Rutgers Biology 115 Exam 1 Review
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
Analysis of ancient rocks has shown that the atmosphere of early Earth was very low in free oxygen (O_2) and that simple organic compounds probably accumulated in shallow water. Which of the following does this support?
a. Serial endosymbiosis
b. Iron-sulfur world hypothesis
c. RNA world hypothesis
d. Oparin-Haldane hypothesis
d. Oparin-Haldance hypothesis
Identify which statement best describes the term 'Chunking' with respect to learning
a. Learning sets of related information.
b. Studying several hours in one day.
c. Organizing the lecture notes alphabetically
d. Going to several lectures in one day.
a. Learning sets of related information.
A brain injury results in the inability to recall old memories, but new memories can be formed. Hypothesize which process was most likely affected.
a. Retrieval from LTM to STM
b. Encoding from LTM to STM
c. Encoding from STM to LTM
d. Retrieval from STM to LTM
a. Retrieval from LTM to STM
Identify which of the following terms describes changes occurring at synapses that cause an increase in synaptic transmission.
a. Neuronal Plasticity
b. Encoding
c. Retrieval
d. Long Term Potentiation
d. Long Term Potentiation
Correctly SEQ memory formation starting with the stimulus from the environment?
I. Encoding to short term memory
II. Long term potentiation
III. Sensory memory storage
IV. Long-term memory storage
III, I, IV, II
Compare and Contrast long-term and short-term memory. Which of the following are TRUE?
I. Long-term memory is limited in capacity
II. Both are longer in duration than sensory memory storage
III. Short-term memory is unlimited in capacity
IV. Long-term memory is unlimited in duration
II and IV
The transfer of information from short term memory to long term memory is called
a. Encoding
b. Plasticity
c. Stimulation
d. Remodeling
a. Encoding
According to what is known about long term potentiation and memory formation, which of the following are the best ways to prepare each week for workshop?
I. Read the lecture notes several times
II. Attend reviews and actively take notes while watching lecture
III. Make your own organizers for each of the outcomes
IV. Retype the notes several times and bring your laptop to workshop
V. Participate in study groups in which students teach each other the material from lecture
II, III, V
Which of the following interactions are ONLY intramolecular attractions?
I. Polar covalent bonds
II. Hydrogen bonds
III. Nonpolar covalent bonds
IV. Ionic Bonds
I and III
Compare and Contrast chemical bonds. Which statement(s) correctly describe(s) BOTH polar covalent bonds and ionic bonds?
I. Result in the sharing of electrons
II. Always result in an electrically charged molecule
III. Require the involvement of a water molecule
IV. Are interactions involving electrons
IV only
Within a single water molecule, a hydrogen forms a _________________ bond with an atom of ______________.
a. Polar covalent, hydrogen
b. Polar covalent, oxygen
c. Hydrogen bond, oxygen
d. Hydrogen bond, hydrogen
b. Polar covalent, oxygen
Compare and contrast emergent properties of water. Which of the following result from attractions between water molecules?
a. Ice is more dense than liquid water
b. Cohesion results in surface tension
c. Water is a polar molecule
d. Water moves by osmosis
b. Cohesion results in surface tension
Identify which of the following is/are TRUE about excited electrons?
I. The charge becomes positive
II. They move away from the atom's nucleus
III. They have higher kinetic energy
IV. They have higher potential energy
II and IV
Identify which of the following is an example of emergence.
a. The mass of a large molecule is the sum of the mass of its atoms
b. Cells can be broken down into organelles and molecules
c. A water molecule has polarity
d. A bicycle can be broken down into small mechanical parts
c. A water molecule has polarity
Hypothesize what kind of bond is most likely to form between two atoms with a very small difference in electronegativity
a. Hydrogen
b. Covalent
c. Peptide
d. Ionic
b. Covalent
Identify which of the following statements correctly describes hydrolysis/
a. Endergonic
b. Results in peptide bonds
c. Breaks down polymers
d. Used to make polysaccharides
c. Breaks down polymers
What is the CORRECT order of the stages of investigating if grass grows faster in July than in August?
I. Grow 10 different plots of grass and measure their rate of growth and moisture for the months of July and August
II. The hypothesis is supported
III. Predict that grass grows significantly faster when the soil has higher moisture
IV. The observation is that grass grows faster in July than August
V. The hypothesis is that that grass grows faster in July because he soil has more moisture than in August
IV->V->III->I->II
Identify which of the following is/are TRUE about hydrocarbon chains?
I. They can diffuse through a plasma membrane
II. They contain a ration of 1C to 2H to 1 Oxygen
III. They are usually non-polar
IV. They are biological monomers
I and III
Hypothesize how changing the R group on a molecule from a methyl group to a hydroxyl group would change the properties of a shot hydrocarbon.
