DSA20 - Pathology of Adrenal and MEN
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
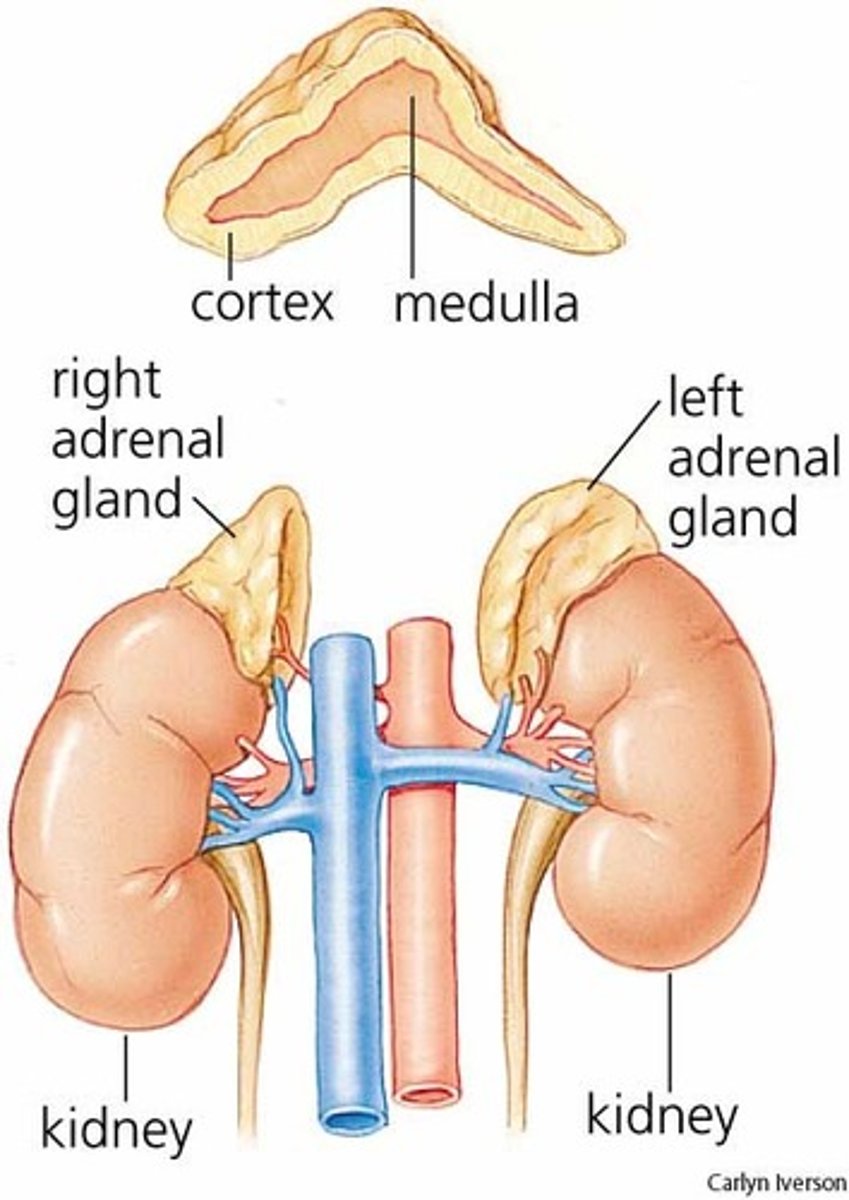
mesoderm; neural crest
The Adrenal Cortex is derived from the (mesoderm/neural crest), while the Adrenal Medulla is derived from the (mesoderm/neural crest)
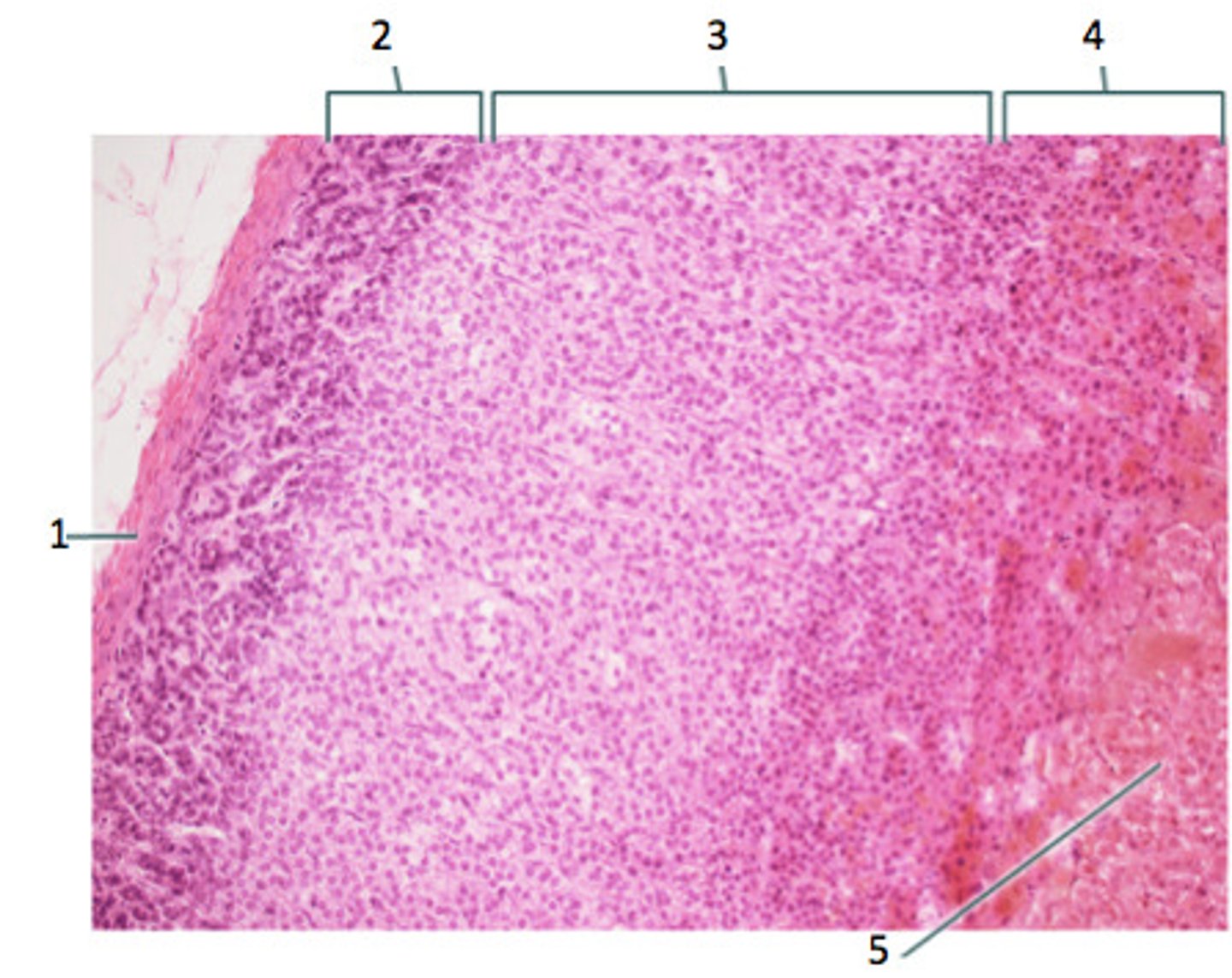
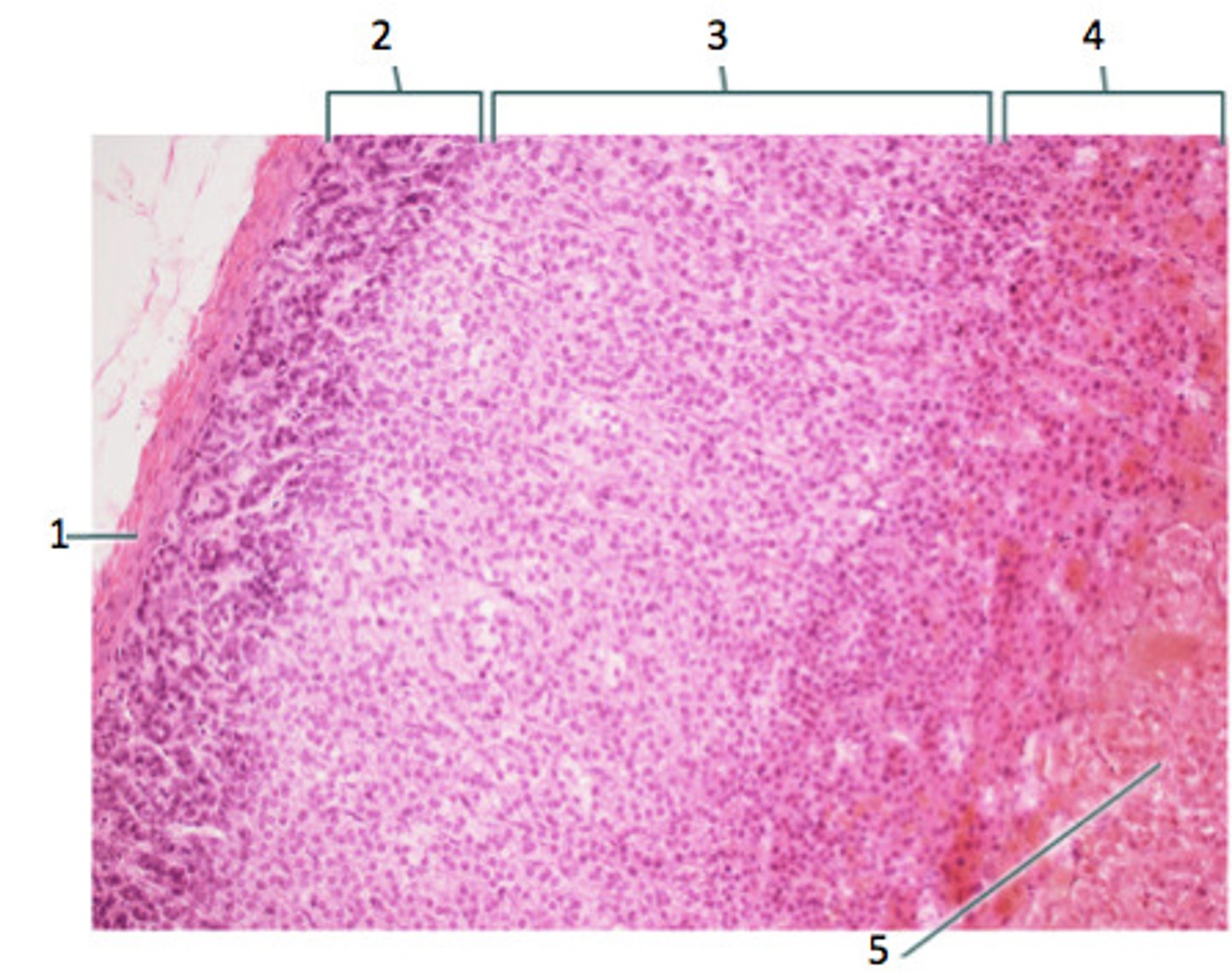
