PTE 722: exam 2
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
cryotherapy
a medical treatment that uses extreme cold to destroy abnormal tissue or relieve pain
5-8 mins of treatment time with cold pack
thermotherapy
a treatment modality that uses heat to relieve pain, improve circulation, and promote healing
list some examples of deep vs. superficial heating agents.
deep: ultrasound, diathermy
superficial: heat packs, infrared lamps
what are the four modes of heat transfer?
conduction: transfer through direct contact between objects
convection: transfer through the movement of a fluid (like air or liquid)
conversion: transfer depends on the power of energy source
radiation: transfer through electromagnetic waves
T or F: the greater the temperature difference between a heating/cooling agent and the body part it is applied to, the faster the rate of heat transfer.
T
what mode transfers heat faster than conduction within the same time period?
convection
what is a natural process that transfers heat via convection throughout our body?
circulation of blood
example: vasodilation increases circulation rate —> increases tissue temp
what factors does the rate of tissue temperature depend on when using conversion heat transfer?
size of area being treated
size of the applicator
efficiency of transmission from the applicator to the patient
type of tissue being treated
T or F: when utilizing conversion transfers, it requires direct contact between the thermal agent and the tissue.
F; doesn’t require direct contact
does require an intervening material to be a good transmitter of energy tho
what factors does the rate of tissue temperature depend on when using radiation heat transfer?
intensity of radiation
relative size of radiation source
size of area being treated
relative size of distance of the source from the treatment area
size of angle of the radiation to tissue
T or F: 5 mins of icing could increase isometric strength.
T
why might a therapist utilize cryotherapy?
to control inflammation, edema, and/or pain in patients or to modify spasticity or to increase viscosity of blood
patients with _____ _____ enjoy cryotherapy because it manages their symptoms.
multiple sclerosis
list some contraindications of cryotherapy.
cold hypersensitivity
cold intolerance
cryoglobulinemia
over-regenerating peripheral nerves
over an area with circulatory compromise
what are some precautions to note when using cryotherapy?
applying over a superficial main branch of a nerve or over an open wound
hypertension
poor sensation or mentation
with very old or very young patients
what is the most severe adverse affect of cryotherapy?
tissue death
caused by prolonged vasoconstriction, ischemia, or thromboses in smaller vessels
temporary or permanent nerve damage can become an adverse effect of cryotherapy. what is the time frame to avoid nerve damage?
limit cold application to under 45 mins
what are the neural stages of sensation with cryotherapy?
cold
burning
aching
numbness
*CBAN
what temperature should cold packs be kept at?
0-5 degrees C or 32-41 degrees F
cold packs should be cooled for at least __ mins between uses and for __ hours or more before initial use.
30 mins
2 hours
T or F: ice packs provide more aggressive cooling than cold packs at the same temp.
T
therefore more insulation should be used when applying ice packs
T or F: a therapist must keep an ice cup/popsicle moving when in contact with patient’s skin
T
what combination has been shown to control swelling, pain, or blood loss the best?
cold AND compression simultaneously
what is a controlled cold compression unit?
a sleeve wrapped around an injured area that alternately pumps cold water and air, with compression being applied by the intermittent inflation of air
what is the purpose of vapocoolant sprays?
to provide a counterirritant stimulus to the cutaneous thermal afferents overlaying muscles to cause a reflex reduction in motor neuron activity and thus a reduction in resistance to stretch
is vapocoolant applied in parallel strokes along the skin before OR after stretching the patient’s muscles?
immediately before
cold whirlpools
indicated in acute and subacute conditions in which exercise of the injured part during cold treatment is desired
contrast baths
used to treat subacute swelling, gravity-dependent swelling, and vasodilation-vasoconstriction response
what is the purpose of cryokinetics?
numb the injured part to the point of analgesia and then work toward achieving normal ROM though progressive exercises (should be pain-free concentrating on both flexibility and strength)
what are some reasons why a therapist would utilize superficial heat?
pain control
increased ROM
decreased joint stiffness
accelerate healing
list the contraindications for thermotherapy usage.
recent or potential hemorrhage at site
thrombophlebitis
impaired sensation or mental ability
malignant tumor at site
list a few examples of precautions for thermotherapy use.
acute injury or inflammation
pregnancy
impaired circulation or poor thermal regulation (cardiac insufficiency)
edema
over an open wound
T or F: burns may occur if heat is applied where protective vasodilation cannot occur.
T
hot packs should be heated for at least __ mins between uses and for __ hours or more before initial use.
