HITT 1305 - Exam 1
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Root
Core meaning of the word, fundamental meaning of the word
Prefix
located at the beginning of a medical term
Suffix
word parts that are located at the end of words
Combining form
When a word root is combined with a combining form vowel the word part =
Combining vowel
used to join word parts and to ease pronunciation. The most common is an “o,” but sometimes it is an “i” or an “e”
All medical terms contain which word part:
root word
Digestive organs
Stomach
Liver
Gall Bladder
Large & Small Intestine
Integumentary organs
Hair
Skin
Nails
Blood organs
Blood cells (RBCs, WBCs, platelets)
Plasma
Lymphatic organs
Thymus
Lymph nodes
Spleen
Lymphatic Vessels
Male Reproductive organs
Epididymis
Testes
Female Reproductive Organs
Mammary glands
Ovaries
Uterus
Cardiovascular organs
Heart
Blood Vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries)
Musculoskeletal organs
Muscular (muscles, tendons, ligaments)
Skeletal (cartilage, bones, joints)
Urinary organs
Kidneys
Urinary Bladder
Respiratory organs
Nasal Passage
Trachea
Lungs
Nervous (system) organs
Brain
Spinal Cord
Peripheral Nerves
Endocrine organs
Pituitary Gland
Thyroid Gland
Pancreas
Adrenal Glands
Testes
Ovaries
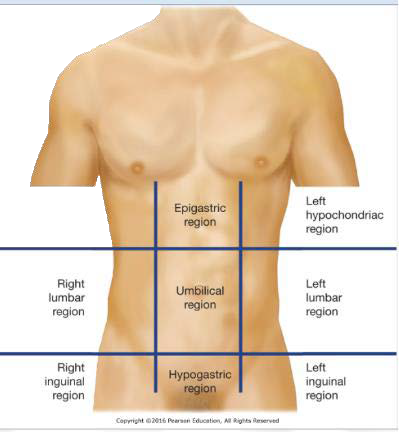
1-RHR
Right Hypochrondriac Region
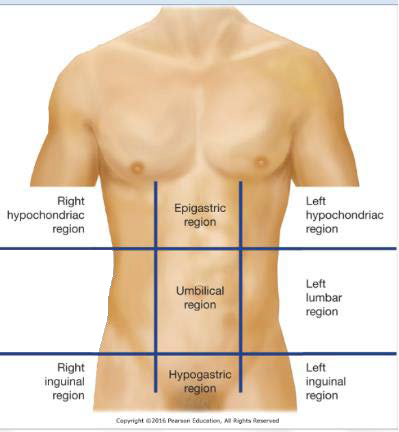
2-RLR
Right Lumbar Region
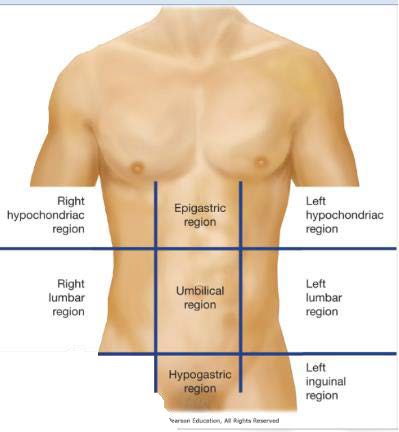
3-RIR
Right Inguinal Region
