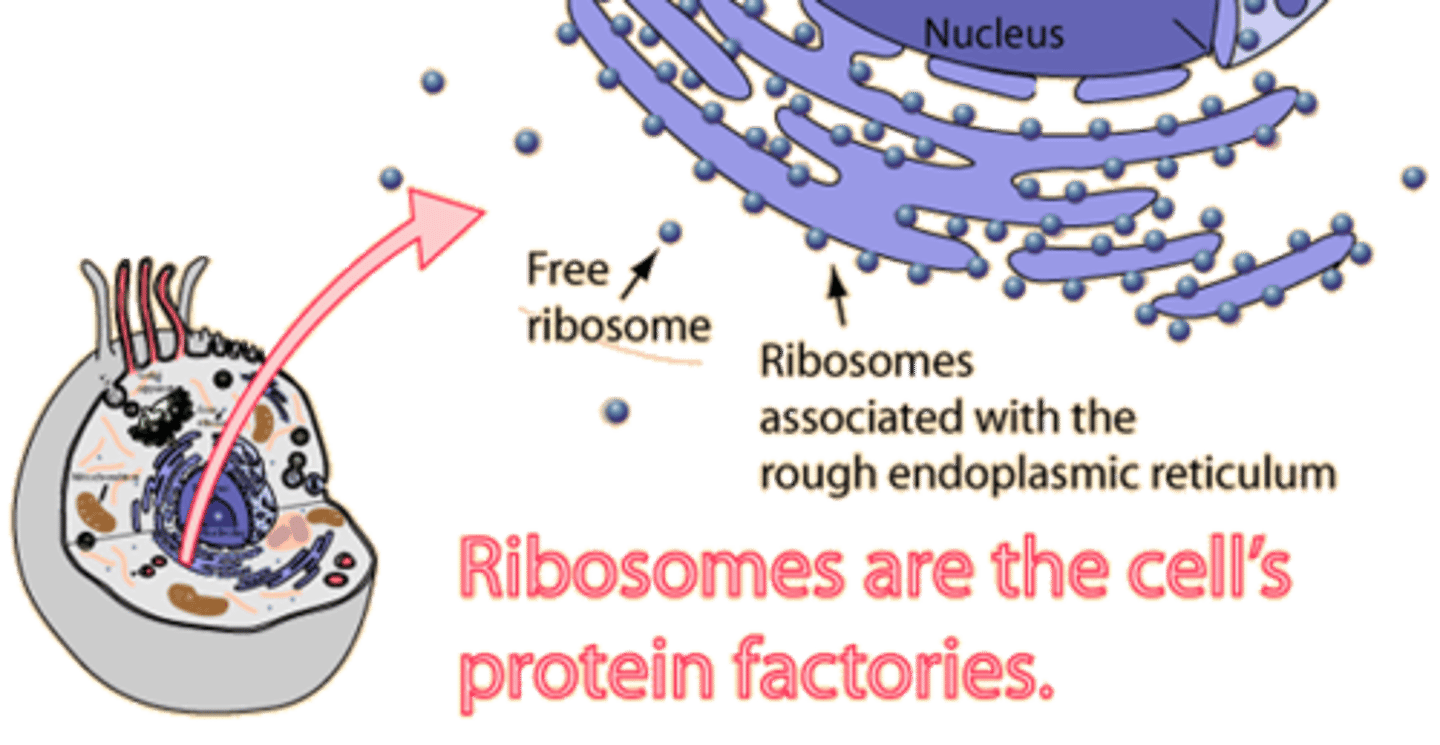
Ribosomes
site of protein synthesis
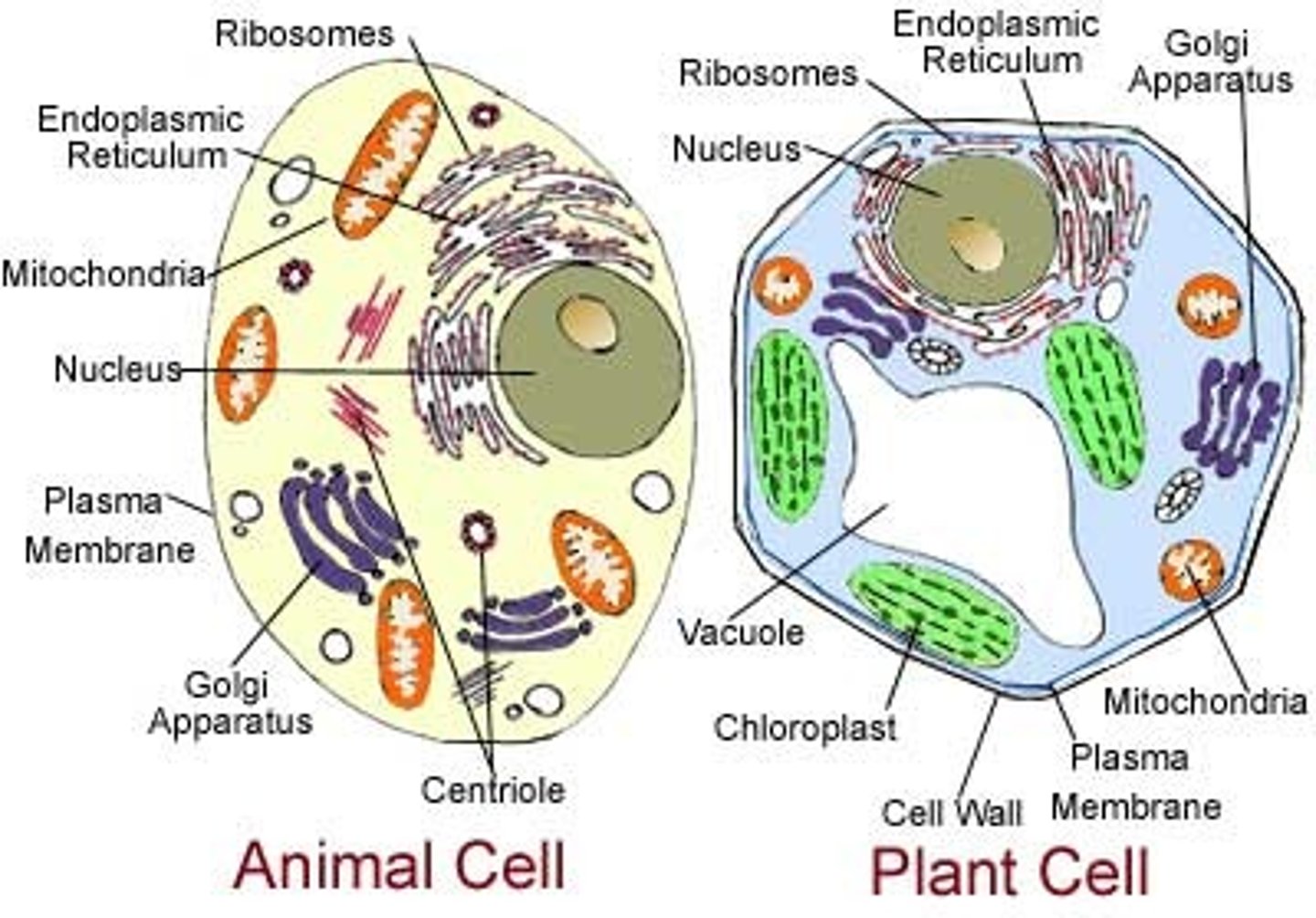
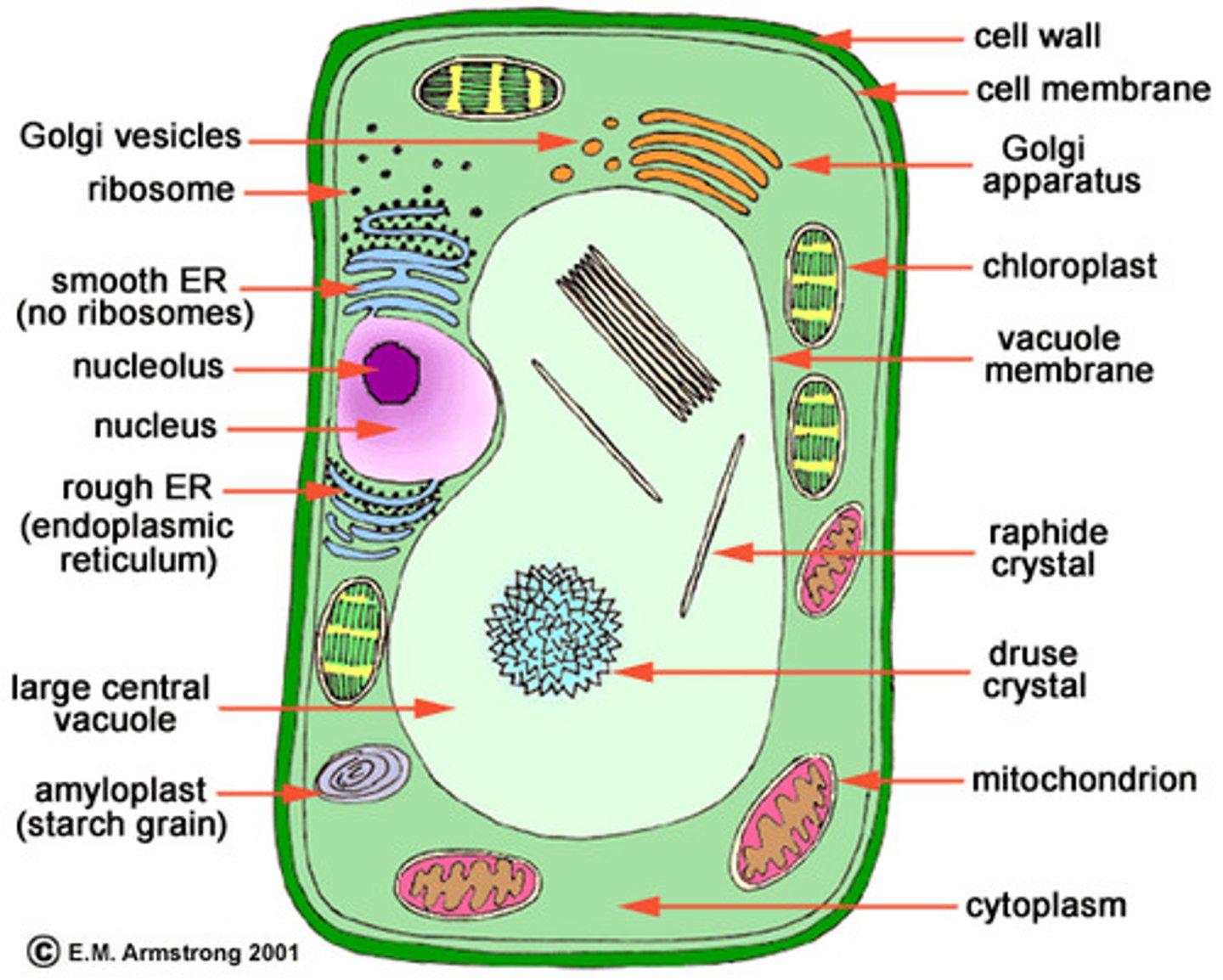
plant cell
contains a cell wall, chloroplast and large vacuole
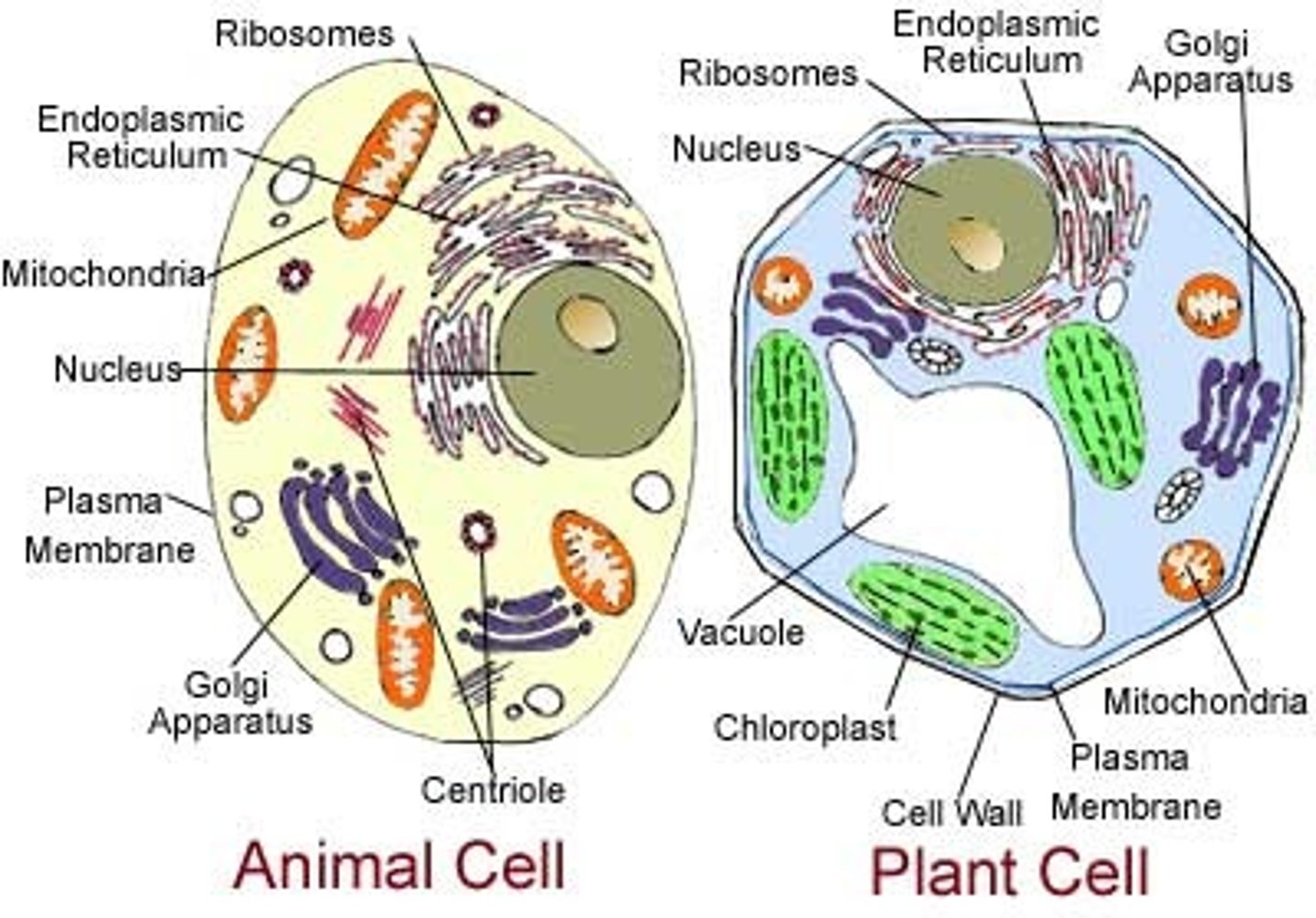
animal cell
does not have a cell wall or chloroplast and a small vacuole
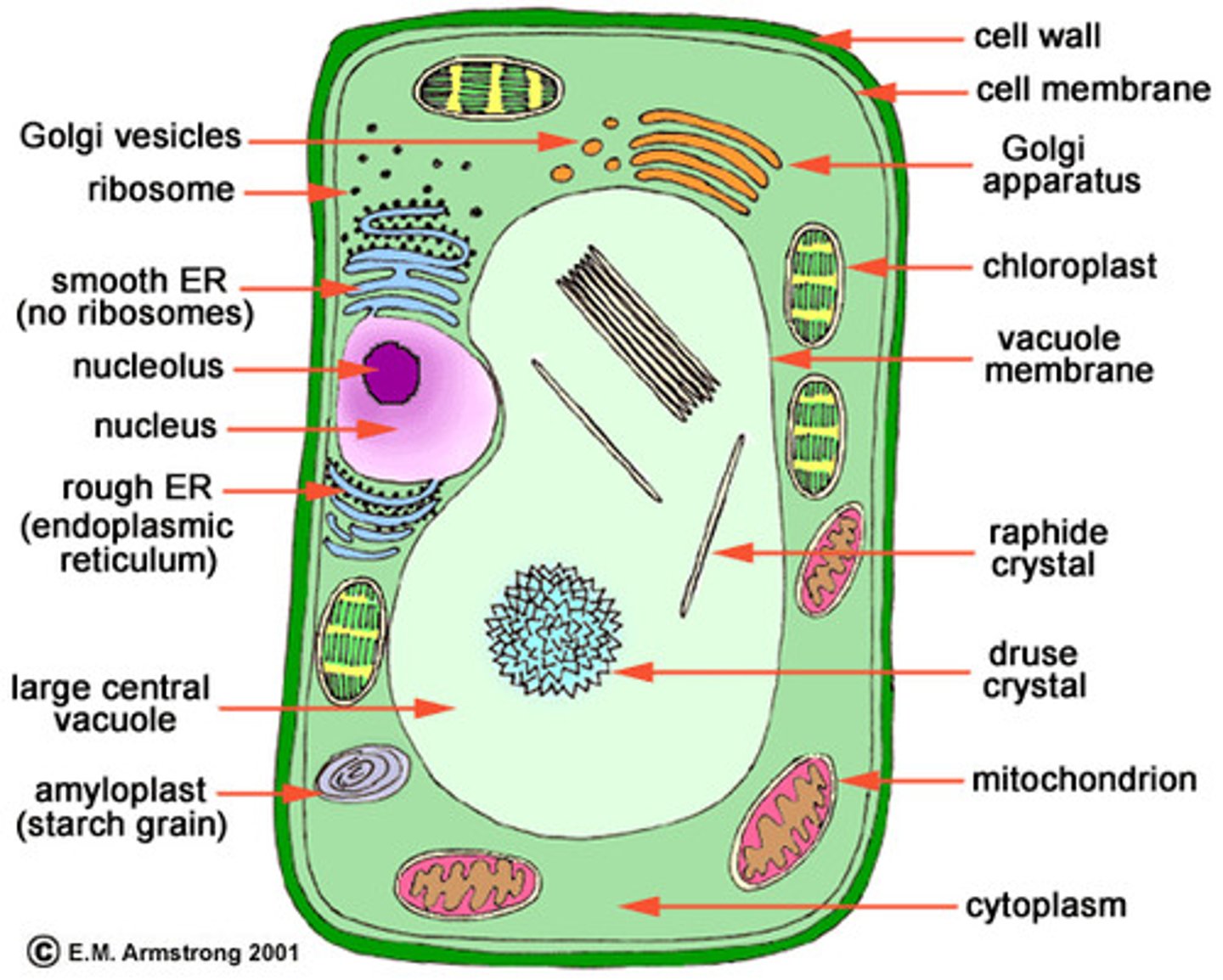
cell wall
A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to the cell
pectin
A carbohydrate that hardens cellulose
Plasmodesmata
Pores in the cell wall that let water and nutrients enter and exit and allows communication with neighboring cells
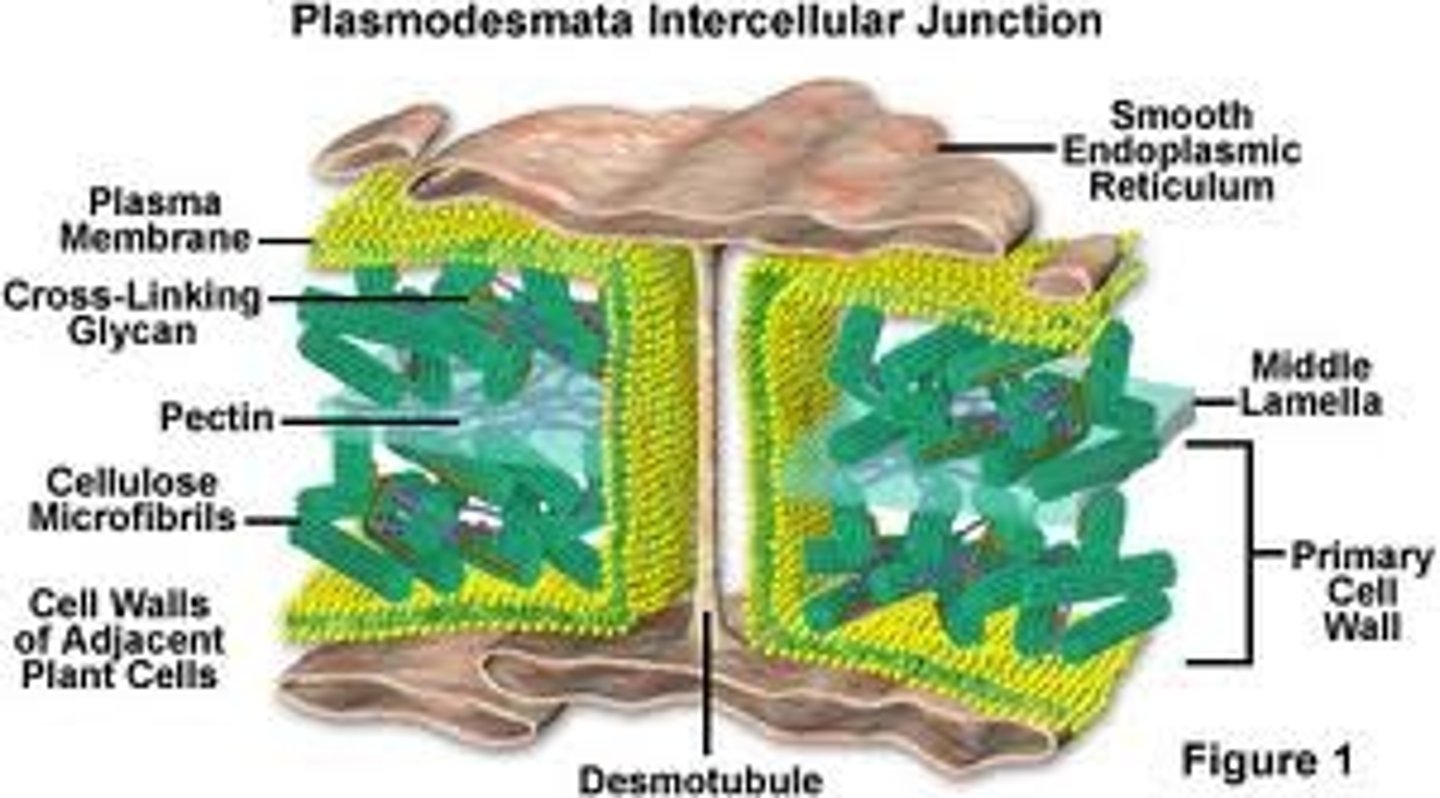
secondary cell wall
A rigid, permeable wall inside the primary wall of many plant cells; forms after the first growing season.
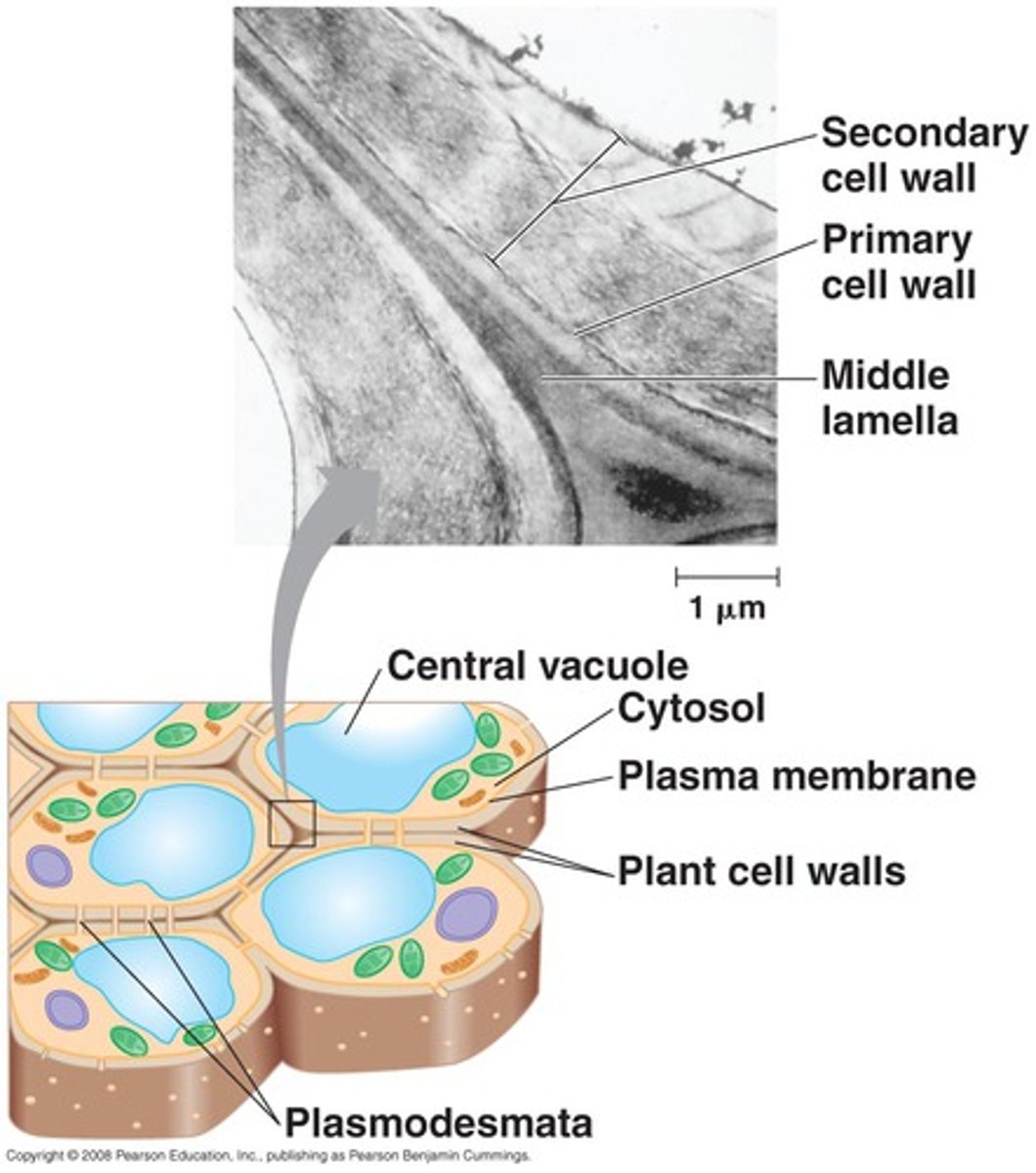
primary cell wall
In plants, a relatively thin and flexible layer first secreted by a young cell.
