Introduction to economics 1 (copy)
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Microeconomics:
A branch of economics which studies the behaviour of individuals and firms in particular markets
Macroeconomics:
A branch of economics which studies the behaviour of the government and the economy as a whole
What type of science is economics?
Social science - studies the behaviour of individuals and societies when allocating scarce resources to meet unlimited needs and wants
The basis of the study of economics:
microeconomics and macroeconomics
The nine central concepts of the economics course:
Well-being
Interdependence
Scarcity
Efficiency
Choices
Intervention
Change
Equity
Sustainability
Define Factors of Production
refers to the resources required to produce goods and services
Factors of Production:
Capital
Entrepreneur
Land
Labour
Define the factors of Production
Capital - man-made resources
Entrepreneur - the skill of organising the three other factors of production
Land - natural resources
Labour - human resources (workers)
What are factors of income?
Factor income is income received from the factors of production
What is the factor of income for capital?
interest
What is the factor of income for Entrepreneur/enterprise?
Profit
What is the factor of income for land?
Rent
What are the 3 basic economic questions?
What how much to produce?
How to produce?
For whom to produce?
What is the process of the circular flow of income?
households provide resources to businesses
firms provide income to households
firms use the resources to produce goods and services for households
households provide expenditure (spend money) to businesses
the cycle repeats
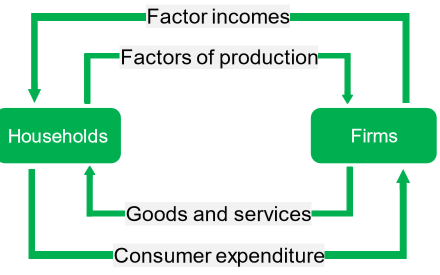
What does the circular flow of income show?
the interaction between households and firms
Why is this model over-simplified? What are the assumptions made?
There are no injections or leakages:
only 2 economic agents
no gov intervention (tax/gov spending)
no financial sector (savings/investments)
no foreign economics involved (trade= imports
/exports)
What is a leakage in the circular flow of income?
What is an injection into the circular flow of income?
refers to the withdrawal of money from the circular flow of income
refers to the additional money added into the circular flow of income
what does sustainability mean?
the ability to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their needs
Why do threats to sustainability arise?
because of scarce resources
Why must choices be made on how to allocate scarce resources?
Because there are limited resources but individuals/societies have unlimited wants
What are the 3 type of economic systems? + explain each
Free market economy —> allocation of resources determined by market forces, less/little gov intervention
Mixed economy —> allocation of resources is determined by consumers, producers and the goverment
planned economy —> allocation resources determined by the goverment
Define opportunity cost
the value of the next best alternative forgone when a choise is made
What are free goods? + 4 examples
They’re naturally abundant with unlimited supply and therefore do not incur any opportunity costs e.g. air, sunlight, sea water and desert sand
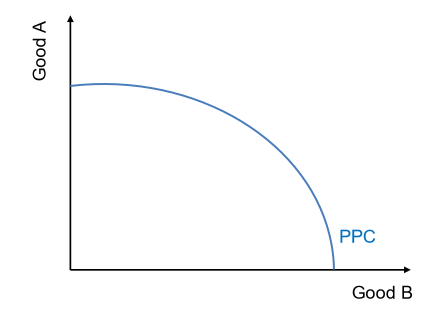
What does the production possibilities curve model illustrate?