I. Becomes hydrophilic
II. Becomes acidic
III. Becomes hydrophobic
IV. Can form hydrogen bonds
I and IV
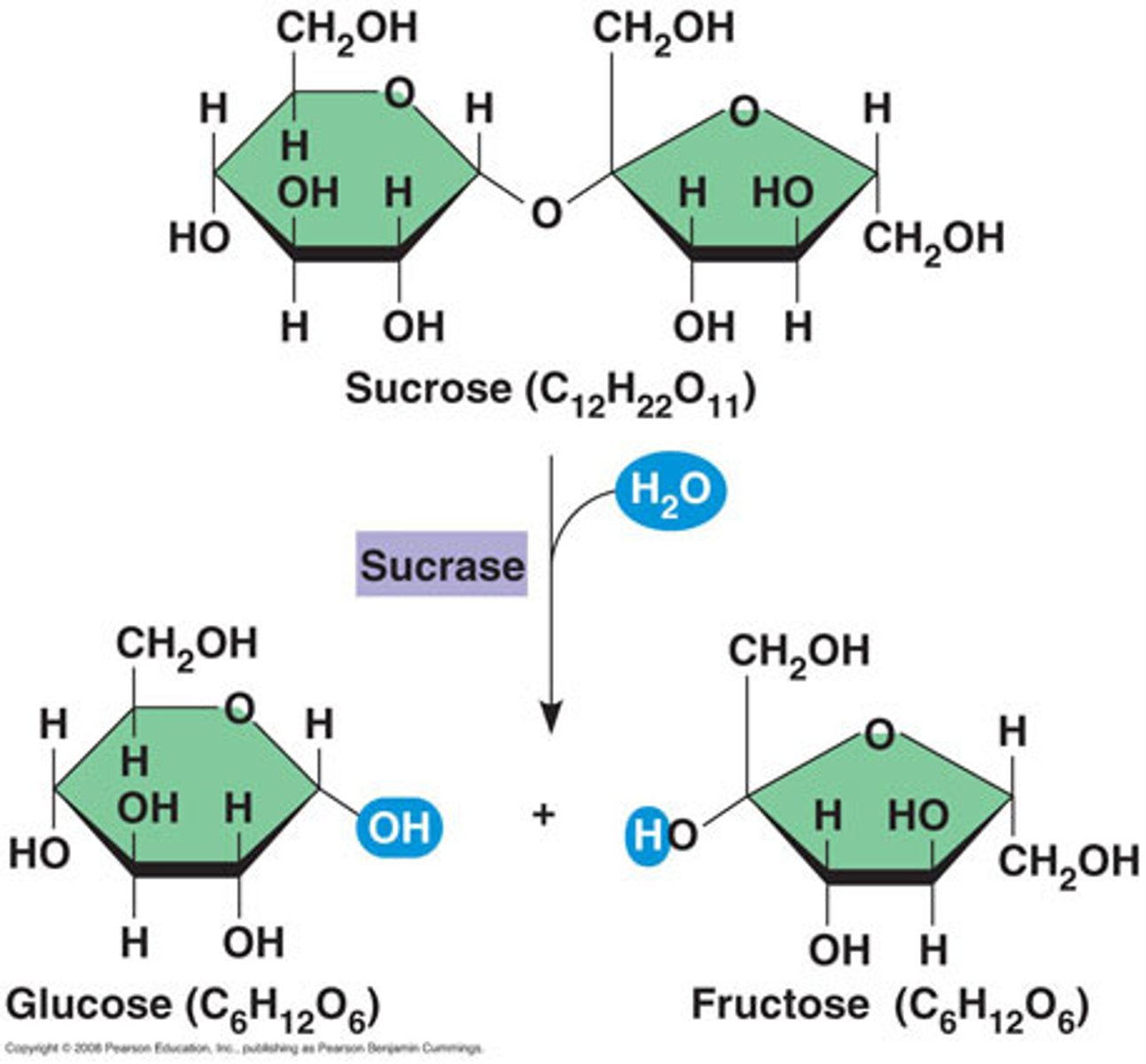
Compare and contrast biological molecules. Which of the following statements correctly describes BOTH of the pictured molecules?
I. Produced as the result of a hydrolysis reaction between monomers
II. Requires the addition of a water molecule to break it into its monomers
III. It is a hydrocarbon
IV. It can interact with water molecules
II and IV
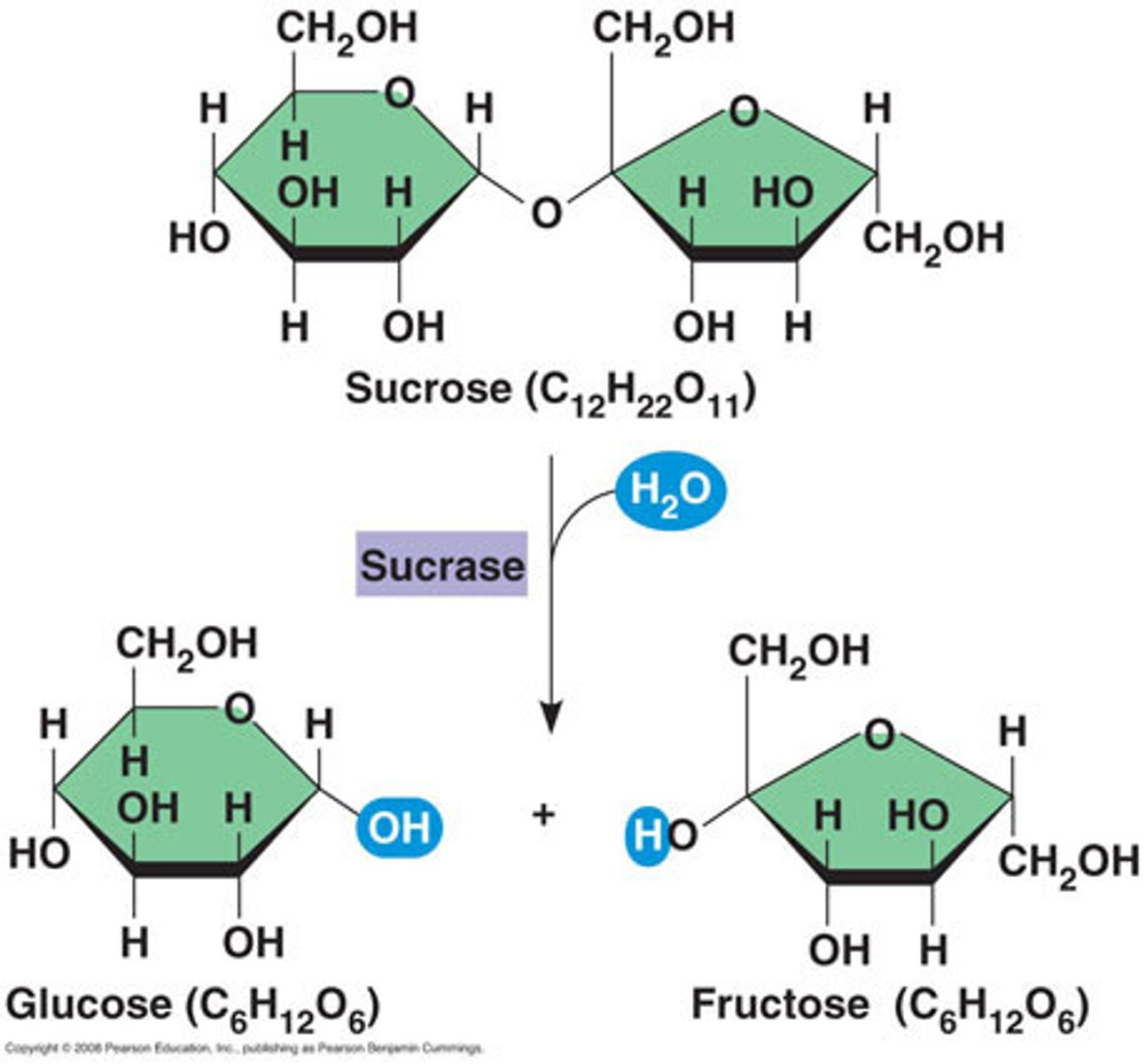
Compare and contrast functional groups. What properties are shared between carbonyl and hydroxyl groups?
a. Are charged
b. Are polar
c. Contain carbon bound to hydrogen
d. Contain nitrogen
b. Are polar
As you sleep all night your blood sugar drops, this triggers the release of glucagon from your pancreas. Glucagon is a hormone that then triggers the release of sugar from your liver. For the sugar to be released, the following reaction must take place in your liver.
a. Dehydration synthesis
b. Hydrolysis
c. Hydrogen bond
d. Glycosidic
b. Hydrolysis
Identify which functional group is primarily responsible for the hydrophilic nature of the primary molecules of plasma membranes.
a. Methyl group
b. Phosphate group
c. Carboxyl group
d. Hydroxyl group
b. Phosphate group
You are swimming in the ocean an encounter a small structure. When you take it back to the lab you find that it is comprised of organic phosphate and hydrocarbons forming a sphere. Inside there are no proteins only some simple sugars and ions. What hav you found?
a. A nucleus
b. Protocell
c. A cell
d. Prokaryotic cell
b. Protocell
In which pair do BOTH terms CORRECTLY describe the earliest cellular life?
a. Autotroph, prokaryote
b. Predator, eukaryote
c. Prokaryote, heterotroph
d. Aerobe, eukaryote
c. Prokaryote, heterotroph
Identify which of the following statements is/are TRUE with regard to protein structure.
I. Formation of primary stricture is spontaneous
II. Alpha helices are an example of tertiary structure