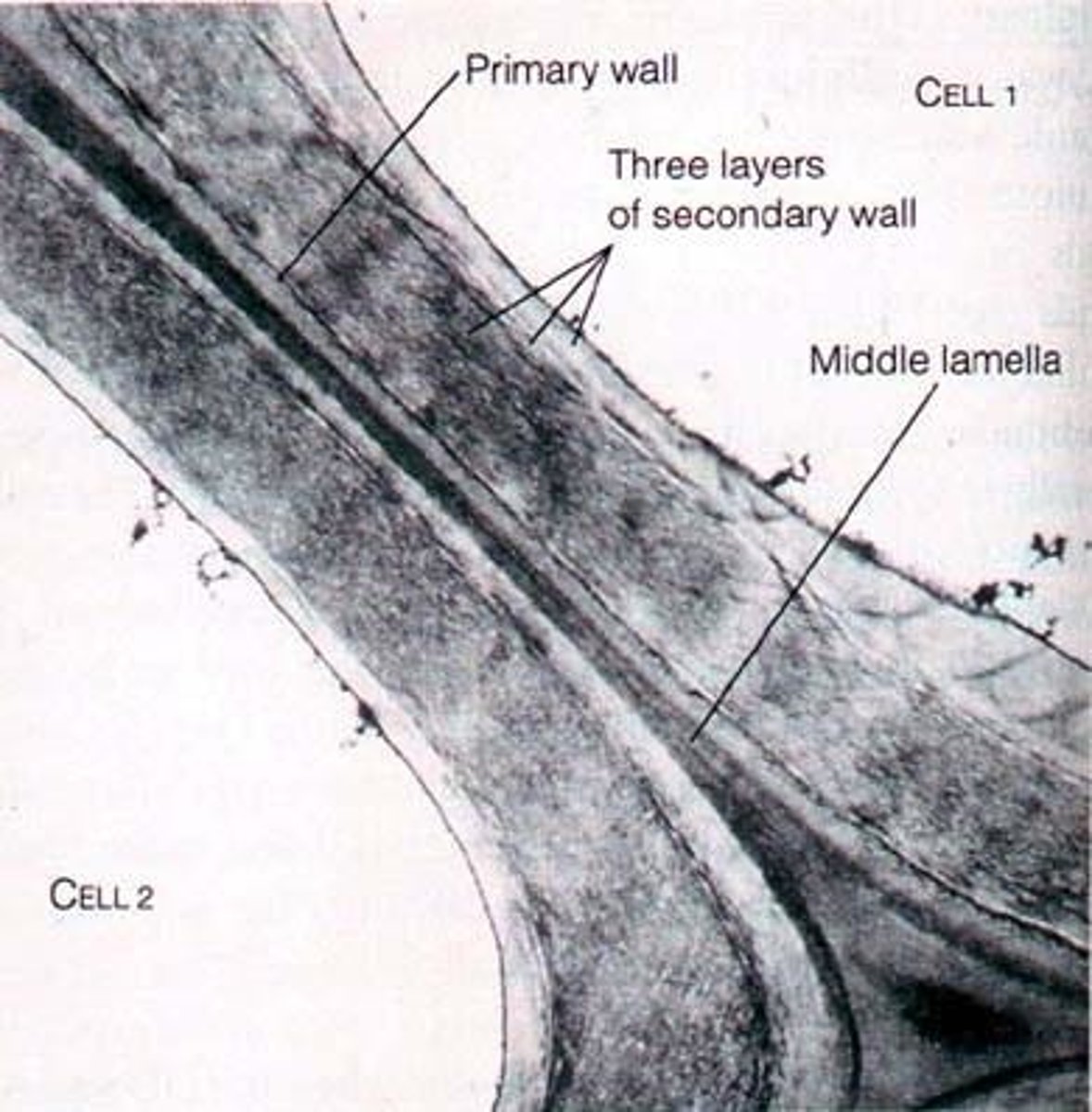
middle lamella
The thin film between the cell walls of adjacent plant cells.
Nucleus
Control center of the cell
nuclear membrane
A highly-porous membrane that separates the nucleus from the cytoplasm
RNA
ribonucleic acid
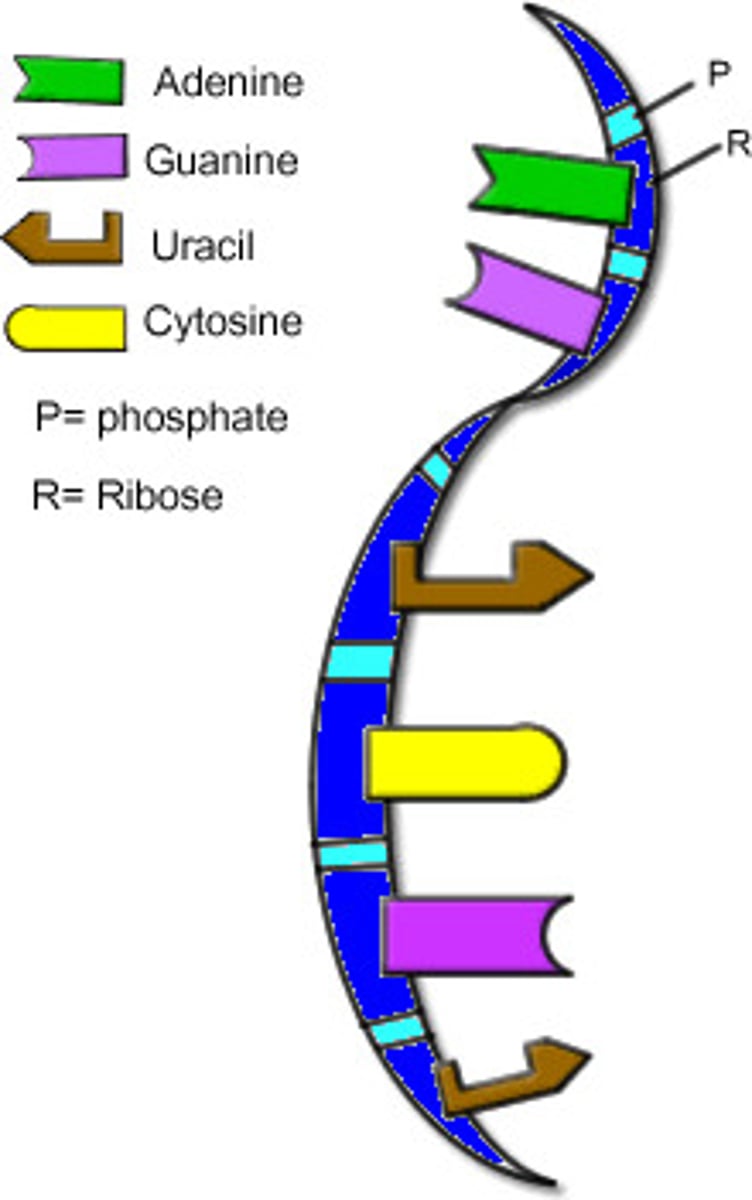
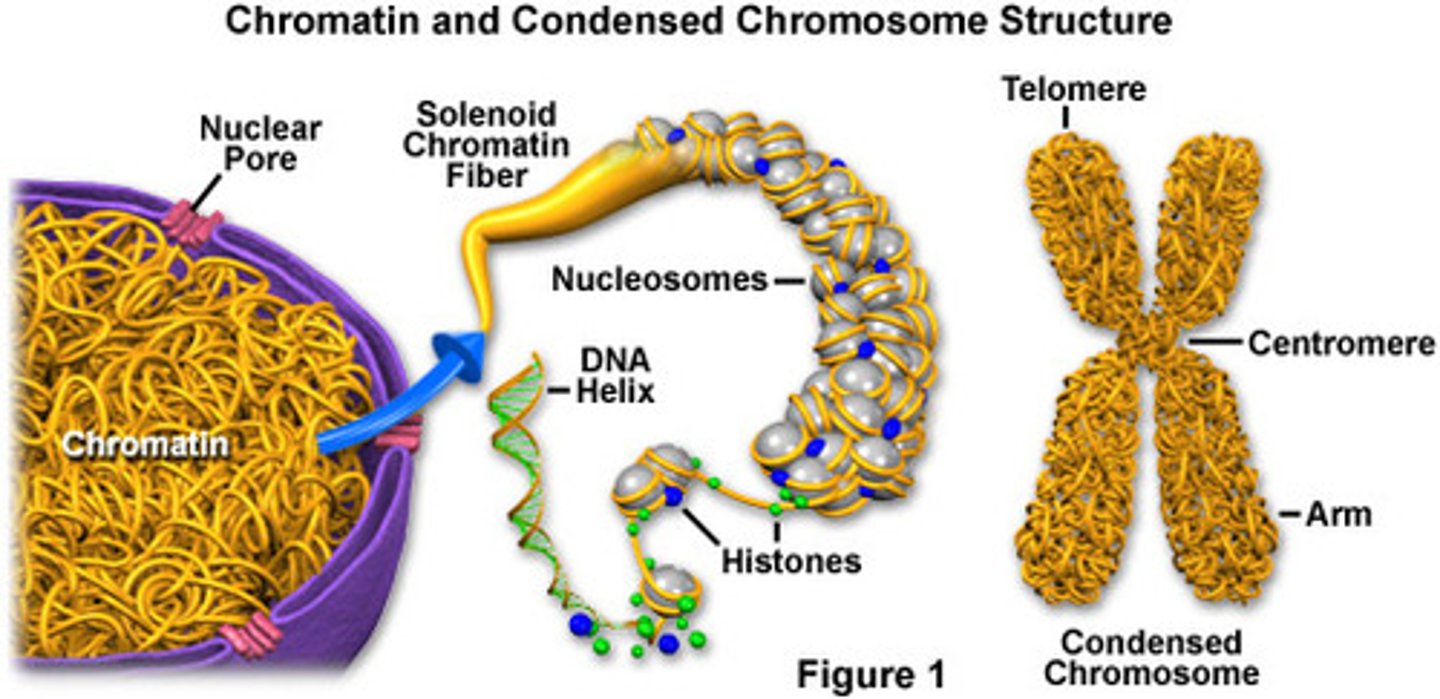
Chromatin
Clusters of DNA, RNA, and proteins in the nucleus of a cell
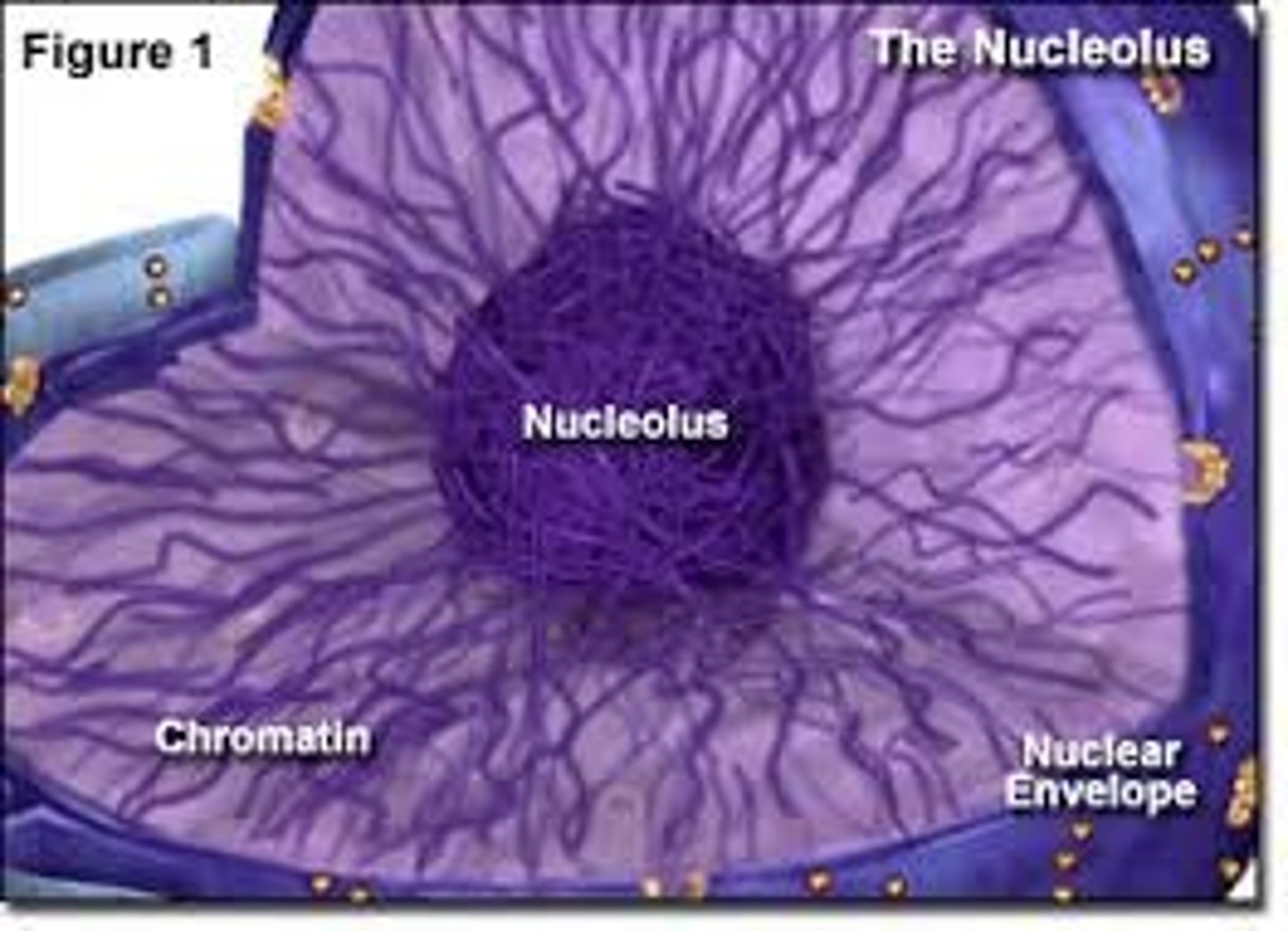
nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes and RNA
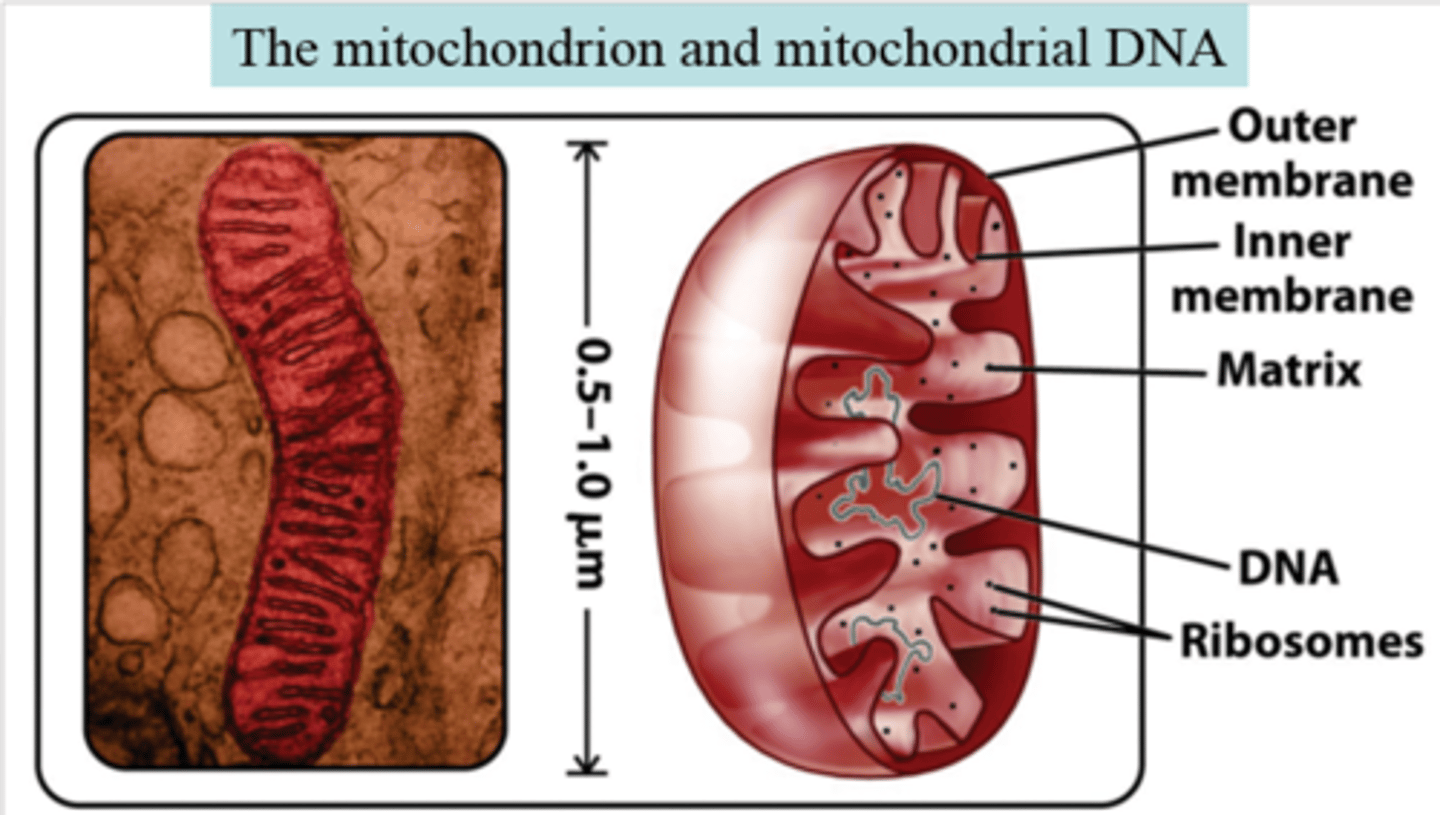
Mitochondrial DNA
A small amount of DNA that is located in the mitochondria of cells.
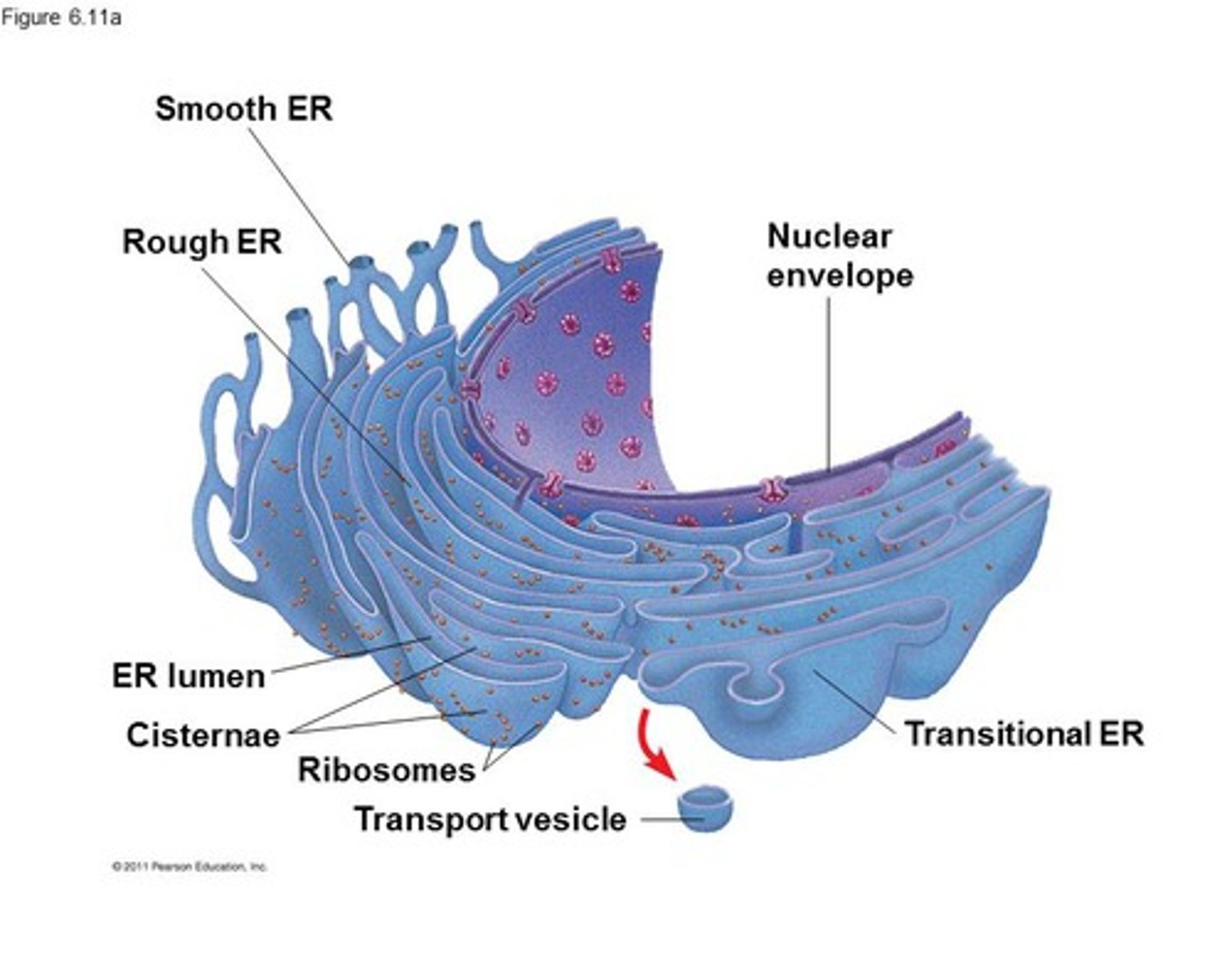
Endoplasmic Reticulum
A system of membranes that is found in a cell's cytoplasm and that assists in the production, processing, and transport of proteins and in the production of lipids.