4-ER
Epigastric Region
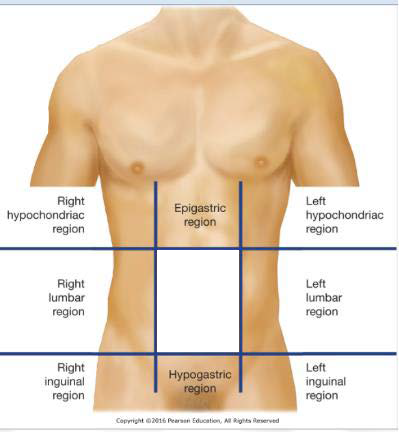
5-UR
Umbilical Region
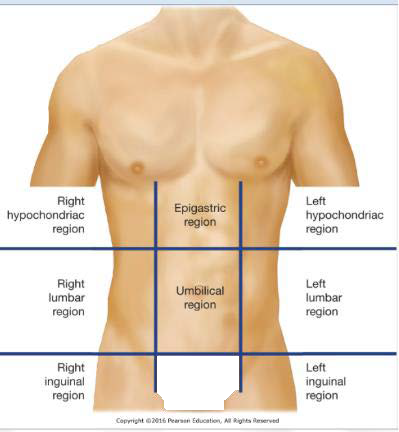
6-HR
Hypogastric Region

7-LHR
Left Hypochondriac Region
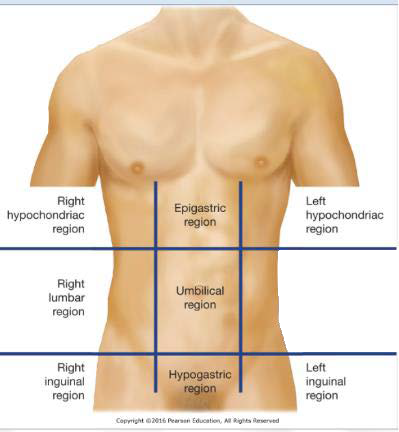
8-LLR
Left Lumbar Region
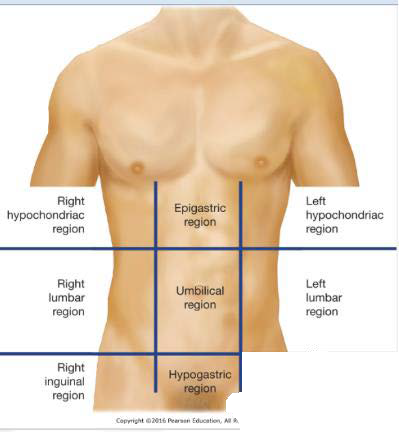
9-LIR
Left Inguinal Region
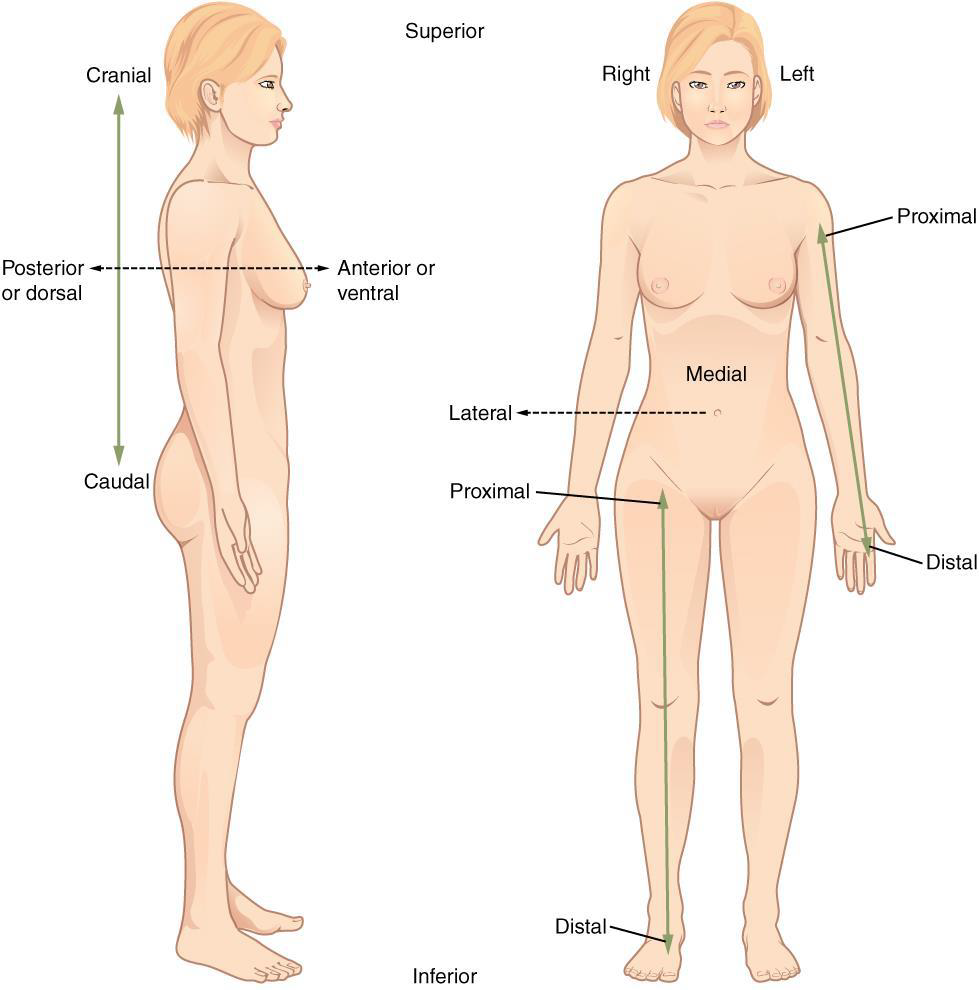
Superior (cranial)
a position above or higher than another part of the body proper
Ex: The orbits are ________ to the oris
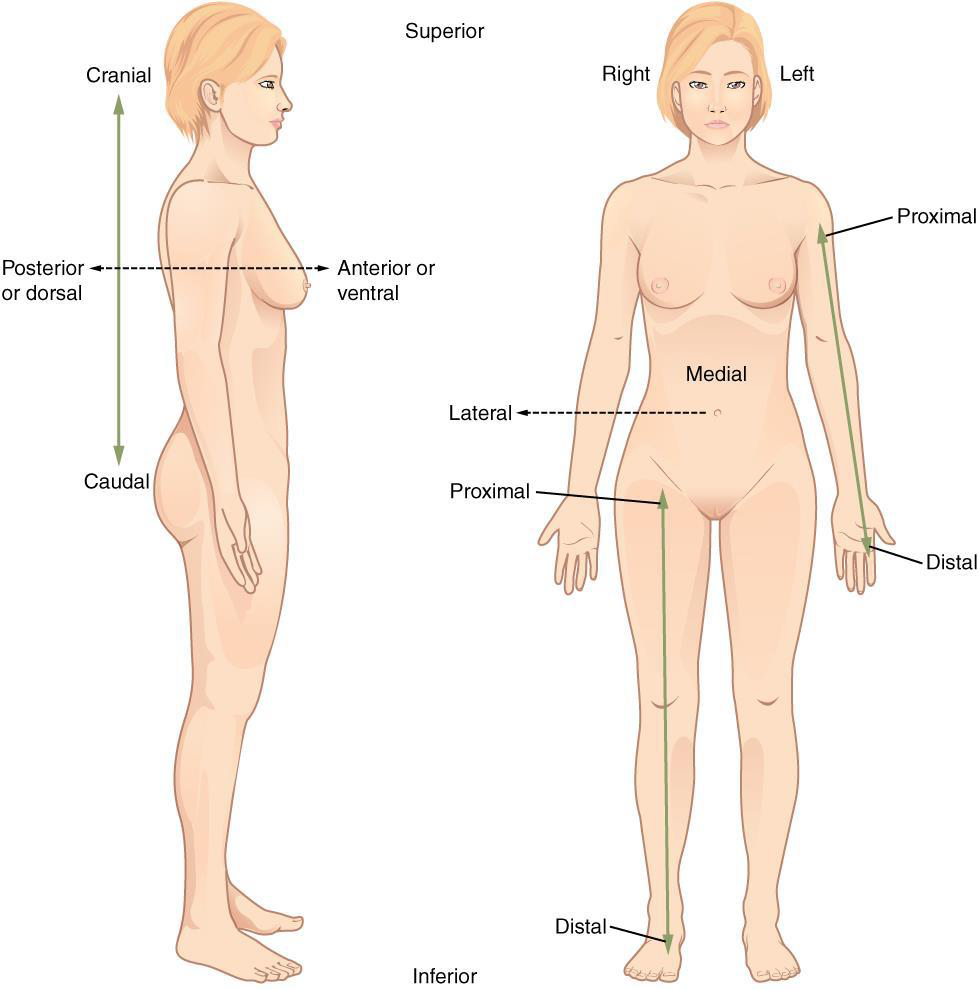
Inferior (caudal)
position below or lower than another part of the body proper; near or toward the tail (in humans, the coccyx, or lowest part of the spinal column)
Ex: The pelvis is _______ to the abdomen
