Module 3.1 Magnetism
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Magnetism:
Charges particles in motion exhibit magnetism
Magnetic Domain:
accumulation of many atomic magnets
Electron needs to be in _____ to display any kind of magnetism
motion
Magnetic materials are usually in a _________ state
non-magnetized
If domains align:
o Results in a magnetized material with a North to South orientation
o Effectively one N pole and one S pole
SI Units
Tesla (T)
Older SI Unit term
Gauss (G)
Classification of Magnets
Natural
Artificial Permanent
Electromagnets
Natural (Found in nature)
Earth is a dipole (has two poles N and S)
Example: Magnetite [lodestone or iron oxide (Fe3O4)]
Artificial Permanent (manmade)
Hardened steel or alloy (alnico)
Example: Compass
Electromagnets (temporary)
Created by a current of e- & iron core
Magnetic Permeability (Susceptibility)
ease with which material can be magnetized
Magnetic Retentivity
Ability of a material to hold magnetization
Permeability & Retentivity are _____ ______
inversely related
Magnetic Classification of Matter
Ferromagnetic
Paramagnetic
Diamagnetic
Nonmagnetic
Ferromagnetic
Materials that can be magnetized
Exhibit strong magnetic properties
Are strongly attracted to a magnet
Paramagnetic
Materials that are only weakly attracted to a magnetic field
Loosely influenced by a magnetic field
Diamagnetic
Materials are weakly repelled by a magnetic field. These materials cannot be magnetized and are not attracted to a magnet.
Nonmagnetic
Materials unaffected by a magnetic field
Magnetic Force Field
Lines of force (magnetic flux lines)
_____ outside the magnet
N → S
_____ inside the magnet
S → N
Field lines pass through both magnetic & nonmagnetic materials
concentrated by magnetic material
unaffected by nonmagnetic materials
Laws of Magnetism
Every magnet has two poles
Magnetic Laws
Analogous to Coulomb's laws
Every magnet has two poles
designated N & S
Magnetic Laws
Like poles repel, unlike poles attract
Analogous to Coulomb's laws
The force between two magnetic poles varies directly as the strength of the poles and inversely as the square of the distance between poles.
Two poles have a magnetic charge of 4 T and 6 T each and they are placed 2 meters apart. What is the force between them?
4T x 6T = 24N
Two poles have a magnetic charge of 4 T and 6 T each and they are placed 2 meters apart. What if the poles were then moved to 1 meter apart?
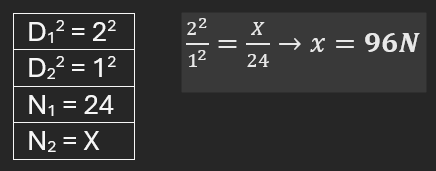
Strength of Magnetism determined by the number of field lines per unit area
· Strong fields = more lines of force
· Strong field = closer lines of force
Is the Earth a strong of weak magnet?
Weak
How to Create a Magnet
1. Stroking an iron bar repeatedly with a magnet
2. Hammering a piece of iron in the presence of a magnet