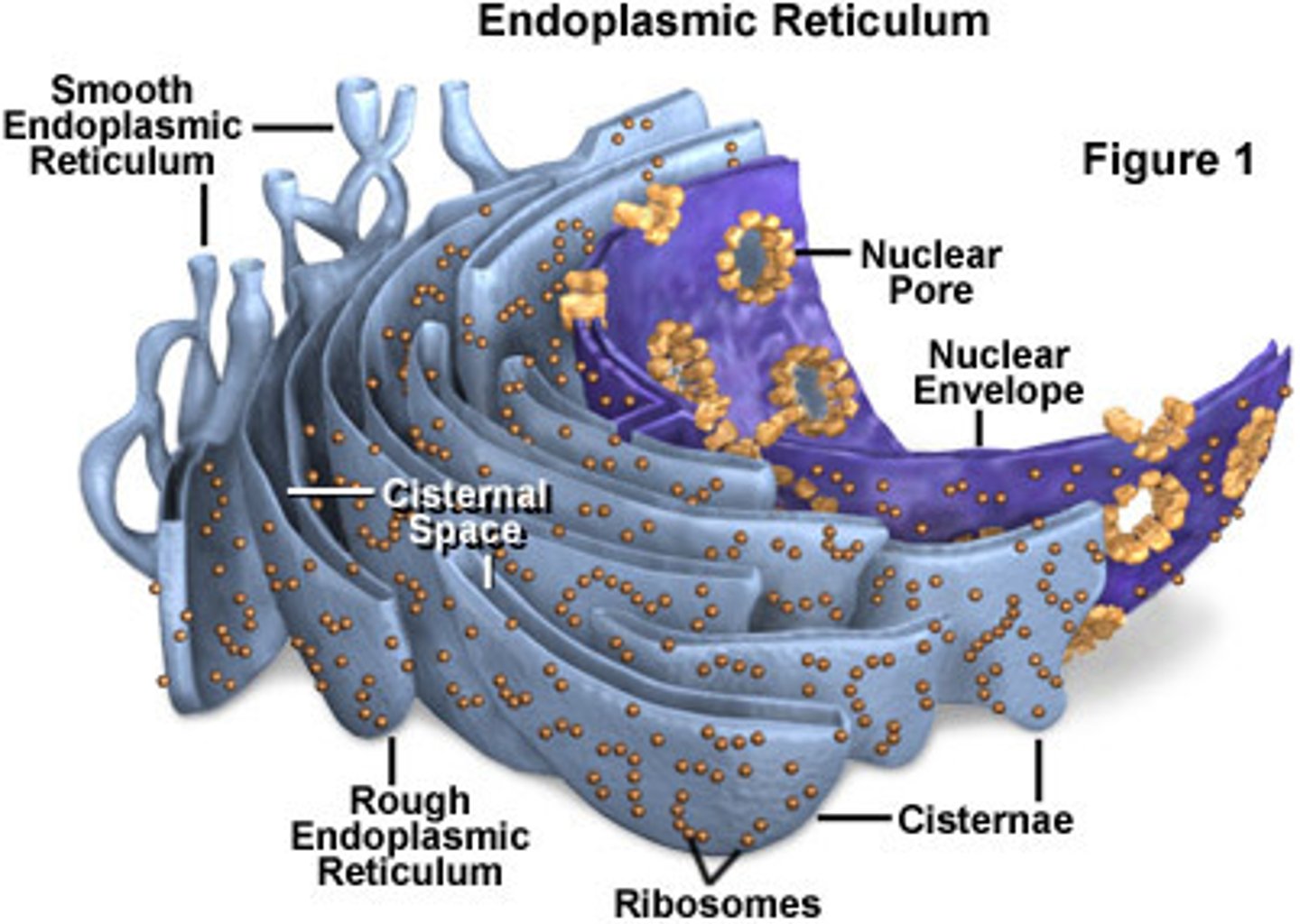
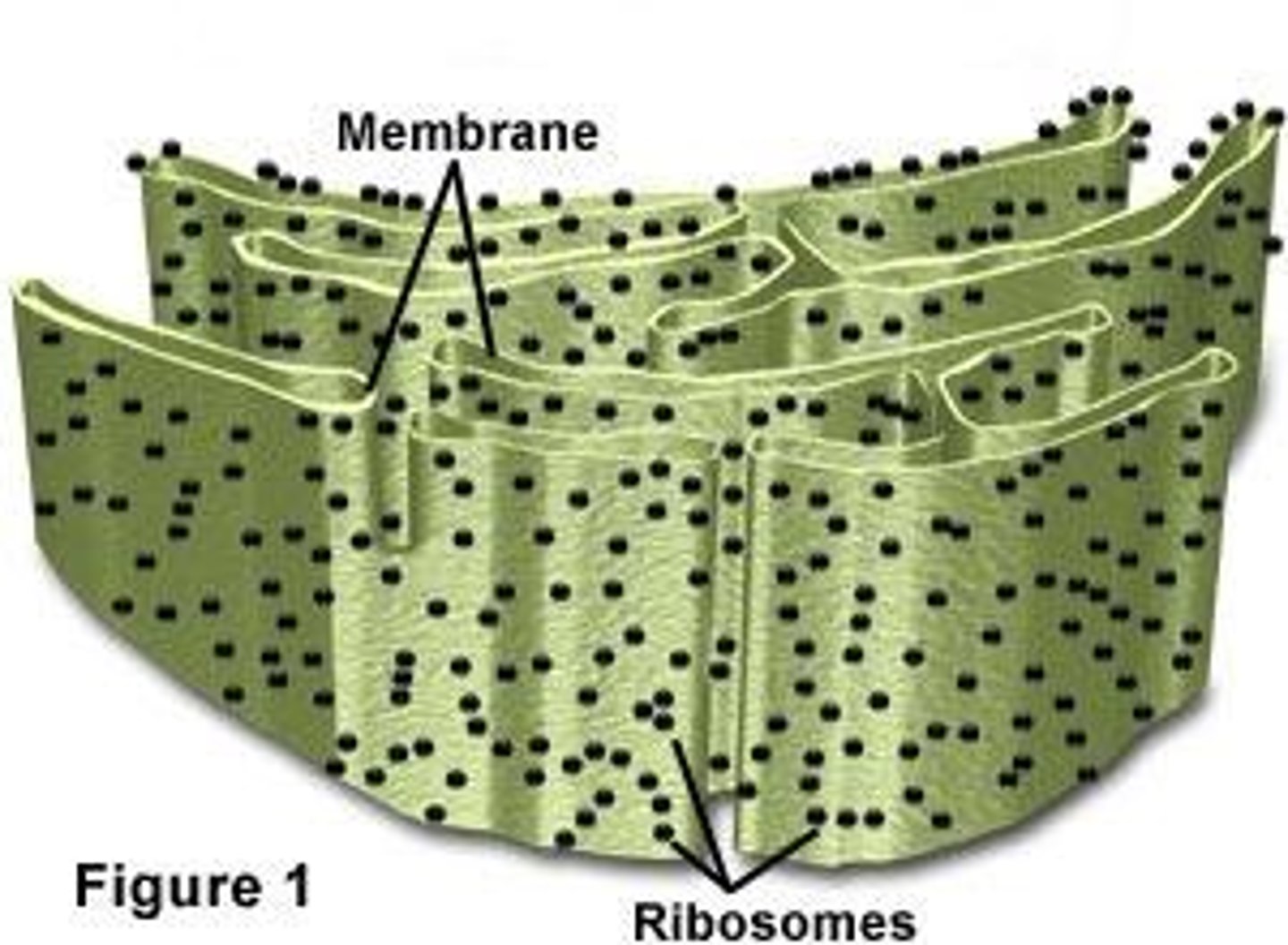
Rough ER
ER that is dotted with ribosomes
Smooth ER
ER that has no ribosomes
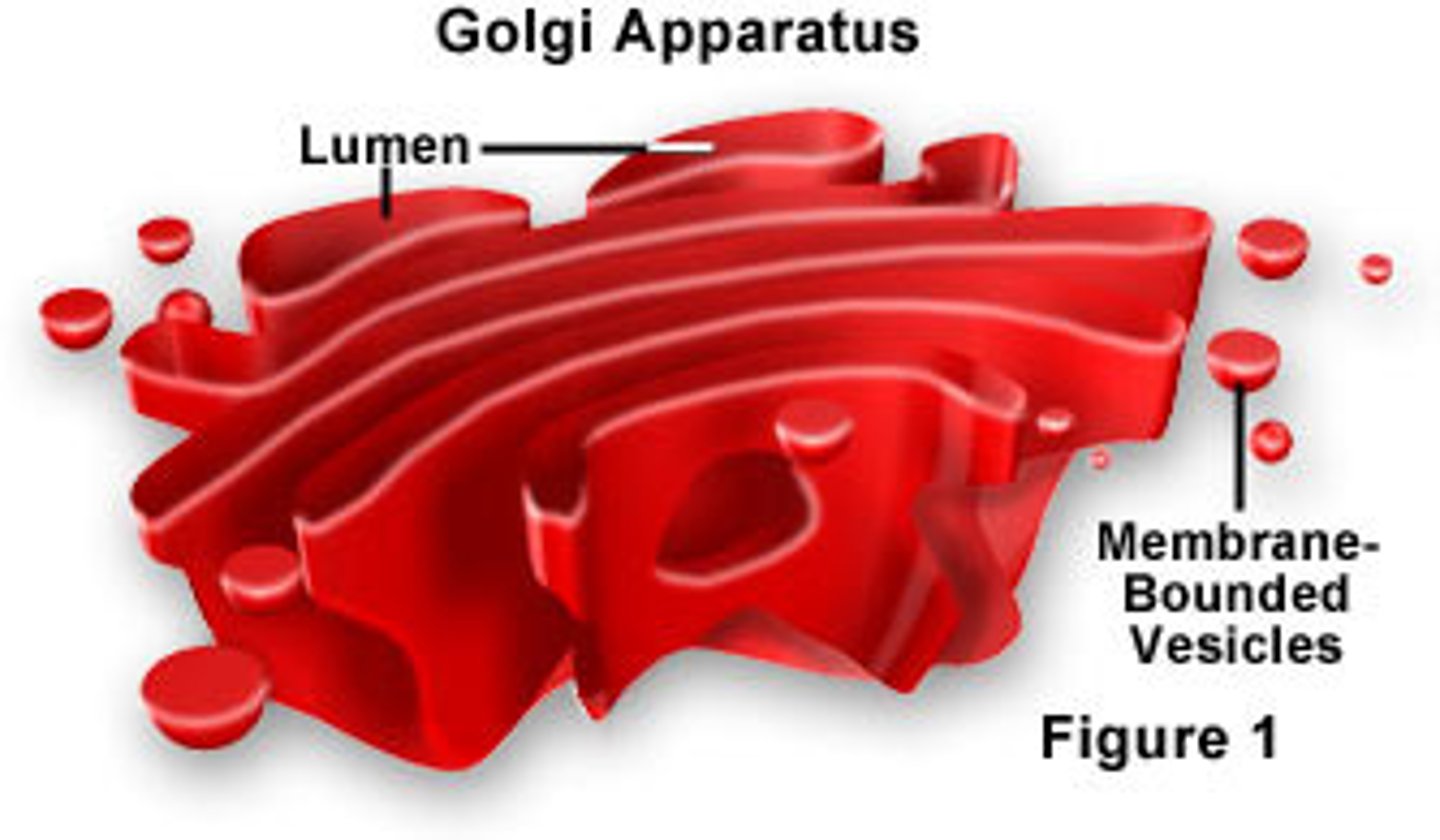
Golgi apparatus
organelle in cells where proteins and lipids are stored and then modified to suit the needs of the cell
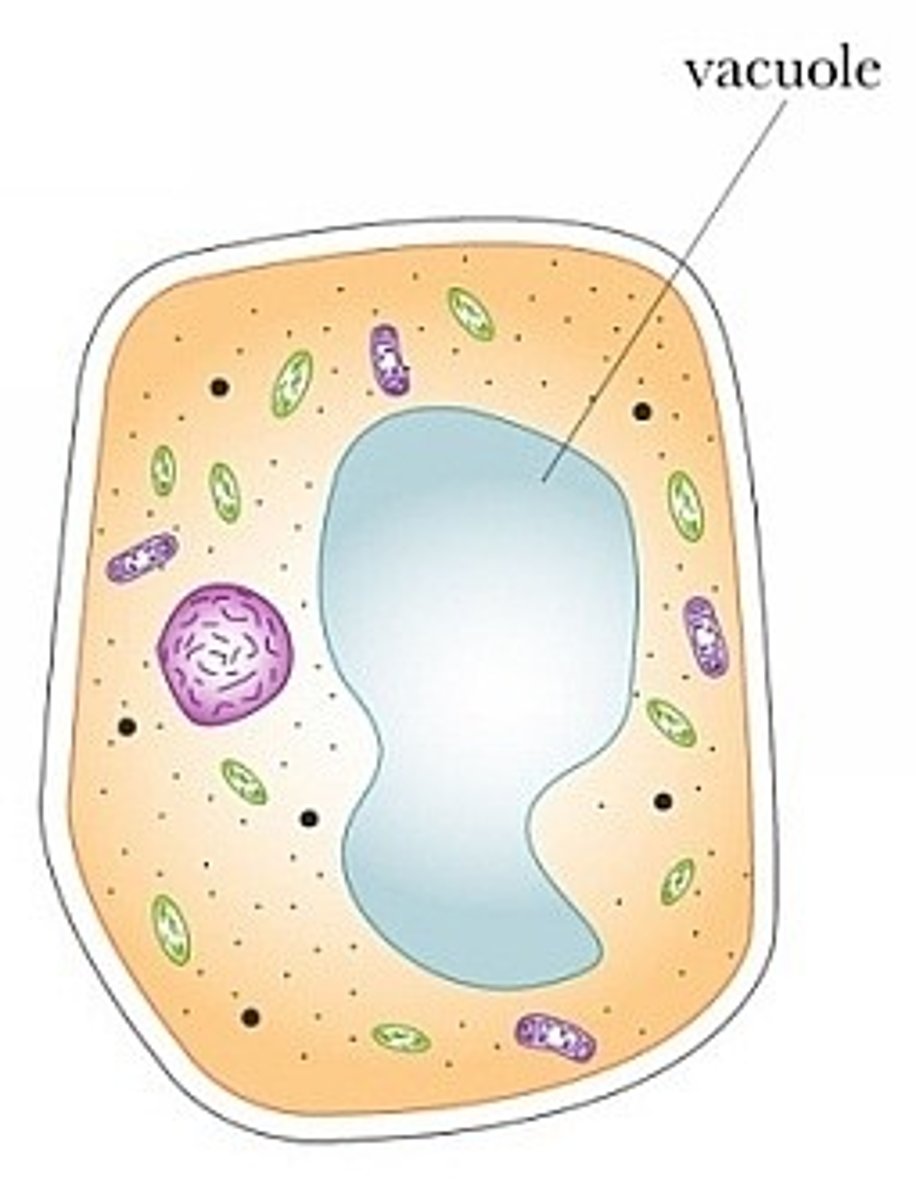
Vacoule
a organelle that stores water, food, or waste
Vesicle
A membrane bound sac that is used in transport of food, waste, or products synthesized for secretion
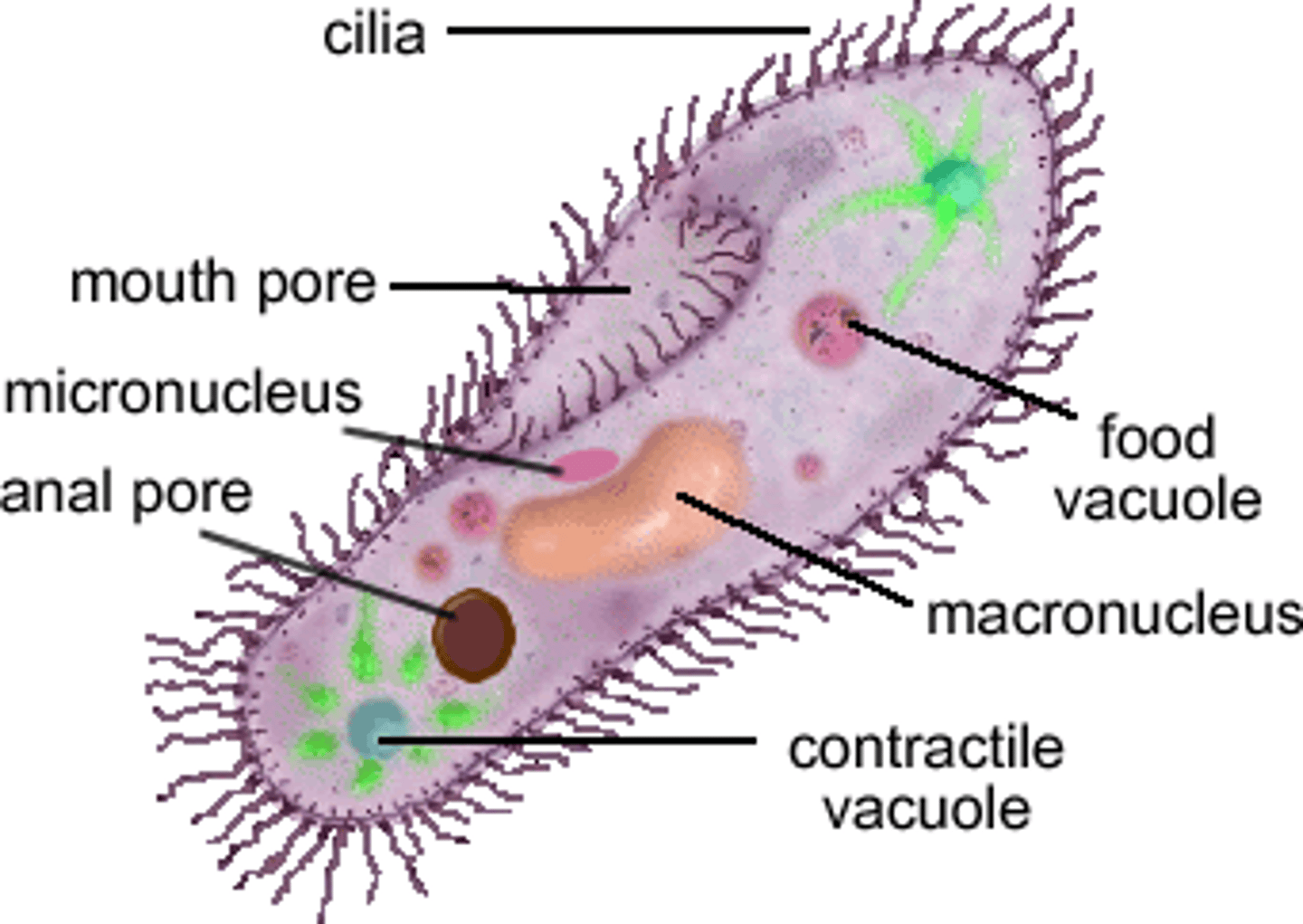
food vacoule
hold and store food while it i being digested
water vacoule
store water
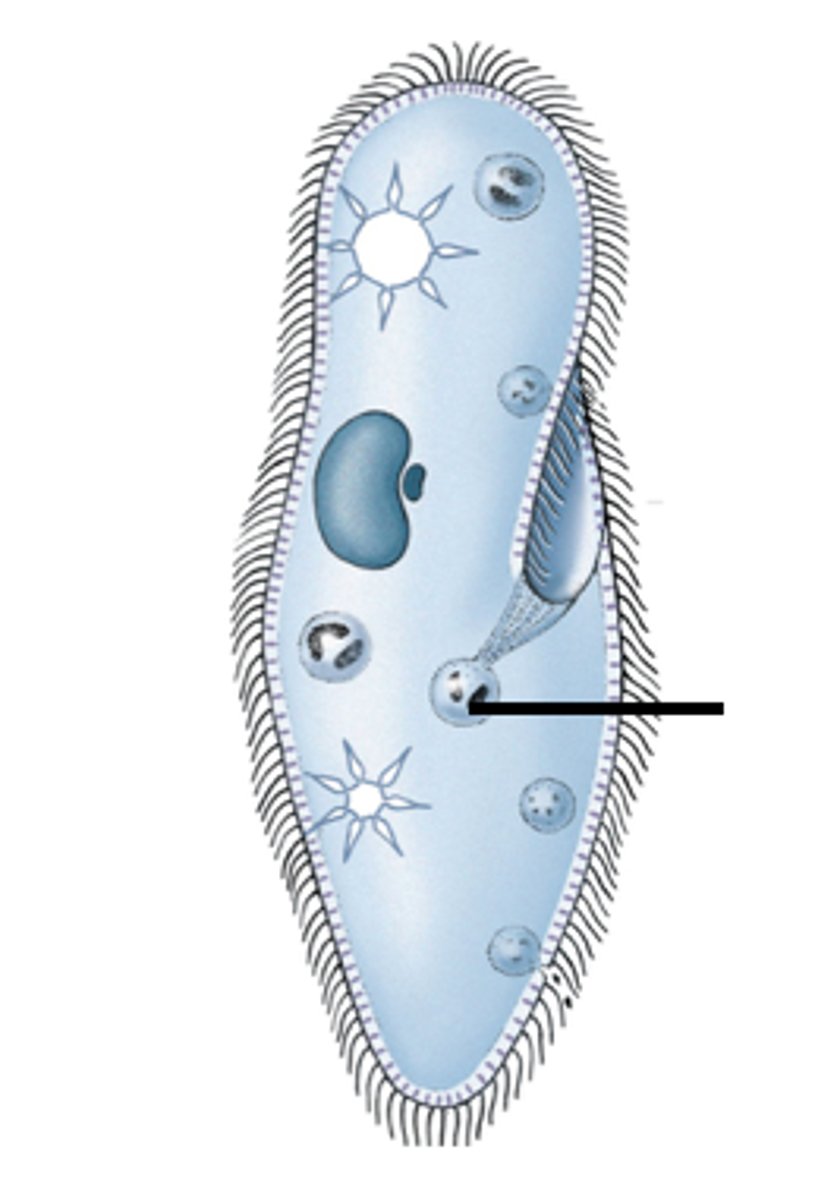
contractile vacuole
regulates the amount of water in the cell
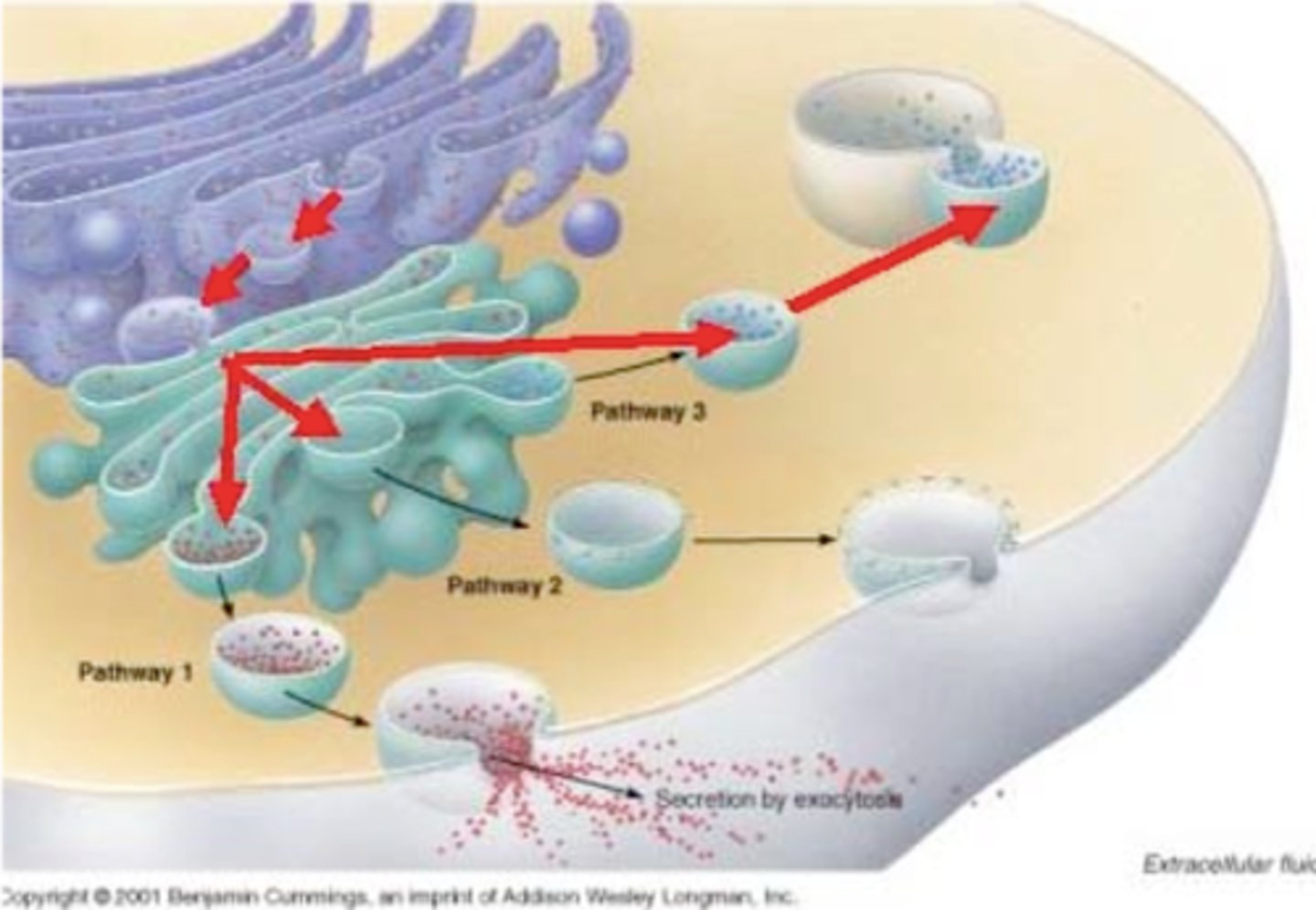
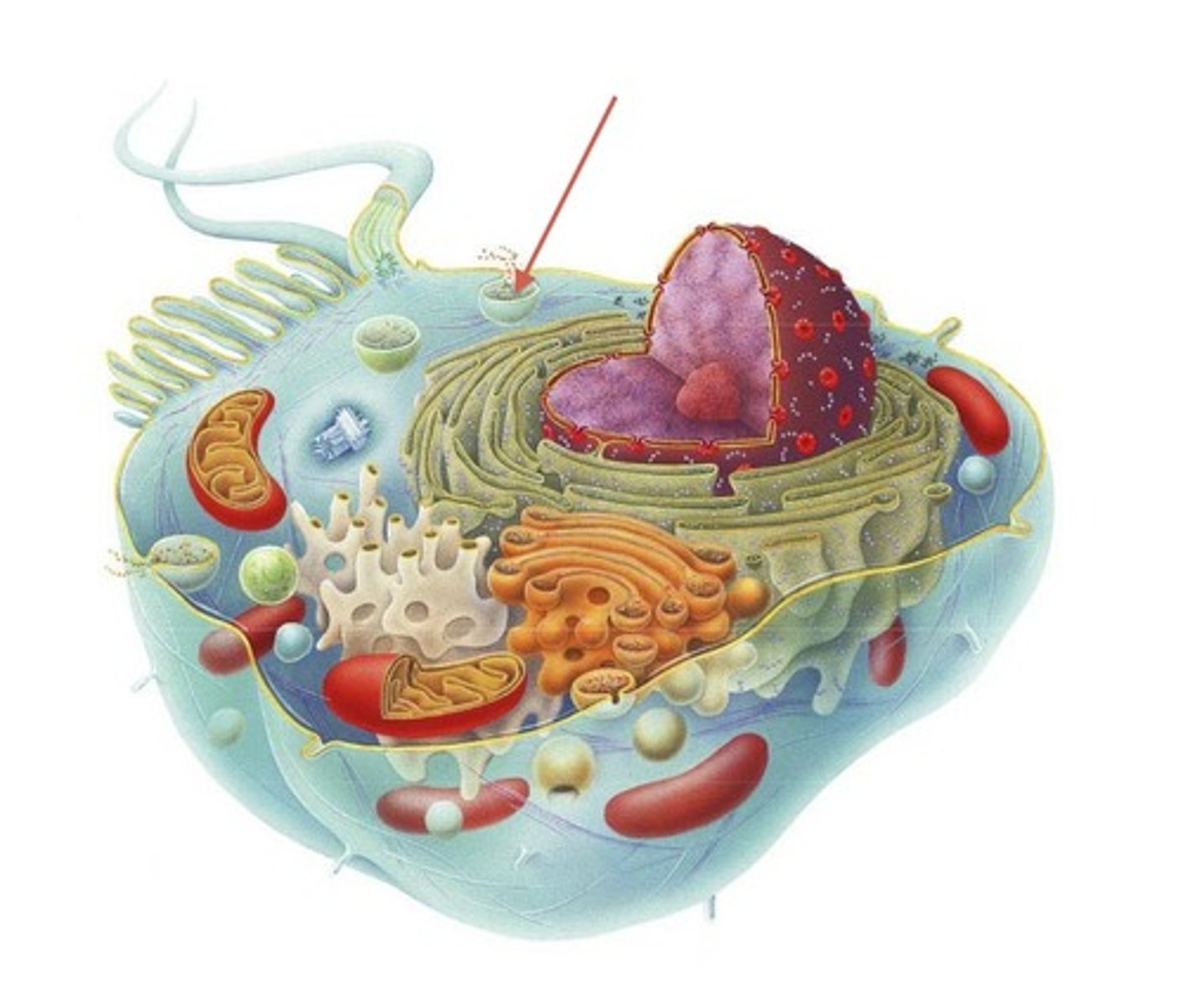
secretory vesicles