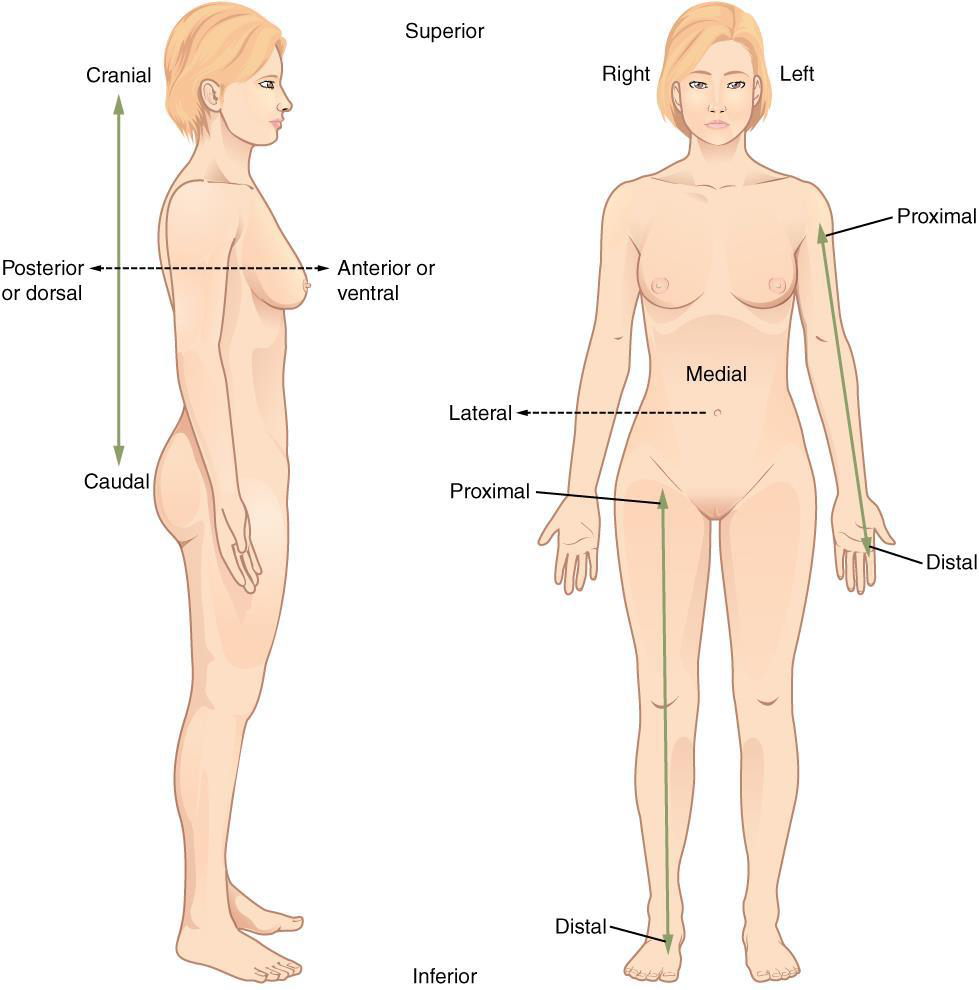
Posterior (dorsal)
the back or direction toward the back of the body
Ex: The popliteus is _________ to the patella
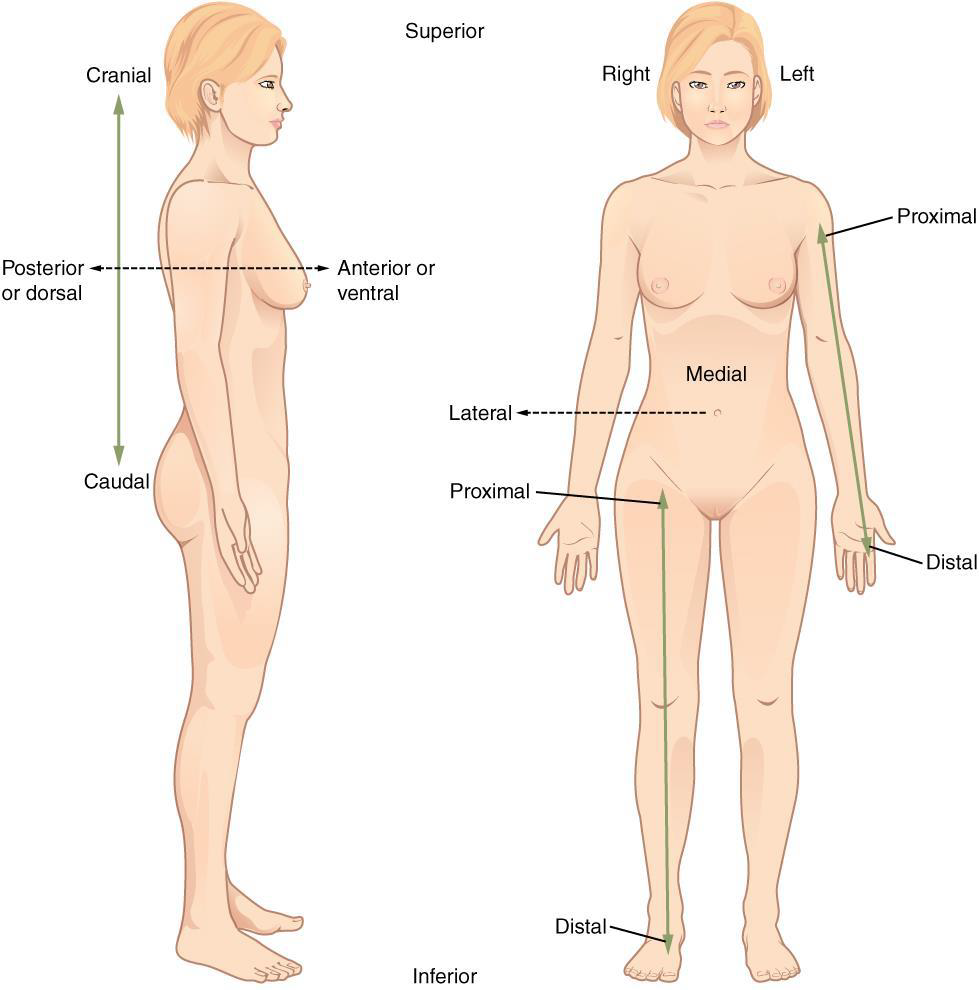
Anterior (ventral)
the front or direction toward the front of the body
Ex: The toes are _______ to the foot
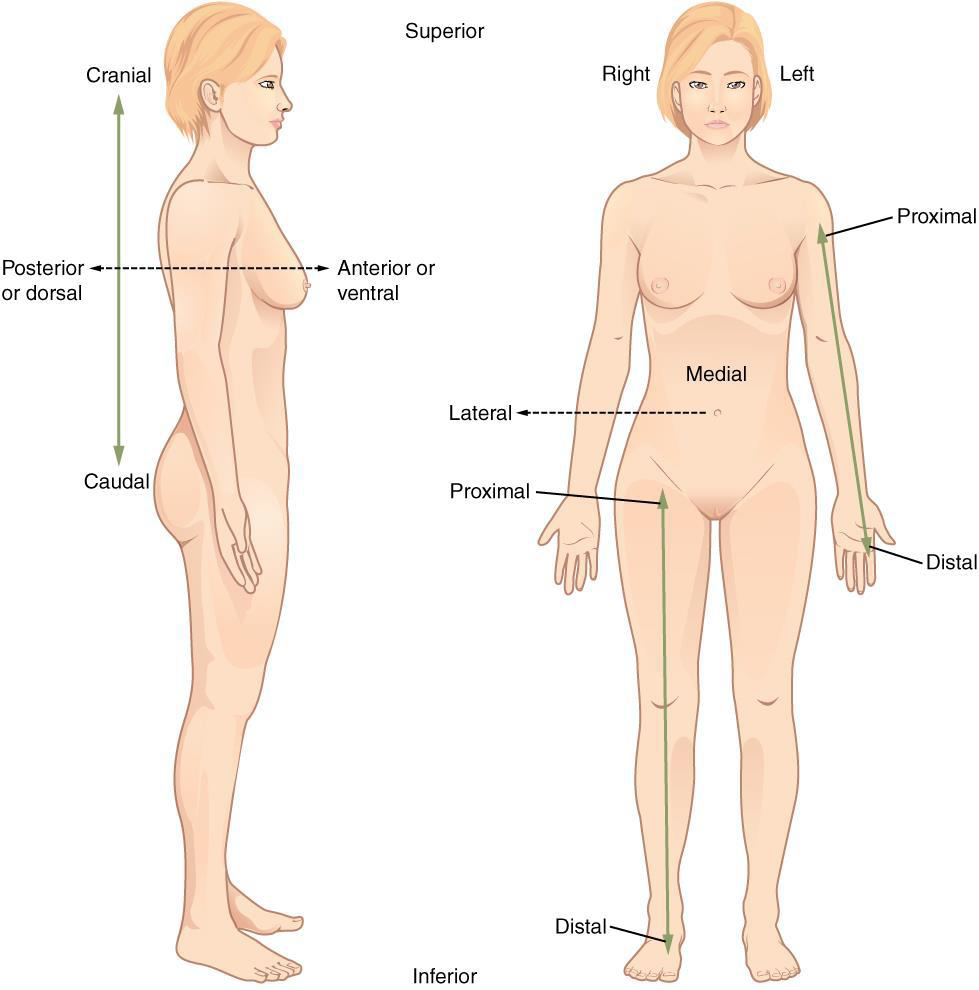
Proximal
a position in a limb that is nearer to the point of attachment or the trunk of the body Ex: The brachium is ________ to the antebrachium
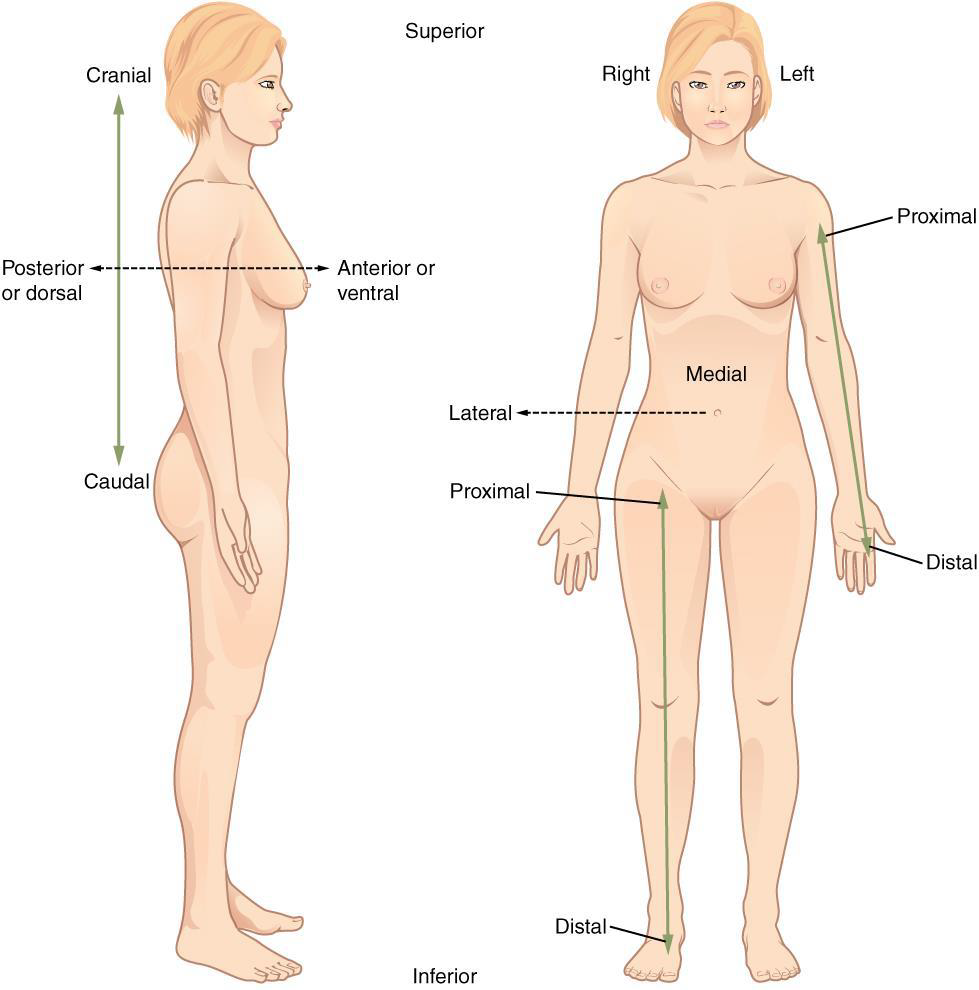
Distal
a position in a limb that is farther from the point of attachment or the trunk of the body
Ex: The crusis is _____ to the femur
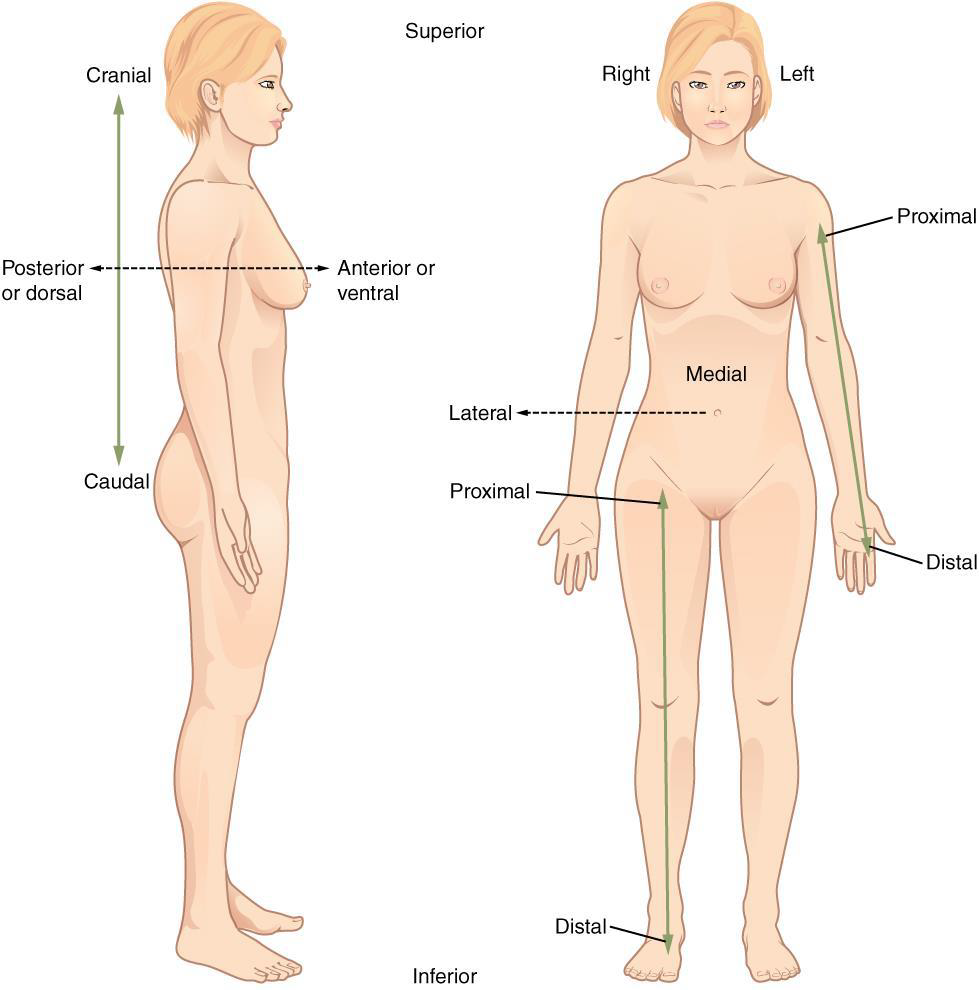
Medial