III. Tertiary structure involves interactions between R groups
IV. Primary structure is the sequence of amino acids in a protein
III and IV
Correctly sequence evolutionary developments in the history of life.
I. Prokaryotes
II. Endosymbiosis
III. Photosynthesis
IV. Multicellular eukaryotes
V. Terrestrial animals
I, III, II, IV, V
Life on Earth did not leave a fossil record until 3.5 bya. Prior to this, scientists have hypothesized that the precursors to cells must have gone through a series of four steps to form a single cell. Correctly sequence the events that occurred prior to the first cells on earth.
I. Formation of macromolecules
II. Formation of protocells
III. Abiotic synthesis of small organic molecules
IV. Self0replicating molecules
III, I, II, IV
Oxygen is detrimental to the spontaneous formation of organic monomers because it
a. is an oxidizing agent
b. requires an enzyme to react with other molecules
c. does not react with existing monomers
d. increases the rate of peptide bond formation
a. is an oxidizing agent
Which of the following are requirements for the abiotic synthesis of organic monomers?
I. Inorganic building blocks like CO_2 and H_2
II. Atmospheric oxygen
III. Protein enzymes
IV. An energy source
I and IV
Identify which of the following structures catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds?
a. Nucleus
b. Golgi apparatus
c. Endoplasmic reticulum
d. Ribosomes
d. Ribosomes
Compare and contrast protocells and living cells. Which of the following are characteristics shared by BOTH?
I. Growth followed by division
II. Osmotic swelling
III. Internal environment different from external environment
IV. Information storage and transmission
I, II, and III
Correctly sequence the order in which a hydrolase enzyme passes through the endomembrane system as it is being synthesized and modified
I. Rough ER
II. Golgi Apparatus
III. Secondary lysosome
IV. Primary lysosome
I, II, IV, III
Compare and contrast the domains of life. Which contain(s) cells with an endomembrane system?