The different combination of two goods or services that economy/firm can produce
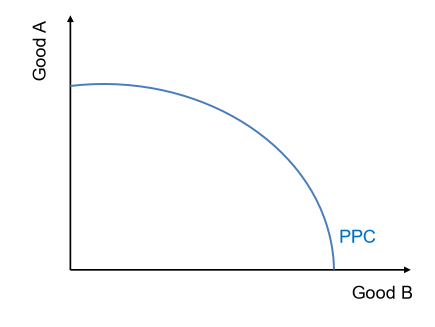
What are some assumptions of the model?
fixed amount of resources
only two goods are being produced
technology and production techniques are fixed
all resources are used efficiently
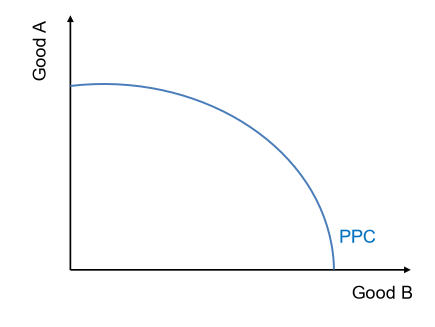

What do the points A B C D and E means?
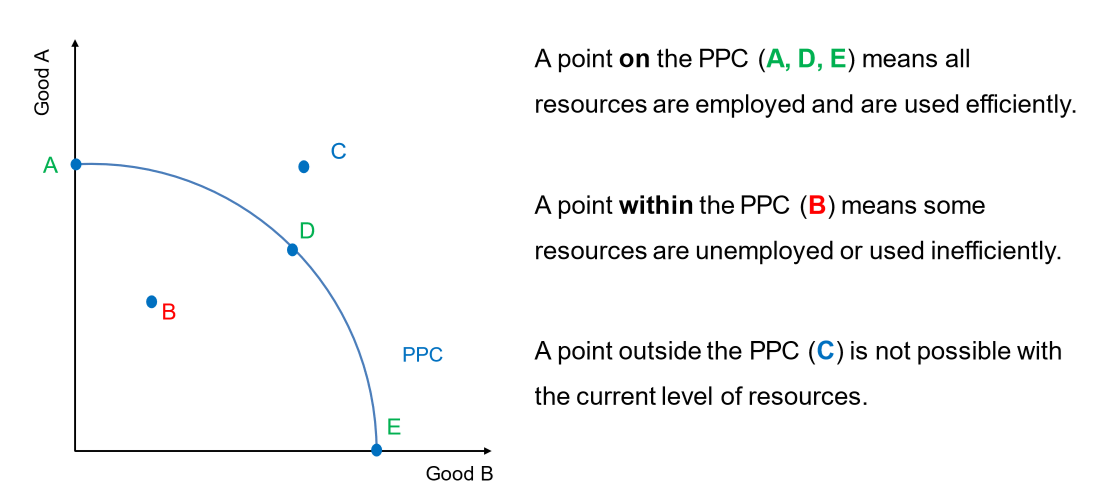
When is the PPC curved and when is it a straight line?
curve = different resources
straight = resources are constant/the same/only one resource
Actual growth: When does an economy move closer to the PPC?
When unemployment decreases, and efficiency decreases
When can an economy’s PPC shift outwards?
increase in QUANITITY of resources
and improvement in the QUALITY of resources
an improvement in TECHNOLOGY
What does economic methodology refer to?
the ways in which economist study the discipline
What is positive economics?
statements that can be tested/accepted/amended based on evidence/refuted (facts)
focuses on what is/was/will be
explains how economy works
relies on scientific methods (logic, hypotheses, models, economic theories, emperical evidence)
What is normative economics?
subjective value judgements that often form the basis of economic policy making
focuses on what SHOULD be
considers how the economy SHOULD work
relies on personal perspectives, values and beliefs
What is Equity and does it fall under normative or positive economics?
refers to the state of being fair
Normative concept as it is subjective
What is equality and does it fall under normative or positive economics?
refers to the state of being equal with respect to something
Positive concept as it is objective
What does positive economics use?
logic and reasoning (for future predictions)
hypotheses, models, theories (for future predictions)
empirical evidence/evidence you measure (to support or refute claims)
ceteris paribus assumption
What is ceteris paribus assumption?
‘other things are equal/stay the same‘
economists can analyse how one variable may affect another, without considering all the other factors that may affect the dependent variable