the middle or direction toward the middle of the body
Ex: The hallux is the ______ toe
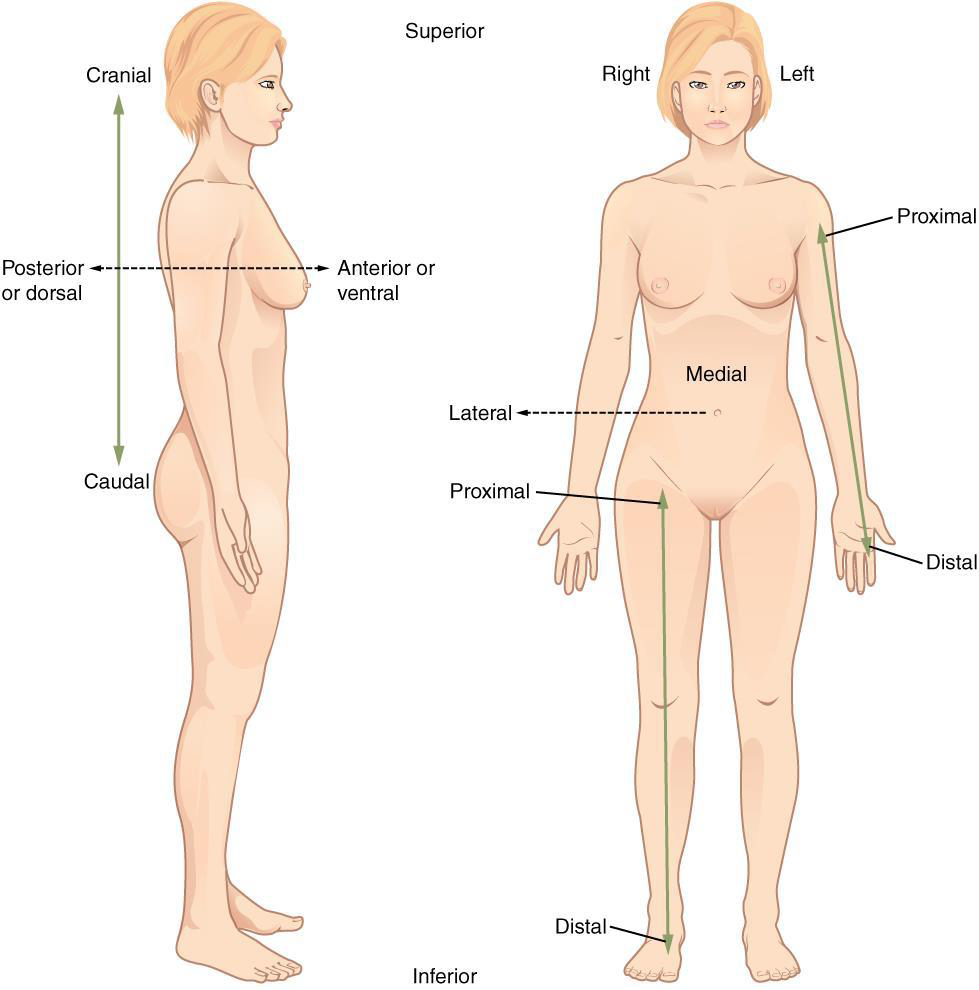
Lateral
the side or direction toward the side of the body
Ex: The thumb (pollex) is ______ to the digits
Deep
position farther from the surface of the body
Ex: The brain is ____ to the skull
Superficial
a position closer to the surface of the body
Ex: The skin is ___________ to the bones
Supine
A body that is lying down is described as either prone or ______
laying on the back, face up
Prone
A body that is lying down is described as either _____ or supine
laying on the stomach, face down
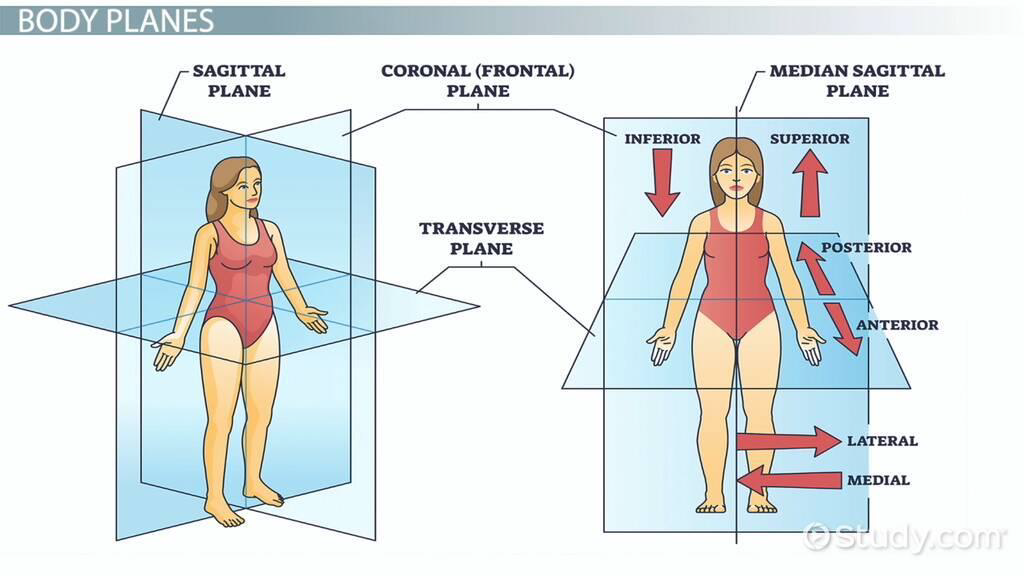
Transverse
The plane that divides the body or organ horizontally into upper and lower portions.
