Genetic Processes: cell parts and functions
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SBI3U Lesson #1 (Secours) [NOTE: note everything in the hyperdoc, just what I needed personally]
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Cell theory
1) every living thing is made of cells
2) all cells come from pre-existing cells
3) cells are the basic unit of life
The two types of cells are
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic
Prokaryotic Cells
Simplest cell types
Evolved 3.5 bya
Very small (0.1-10 micrometers)
Don’t have membrane-bound organelle
ex: bacteria
Eukaryotic Cells
More complex, exolved from prokaryotic cells 2 bya
Means “true nuceus”, DNA is condensed inside a nuclear membrane
Large (10-100 micrometers)
Have membrane bound organelle (mitochondria, chloroplasts, etc)
ex: fungi, plants
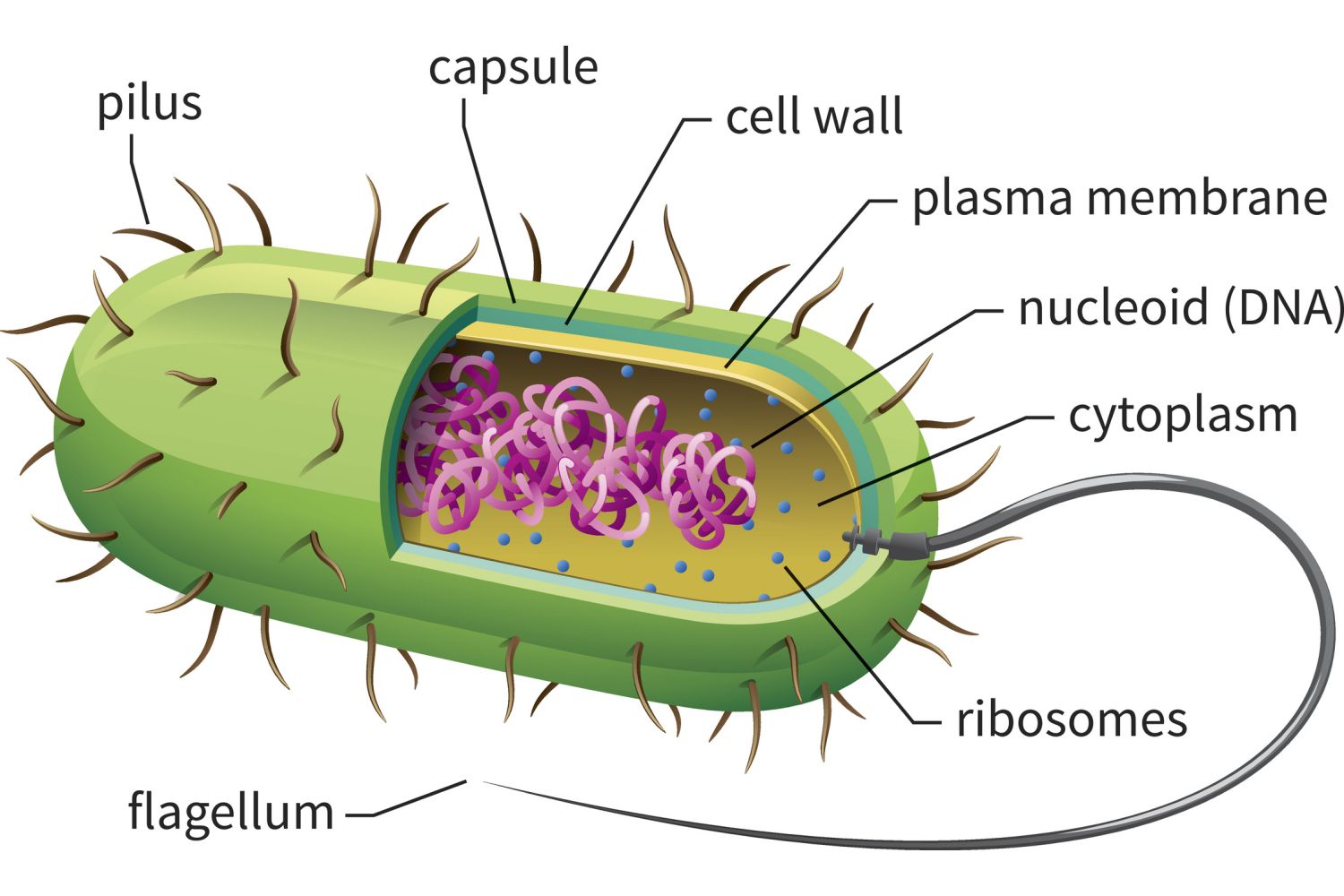
identify and label