holds products of biosynthesis and transports them to plasma membrane for secretion
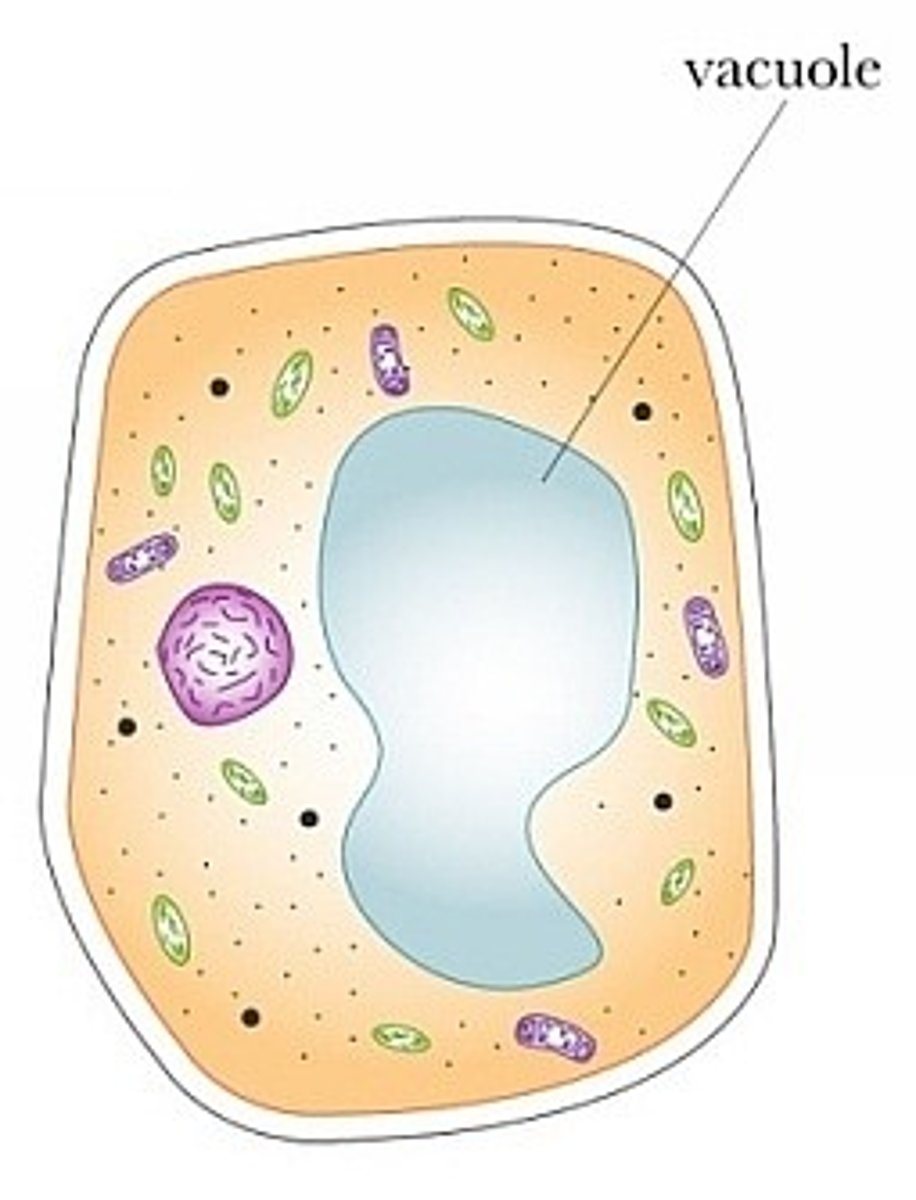
Central Vacoule ( plant cell )
resta at the center of plant cells and is filled with water
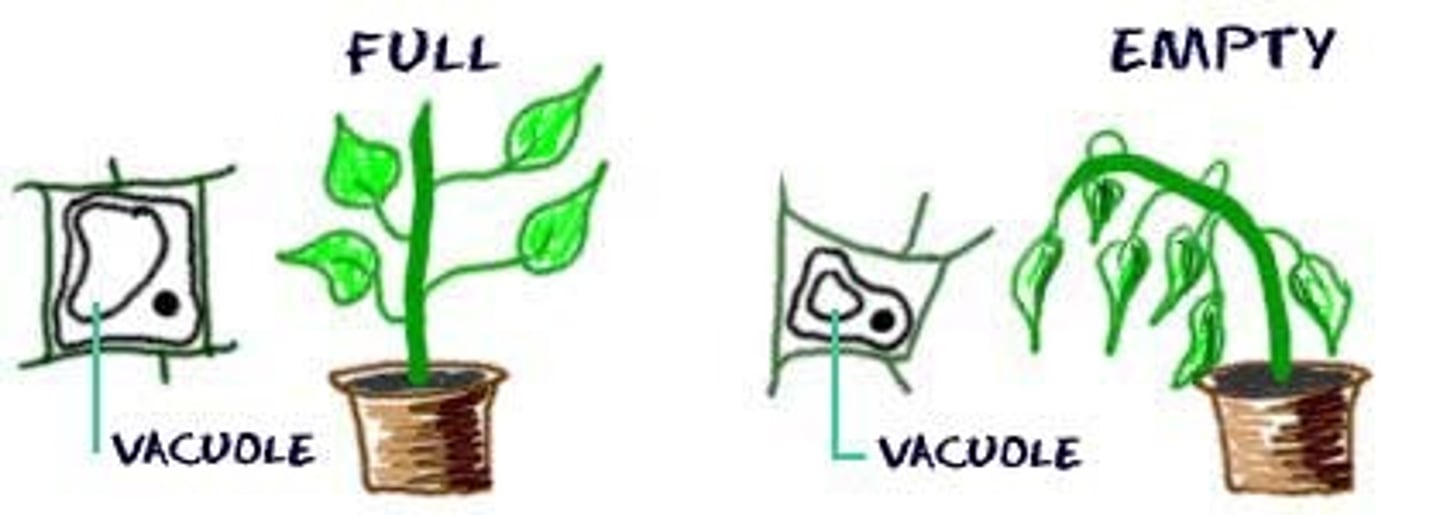
turgor pressure
The pressure that water molecules exert against the cell wall
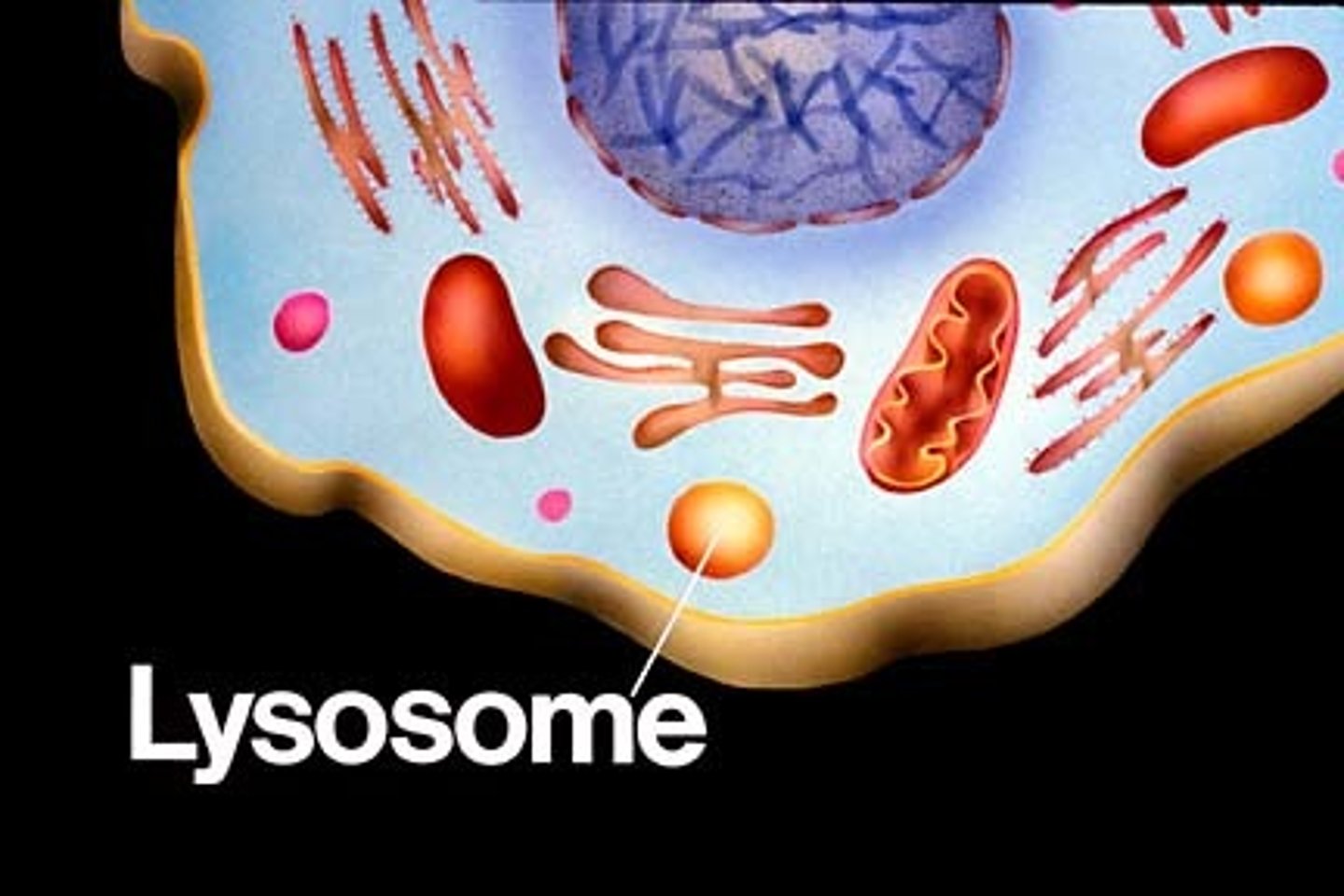
lysosome
cell organelle responsible for hydrolysis reactions
Peroxisomes
organelle containing enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of fatty acids and hydrogen peroxide
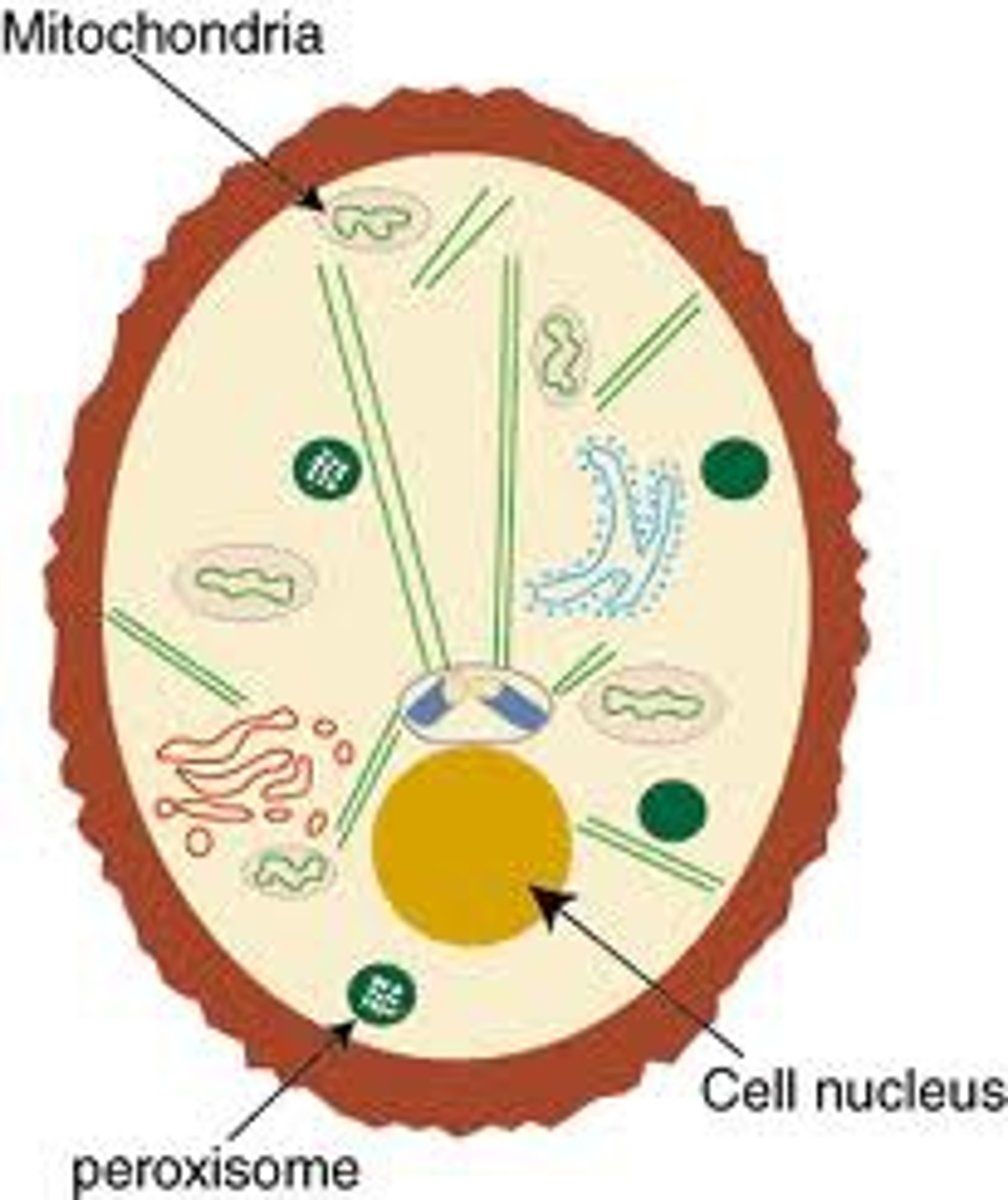
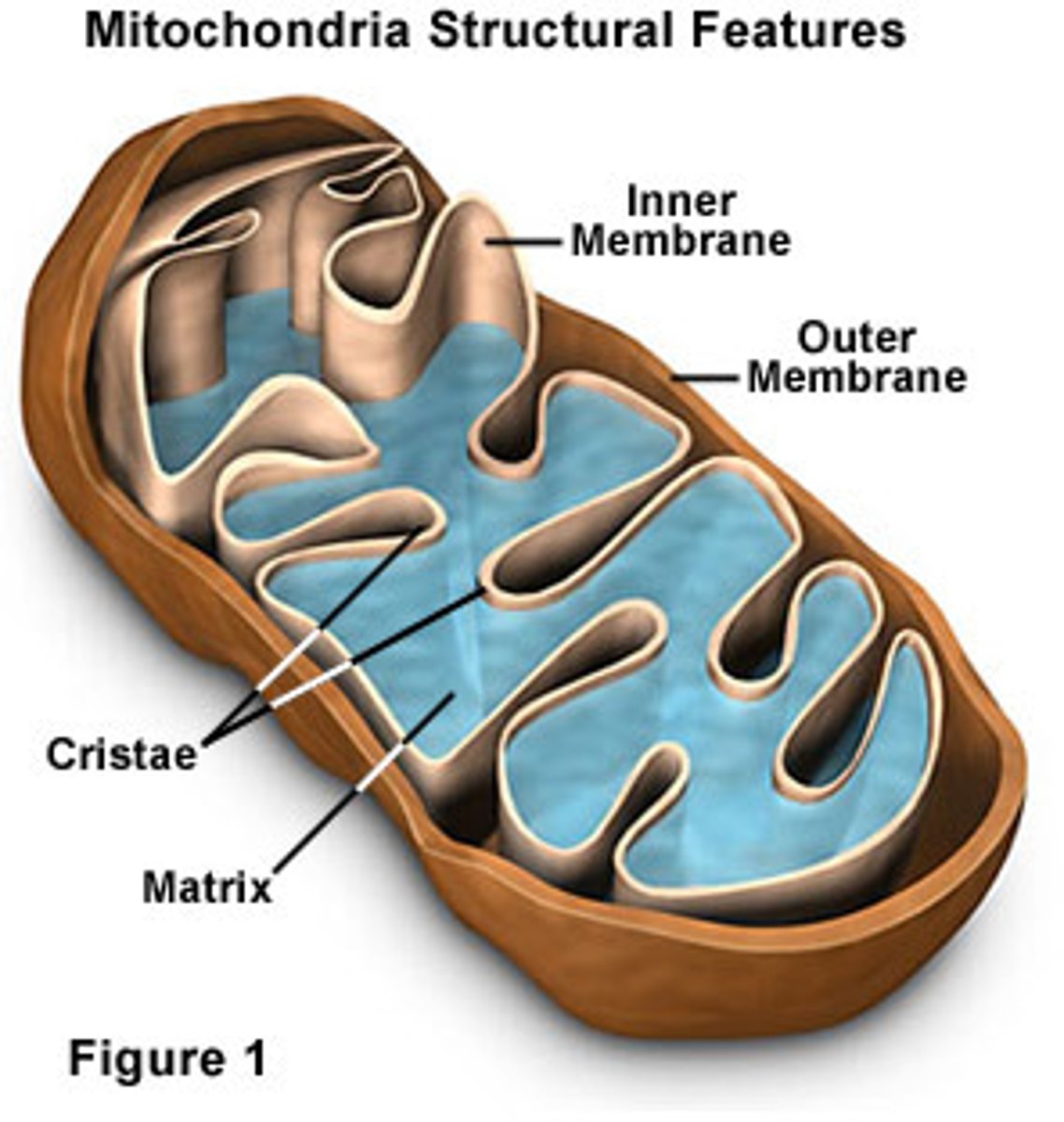
Mitochondria
organelle in which nutrients are converted to energy
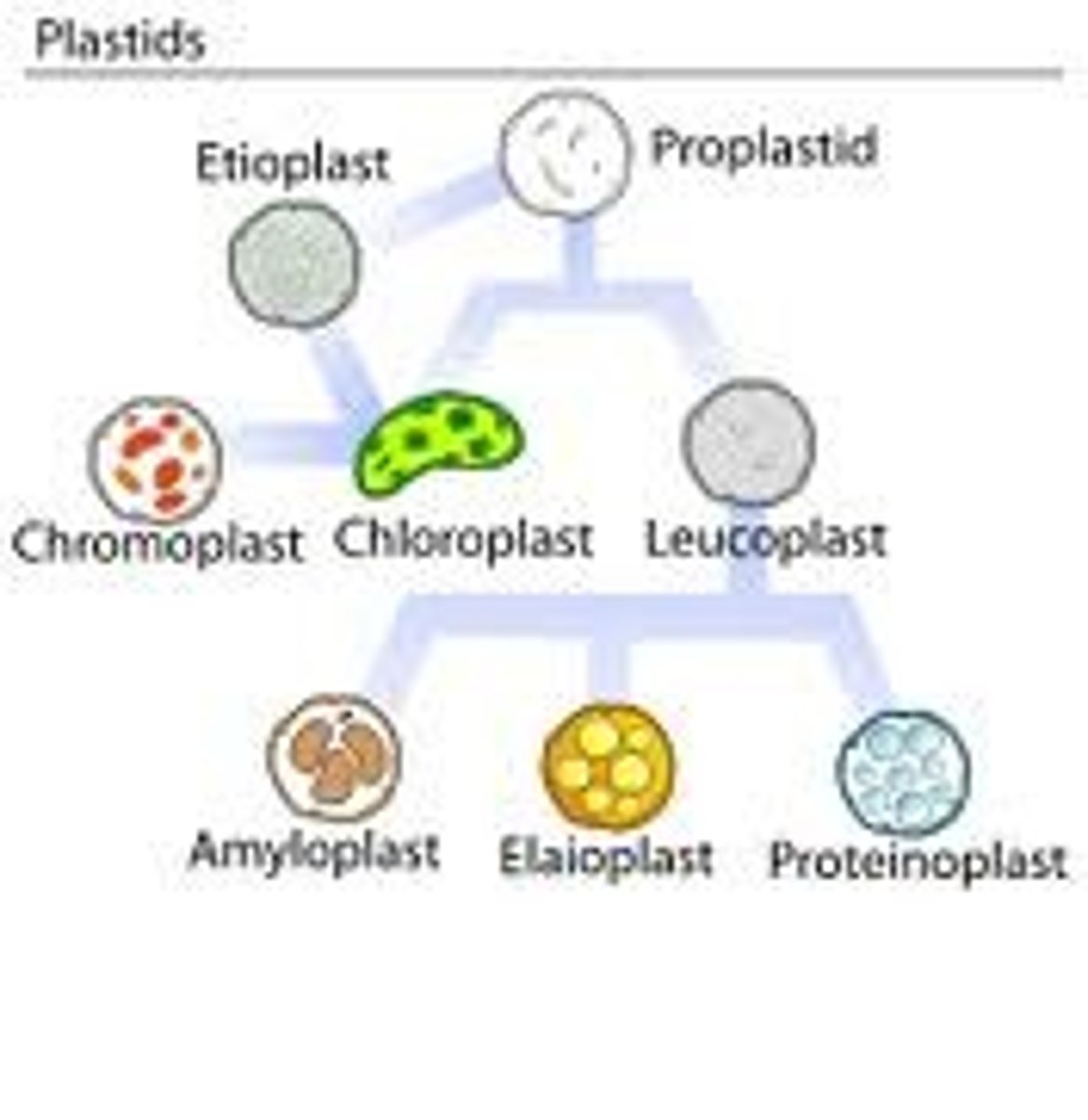
Plastids
double-membrane-bound organelles found in plants, algae, and some protozoa, generally involved in either the manufacture or storage of food
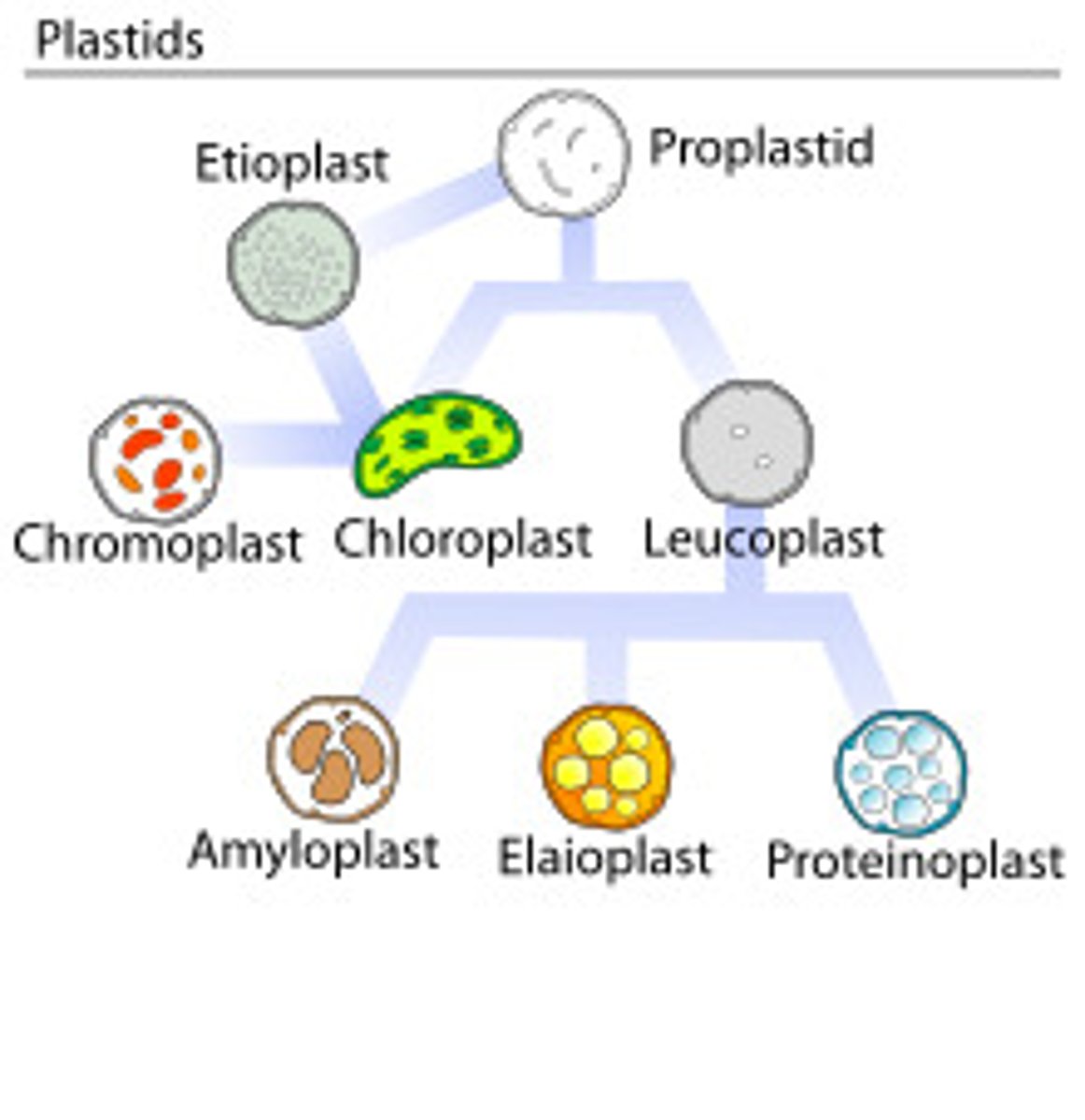