___________ planes produce images referred to as cross-sections
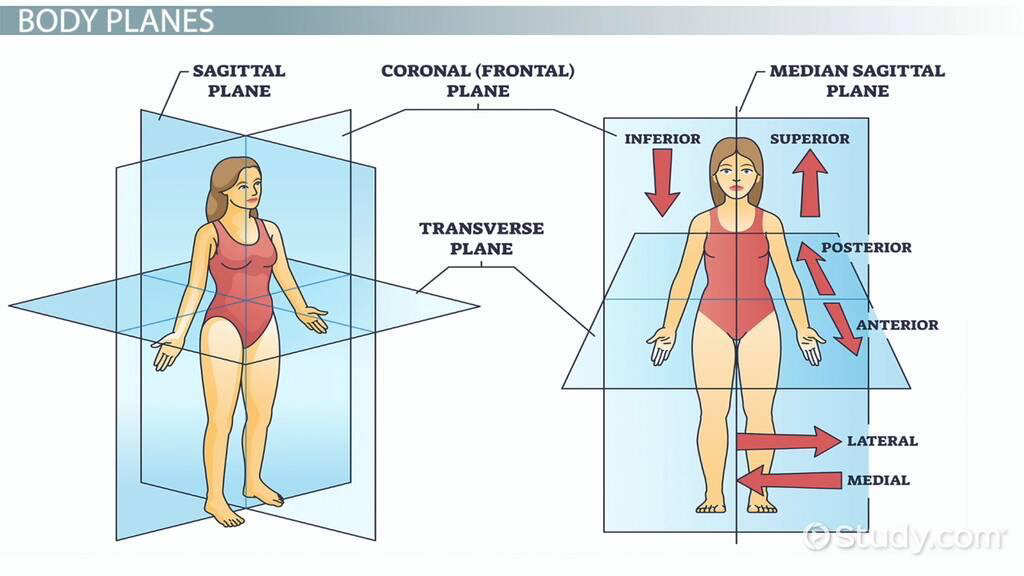
Frontal
The plane that divides the body or an organ into an anterior (front) portion and a posterior (rear) portion.
The _______ plane is often referred to as a coronal plane (“corona” is Latin for “crown”).
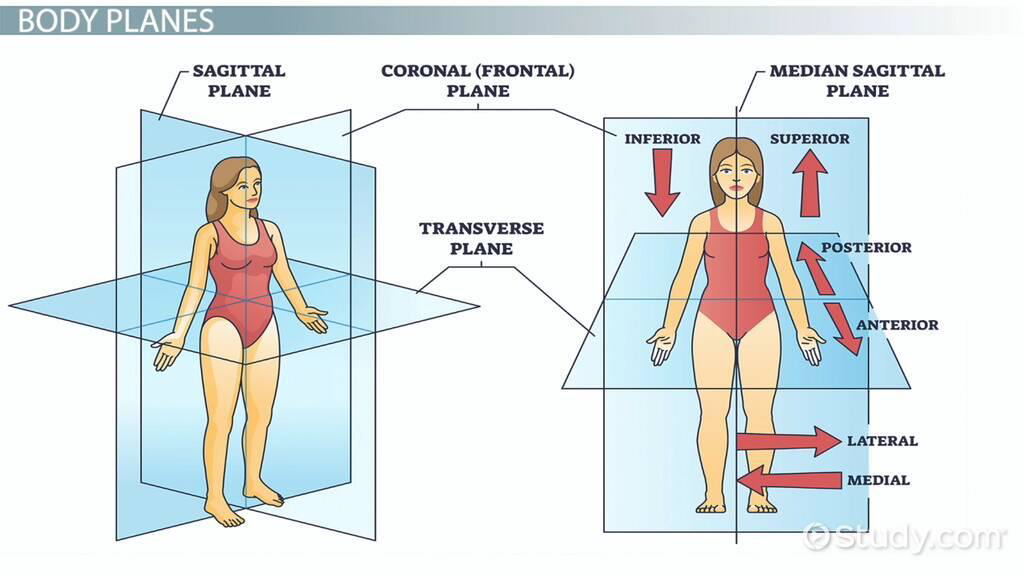
Sagittal
The plane that divides the body or an organ vertically into right and left sides.