I. Archaea
II. Bacteria
III. Eukarya
III only
You are studying a poison that inhibits the formation of vesicles by the endoplasmic reticulum. Hypothesize which of the following steps in protein transport will NOT occur as a result of a cell being exposed to this poison.
I. Tertiary folding of the polypeptide
II. Exocytosis of the protein
III. Synthesis of ribosomes
IV. Formation of peptide bonds
V. Protein modification in Golgi apparatus
II and V
Identify where DNA is found within a bacterium.
a. Lysosome
b. Plasma membrane
c. Nuclear envelope
d. Cytoplasm
d. Cytoplasm
Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Which structures are found in BOTH types of cells?
I. Nucleoid
II. Ribosomes
III. DNA
IV. Plasma membrane
V. Proteins
II, III, IV, and V
Identify which of the following is a characteristic of the nuclear envelope?
a. Synthesizes ribosomes
b. Is only present in prokaryotes
c. Separates nucleus from cytoplasm
d. Contains structures involved in protein synthesis
c. Separates nucleus from cytoplasm
A researcher is able to use a radioactive marker to label the phospholipids in the membrane of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. She is also able to track the movement of the marker through the cell. If the cell is functioning normally, hypothesize in which cell structures these labeled phospholipids could eventually be found?
I. Ribosomes
II. Nucleus
III. Golgi apparatus
IV. lysosomes
II, III, and IV
The bulk transport of large molecules by cells
a. Occurs in prokaryotes, but not in eukaryotes
b. Always depends on the input of energy by the cell
c. Is a type of facilitated diffusion
d. Always results in the movement of materials into the cell
b. Always depends on the input of energy by the cell
Identify the type of lipids that are the primary component of the cell membrane.
a. Triglycerides
b. Phospholipids
c. Cholesterol
d. Saturated fats
b. Phospholipids
Hypothesize which of the following membrane functions would be interrupted if all transmembrane proteins were removed from the plasma membrane.
I. Active transport
II. Signal transduction
III. Facilitated diffusion
IV. Simple diffusion
I, II, and III
Identify which of the following move substances BOTH across a membrane and AGAINST the concentration gradient?
a. Proton (H+) pumps
b. Exocytosis
c. Facilitated diffusion
d. Phagocytosis
a. Proton (H+) pumps
Two solutions that are separated by a membrane are at dynamic equilibrium. Water molecules can cross the membrane, but solute molecules cannot. Which statement correctly described this scenario?
a. Water molecules move in both directions across the membrane
b. One solution is hypotonic and the other is hypertonic
c. There is no movement occurring across the membrane
d. Both solutions are hypertonic
a. Water molecules move in both directions across the membrane
A solution that surrounds a cell and causes it to lose water is:
a. Hypertonic
b. Isotonic
c. Hypotonic
d. Odmotic
a. Hypertonic
Which of the following are UNABLE to move through a phospholipid bilayer via simple diffusion?
a. Small polar molecules like H2O
b. Nonpolar gasses like CO2
c. Large polar molecules like glucose
d. Hydrocarbons
c. Large polar molecules like glucose
Identify which of the following types of membrane transport are specific.
I. Exocytosis
II. Pinocytosis
III. Facilitated diffusion via ion channels
IV. Simple diffusion
V. Receptor-mediaed endocytosis
III and V
Identify which of the following functional groups is removed from ATP to drive endergonic reactions?
a. -CH3
b. -OPO3^-2
c. -OH
d. -COOH
b. -OPO3^-2
In a redox reaction:
I. The molecule that is oxidized gains an electron(s)
II. At least one free electron is released into the solution
III. The molecule that is reduced gains an electron(s)
III only
Which of the following are TRUE about this reaction?
I. Anabolic
II. Catabolic
III. Exergonic
IV. Endergonic
V. Delta G
II and III
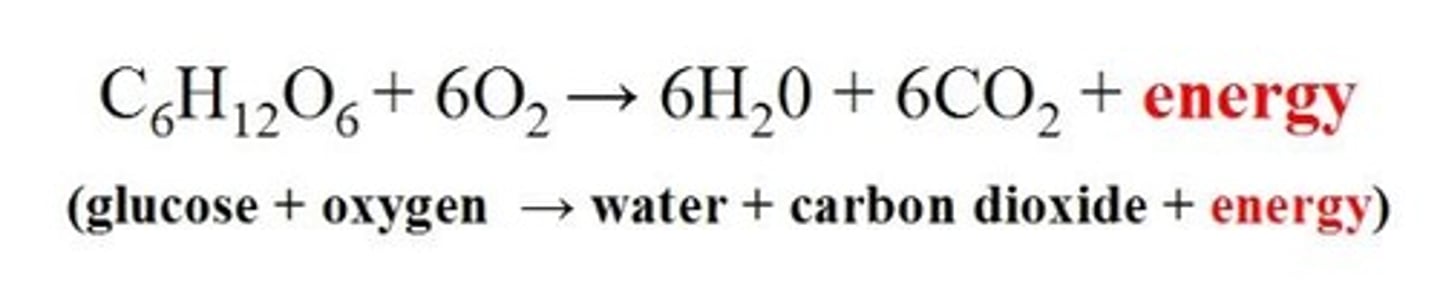
Identify which statement correctly describes ATP.
a. Its hydrolysis is coupled to exergonic reactions
b. It stores potential energy in bonds between phosphate groups
c. Its main components are a lipid and 3 phosphate groups
d. Its hydrolysis is an endergonic reaction
b. It stores potential energy in bonds between phosphate groups
Compare and contrast anabolism and catabolism. Which of the following statements are TRUE?