Chloroplast
A plastid containing chlorophyll, the site of photosynthesis
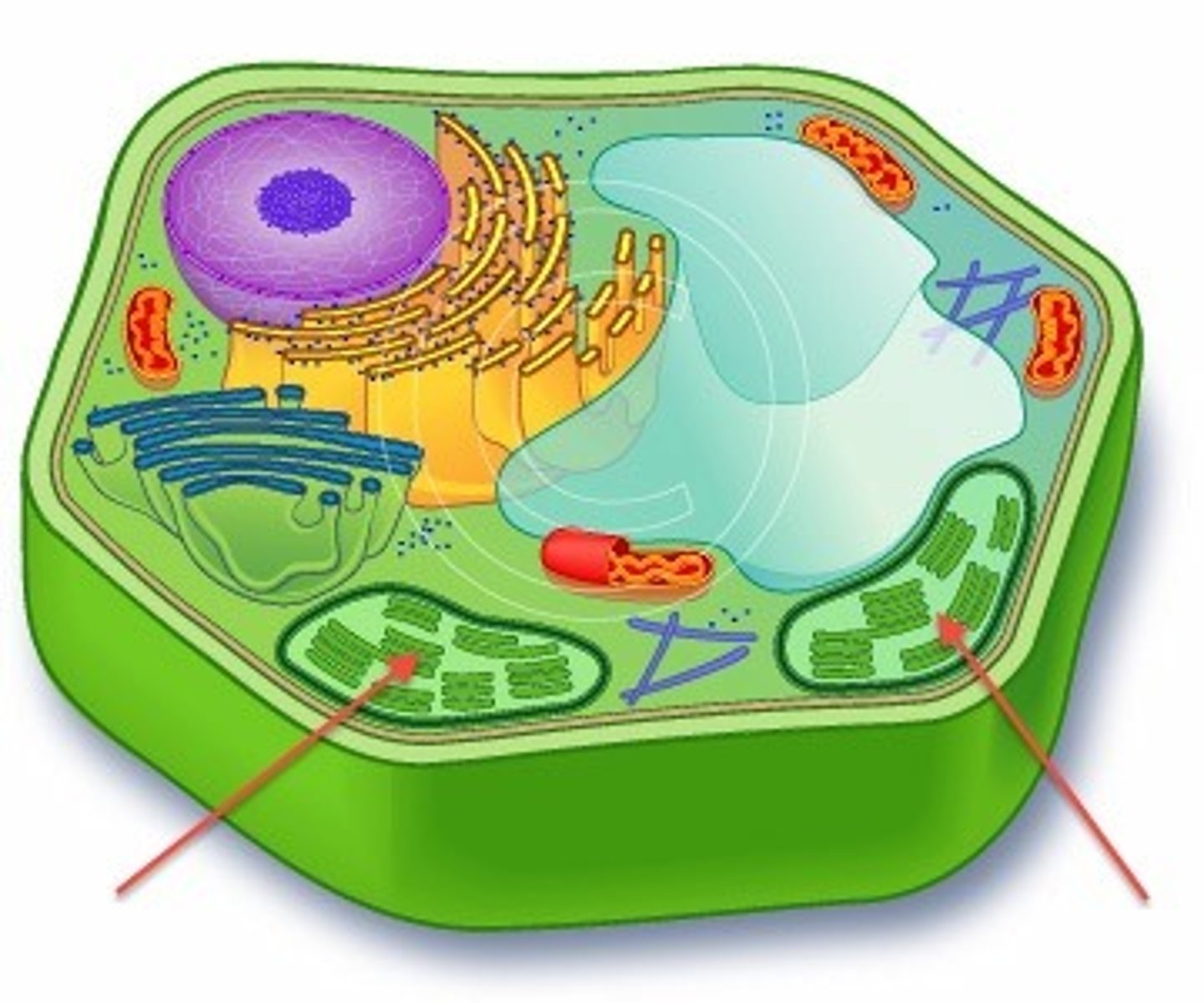
Chromoplasts
plastids that contain colorful pigments used in photosynthesis

Leucoplasts
non-pigmented plastids that store starches or oils
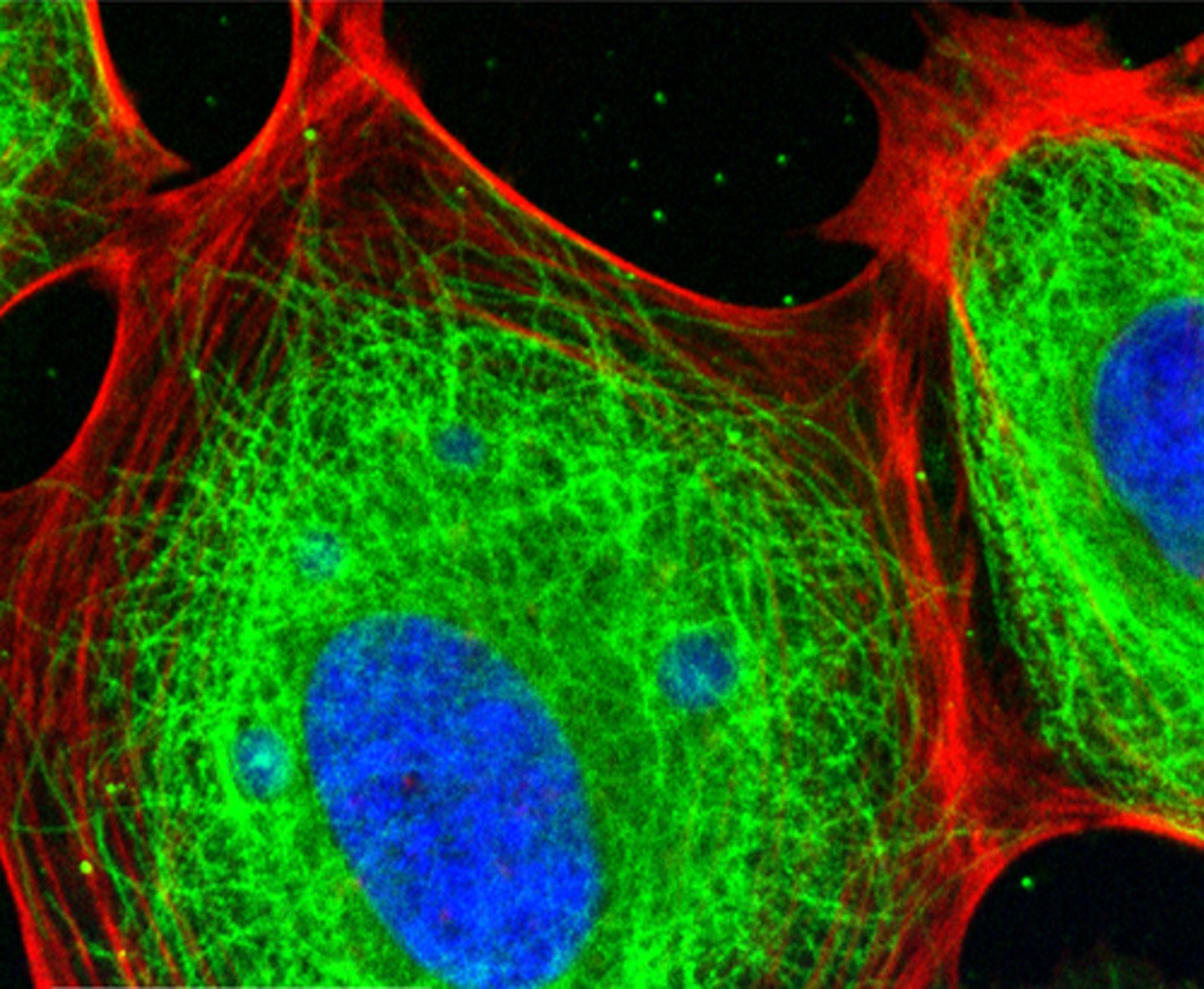
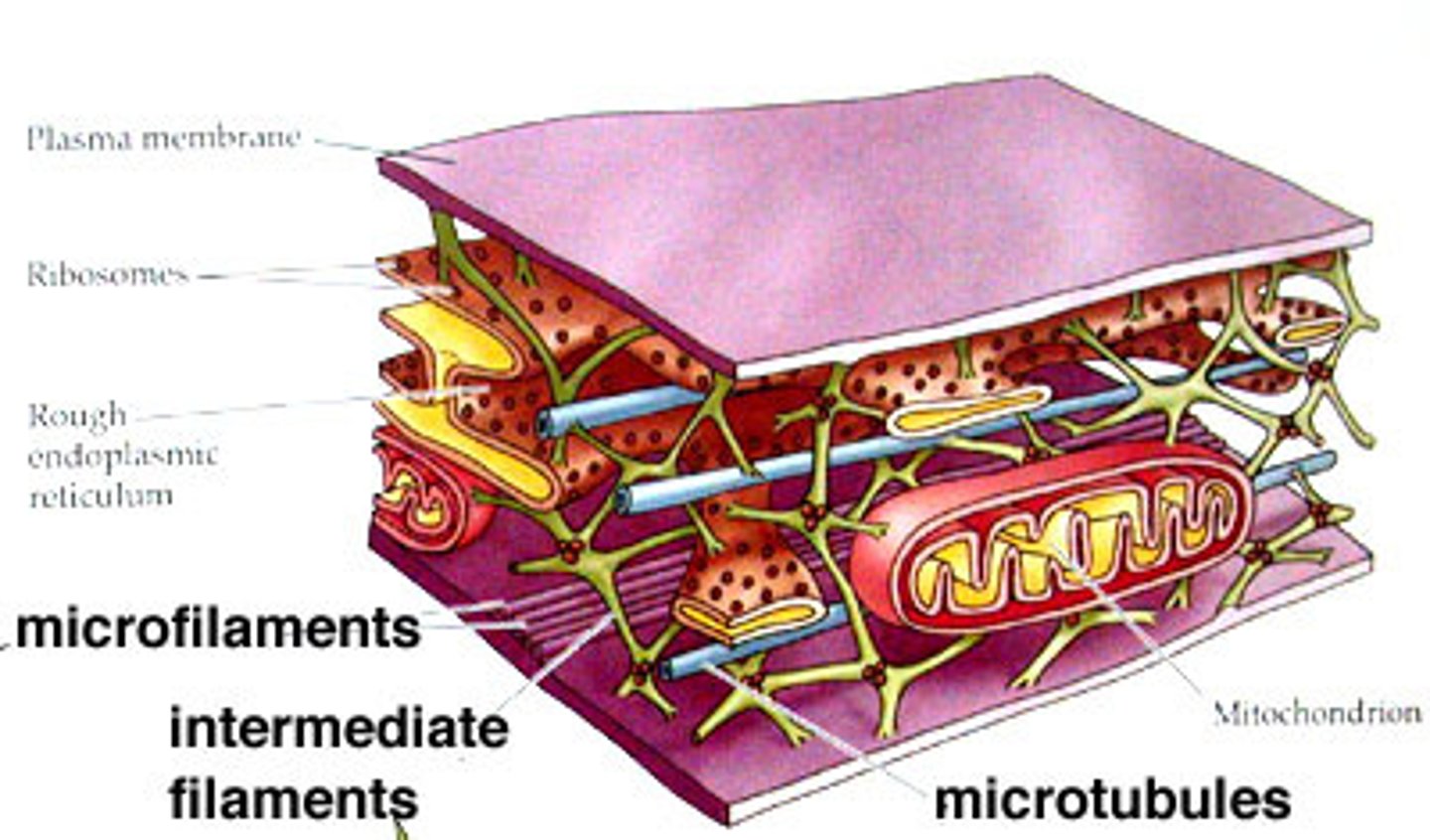
Cytoskeleton
A network of fibers that holds the cell together, helps the cell to keep its shape, and aids in movement
Microfilaments
Fine, threadlike proteins found in the cell's cytoskeleton
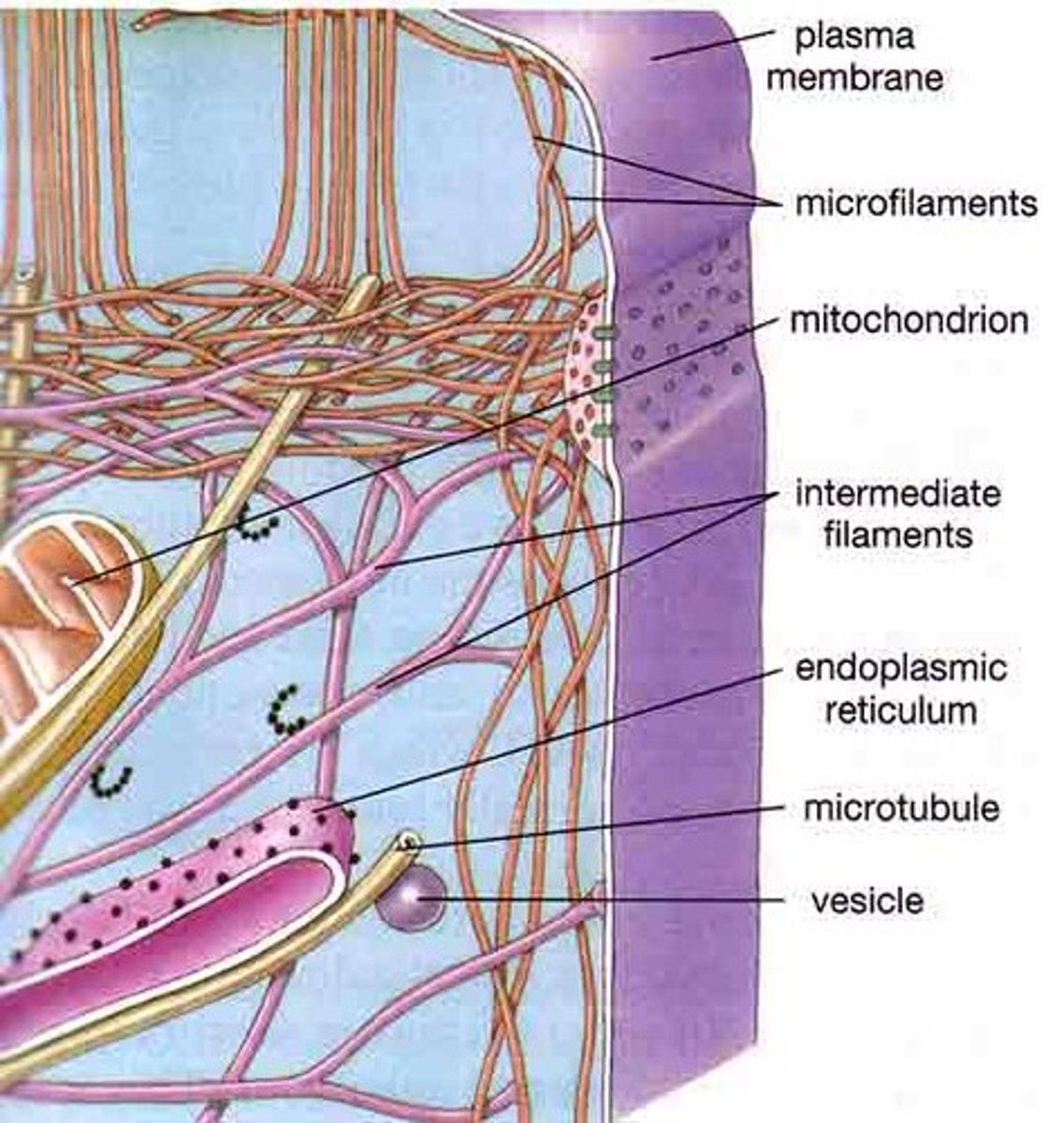
intermediate filaments
Threadlike proteins in the cell's cytoskeleton that are roughly twice as thick as microfilaments
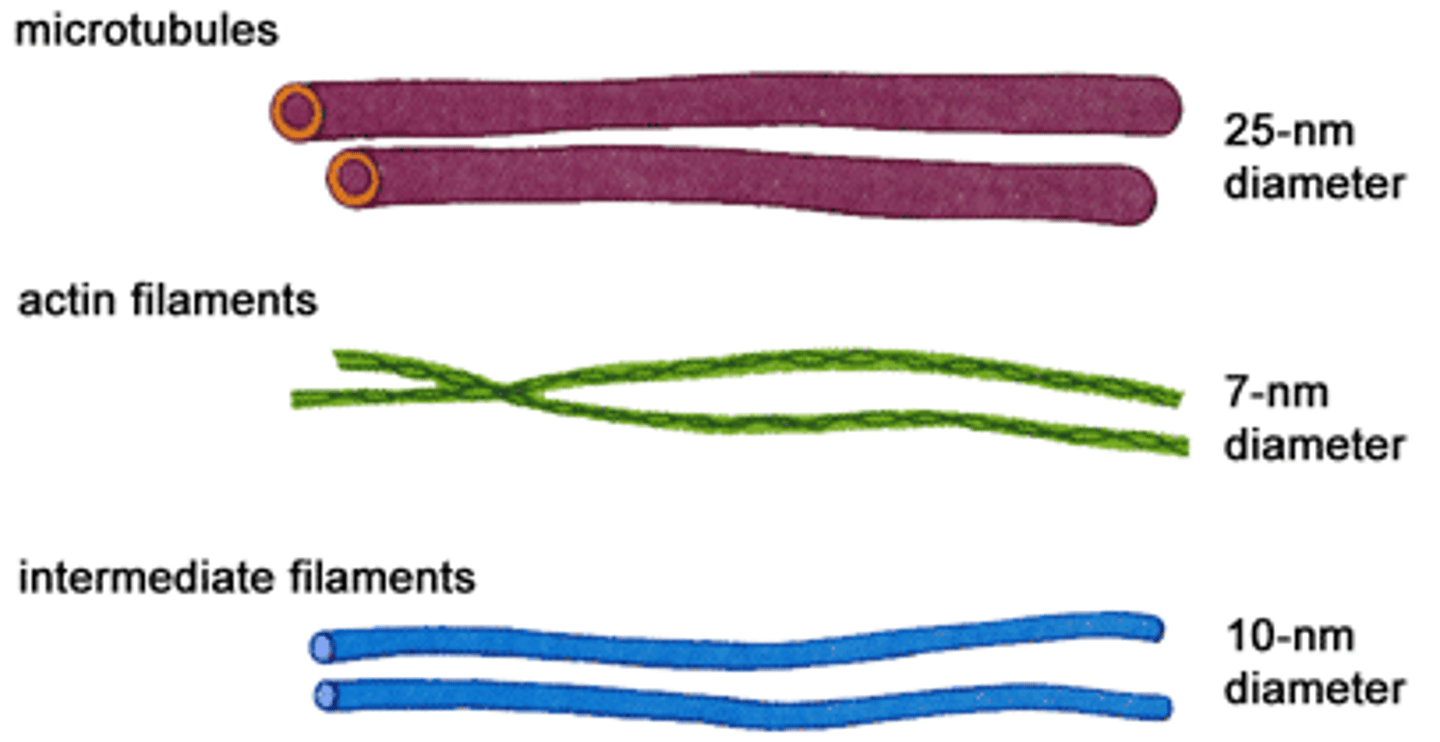
Microtubules
Spiral strands of protein molecules that form a tubelike structure
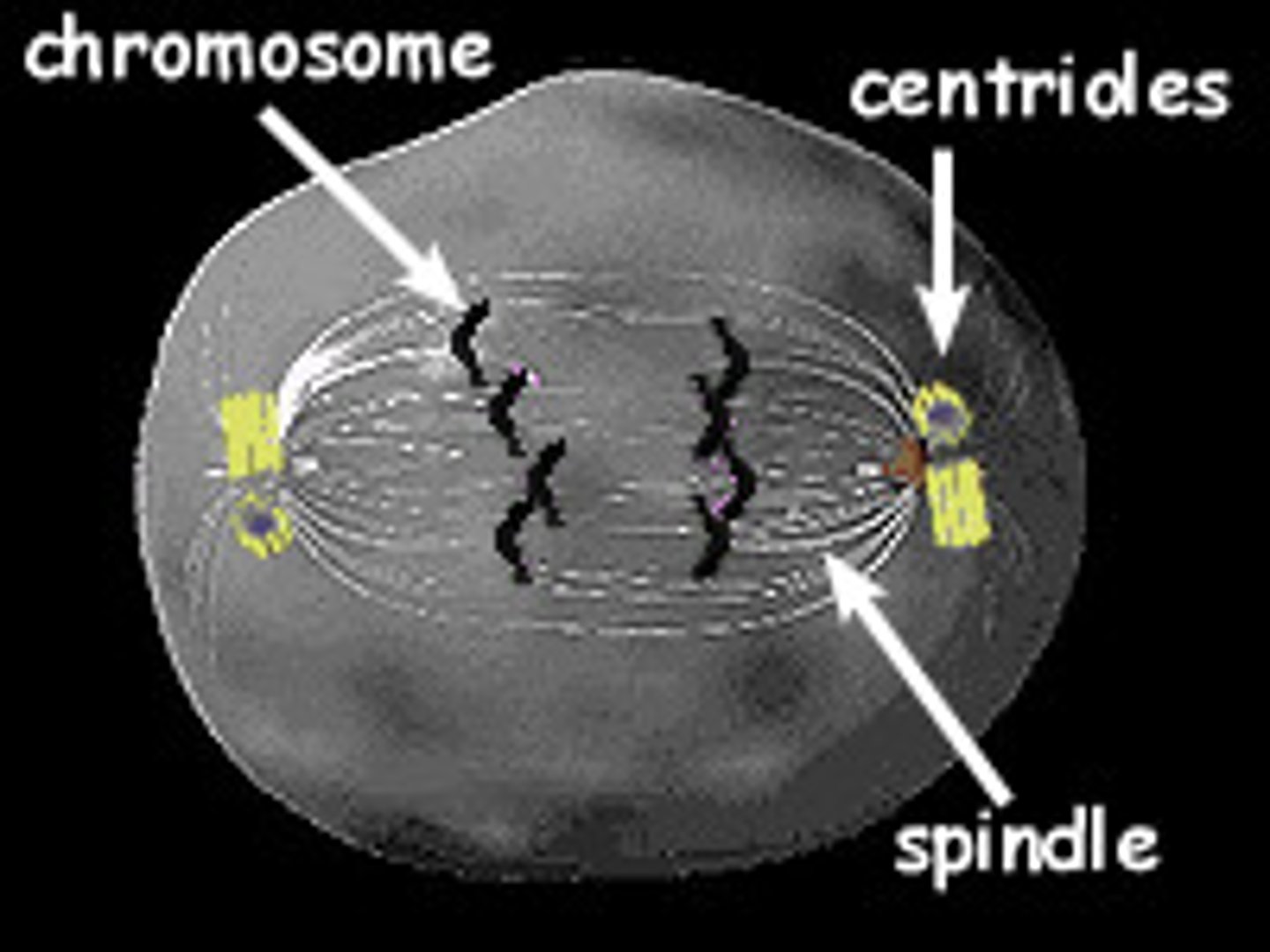
Centrioles