If this vertical plane runs directly down the middle of the body, it is called the mid_______ or median plane. If it divides the body into unequal right and left sides, it is called a para________ plane or, less commonly, a longitudinal section

Mid-sagittal (median)
vertical plane that runs directly down the middle of the body

Anatomical Position
The body standing upright with the feet at shoulder width and parallel, toes forward. The upper limbs are held out to each side, and the palms of the hands face forward
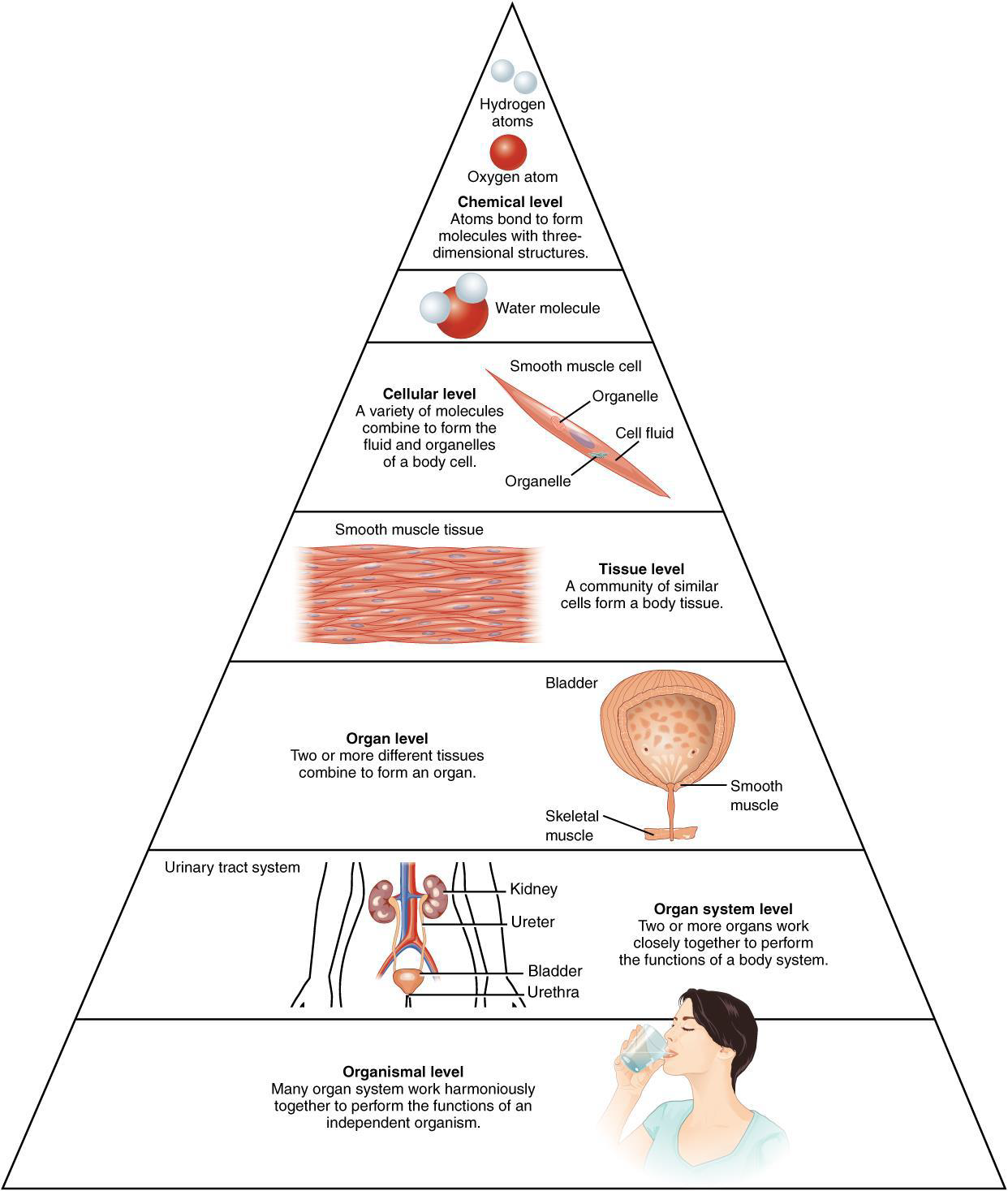
5 levels of body organization: (smallest (1) to largest (5))
1. cells
2. tissues
3. organs
4. organ systems
5. organisms
Ventral (anterior)
Thoracic cavity - lungs and the heart
Abdominopelvic cavity (digestive organs, pelvic cavity, reproductive organs)
Dorsal (Posterior)
Cranial cavity - brain
Spinal (vertebral) cavity - spinal cord
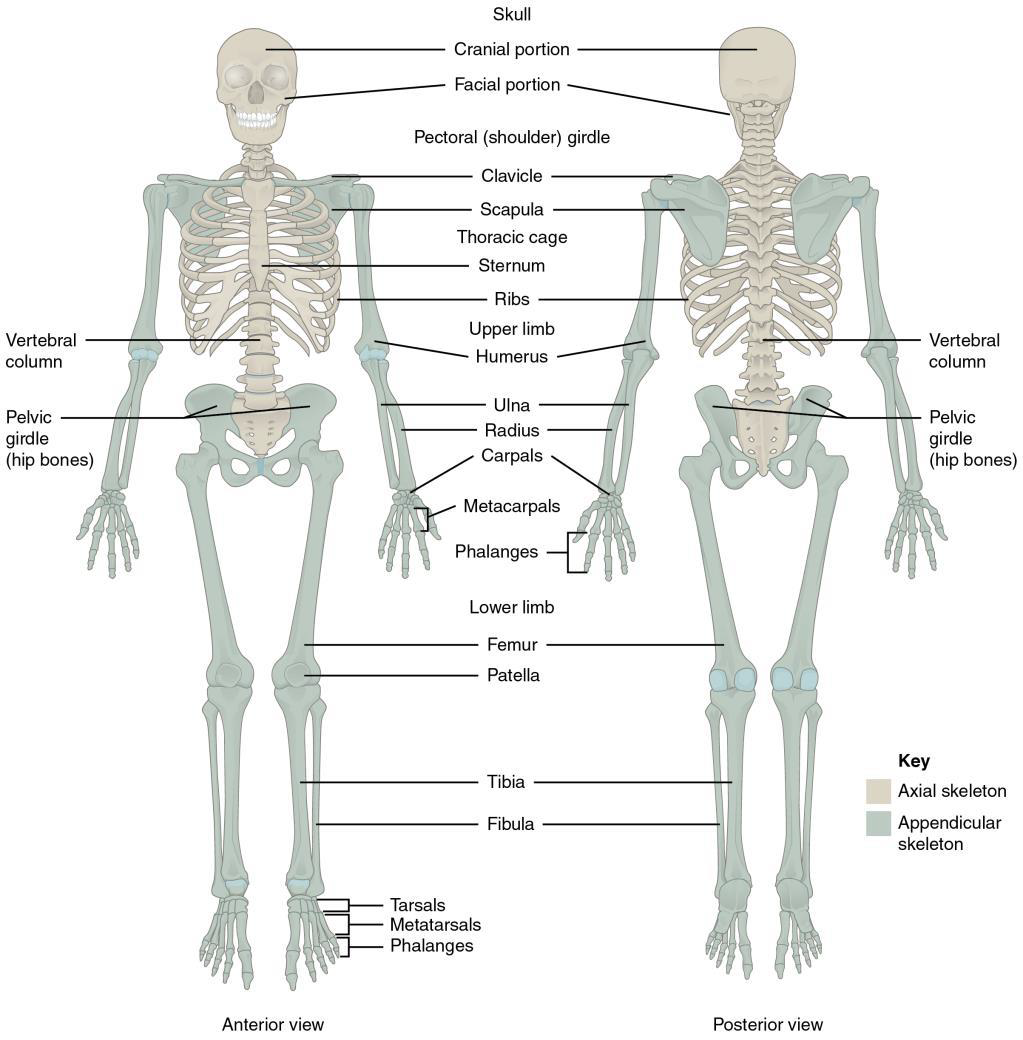
Axial Skeleton
Skull
Vertebral column (spine)
Ribs
Sternum (breastbone)
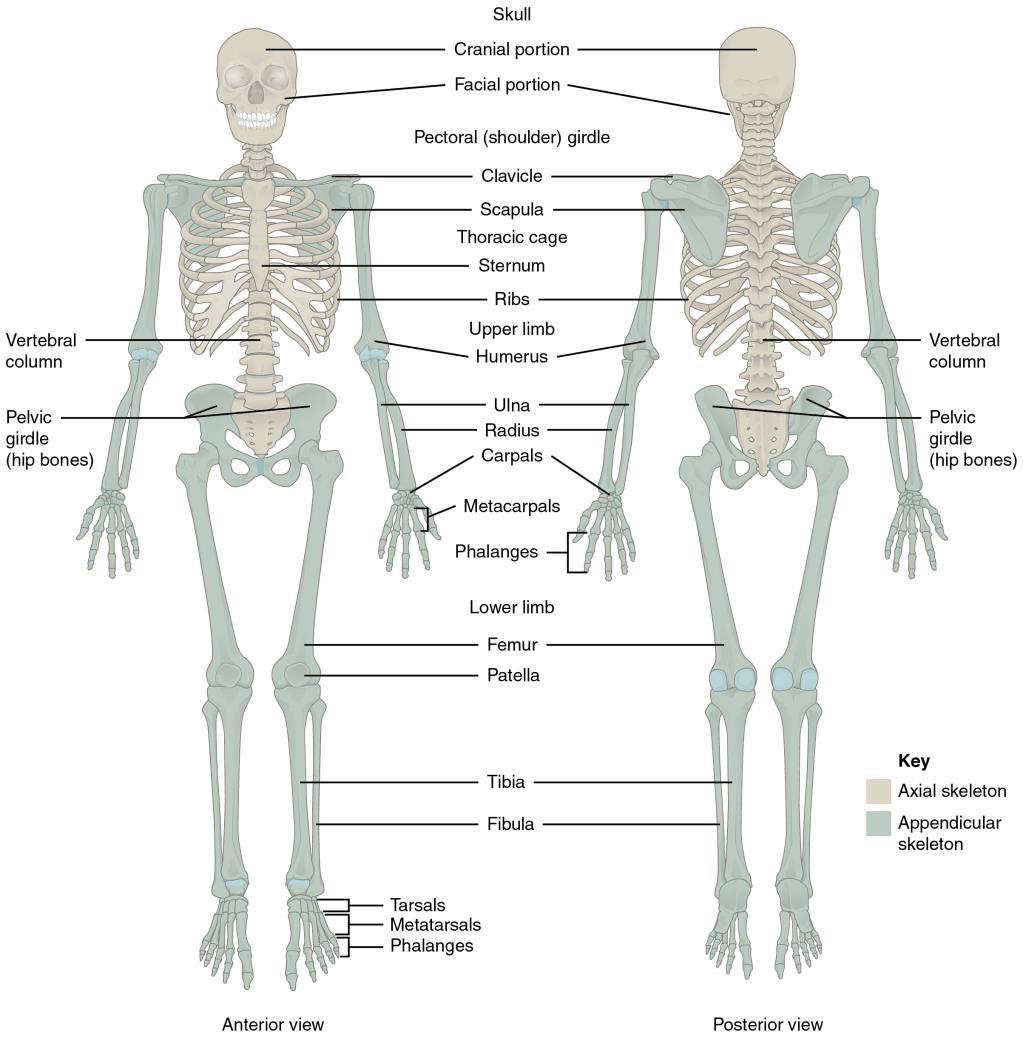
Appendicular Skeleton
Shoulder and pelvic girdles
Arms and hands
Legs and feet
Closed/Simple (fracture type?)
bones are broken but do not protrude the skin
Open/Compound (fracture type?)
bones are broken and pierce through the skin
Transverse (fracture type?)
bone is broken straight across
Spiral (fracture type?)
the bone has twisted apart
Comminuted (fracture type?)
bones are broken and crushed into pieces
Greenstick (fracture type?)
bones are partially broken (occurs mainly in children)
Oblique (fracture type?)
bones are broken at an angle
Coles {Colles} (fracture type?)
bones are broken at the wrist or distal radius
Stress (fracture type?)
a small crack in the bone
1st degree burn
a superficial burn that affects epidermis only
skin is painful and swollen, but typically heals on its own within a few days
Ex: Mild sunburn
2nd degree burn
deeper; affects epidermis & some of the dermis
result in swelling and a painful blistering of the skin