prokaryotic cell
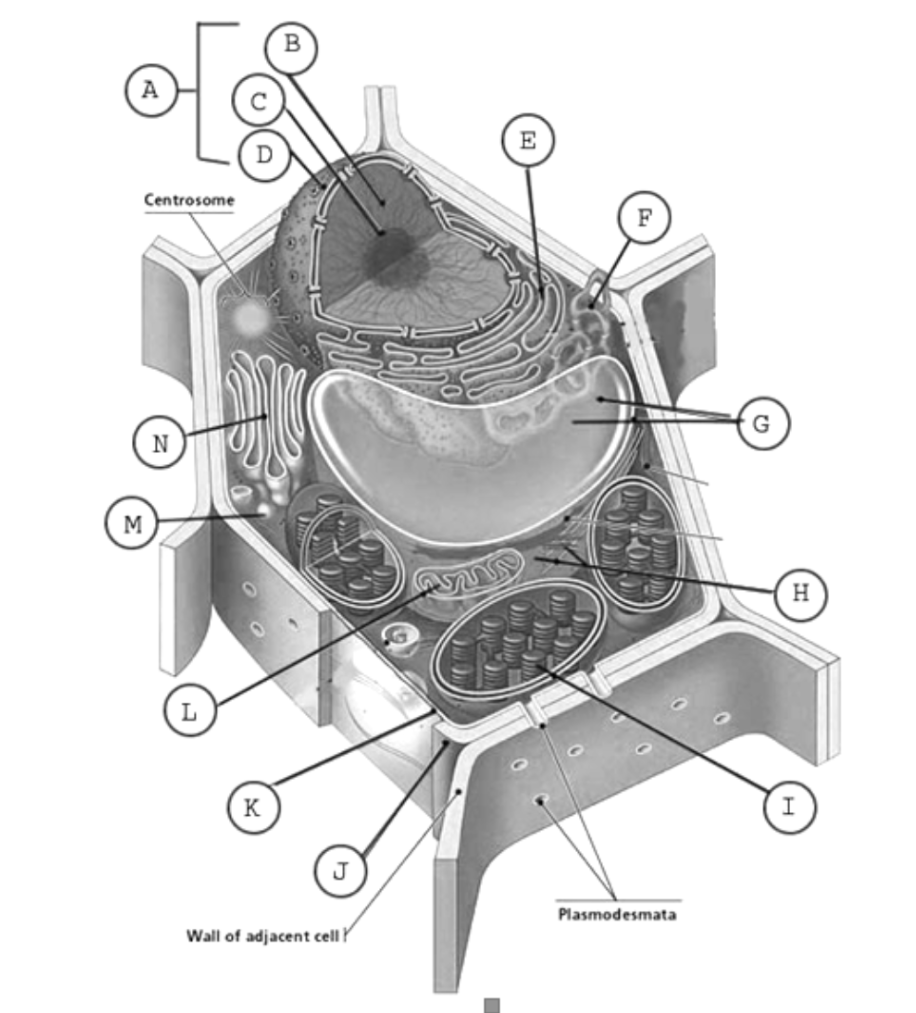
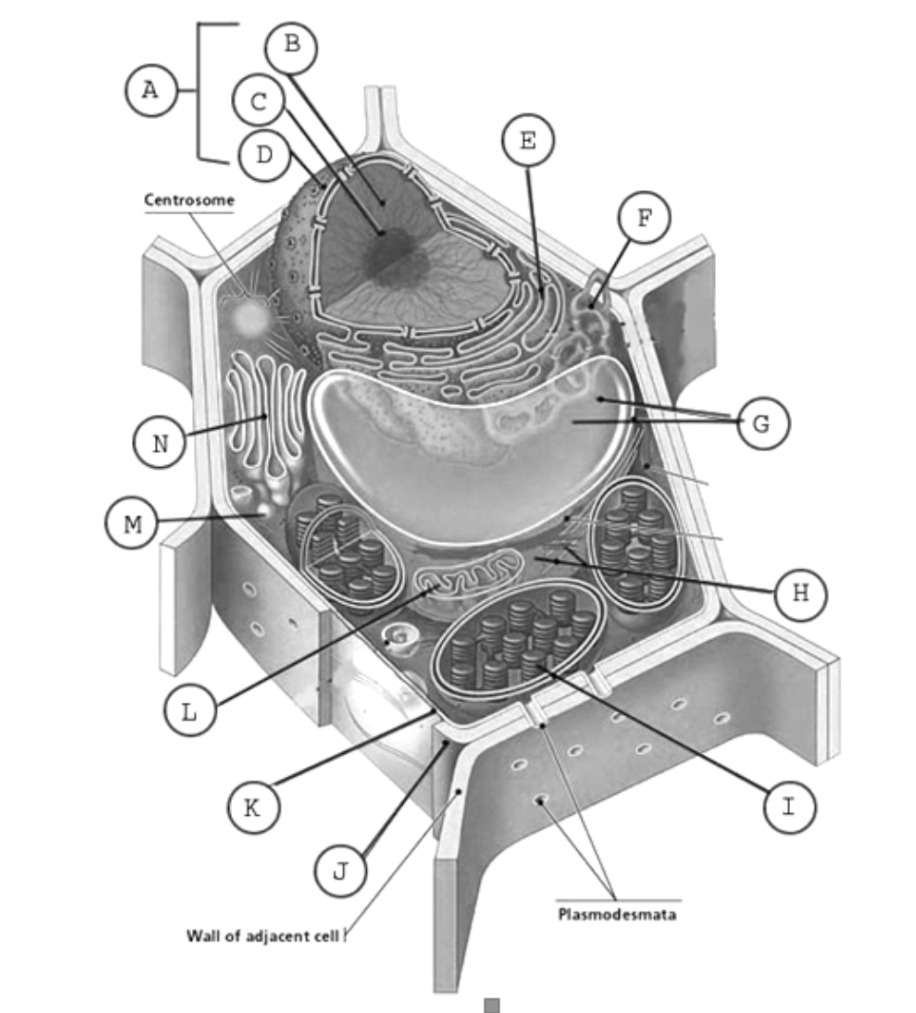
label the plant cell
A: Nucleus
B: Nucleoplasm
C: Nucleolus
D: Nuclear membrane
E: Rough ER
F: SER
G: Vacuole
I: Chloroplasts
J: Cell wall
K: Cell membrane
L: Mitochondria
M: Golgi vesicles
N: Golgi apparatus
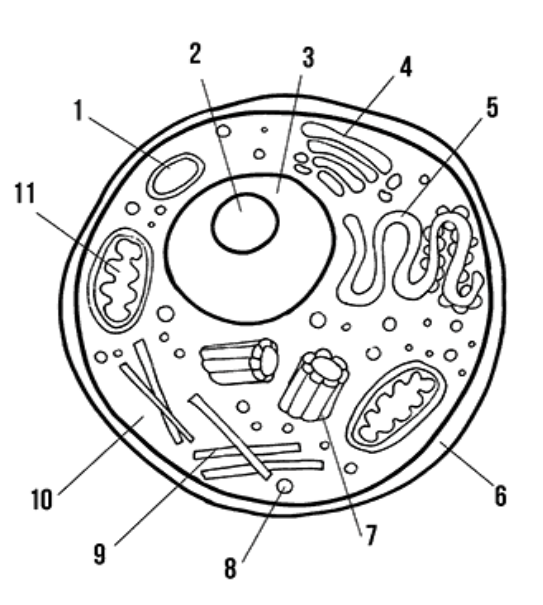
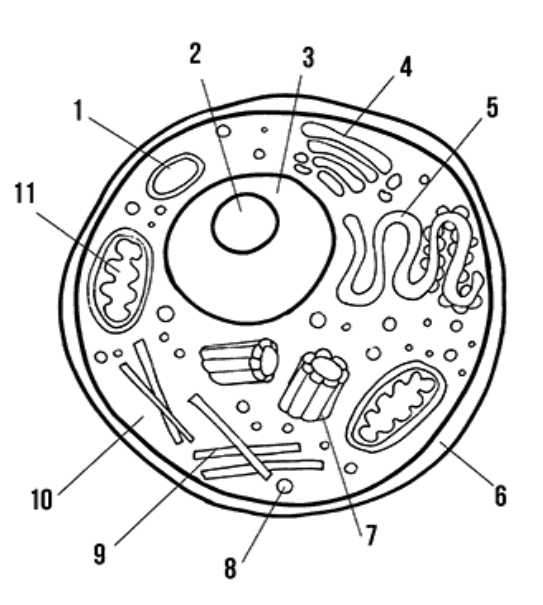
label the animal cell
1: Vacuole
2: Nucleolus
3: Nucleoplasm
4: Golgi apparatus
5: Smooth and Rough ER
6: Cell membrane
7: Centriole
8: Lysosome
9: Microtubes/Cytoskeleton
10: Cytoplasm
11: Mitochondria
Nucleoplasm
where genetic info is found, contains enzymes for DNA synthesis
Nucleolus
center for ribsome synthesis and production of certain proteins
nuclear membrane
protects and controls what enters and exits nucleus (contains pores)
Rough ER
characterized by the presence of ribsomes on the surface, synthesizes and transports proteins