30 mins
2 hours
which tissues transfer heat well?
muscles, tissues high in collagen
thickness of subcutaneous fat does not transfer heat well
when would a therapist use ice vs heat with a patient? (Dr. Robinson question)
ice: injury occurred recently (inflammation)
heat: injury occurred a while ago (stiff)
take note of patient’s preference too
a hydrocollator is a purpose-designed, thermostatically controlled water cabinet that stays on at all times. what temperature should the hot water be kept at?
between 70-75 degrees C or 158-167 degrees F
paraffin, fluidotherpay, and infrared lights also act as a heat modality. what are they?
paraffin: a warm, melted wax mixed with mineral oil that can be safely applied directly to skin as a heating modality
fluidotherpay: cabinet containing finely ground cellulose particles where heated air is circulated through through
infrared lights: emit electromagnetic radiation within the frequency range that gives rise to heat when absorbed by matter
what is ultrasound?
sound with a frequency greater than 20,000 cycles per second (beyond the hearing of humans)
list the types of diagnostic ultrasound
echocardiography 5 MHz
echocephalography 5 MHz
doppler blood 5-10 MHZ
obstetrical doppler 2.25 MHz
what are the characteristics that make up therapeutic ultrasounds?
deeply penetrating modality that has thermal and non-thermal effects
between 0.7-3.3 MHz
maximizes energy absorption at a depth of 2-5 cm
T or F: ultrasound waves do not require a dense medium in which to travel
F; they need a dense medium, usually a gel-like substance
if no significant temperature increase arises from fat and skin when using an ultrasound, then what structures can be heated to a therapeutic range?
tissues high in collagen
tendons, muscles, ligaments, joint capsules, meniscus, and cortical bones
the transducer is an important aspect of an ultrasound machine. why?
its where the electrical energy is converted to acoustic energy and is where the crystal is housed
what happens during the compression and rarefaction phases of a therapeutic ultrasound wave?
compression phase: positive pressure; tissue molecules in the wave’s path are compressed
rarefaction phase: negative pressure; tissue molecules in the wave’s path spread out more
when the compression and rarefaction occurs in the same direction that the wave is traveling, a ____ wave forms.
longitudinal
when the compression and rarefaction occurs in a right angled direction that the wave is traveling, a ____ wave forms.
shear
shear waves tend to form at surfaces of bone (periosteum)
T or F: when a beam enters the body it is either transmitted, reflected, refracted, or absorbed.
T
what are the characteristics of an ultrasound beam?
sound wave is collimated as it leaves the transducer but begins to diverge when it penetrates to deeper tissues
larger diameter transducers produce a more collimated bean than smaller transducers
the sound field intensity is very non-uniform near the transducer head —> “near field”
T or F: tissue with more blood supply will heat up faster through ultrasound than tissues with less blood supply. (Dr. Robinson question)
F; tissues with more blood supply will dissipate through blood stream
what happens when an ultrasound hits soft tissue or bone? (Dr. Robinson question)
reflects off
spatial average intensity
represents the amount of energy in a specific area; represented as W/cm²
spatial peak intensity
represents the maximum intensity point in the beam; located in the far field of the beam
beam non-uniformity ratio
the ratio between the spatial peak intensity and the spatial average intensity (ex: 4:1 = spatial peak is 4, spatial average is 1)
a 1:1 ratio is theoretically ideal for a BNR but clinically unattainable, so ratios up to ___ are acceptable.
8:1
what MHz are wave frequencies typically delivered?
1 or 3 MHz
a 1 MHz beam is more collimated nad penetrates deeper than a 3 MHz beam
what’s the main difference between continuous ultrasound and pulsed ulstrasound?
continuous is used primarily for its thermal effects
pulsed is used for its non-thermal effects
how is ultrasound generated?
by the application of a high frequency alternating electrical current to the crystal in the transducer of an ultrasound unit
what are some examples of thermal effects when using an ultrasound?
acceleration of metabolic rate
control of pain and muscle spasm
alteration of nerve conduction velocity
increased circulation/altered blood flow and enzymatic activity
increased soft tissue extensibility
T or F: to increase the total amount of heat delivered to the tissue the duration of ultrasound application and/or the average intensity of ultrasound application must be increased.
T
describe the frequency of ultrasound application.
1 MHz to heat tissues up to a depth of 5 cm
3 MHz to heat tissues up to a depth of 1-2 cm
T or F: 3 MHz ultrasound has a lower depth of penetration therefore the maximum temperature increase is lesser than 3-4 times.