paired organelles that organize fibers required for cell division: found in animals
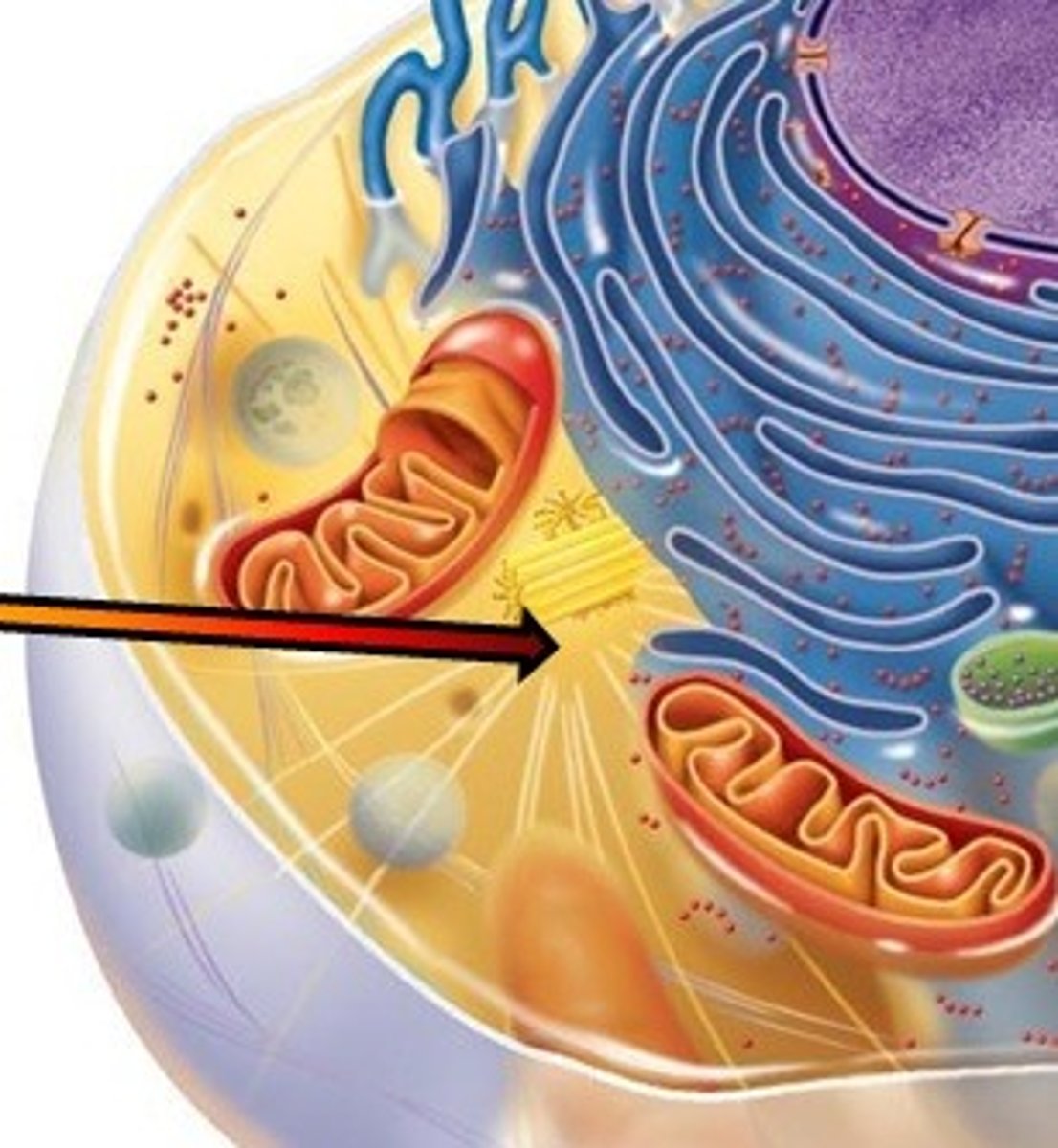
Centrosome
small region of cytoplasm that produces microtubules
fluid mosaic model of membrane structure
a model that describes the phospholipid bilayer as fluid and proposes that integral membrane proteins float freely in the lipid bilayer
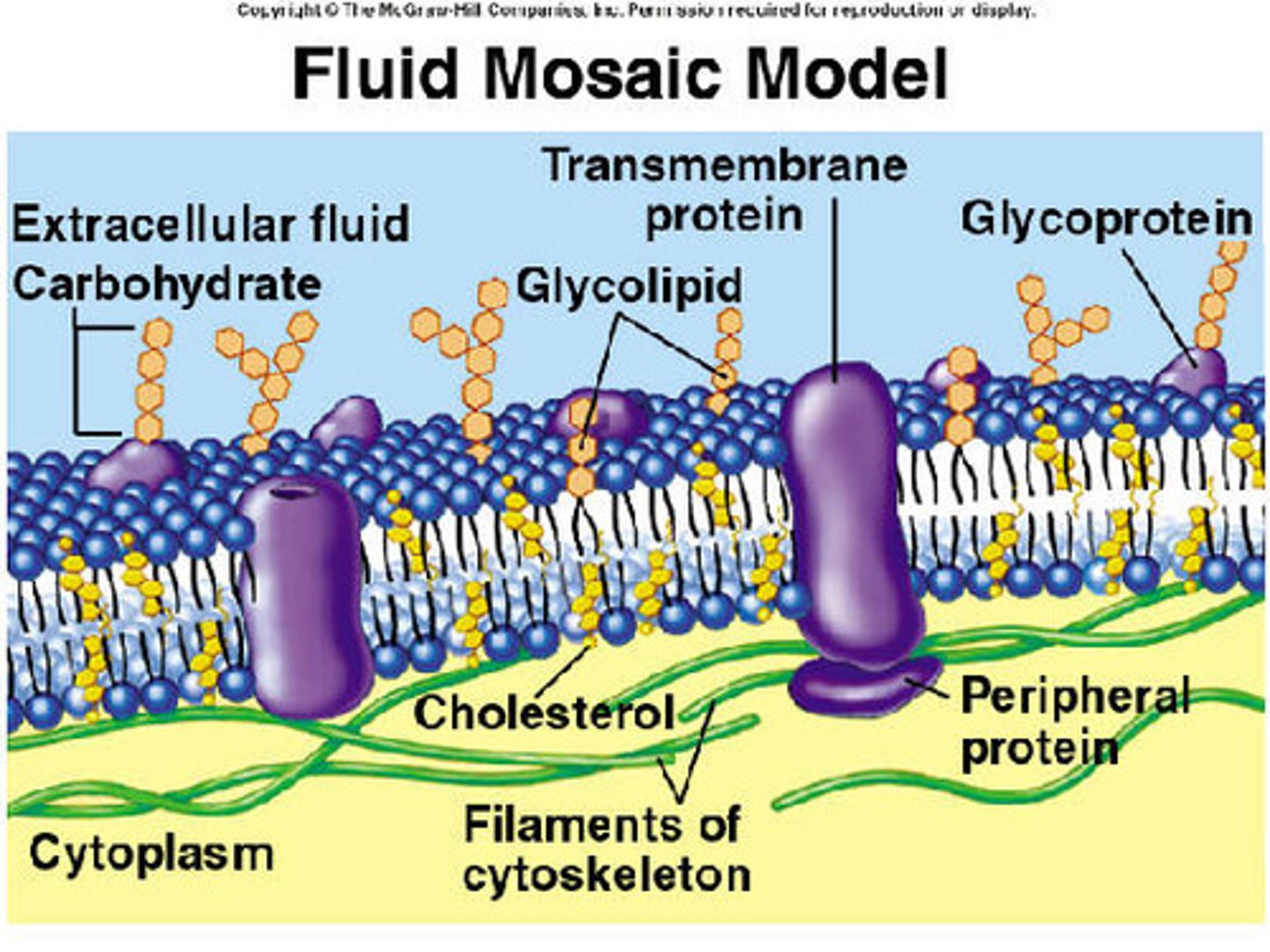
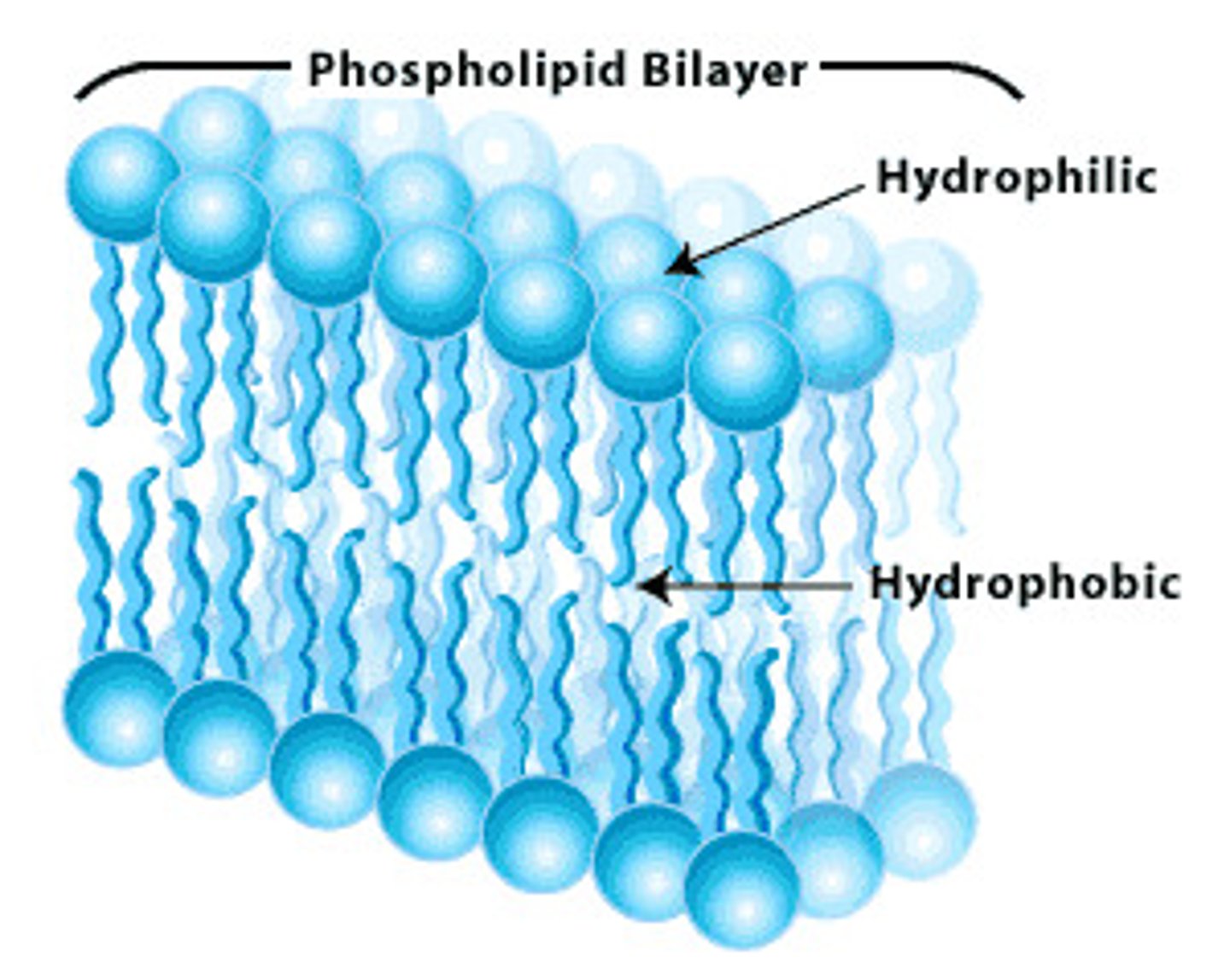
Phospholipids
a lipid consisting of a glycerol bound to two fatty acids and a hydrophilic phosphate group.
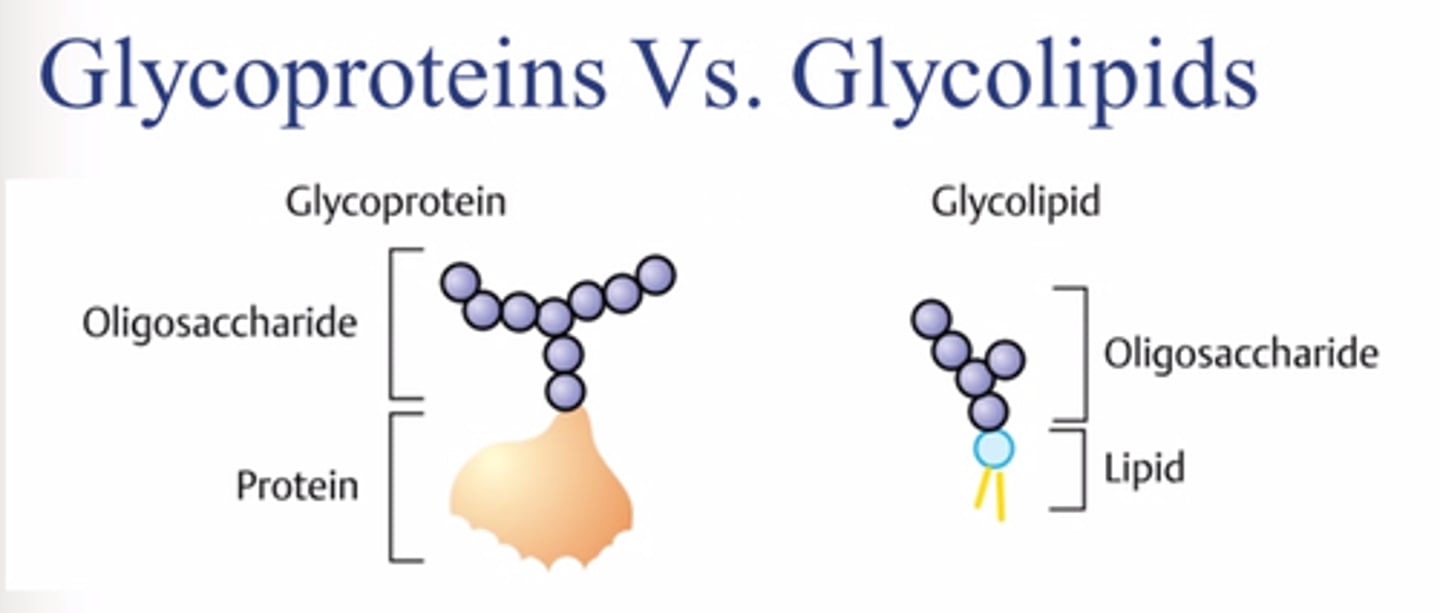
Glycoproteins
Membrane carbohydrates that are covalently bonded to proteins.
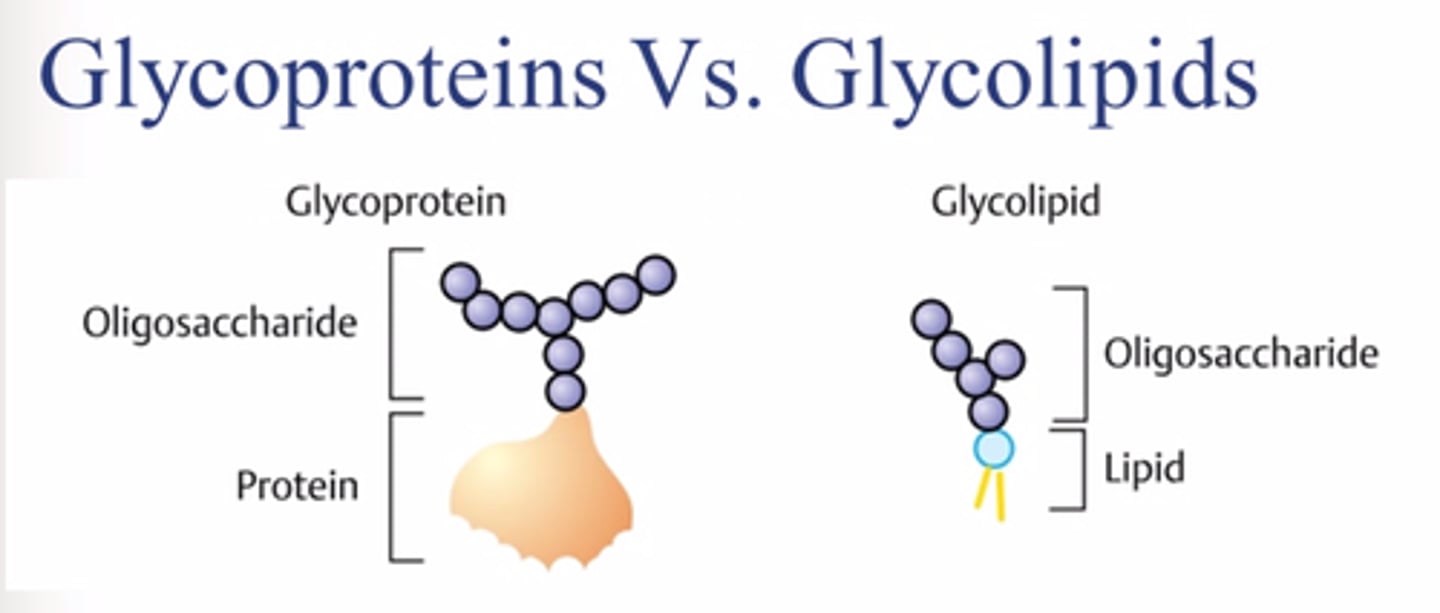
Glycolipids
Membrane carbohydrates that are covalently bonded to lipids.
semipermeable membrane
A membrane that allows some molecules to pass through but does not allow other molecules to pass through.