Must keep the burn site clean and sterile to prevent infection (If done, will heal within several weeks)
3rd degree burn
fully extends into the epidermis and dermis, destroys tissue & affects nerve endings & sensory function
serious burns that may appear white, red, or black
require medical attention & heal slowly without any
4th degree burn
severe
affects underlying muscle and bone
Rule of nines
Burns are sometimes measured in terms of the size of the total surface area affected. This is referred to as the _____________, which associates specific anatomical areas with a percentage that is a factor of nine
Sun exposure and vitamins
The absence of ____________ can lead to a lack of vitamin D in the body.
In children, causes rickets. Vitamin D deficiency in elderly may lead to osteomalacia.
Pleura (type of serous cavity)
surrounds the lungs in the pleural cavity and reduces friction between the lungs and the body wall
Pericardium (type of serous cavity)
surrounds the heart and reduces friction between the heart and the wall of the _____________
Peritoneum (type of serous cavity)
surrounds several organs in the abdominopelvic cavity. The ____________ cavity reduces friction between the abdominal and pelvic organs and the body wall
Debridement
Excision of damaged tissues and cell debris from a wound or burn to prevent infection and promote healing
Rebels
do not follow standard medical terminology language rules
ex: Oste/o/arthr/itis (inflammation of the bone and joint). Instead of keeping the 'o' from arthr/o, the vowel is dropped.
Stye
Infection of an oil gland of the eyelid (hordeolum)
Contusion
Injury resulting in a bruise
Nociceptors
Sensory neurons that respond to pain
Cataract
A condition in which the lens of the eye becomes cloudy
Diplopia
Double vision
Proprioception
Sense of position and movement of the body
Athlete’s feet
Tinea pedis – commonly referred to as _______________
Keloid
A raised or hypertrophic scar
Benign
Non-cancerous
Pallor
Unnatural paleness of the skin
Myopia
Nearsightedness
Hyperopia
Farsightedness
Visual acuity
Sharpness of vision