F; greater by 3-4 times
what unknown variables make it difficult to predict the temperature increase of ultrasound absorption?
thickness of each tissue layer
amount of circulation
distance of reflecting soft tissue/bone interfaces
law of Grotthus-Draper
as superficial tissues absorb more energy, less energy is transmitted to underlying tissues
what is used to determine the final ultrasound intensity?
the patient’s report of warmth
at what temperatures should an ultrasound be maintained to achieve a therapeutic effect?
40-45 degrees C for at least 5 mins
what factors does the degree of tissue temperature rising depend on?
mode of application
intensity and frequency of the output
vascularity and type of tissue
speed at which the sound head moves
thermal ultrasound chart
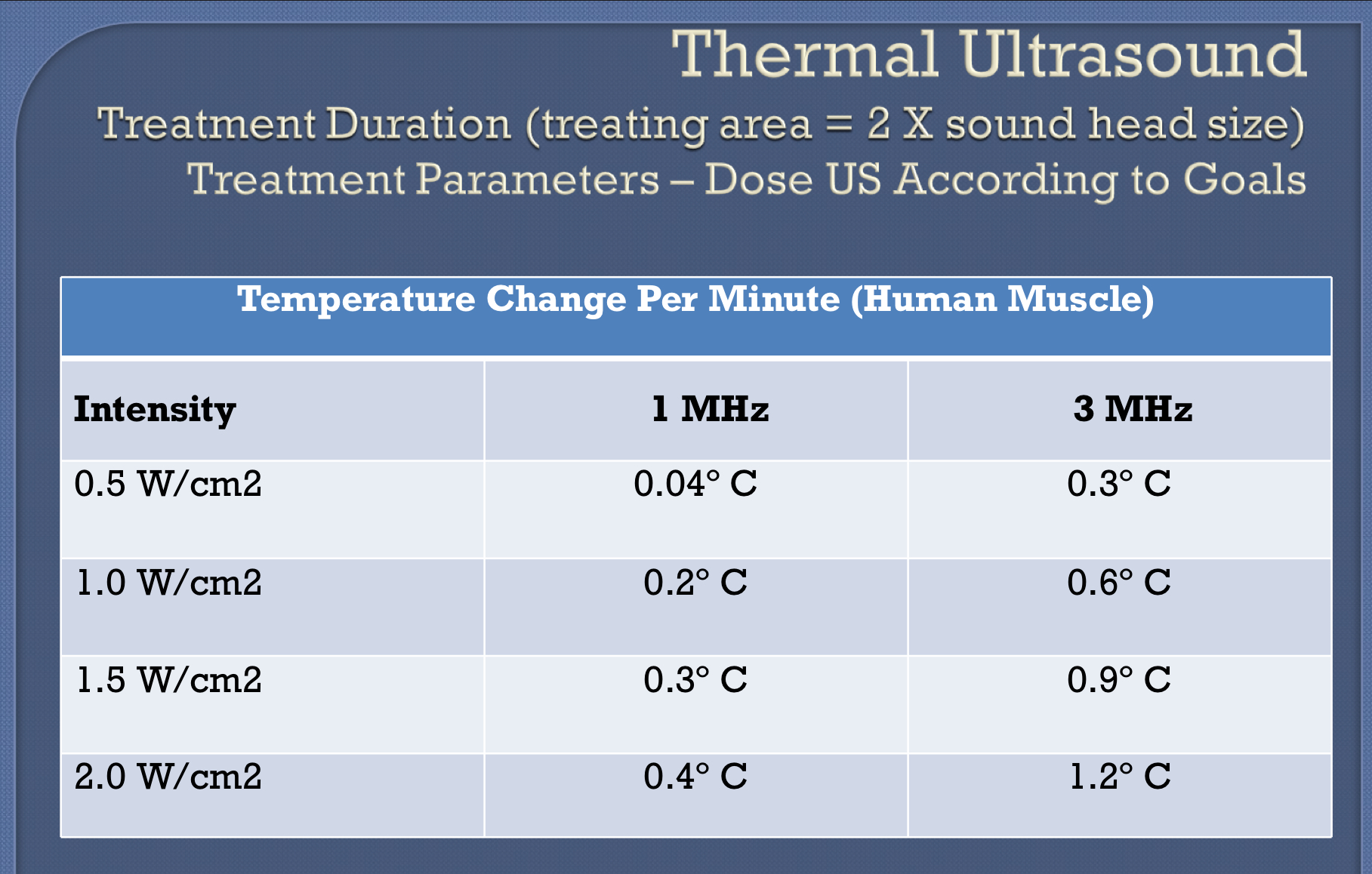
what are some examples of non-thermal effects when using an ultrasound?