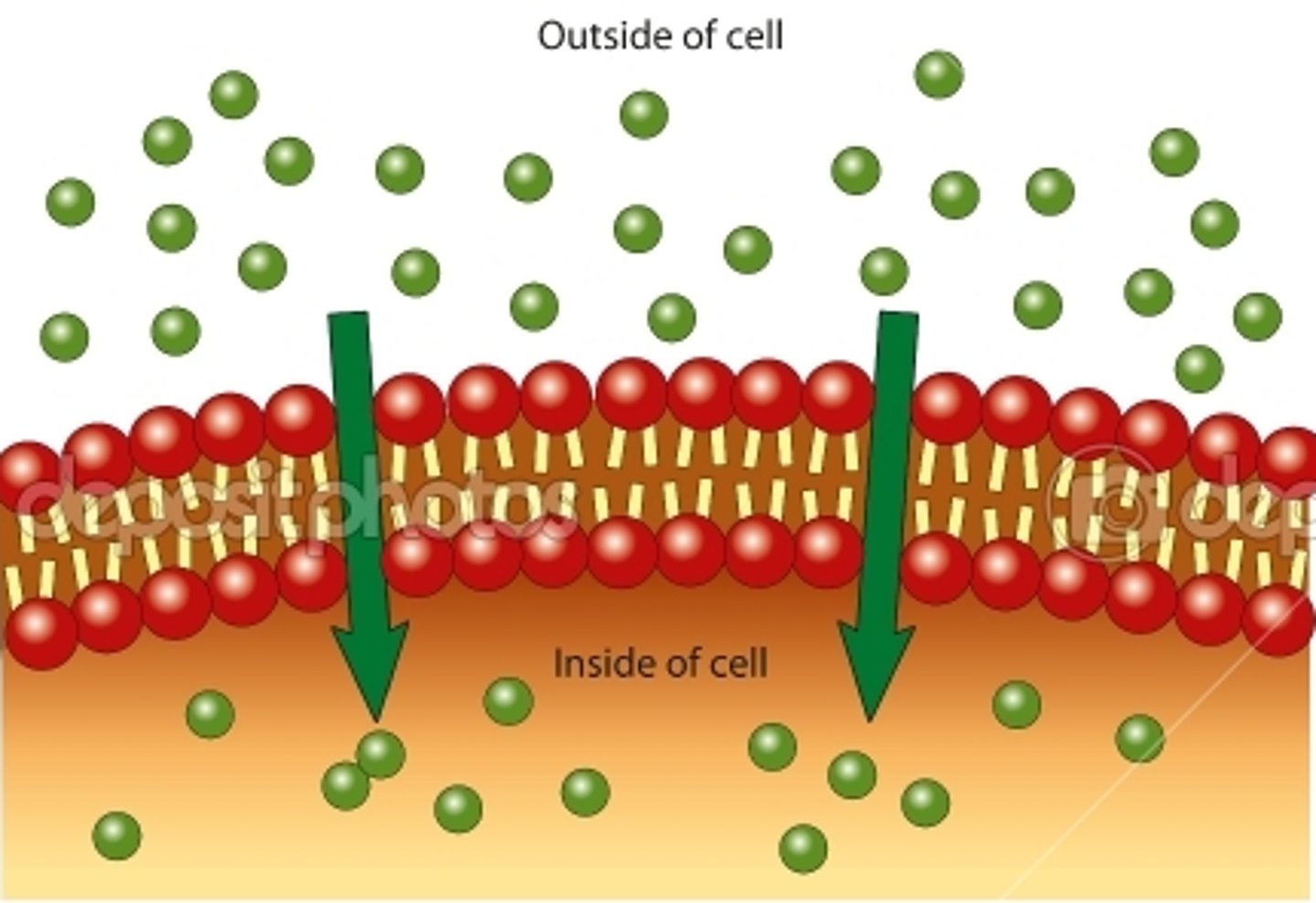
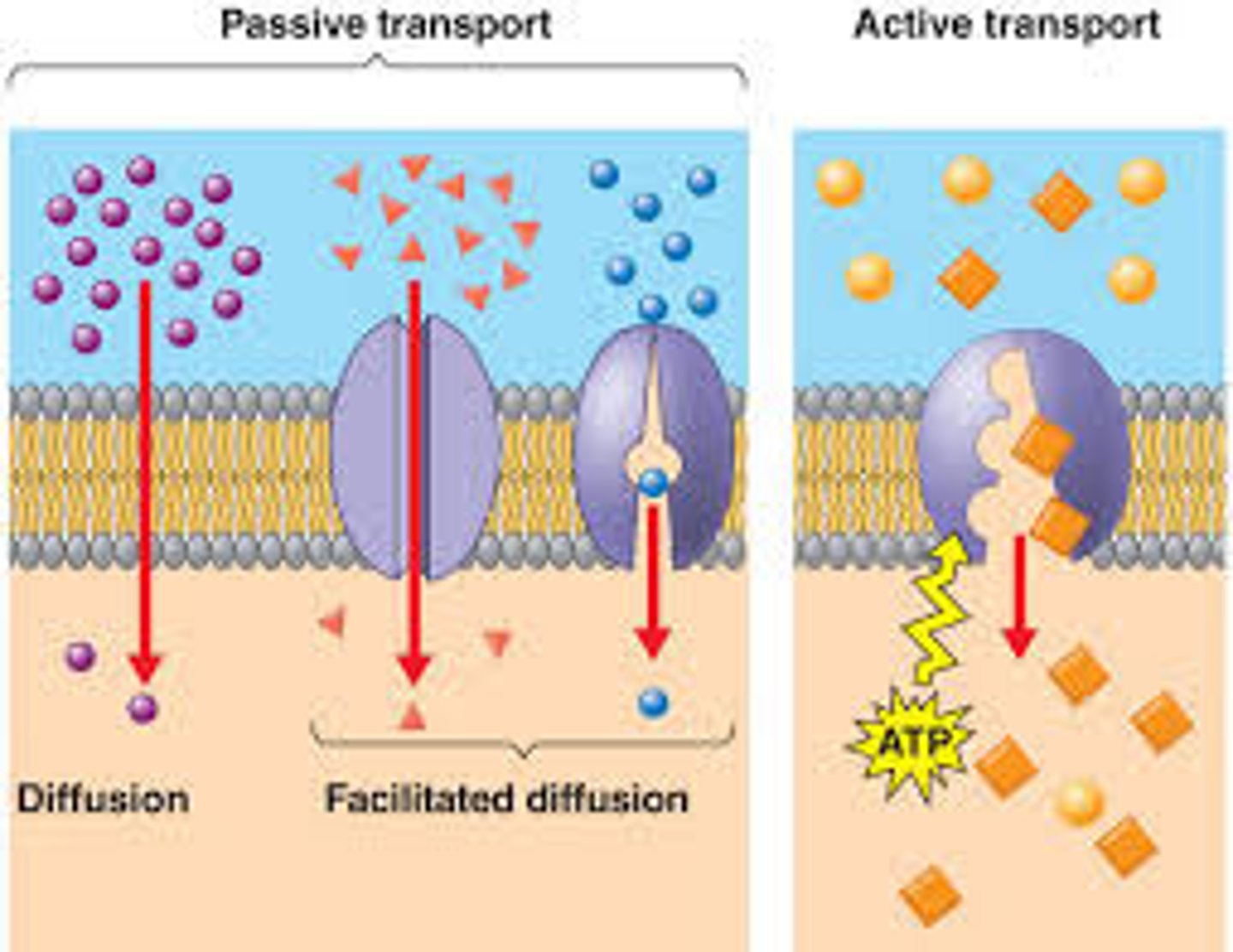
passive transport
The movement of materials through a cell membrane without using energy
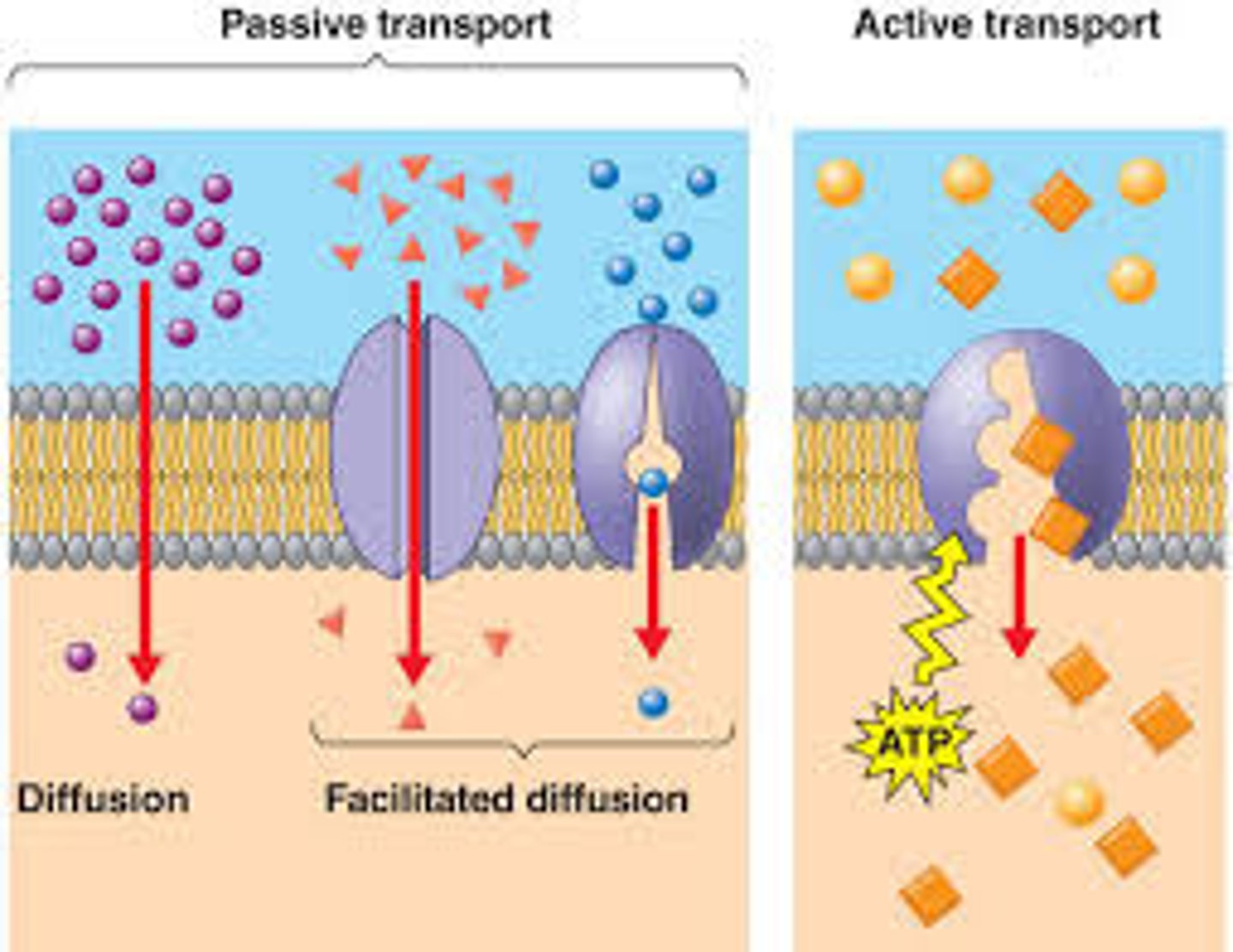
active transport
the movement of materials through a cell membrane using energy
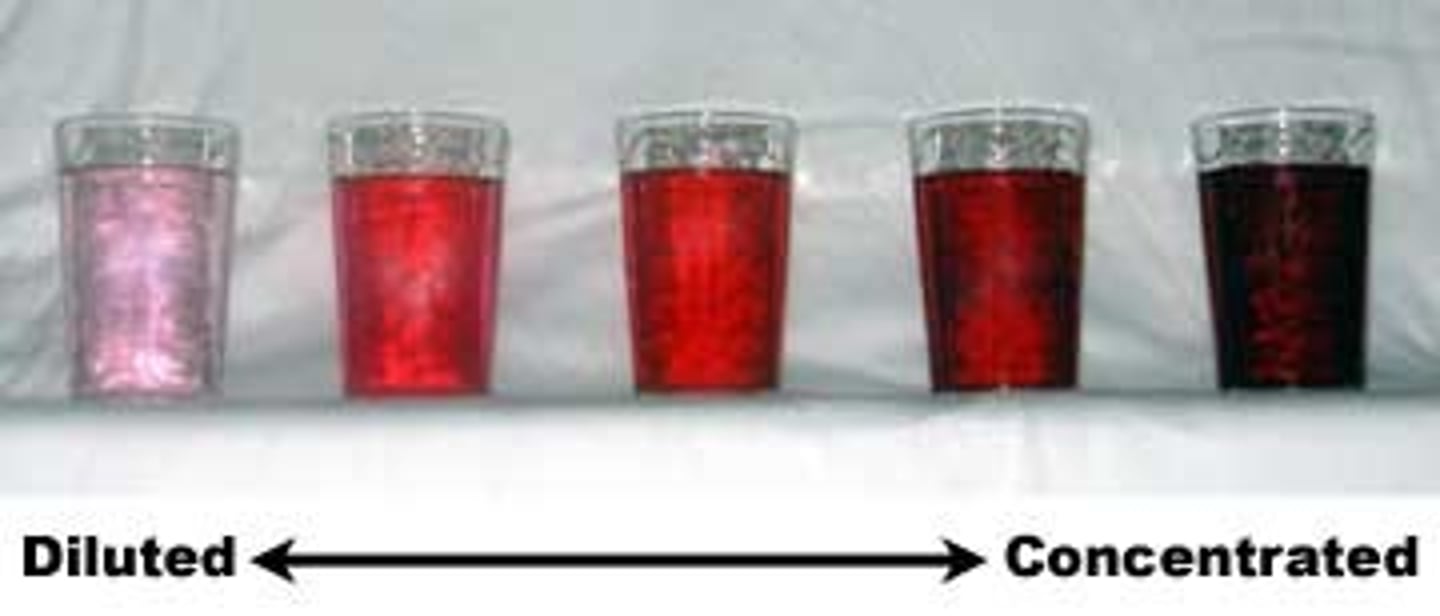
Concentration
A measurement of how much solute exists within a certain volume of solvent
concentration gradient
a difference in the concentration of a substance across a space
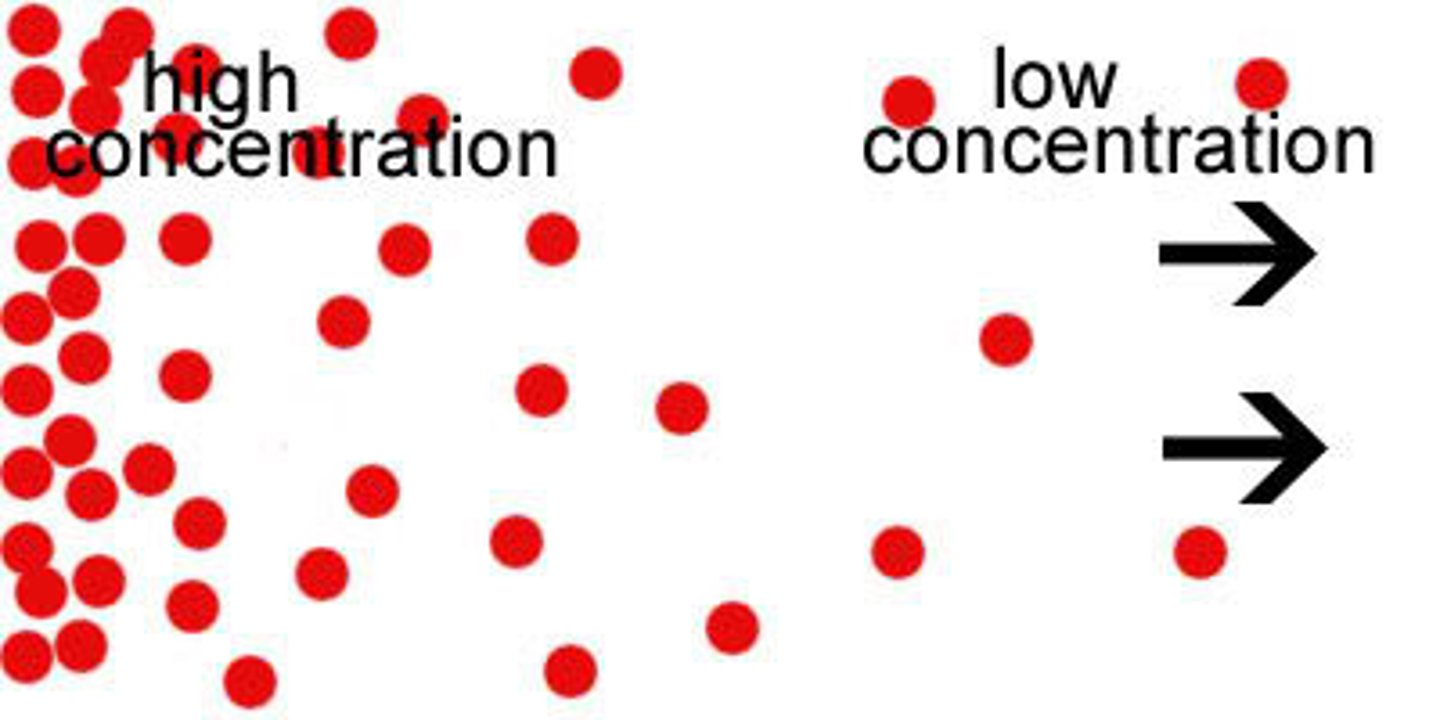
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration until its concentration becomes equal throughout.
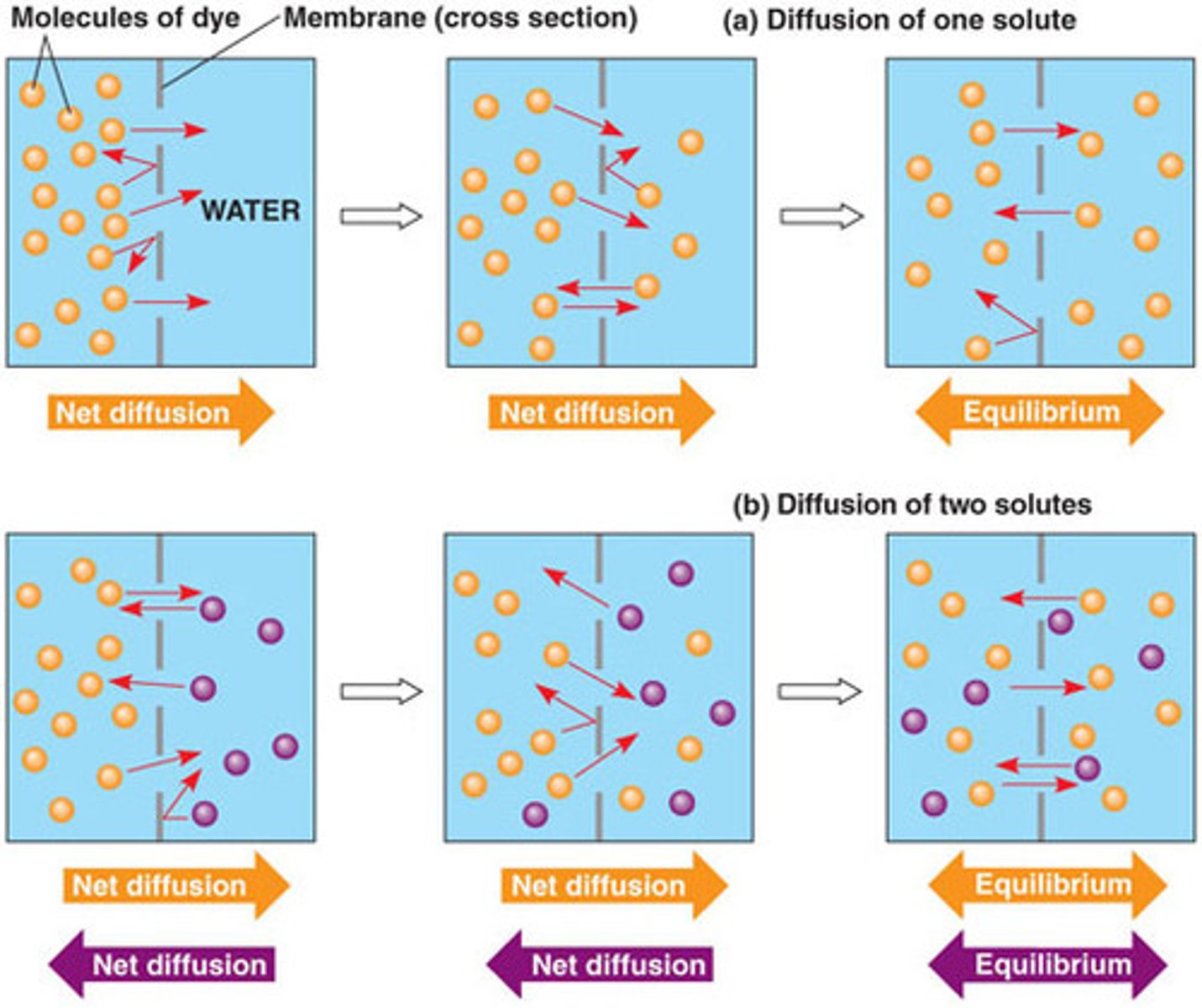
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane from high concentration to low concentration
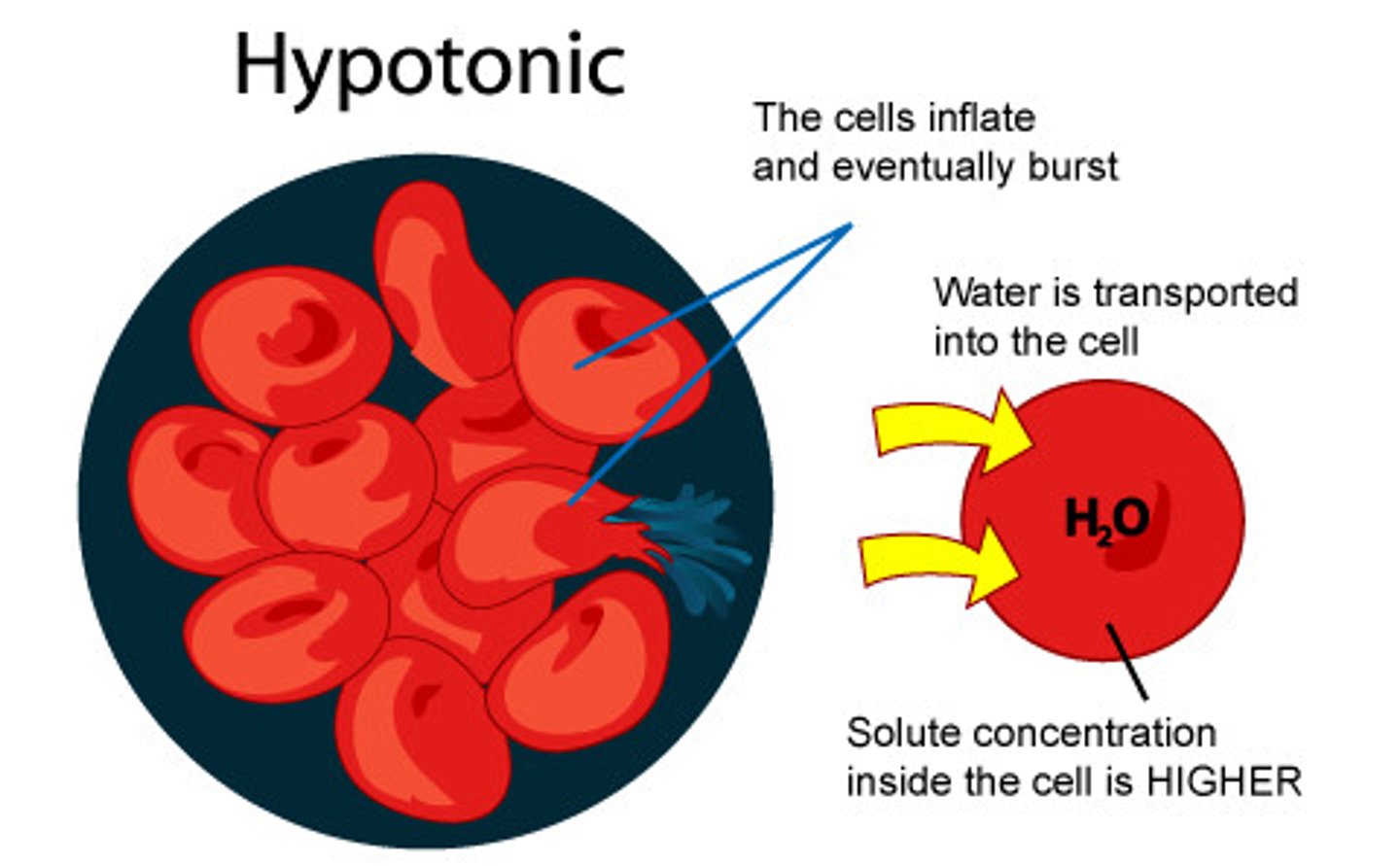
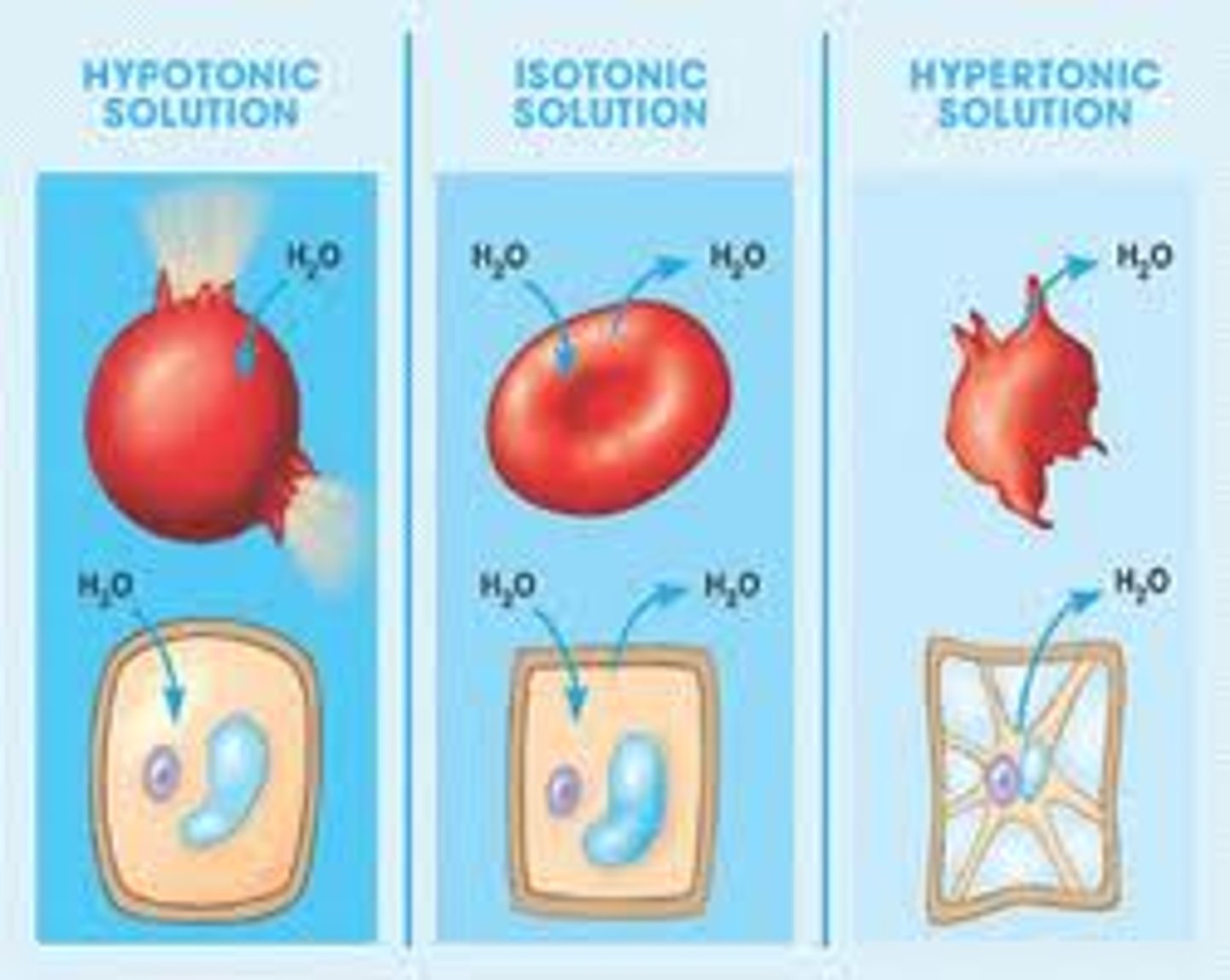
hypotonic solution
Solute concentration is less than that inside the cell; cell gains water
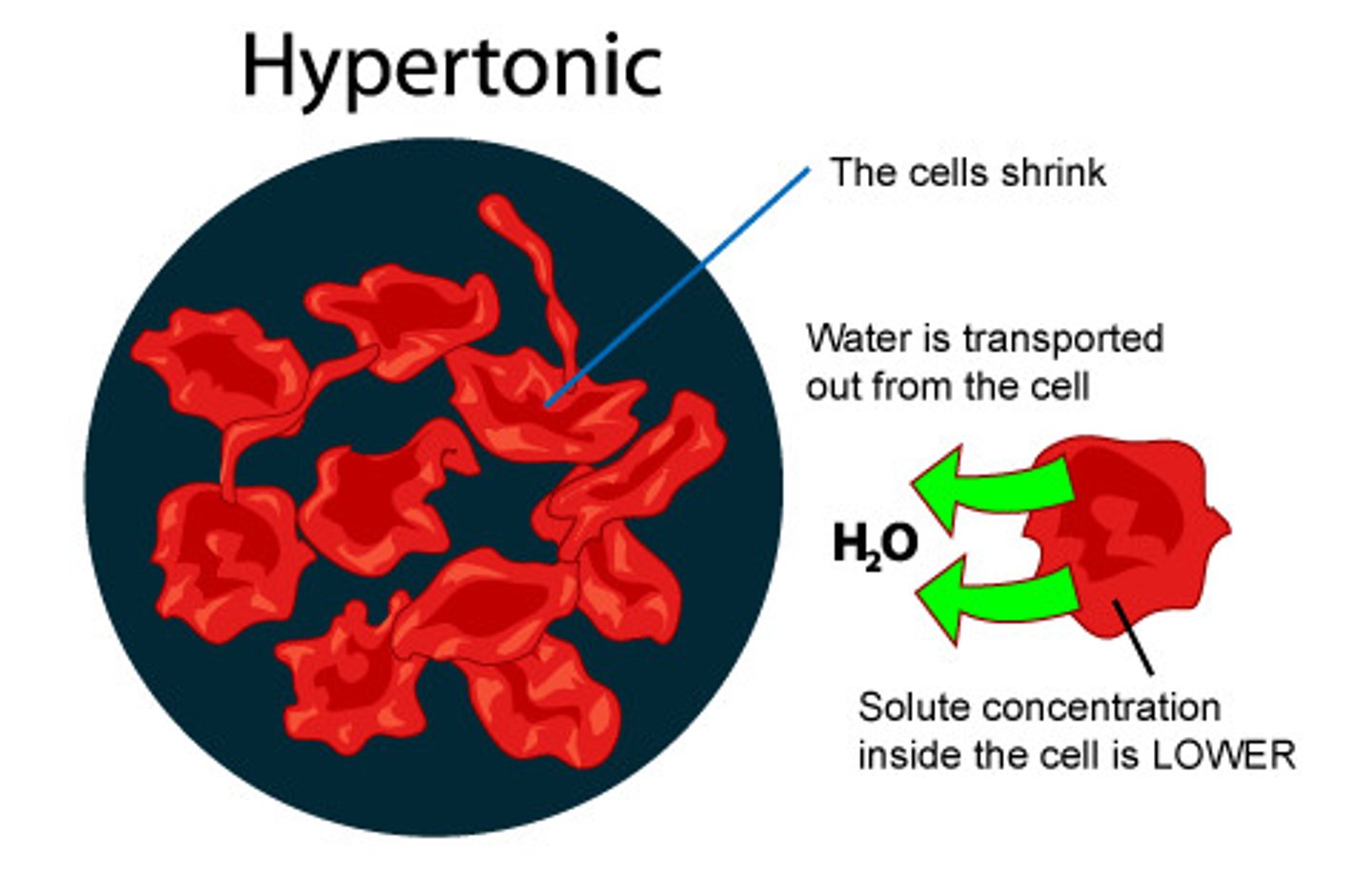
hypertonic solution
a solution that has a high solute concentration and so a low water concentration relative to another solution
isotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is essentially equal to that of the cell which resides in the solution
Plasmolysis
Collapse of a walled cell's cytoplasm due to a lack of water
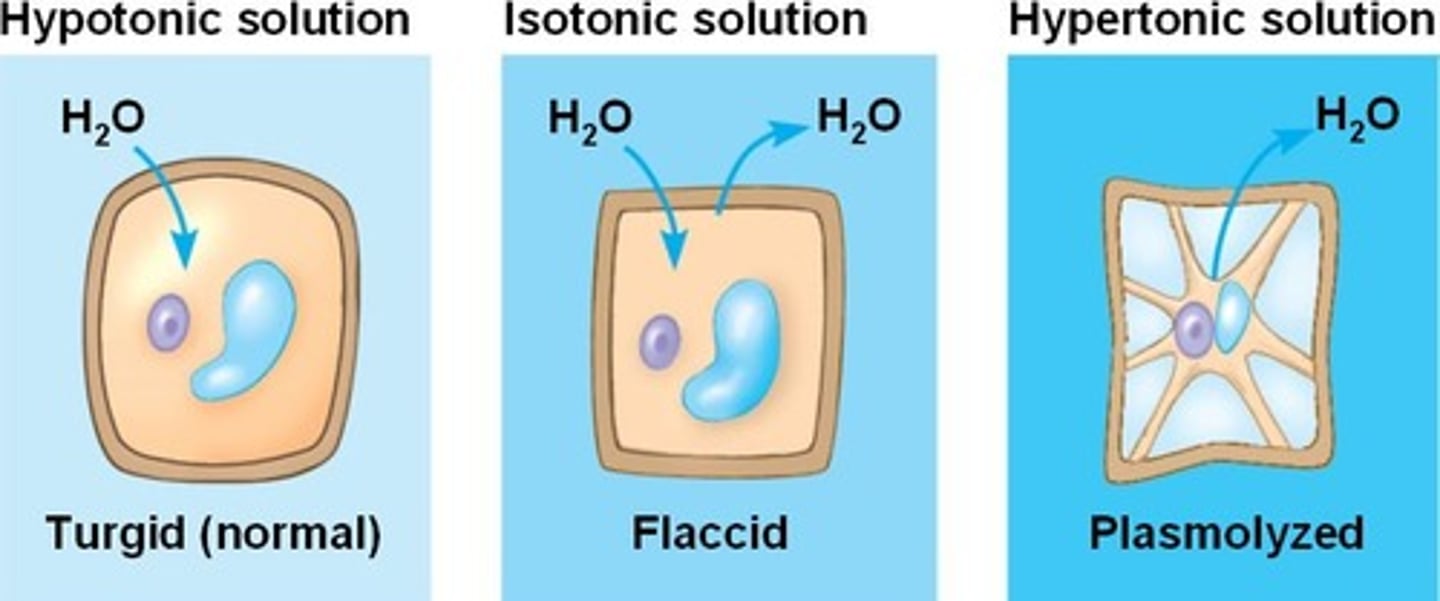
Cytolysis
The rupturing of a cell due to excess internal pressure.