I. Catabolic reactions build complex molecules
II. Anabolic reactions build complex molecules
III. Anabolic reactions require energy
IV. Catabolic reactions release energy
II, III, and IV
An enzyme that catalyzes an exergonic reaction has been treated with an irreversible inhibitor. Hypothesize how the reaction will change compared to before the inhibitor was introduced.
a. The activation energy will be higher
b. Delta G will change from positive to negative
c. Delta G will change from negative to positive
d. The activation energy will be lower
a. The activation energy will be higher
Which of the following best describes free energy?
a. Energy lost has heat
b. Disorder in a system
c. Energy available to do work
d. Energy in motion
c. Energy available to do work
A gene for a human enzyme (body temperature of 37°C) is inserted into a bacterium that lives in a hot spring (77°C). Hypothesize how this enzyme's activity will change.
a. Denature and stop working
b. It will be unaffected
c. Operate slower due to higher temperature
d. Operate faster at higher temperature
a. Denature and stop working
Identify the main source of energy that excites the electrons during photosynthesis.
a. C6H12O6
b. ATP
c. Light
d. NADPH
c. Light
Correctly sequence the events that occur during photosynthesis
I. Energy used to synthesize ATP
II. Electron moves to a higher energy orbital
III. Energy absorbed from a photon
IV. Electron leaves an atom and is captured by an acceptor
III, II, IV, I
Where does the carbon used in photosynthesis come from?
a. CO2 in the air
b. CO in the air
c. Glucose stored in roots
d. Carbon compounds in the soil
a. CO2 in the air
Identify which of following is the SOURCE of electrons during photosynthesis?
a. C6H12O6
b. CO2
c. O2
d. H2O
d. H2O
Identify which of the following is TRUE for photosynthesis.
a. The overall free energy change is negative
b. Oxygen is a reactan
c. Carbon dioxide is a reactant
d. Overall, it is an exergonic reaction
c. Carbon dioxide is a reactant
Sequence photosynthesis. During the Calvin cycle electrons move:
a. from the stroma to the thylakoid space
b. from CO2 to a sugar
c. from NADPH to G3P
d. from ATP to NADPH
c. from NADPH to G3P
How is O2 used by a plant cell?
a. During respiration as the terminal electron acceptor
b. As the terminal electron acceptor during photosynthesis
c. Plant cells do not require O2
d. As an electron carrier during the light dependent reactions
a. During respiration as the terminal electron acceptor
Compare and Contrast aerobic respiration and photosynthesis. Which of the following occur during BOTH?
I. Protons are pumped across a membrane
II. ATP are produced
III. Electrons move down an electron transport chain
IV. Energy is converted from one form to another
V. Protons (H+) diffuse through ATP synthase
I, II, III, IV, and V
Identify which molecule is oxidized during glycolysis.
a. Glucose
b. Oxygen
c. NAD+
d. Water
a. Glucose
Compare and contrast photosynthesis and aerobic cellular respiration. Which of the following statements are TRUE for BOTH?
I. Water is reduced and organic carbon is oxidized
II. They are anabolic reactions
III. On net, ATP is produced
IV. Chemiosmosis occurs
IV only
Which of the following is the ultimate destination for electrons in aerobic respiration?
a. CO2
b. ATP
c. H2O
d. Glucose
c. H2O
Glucose enters into a eukaryotic cell through an integral protein that is embedded into the cell's plasma membrane. This protein, called GLUT 1, moves high levels of glucose into the cell through facilitated diffusion. How many ATP are required to move one glucose molecule into a eukaryotic cell?
a. 4
b. 2
c. 0
d. 28
c. 0
Identify where the electron transport chain is located in animal cells.
a. Inner mitochondrial membrane
b. Outer mitochondrial membrane
c. Endoplasmic reticulum
d. Plasma membrane
a. Inner mitochondrial membrane
Sequence cellular respiration. NAD+ is reduced during:
I. Glycolysis
II. Pyruvate oxidation
III. The citric acid cycle
IV. Oxidative phosphorylation
I, II, and III
Sequence cellular respiration. During cellular respiration which of the following molecule(s) is/are reduced?
I. Glucose
II. FAD
III. Carbon dioxide
IV. ATP
V. O2
II and V
Chemiosmosis
Process by which a Hydrogen pump pumps protons into the thylakoid membrane. H+ passively flows through the ATP synthase which leads to the creation of ATP.
Hypertonic
Having a higher concentration of solute than another solution.
Hypotonic
when comparing two solutions, the solution with the lesser concentration of solutes
Isotonic
when the concentration of two solutions is the same
Osmotic solution
The solution outside a cell.
Anabolic
A process in which large molecules are built from small molecules
Catabolic
A process in which large molecules are broken down
exergonic reaction
A spontaneous chemical reaction in which there is a net release of free energy.
endergonic reaction
A non-spontaneous chemical reaction in which free energy is absorbed from the surroundings.
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
active transport
Energy-requiring process that moves material across a cell membrane against a concentration difference
facilitated diffusion
process of diffusion in which molecules pass across the membrane through cell membrane channels
signal transduction
A series of molecular changes that converts a signal on a target cell's surface to a specific response inside the cell.
bulk transport
The process by which large particles and macromolecules are transported through plasma membranes. Inc. exocytosis and endocytosis
phospholipid bilayer
Plasma membrane layers composed of phospholipid molecules arranged with polar heads facing the outside and nonpolar tails facing the inside.