- LIPID POOR & less cytoplasm (other than cortical cells)
- Secretes MINERALOCORTICOIDS (Aldosterone)
How does the Zona Glomerulosa (2) appear and what does it secrete?
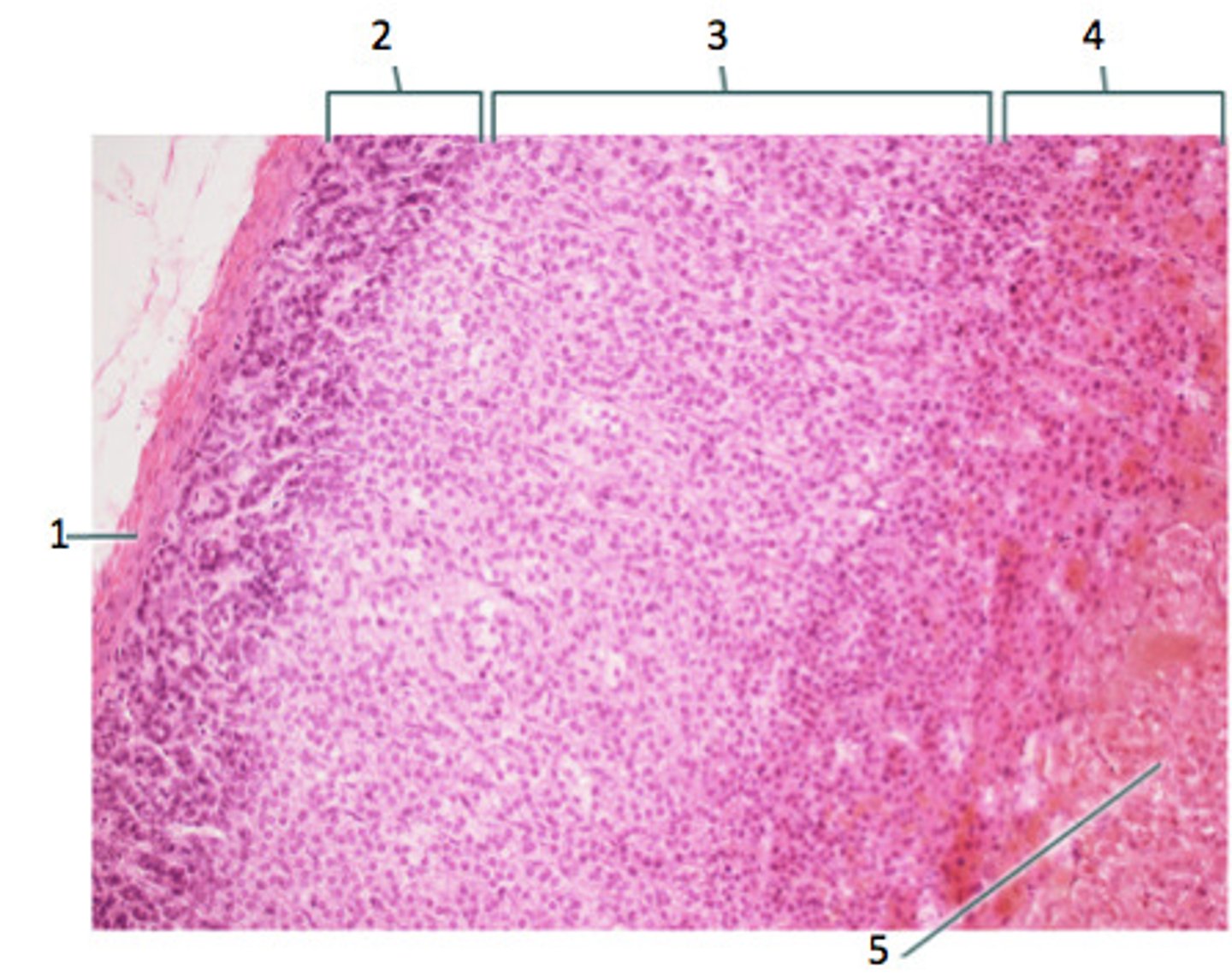
- LARGEST LAYER
- Has FOAMY CYTOPLASM (cytoplasm w/ small lipid vacuoles)
- Secretes GLUCOCORTICOIDS
How does the Zona Fasciculata (3) appear and what does it secrete?
