4.2.1 Absolute and Relative Poverty
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Define Income.
A flow of money over a period of time
How can individuals earn an income?
Salary
Rent
Interest
Profit
Benefits
How has the distribution of income in the UK changed?
The growth of the financial sector so individuals now have higher incomes
A decrease in trade union membership, this decreases wages for low income individuals
De-industrialisation has created the North and South divide
Define Absolute Poverty
Where individuals have insufficient income to afford the necessities essential for survival, like food water warmth shelter and clothing
Define Relative Poverty.
Where household income is lower than 60% the median income in a country
What are the causes of income inequality and poverty?
Differences in skills and qualifications. High skilled individuals are very productive which increases income
De industrialisation. Lower wages in the North vs the South
Spare capacity. Lack of housing due to lack of land in areas like london house prices going to be very high
Unequal holdings of wealth. Wealth generates income, unequal differences in wealth differences in income
Differences in household composition. Families made up of different age groups demographics experience differences in earnings
How can the distribution of income be illustrated?
Lorenz curve
Draw the Lorenz curve and explain its sentence
Poorest X percent of households have Y percent of national income
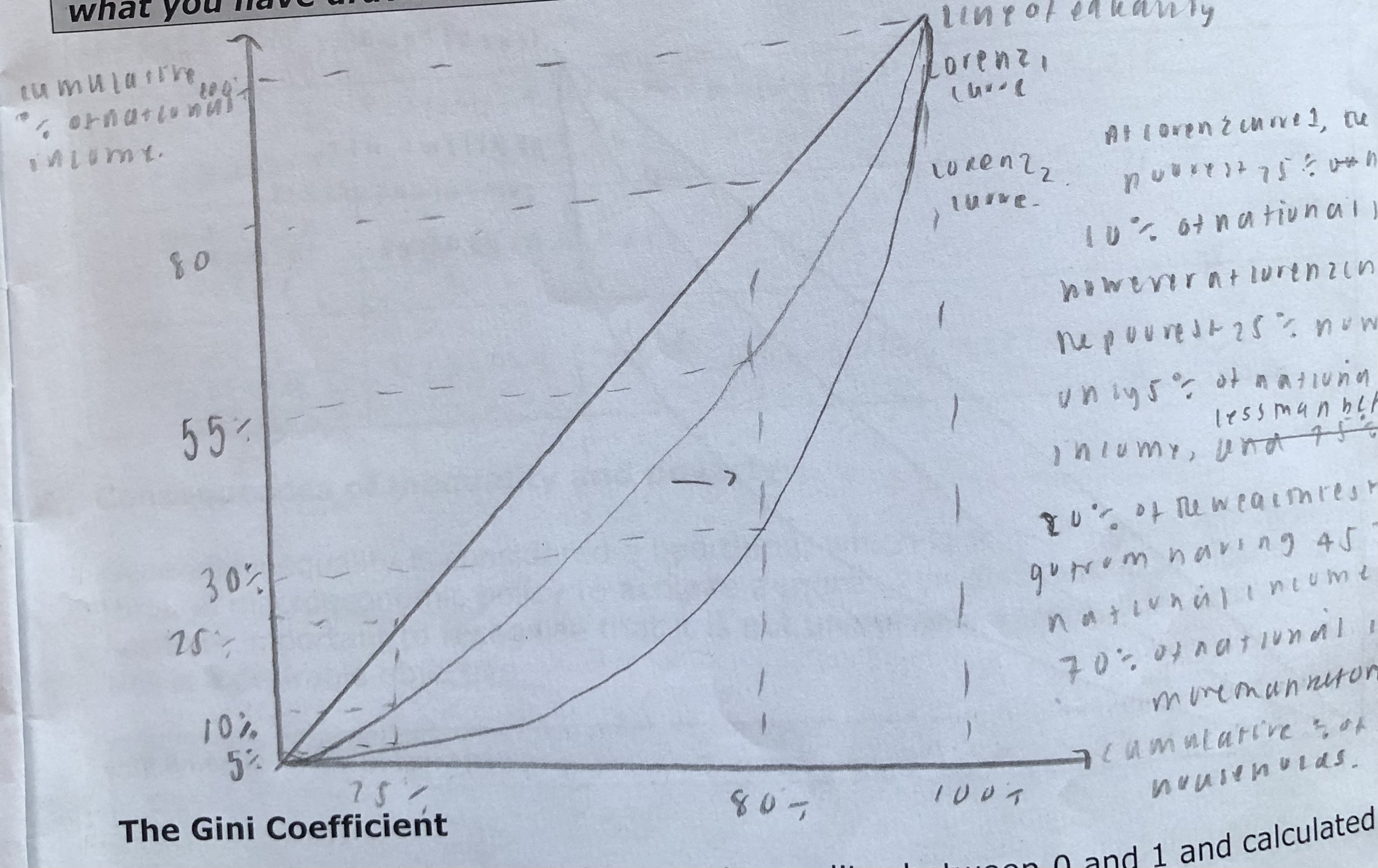
What is the gini coefficient?
A numerical measure of income inequality between 0 and 1
How is the gini coefficient calculated?
A/(A+B)
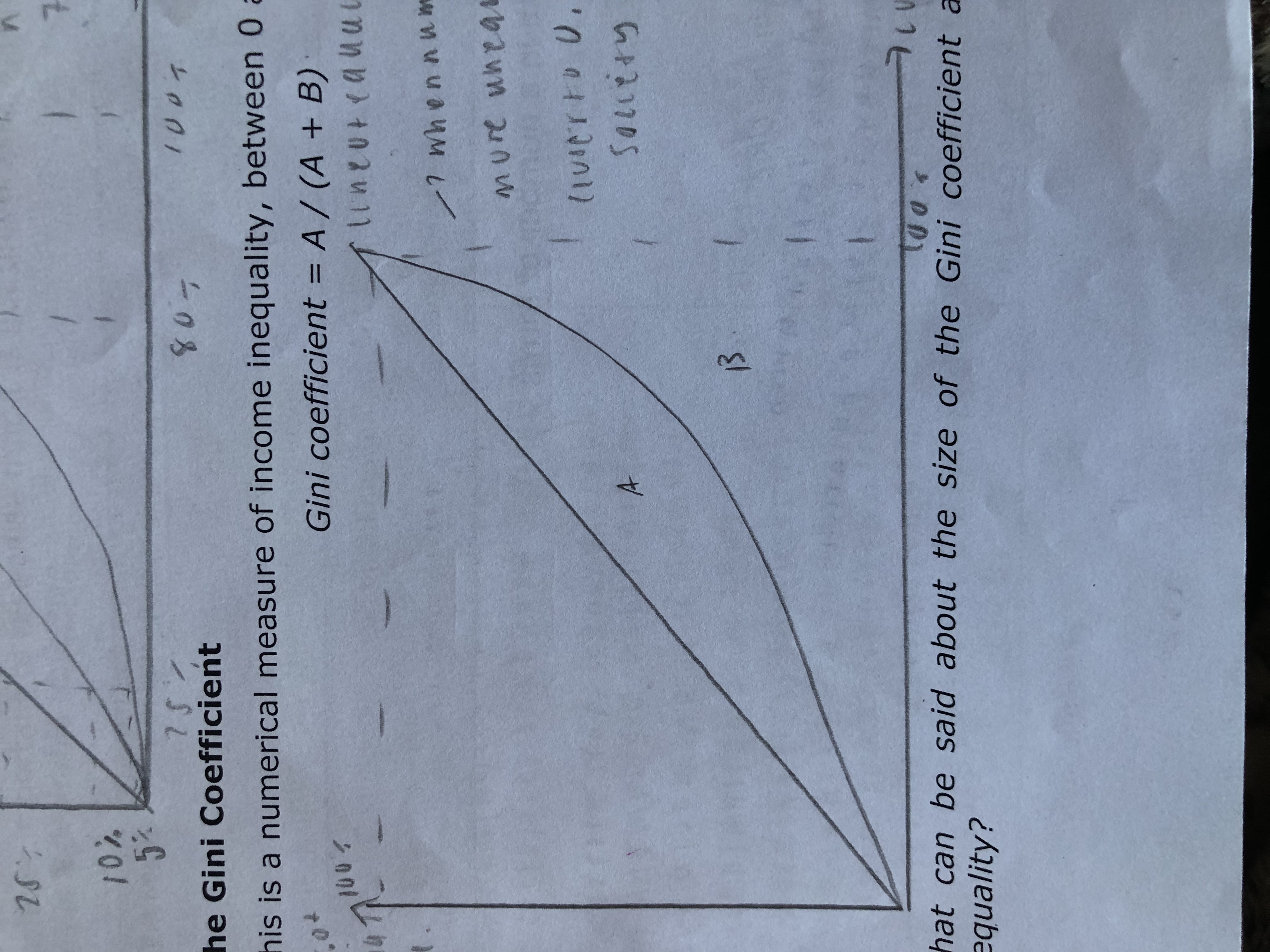
What do the numbers close to 0 or 1 represent in terms of equality?
Closer to 1 More unequal society
Closer to 0 more equal society
Define wealth
A stock of assets that have a financial value
What is one statistic showing how wealth is distributed in the UK?
20% of the UK wealth is owned by 1% of the population
What are 4 causes of wealth inequality?
Inheritance. Wealth is passed down generation to generation
Income inequality. Higher incomes more wealth as they are more able to save
Differences in entrepreneurship skills. EG elon musk
Marriage patterns of the wealthy. Wealthy people marry other wealthy people
Define capitalism
Capitalism is where there is minimal government intervention and resources are distributed according to the market
In a capitalist society entrepreneurs take risks and are driven by the profit motive
What are the 2 disadvantages of capitalism?
Low incomes. Lower living standards cannot afford basic necessities like food and housing
Cause poverty trap, if an individual is unemployed children see this as normal and acceptable to do the same (working class subculture). May not have equal educational opporunities 90% of failing schools are in deprived areas
What are 2 arguments for capitalism?
Inequality is required or there is no incentive to work harder
If you do not have a job you will be given benefits, helps people overcome ansolute poverty. Also free and equal access to health and education
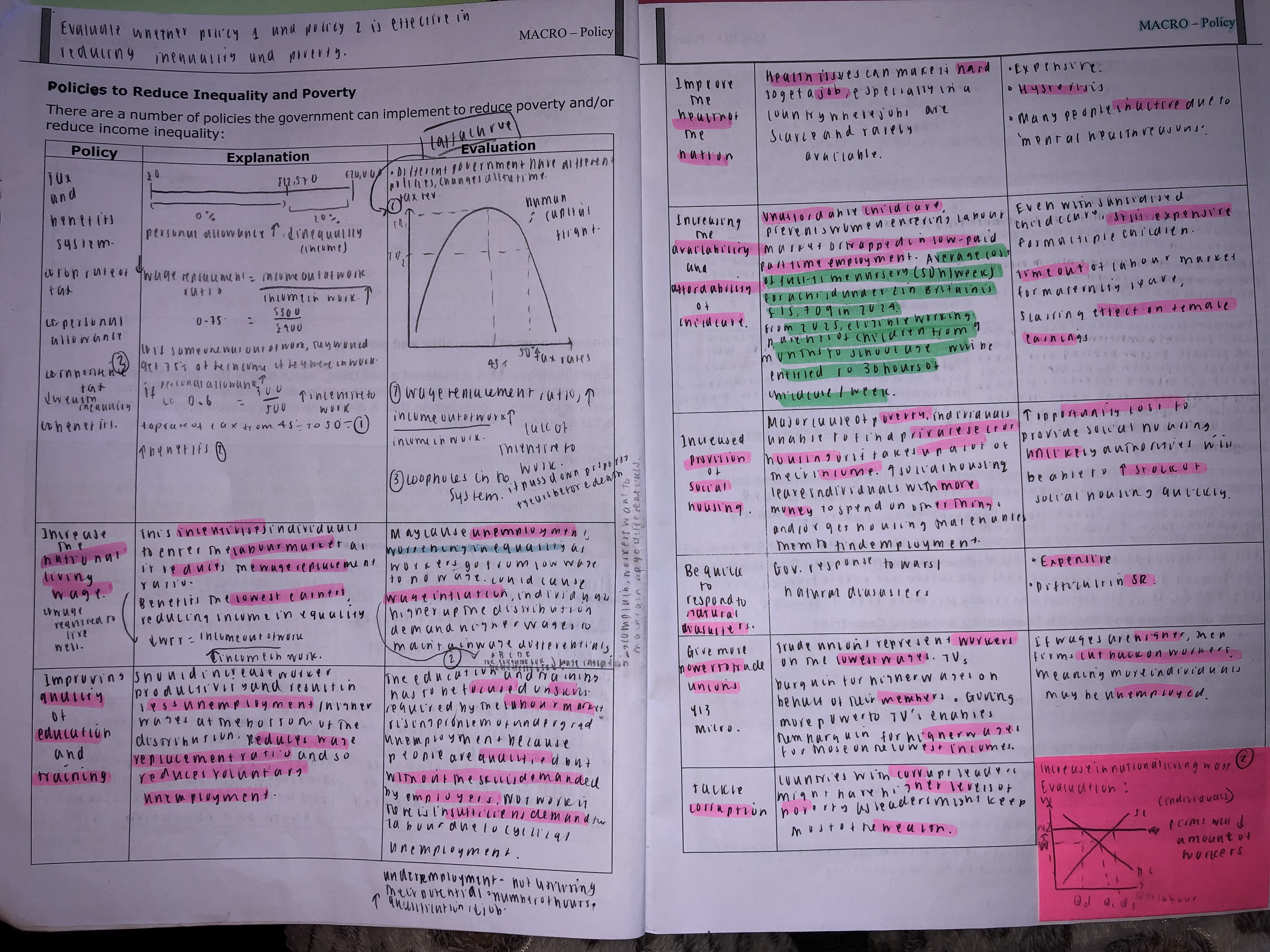
What are the 6 polifies which can be used to reduce inequality and poverty?
Tax and benefits system
Increase in the national living wage
Improving quality of education and training
Improve the health of the nation
Increasing the availability and affordability of childcare
Increased provision of social housing
Showwww the policies on handout soz too lazy
What does the kuznets inequality curve states?
Inequality in poor countries is a transitional phase and once nations become economically developed inequality reduced
As we move from a primary sector to a secondary sector income inequality increases. Wages of thosr in manyfacturing sector are rising faster than those working in the agricultural sector. When incomes increase even further government increases tax revenue and increases spending on education healthcare benefits which increases skills.