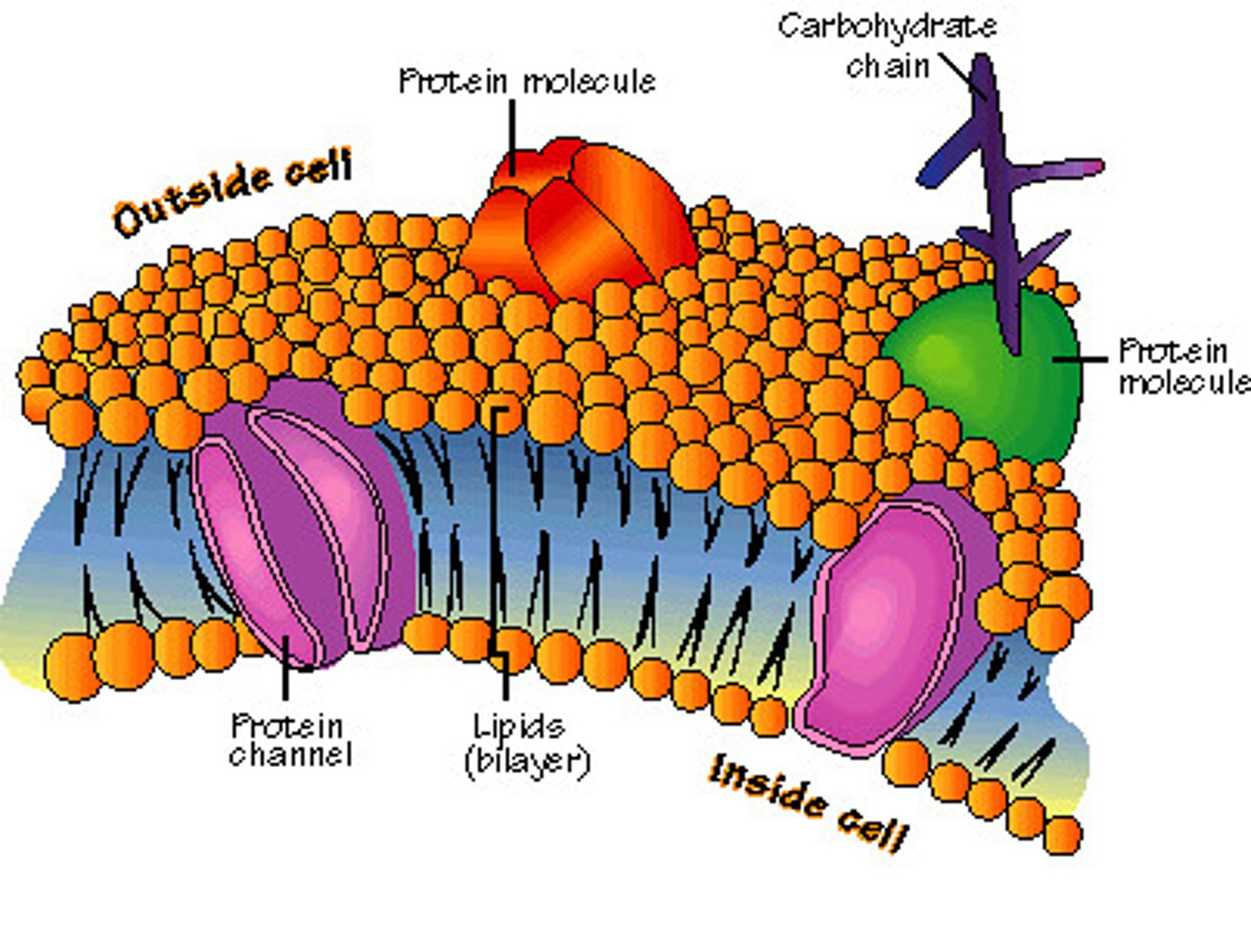
concentration gradient
difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells, cell eating
Pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which the cell ingests extracellular fluid and its dissolved solutes. (cell drinking, ex: Pino is a kind of drink)
Phospholipids
a lipid consisting of a glycerol bound to two fatty acids and a phosphate group.