Smooth ER
synthesizes lipids (steroids, phospholipids)
Golgi Apparatus
stores and transports proteins and lipids
Golgi Vesicles
transport molecules produced by other organelles
Lysosomes
acts as “garbage collectors”
Microtubes
filaments that help with structure
what do plant cells have that animal cells lack?
Cell wall
Chloroplasts
Single large vacuole
what do animal cells have that plant cells lack?
lysosomes
multiple small vacuoles
asexual reproduction types
Budding: formation from a bud, like yeast
Vegetative Reproduction: formation of a new plant from stolon🍓, tubers🥔, or rhizomes🍃
Parthogenesis: egg is fertilized without sperm (technically not really asexual since sperm is dormant)
Fragmentation: parent divides into pieces
how do bacteria and protists divide asexually
binary fission
90% of the cell cycle is spent in
interphase
The three phases of interphase
G1: rapid growth, organelles increase in # and size
Synthesis: DNA synthesizes and replicates
G2: replicates centrioles, prepares the cell for division
Apoptosis
If something goes wrong, one of the control points will detect it, causing the cell to self-destruct. This type of cell death is apoptosis.
In _____, each daughter cell has the ____ # and type of ________as the parent cell
mitosis, same, chromosomes
Which cells in our body get replaced the most?
Stomach cells
the cell cycle’s length is ______ for different cells
different
what makes a cell cancerous?
Many aspects, called hallmarks.
uncontrolled cell growth (insensitivity to anti-growth signals)
evasion of apoptosis
hide from white blood cells
and more!
How is cancer treated?
surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, oncolytic viruses (emerging)
Stem cell
undifferentiated cell, can develop into different types