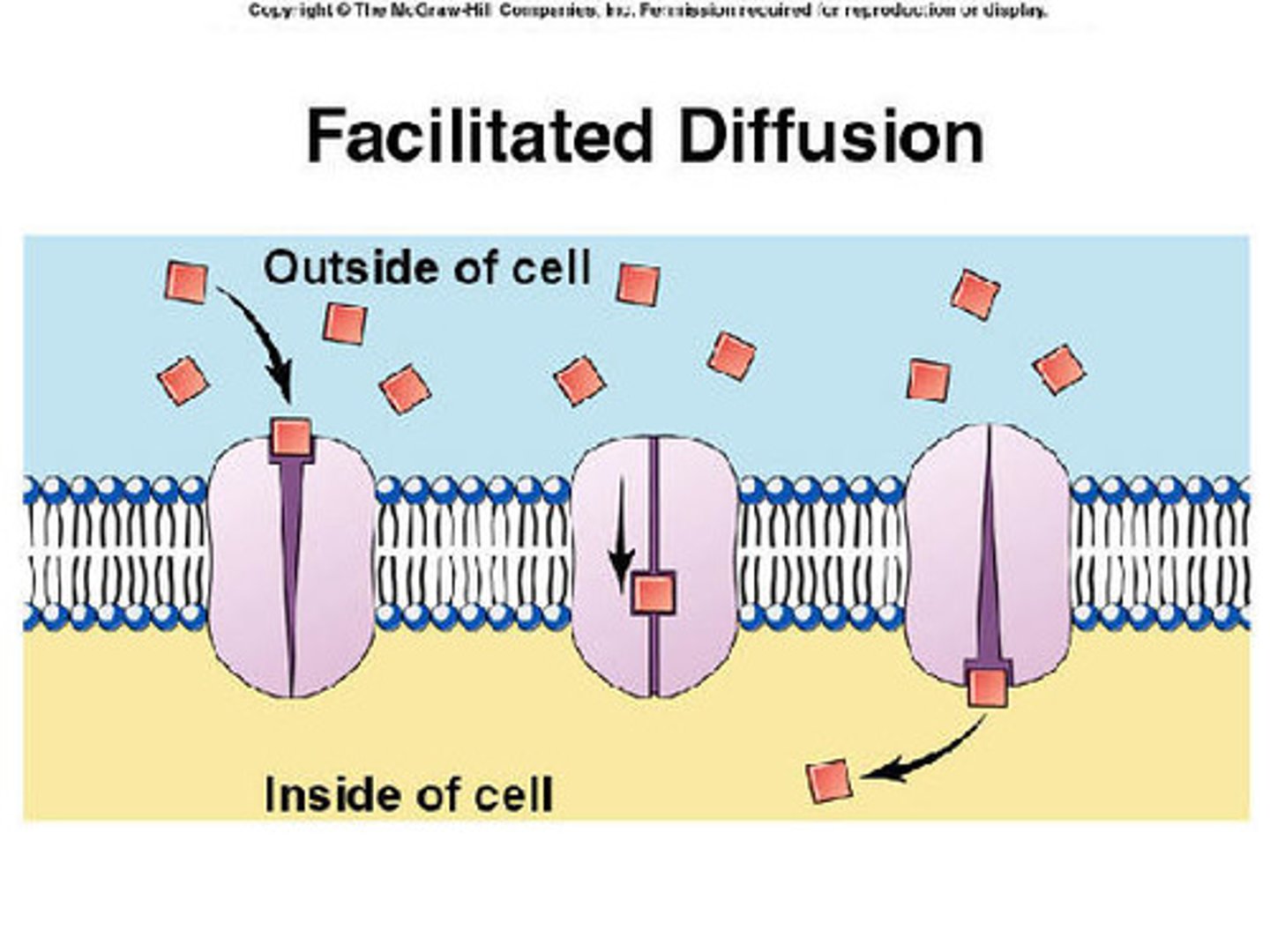
facilitated diffusion
Movement of specific molecules across cell membranes through protein channels from high concentration to low concentration
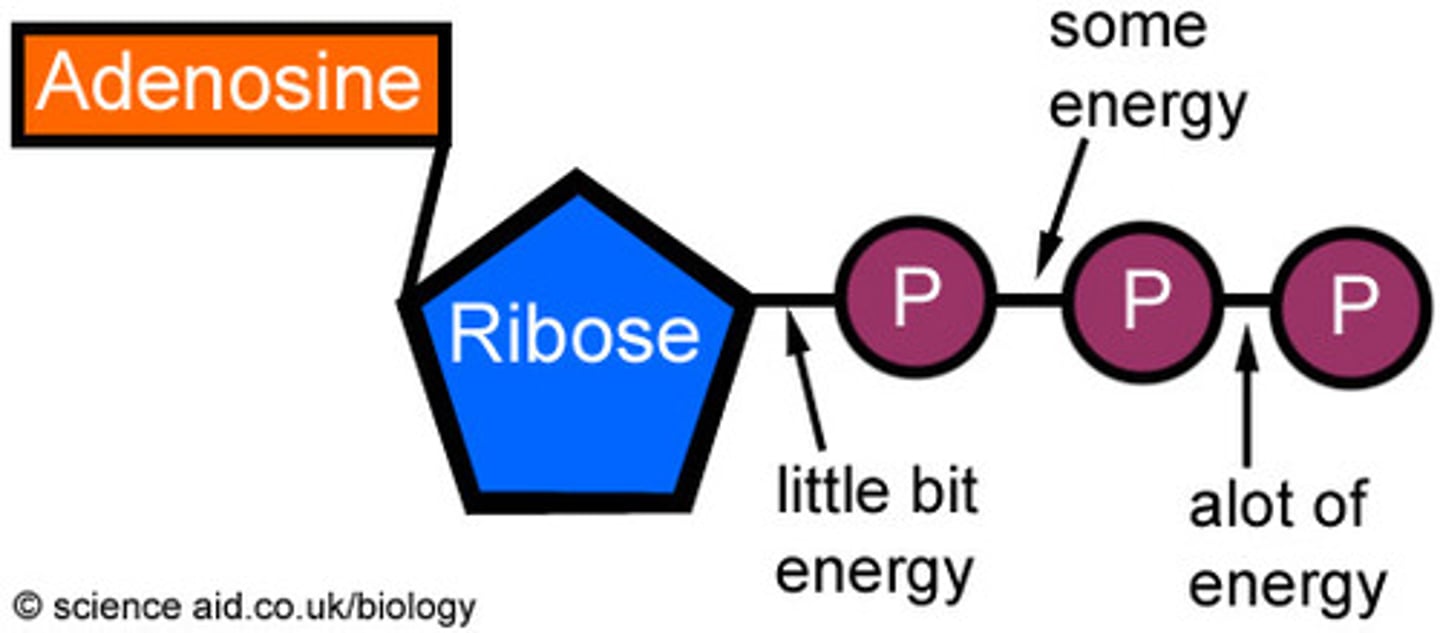
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
compound used by cells to store and release energy
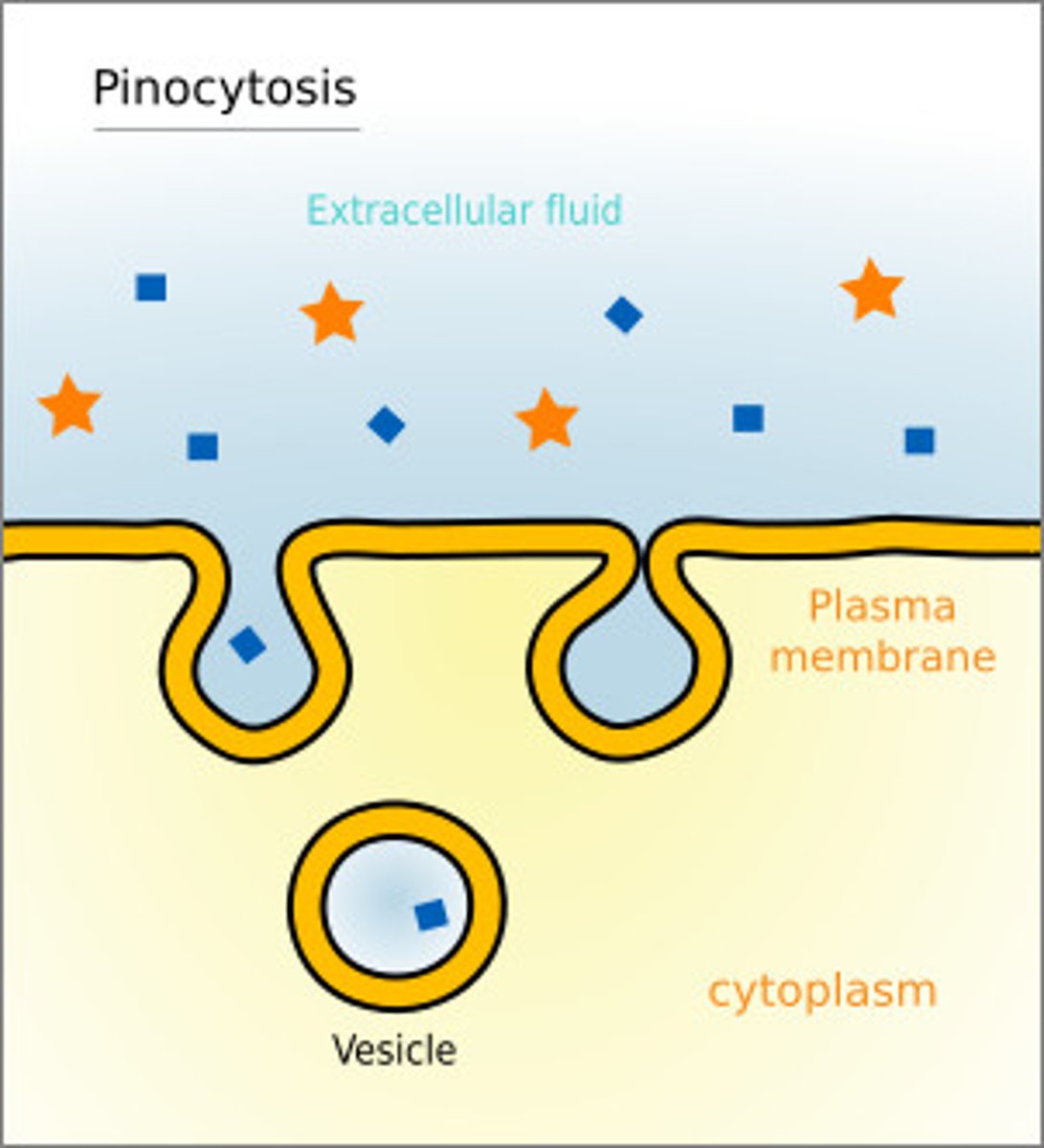
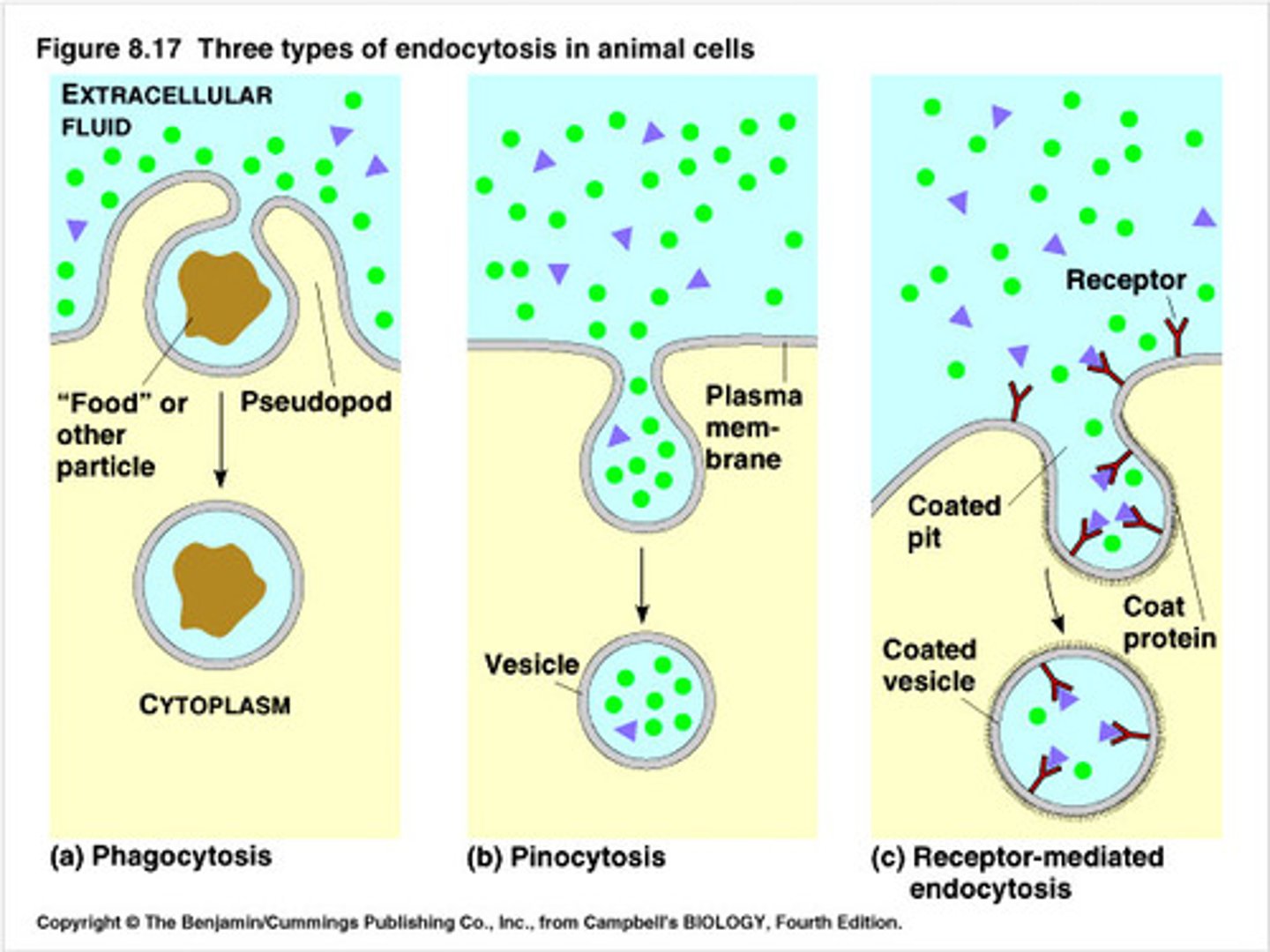
Endocytosis
process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane (vesicles)
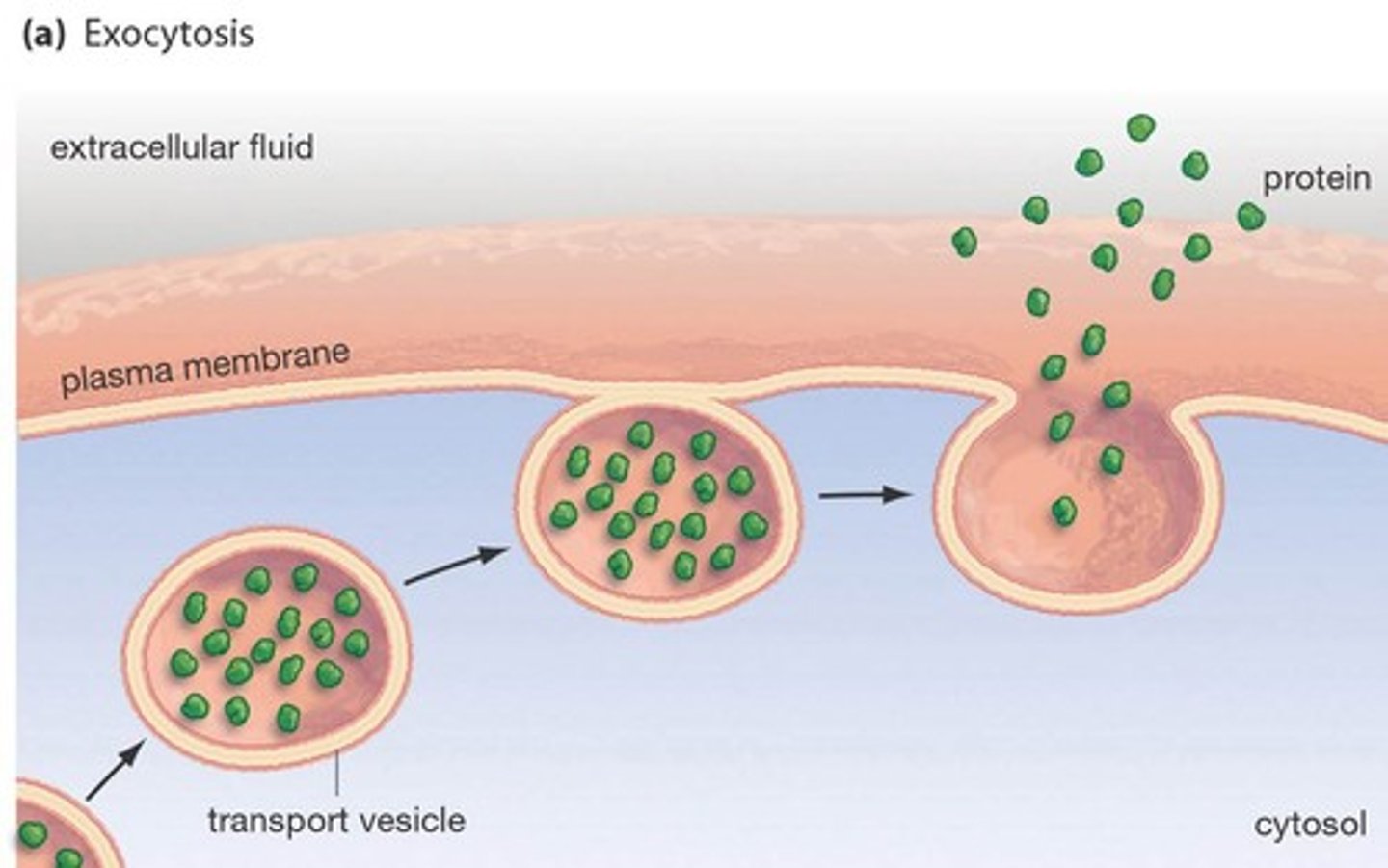
Exocytosis
release of substances out a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the membrane.
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells
Pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which the cell ingests extracellular fluid and its dissolved particles.