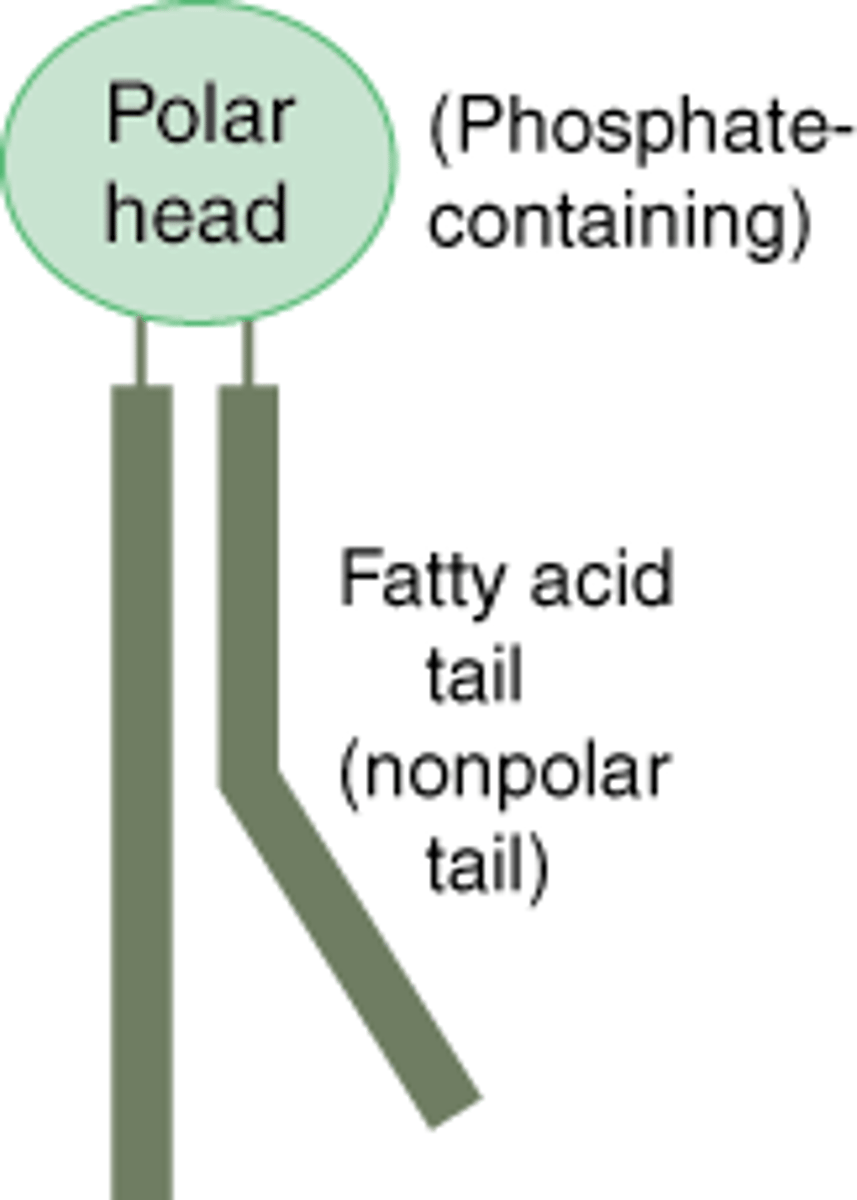
Cholesterol
A lipid that forms an essential component of animal cell membranes and acts as a precursor molecule for the synthesis of other biologically important steroids.
Triglycerides
an energy-rich compound made up of a single molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid.
Lysosomes
cell organelle filled with enzymes needed to break down certain materials in the cell
protocell
a large, ordered structure, enclosed by a membrane, that carries out some life activities, such as growth and division
RNA world hypothesis
Hypothesis that describes how the Earth may have been filled with RNA-based life before it became filled with the DNA-based life we see today.
iron-sulfur world hypothesis
hypothesis that life began in rocks rich in iron sulfide near deep-sea hydrothermal vents
Oparin-Haldane hypothesis
how life on earth could have formed gradually from nonliving chemicals
Endosymbiosis
symbiosis in which one of the symbiotic organisms lives inside the other.
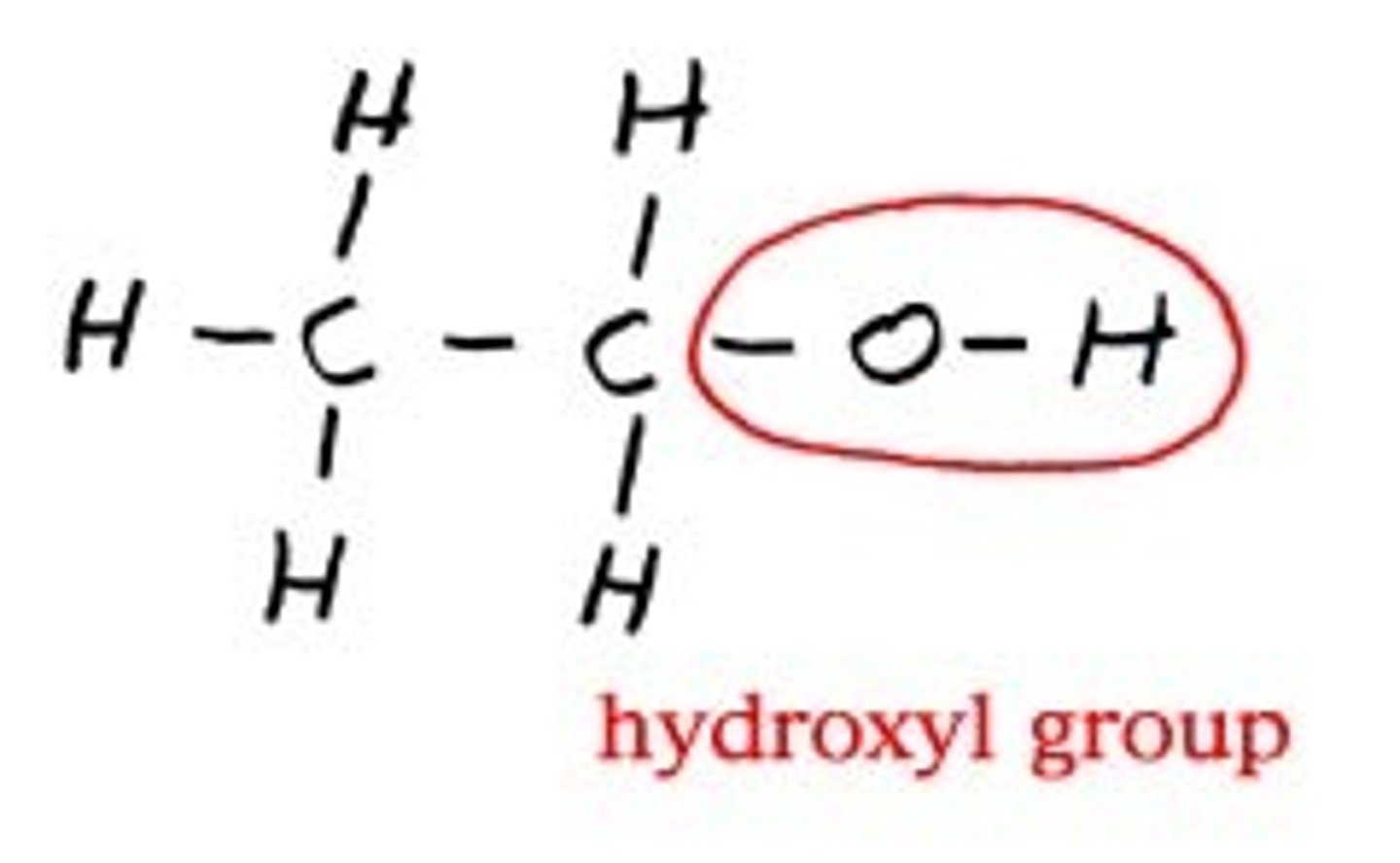
hydroxyl group
A functional group consisting of a hydrogen atom joined to an oxygen atom by a polar covalent bond. Molecules possessing this group are soluble in water and are called alcohols.