-Appetitie (MORE)
-BP (MORE via more Aldo or sensitivity to NE/Epi)
-Insulin resistance (MORE)
-Glucose (MORE via more Gluconeogenesis/Lipolysis/Proteolysis)
-Fibroblast (LESS ==> less healing from less collagen synthesis)
-Immune/Inflammatory Response (LESS)
-Bone Forming (LESS via less osteoblast & collagen --> osteoporosis)
What are the functions of Cortisol (a major Glucocorticoid)?
(think "A BIG FIB")
- DARKEST LAYER (GRANULAR and EOSINOPHILIC Cytoplasm)
- Secretes ANDROGENS
How does the Zona Reticularis (4) appear and what does it secrete?
cholesterol
All adrenal cortex hormones are derived from ()
Part of the SNS - releases "Stress Hormones"
What is the function of the Adrenal medulla?
CHROMAFFIN CELLS
- Large polygonal neuroendocrine cells in nests & clusters around vessels
-BASOPHILIC (BLUE) CYTOPLASM (stains yellow/brown w/ chrome stain)
How does the Adrenal Medulla appear?
ACTH-INDEPENDENT Cushing Syndrome (Hypercortisolism)
Define Condition:
-Hx & Path:
> Exogenous Use
>> MCC overall
>> Path: Bilateral Adrenal Cortical Atrophy d/t negative feedback inhibition of ACTH (More exogenous cortisol --> LESS ACTH ==> Atrophy)
> Primary Adrenal Neoplasm (Adenoma/Carcinoma)
>> Path: More Endogenous cortisol --> Less ATCH --> Atrophy of ONLY the uninvolved adrenal gland
-Sx/PE: MOON FACIES
> Metabolic Syndrome (HTN, Hyperglycemia, HLD)
> Obesity (TRUNCAL, ROUND MOON FACIES)
> Osteoporosis
> Neuropsych (Depression, Anxiety, Irritability)
> Facial plethora (excess blood flow ==> REDNESS)
> Androgen Excess (Acne, Hirsuitism)
> Cataracts
> Immunosuppression
> Ecchymoses (easy bruising)
> Skin changes (STRIAE: More MSH --> Hyperpigmentation)
-Dx: Labs
Adrenal Neoplasm
> ACTH = LOW
> High Dose Dexa Test = Not Needed
> CRH Stim Test = Not Needed
ACTH-DEPENDENT Cushing Syndrome (Hypercortisolism)
Define Condition:
-Hx & Path:
> Secreting Pituitary Tumor (DISEASE)
>> Path: More ACTH --> Bilateral Adrenal Cortical Hyperplasia ==> MORE CORTISOL
> Ectopic ACTH production (Paraneoplastic from SCLC)
>> Path: More ACTH --> Bilateral Adrenal Cortical Hyperplasia ==> MORE CORTISOL
-Sx/PE: MOON FACIES
> Metabolic Syndrome (HTN, Hyperglycemia, HLD)
> Obesity (TRUNCAL, ROUND MOON FACIES)
> Osteoporosis
> Neuropsych (Depression, Anxiety, Irritability)
> Facial plethora (excess blood flow ==> REDNESS)
> Androgen Excess (Acne, Hirsuitism)
> Cataracts
> Immunosuppression
> Ecchymoses (easy bruising)
> Skin changes (STRIAE: More MSH --> Hyperpigmentation)
-Dx: Labs
DISEASE (Pituitary Tumor)
> ACTH = HIGH
> High Dose Dexa Test = Suppression (Less ACTH/cortisol)
> CRH Stim Test = More ACTH/Cortisol
ECTOPIC
> ACTH = HIGH
> High Dose Dexa Test = No Change
> CRH Stim Test = No Change
Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH)
Define Condition:
Autosomal RECESSIVE disorders that are caused by a deficiency of congenital adrenal enzymes (21-hydroxylase & 11Beta-hydroxylase) involved in adrenal steroid biosynthesis
-Path: Enzyme deficiency -> ↓ cortisol -> ↑ ACTH -> bilateral adrenal hyperplasia -> ↑ non-cortisol hormone synthesis (MORE ANDROGENS, mineralocorticoids)
> 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency (95%)
>> Shunted toward MORE ANDROGENS --> Ambiguous genitalia & virilization in females
>> LESS ALDOSTERONE =
>>> MORE Potassium, but LESS SODIUM
>>> MORE Renin
> 11B-Hydroxylase Deficiency (5%)
>> Some more Androgens --> Ambiguous genitalia & virilization in females
>> MORE 11-DEOXYCORTICOSTERONE (EFFECTIVE MINERALOCORTICOID)
>>> More Na retention ==> Higher BP
>>> Less K, Less Renin
-Sx/PE:
> Ambiguous Genitalia and Virilization in FEMALES
> 11B-Hydroxylase Deficiency
>> HIGHER BP
-Dx: Labs
> 21-Hydrox
>> Potassium = HIGH
>> Sodium = LOW
>> Renin = HIGH
> 11B-Hydrox
>> Potassium = LOW
>> Sodium = HIGH
>> Renin = LOW
Primary Adrenocortical Insufficiency
Define Condition:
Deficiency of Adrenal Hormones d/t issues w/ Adrenal Gland itself
-Hx: Damage to Adrenal Gland (ACUTE or CHRONIC)
> Autoimmune Adrenalitis
> Adrenal Infex
> Metastatic cancer to Adrenals
> Adrenal Hemorrhage
-Sx/PE:
> Weakness
> Fatigue
> SALT CRAVING (Can't reabsorb Na+)
> Hypotension
> Wt Loss
> N/V
> Hyperpigmentation (More POMC --> More ACTH & MSH) esp in sun exposed areas, palmar creases, nail beds, mucous membranes
-Dx: Depends on cause
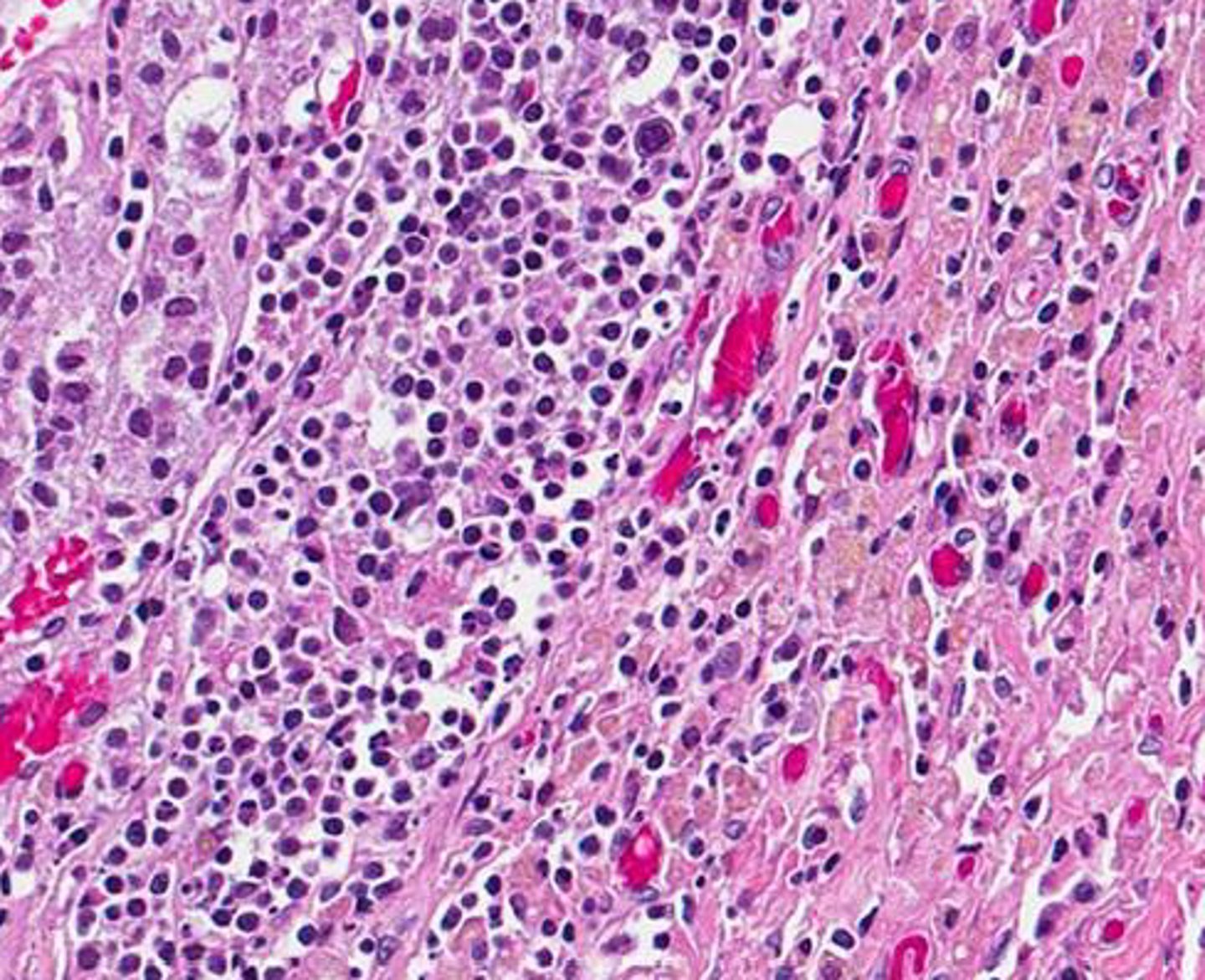
Autoimmune Adrenalitis
Define Cause of Primary Adrenocortical Insufficiency:
-Hx:
> MCC of Primary Adrenocortical Insufficiency in HIGH INCOME COUNTRIES
-Path/Sx/PE: May be a/w Autoimmune Polyglandular Syndrome (APS) 1
> Adrenocortical Insufficiency
> Muco-cutaneous Candidiasis
> Hypoparathyroidism
-Dx:
> Gross: Adrenal glands are irregularly shrunken due to autoimmune destruction
> Micro: Lymphocytic infiltrate in cortex
Adrenal Infection
Define Cause of Primary Adrenocortical Insufficiency:
-Hx:
> MCC = TB (esp in low-income countries)
> Disseminated fungal infections (Histoplasma capsulatum, Coccidioides immitis)
> AIDS induced infections (CMV, Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare)
-Dx: if TB
> Caseating Granuloma in gland
Metastatic spread to Adrenals
Define Cause of Primary Adrenocortical Insufficiency:
Cancer spread to adrenals from LUNG or BREAST cancer
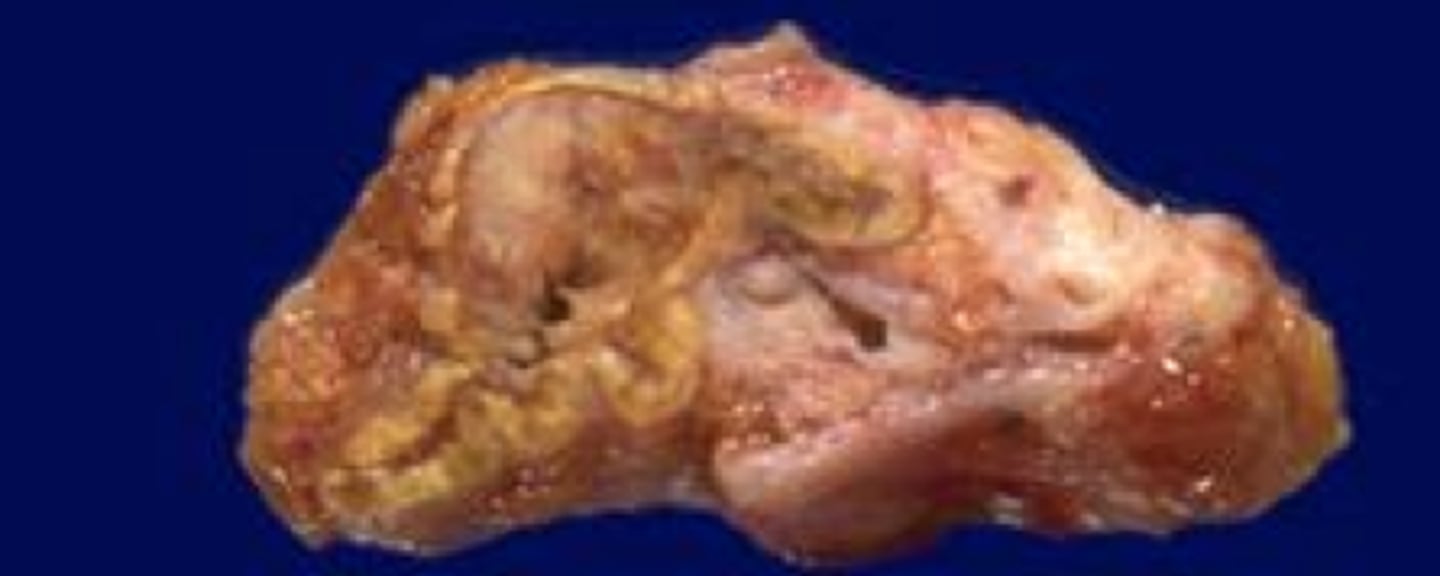
Adrenal Hemorrhage
Define Cause of Primary Adrenocortical Insufficiency:
-Hx:
> Waterhouse-Friderichsen Syndrome = bilateral adrenal hemorrhage in the setting of sepsis (usually d/t Neisseria meningitidis); usually d/t sepsis-induced endothelial injury or DIC
> Anticoagulant Therapy
> Trauma
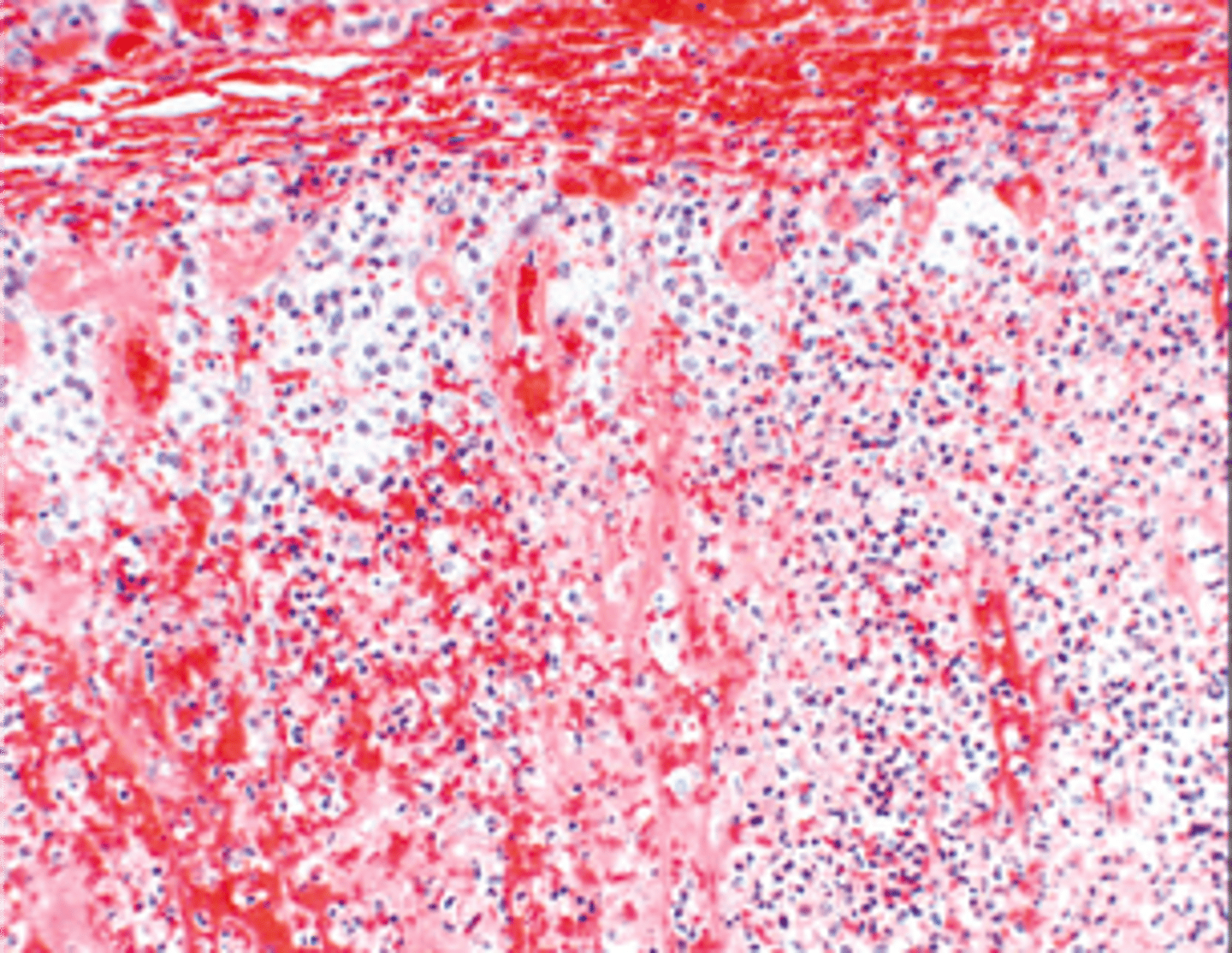
Secondaty Adrenocortical Insufficiency
Define Condition:
Deficiency of Adrenal Hormones d/t issues w/ PITUITARY
-Path: Hypopituitarism = ↓ pituitary ACTH -> ↓cortisol, ↓androgens
-Sx/PE: No Hyperpigmentation (b/c no ACTH or MSH)
-Dx: Labs
> No Hyperkalemia
Mixed Adrenocortical Insufficiency
Define Condition:
Deficiency of Adrenal Hormones d/t issues w/ PITUITARY AND ADRENAL GLAND
-Hx: From Abrupt withdrawal of Long-Term Exogenous Glucocorticoids (TRANSPLANT PTS)
-Path: Glucocorticoids stopped --> Adrenal Gland atrophy
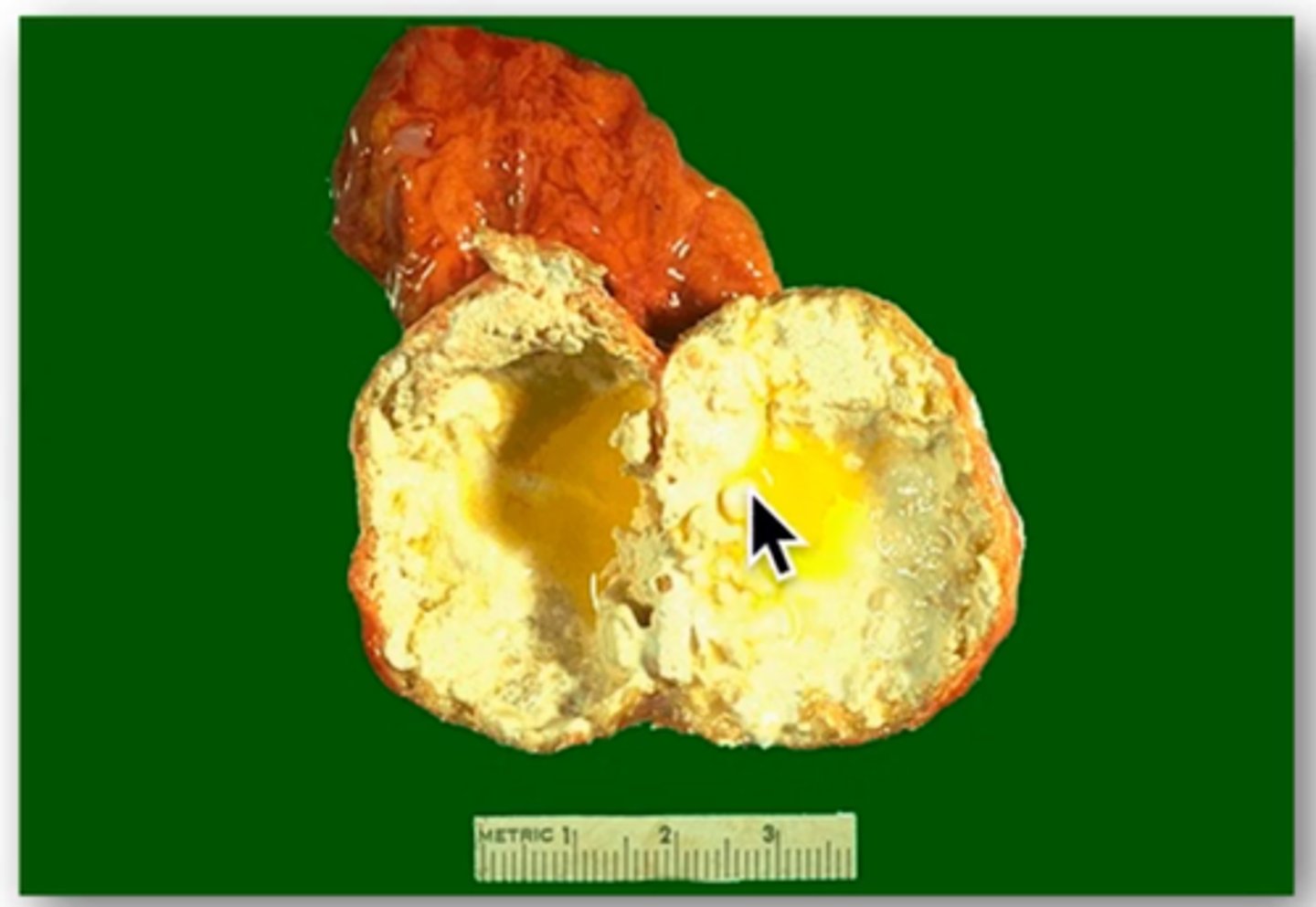
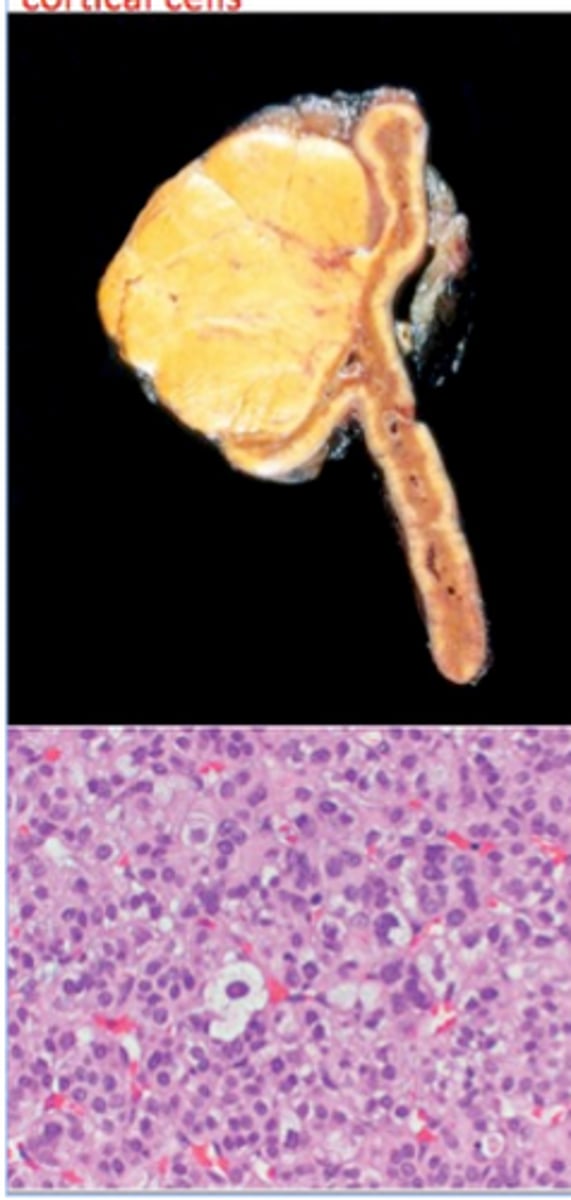
Adrenocortical Adenomas
Define Condition:
BENIGN; Most are NONFUNCTIONAL (90%)
-Hx: Found incidentally (incidentalomas)
-Dx:
> Gross:
>> Well-circumscribed yellow tumor with capsule
>> Small (1-2 cm)
> Micro: Cells similar to cells found in zona fasciculata
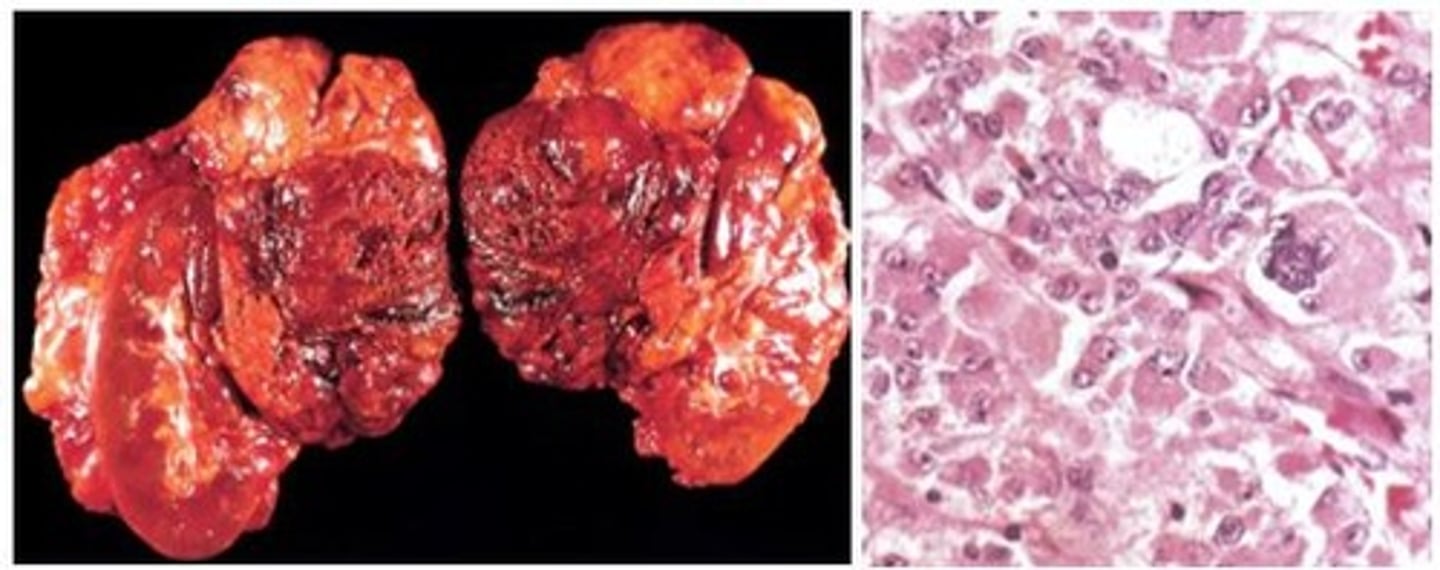
Adrenocortical Carcinomas (ACC)
Define Condition:
RARE & MALIGNANT Epithelial tumor (1/2 are functional)
-Prog: SIZE (larger => worrisome); Overall poor prognosis with 5 year mortality 50 - 90%
-Tx: Surgical Resection
Pheochromocytoma
Define Condition:
Proliferation of chromaffin cells
-Hx: MC Tumor of Adrenal Medulla in Adults
-Path: Most FUNCTIONAL (Secrete Catecholamines)
> A/w mutations
>> RET (MEN2A & MEN2B)
>> VHL
>> NF-1
**Rule of 10s**
> 10% = Malignant
> 10% = Bilateral
> 10% = OUTSIDE Adrenal Glands (paragangliomas = thorax, abdomen, pelvis)
> 10% = Children
-Sx/PE: EPISODIC SX (5Ps)
> Pressure (More BP)
> Pain (HA)
> Perspiration
> Palpitation/Tachycardia
> Pallor
-Dx:
> Labs:
>> 24 Hr Urine =
>>> MORE CATECHOLAMINES (Epi/ME)
>>> MORE METANEPHRINES (Metabolites) in Urine OR PLAMSA
> Gross:
>> Well circumscribed tumor
>> Size varies from small to large masses
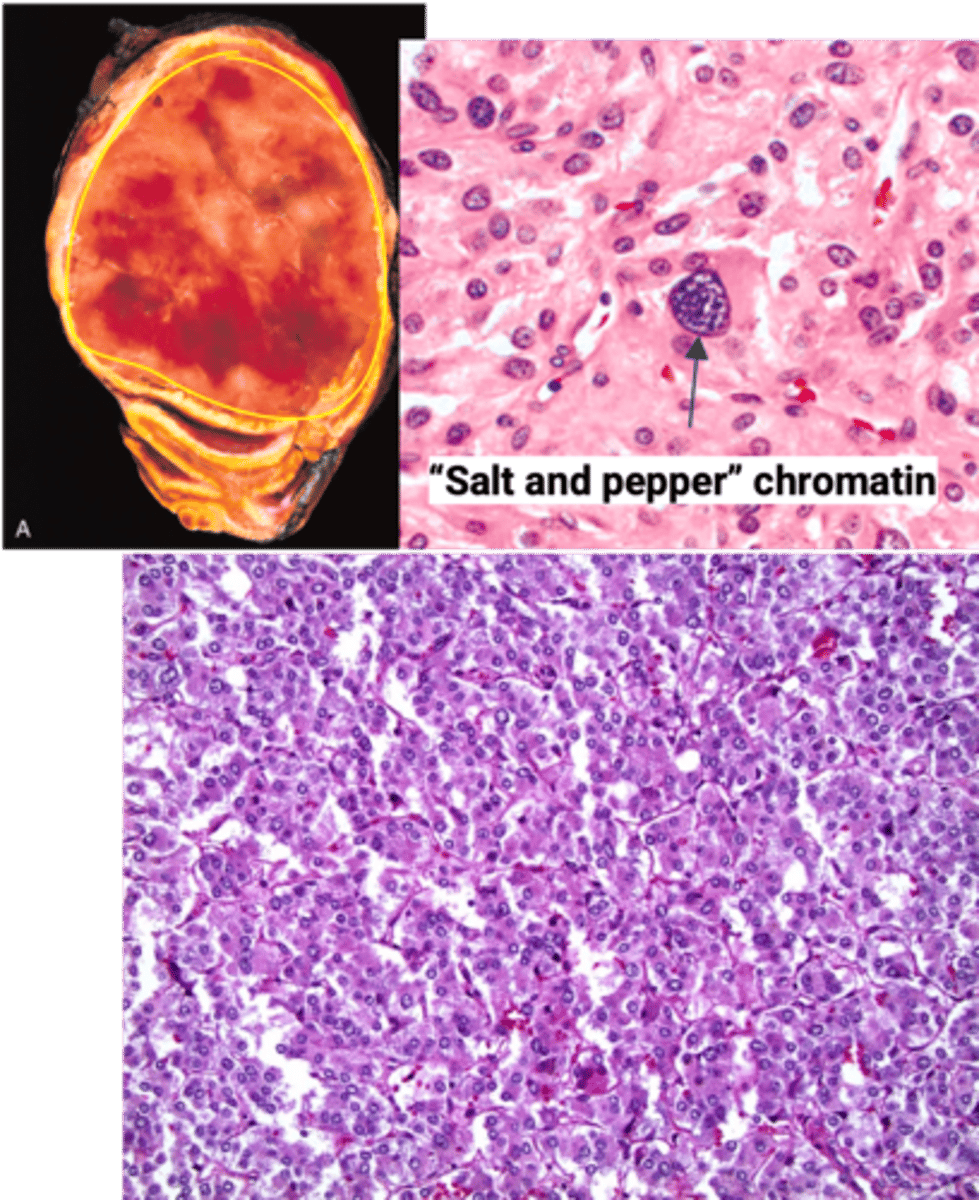
> Micro:
>> Polygonal to spindle-shaped cells arranged in nests
>> Cells have abundant finely granular cytoplasm due to neurosecretory granules containing catecholamines
>> “Salt and pepper” chromatin - characteristic of neuroendocrine tumors
>> (+) chromogranin,
(+) synaptophysin (neuroendocrine markers) immunohistochemistry stains
-Prog: Depends on METASTASES
MEN1
Define Condition:
AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT Inherited Genetic Syndrome d/t mutation in the MEN1 Tumor Suppression gene on Chromosome 11
-Hx:
> Usually at YOUNGER AGE than sporadic tumors
> Often Multifocal
> More aggressive and recur more
-Path:
> Preceded by clonal endocrine hyperplasia
> Mutations of gene stops encoding of menin protein (regulates gene transcription) --> Increased risk of Endocrine Tumors:
>> Primary Hyperparathyroidism (Parathyroid Adenoma)
>> Pancreatic Endocrine Tumors
>>> Leading cause of death in Syndrome
>>> Aggressive/Functional
>>> Ex: Gastrinomas, Insulinomas, Glucagonomas, Somatostatinomas
>> Pituitary Tumors
>>> MC = Lactotroph adenoma/prolactinoma
>>> Somatotroph (GH) Adenoma
MEN Type 2A
Define Condition:
AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT Inherited Genetic Syndrome d/t mutation in the RET Tumor Proto-oncogene on Chromosome 10
-Path: GAIN OF FUNCTION MUTATION of RET Tumor Proto-Oncogene that encodes TK Receptor
> 2 Ps, 1 M
>> Parathyroid (10-20% --> Primary Hyperparathyroidism)
>> Pheochromocytoma (50%)
>> Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (in almost ALL pts)
>>> Usually multifocal
>>> C-cell hyperplasia in adjacent "normal" thyroid
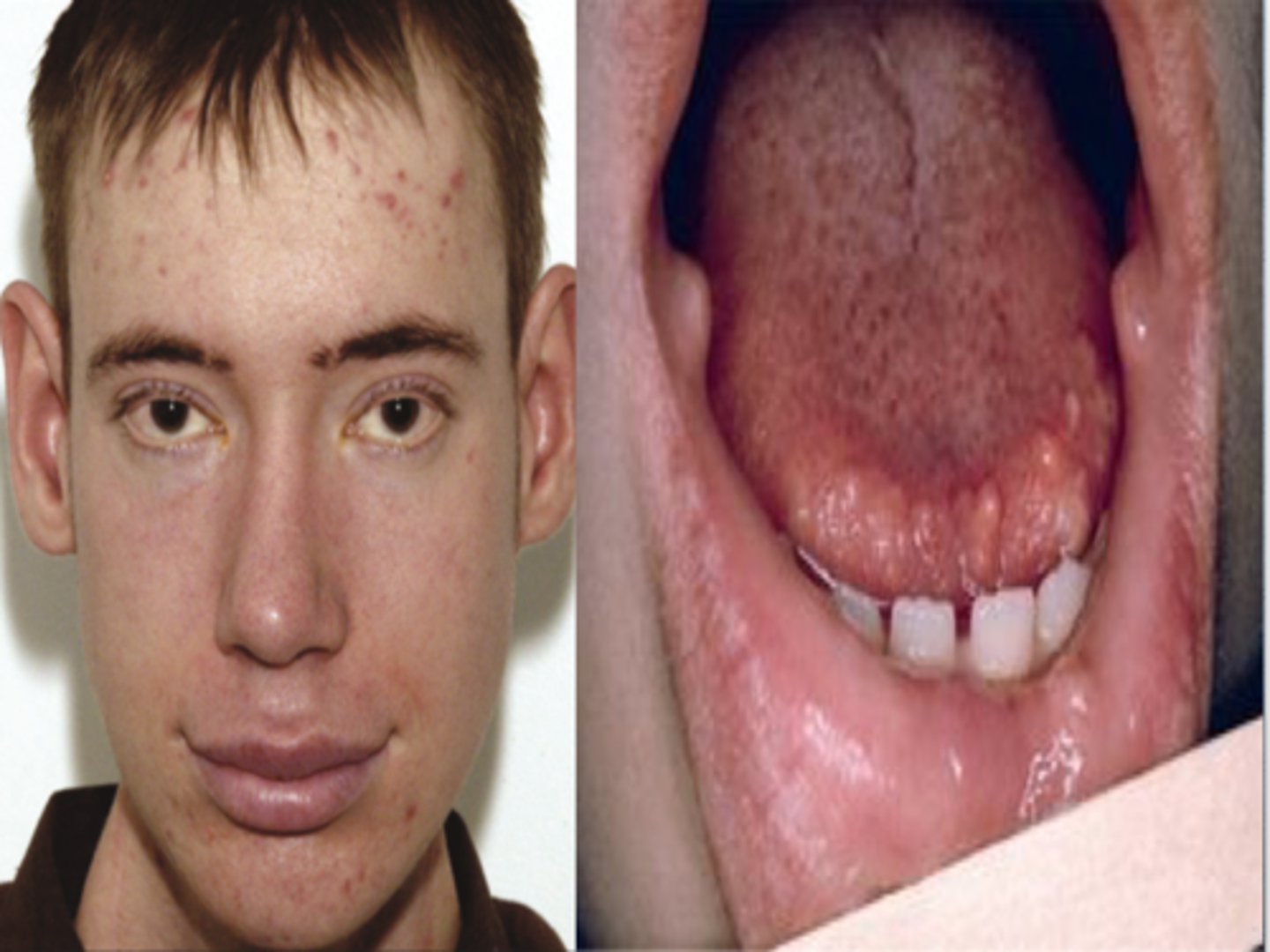
MEN Type 2B
Define Condition:
-Path: 95% of cases are from a single amino acid substitution mutation in RET proto-oncogene
1 P, 2 Ms
> Medullary thyroid carcinoma
>> Tumors usually multifocal
>> More aggressive than in MEN 2A
> Pheochromocytoma
> Extra endocrine manifestations
>> Mucosal neuromas (lips, tongue)
>> Intestinal ganglioneuromas (GI tract)
>> Marfanoid habitus (i.e. tall, lanky)
> No hyperparathyroidism