increased skin and cell membrane permeability
increased mast cell degranulation
increased chemotactic factor and histamine release
increased responsiveness of macrophages
increased rate of protein synthesis by fibroblasts
the non-thermal effects of ultrasound include cavitation (mechanical vibration) and acoustic micro-streaming. what do these effects do to cell membranes?
distort them causing deformation of tissue molecules
cavitation
term given to the expansion and contraction of the gas bubbles due to the compression and rarefaction phases of the ultrasound wave
what’s the difference between stable and unstable cavitation?
stable: the gas bubbles expand and contract without growing to critical size
unstable: the gas bubbles expand too far and suddenly collapse, resulting in increased pressure and temp
acoustic microstreaming
term describing the fluid movement in and around tissue cells caused by the ultrasound wave
T or F: the primary site of ultrasound interaction is the cell membrane where the destabilization of the membrane leads to increased permeability. From here, various ions nad molecules can diffuse into the cells where they precipitate secondary events.
T
what chemical has been studied due to its influence on circulation and stimulating effect on protein synthesis?
histamine
list some examples of non-thermal or mechanical effects of ultrasound.
increased histamine release
increased phagocytic activity of macrophages
increased protein synthesis
increased capillary density of ischemic tissue
cell membrane alterations
what are some clinical applications of ultrasound?
soft tissue shortening
pain control
dermal ulcers
surgical skin incisions
tendon injuries or bone fractures
list examples of contraindications for utilizing ultrasound.
malignant tumor
pregnancy
joint cement
pacemaker
reproductive organs
what are the four precautions for utilizing ultrasound?
acute inflammation
epiphyseal plates
fractures
breast implants
what type of knee or hip replacement does a therapist not want to ultrasound? (Dr. Robinson question)
cemented plastic
describe the transducer (soundhead) movement during applicaiton?
slow strokes at 4cm/sec in a back and forth or circular movement while maintaining good contact on surface
what are the physical properties of electromagnetic radiation?
composed of electric and magnetic fields that are oriented perpendicular to each other
does not need a medium to travel through
natural and manufactured sources
categorized by frequency and wavelength (inversely proportional to each other)
what’s a key difference between low frequency and high frequency electromagnetic radiation (ER)?
low frequency: cannot break molecular bonds or produce ions
high frequency: can break molecular bonds and produce ions
how do you determine the intensity of ER?
its proportional to the energy output from the source and the inverse square of the distance of the source from the patient and to the cosin of the angle of incidence
T or F: intensity is greater when the source is close to the skin and parallel to the skin.
F; it must be perpendicular to skin
Arndt-Schulz law
a minimum stimulus is required to initiate a biological process, beyond a certain level, stronger stimuli will have less positive result, may cause damage
T or F: laser has no thermal affect.
T
what are the physical properties of ultraviolet radiation?
frequency range of 7.5 × 1014-1015 Hz
wavelength from 400-290 nm
between x-ray and visible light
what are the factors that determine the physiological effects of UV radiation?
influenced by wavelength and intensity
size of area being treated
thickness and pigmentation of skin
duration
what are the effects of ultraviolet radiation?
erythema production
tanning
epidural hyperplasia
vitamin D synthesis
bactericidal
______ and ______ are clinical indications for the use of UV.
psoriasis
wound healing
what are the contraindications for using UV radiation?
irradiation of the eyes
treating patients with skin cancer, pulmonary tuberculosis, cardiac, kidney, or liver disease, systemic lupus, erythematosis, and fever
what are the precautions for using UV radiation?
photosensitizing medication use
photosensitivity
recent x-ray therapy
list the adverse effects UV radiation.
burning
premature aging of the skin
carcinogenesis
eye damage
what are the three physical properties of lasers?
coherence: all photons of laser light are the same wavelength and individual wavelengths are in phase with one another
monochromaticity: single defined wavelength
collimation: photons move in a parallel manner, with minimal divergence, conentrating a beam of light
how are lasers classified?
classified by the type of material between the two reflecting surfaces
examples: crystal, gas, liquid, diode, or chemical
what does MED stand for?
minimal erythemal dose
will be on test!
what is the proper time frame for MED’s treatment response? (Dr. Robinson question)
shows up within 8 hrs, disappears after 24 hrs
what are low level lasers?
considered a low-power laser or cold, soft laser
good for treating tendon/ligament injury, arthritis, edema, ulcer and burn care
what are the clinical indications for using a low-level laser?
wound and fracture healing
musculoskeletal disorders
pain management