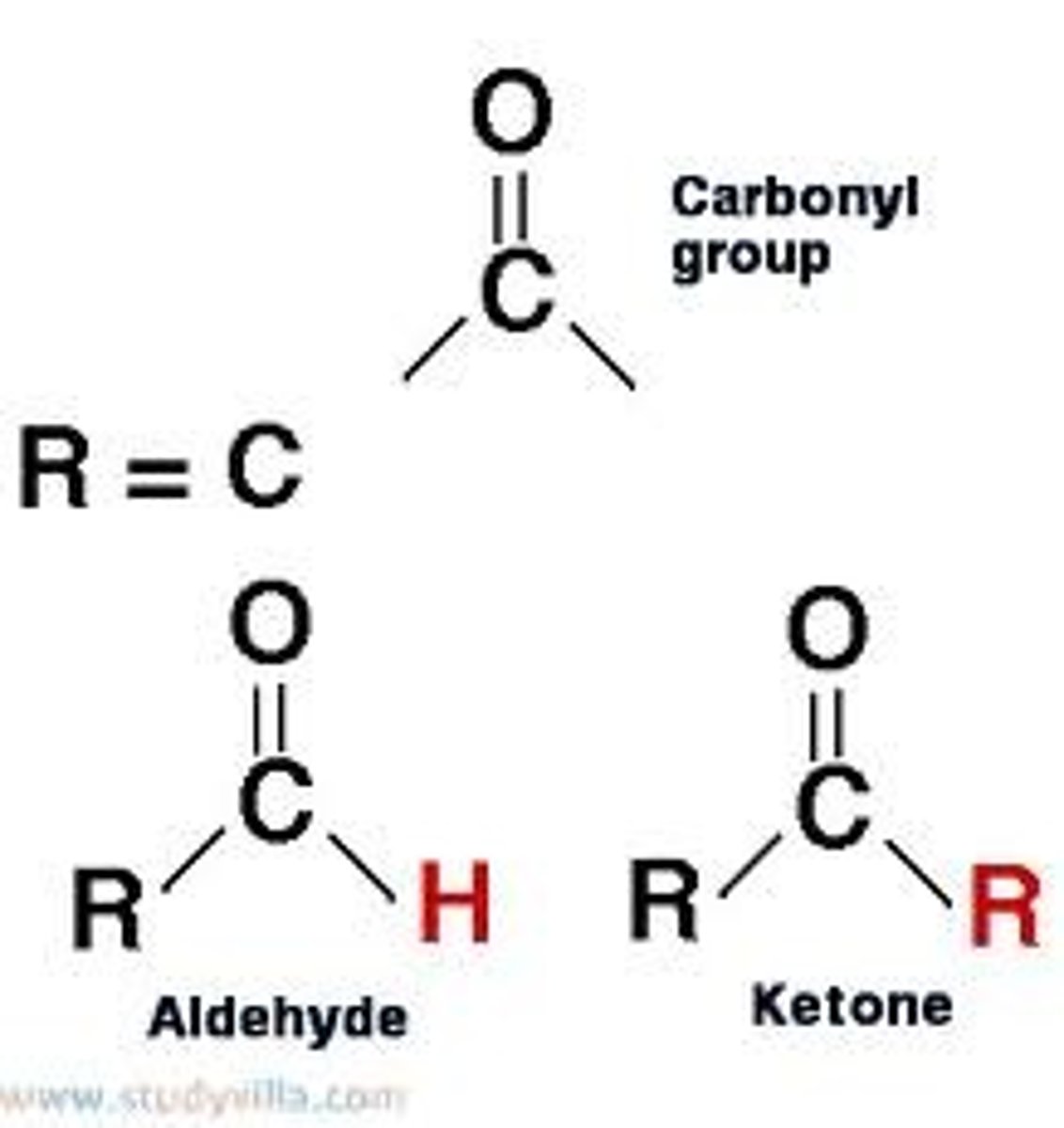
carbonyl group
a chemical group consisting of a carbon atom linked by a double bond to an oxygen atom
Macromolecules
A very large organic molecule composed of many smaller molecules,
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids