part 16: pH
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Arrhenius theory
Bronsted-Lowry
Lewis theory
Theories of Acids and Bases
Svante Arrhenius
Arrhenius theory was proposed by?
H+
In Arrhenius theory, acids are substances that dissociates when dissolved in water and produces _____________
OH-
In Arrhenius theory, bases are substances that dissociate and release ______________ ions
Arrhenius theory is limited to behavior of acids and bases in aqueous solutions and not in non-aqueous media
Many substances do not have H+ yet they behave as acids
Many substances do not have OH- yet behave as bases
Limitations of Arrhenius theory
Johannes Bronsted
Thomas Lowry
Bronsted-Lowry theory was proposed by?
donate
In Bronsted-Lowry theory, acids are Hydrogen containing substance that _______ a proton (H+ ) to another
accept
In Bronsted-Lowry theory, bases are substances that _______ proton
Gilbert Lewis
Lewis theory was proposed by?
accept
In Lewis theory, an acid is a molecule or ion that can ________ a pair of electrons to form a dative bond
donate
In Lewis theory, a base is a molecule or ion that can ________ an electron pair to form a dative bond
Equilibrium dissociation constant
Quantitative measure of the amount of dissociation in aqueous solutions
Quantitative measure of the strength of an acid or base in solution
Acidity Constant or Acid Ionization Constant
“ka” is also known as?
↑ acidity
↑ ka = ___ acidity
↑ acidity
pka = -logka
↓ pka = ___ acidity
Basicity Constant or Base Ionization Constant
“kb” is also known as?
↑ basicity
↑ kb = ___ basicity
↑ basicity
pkb = -logkb
↓ pKb= ___ basicity

Formula for strong acids and bases

Formula for weak acids and weak bases
2.15
Sample problem: pH
Compute for the pH of a solution containing 0.5 M boric acid with ka of 1x10-4 .
3.09
Sample problem: pH
What is the pH of a 0.01 M benzoic acid solution?
Given: benzoic acid
ka= 6.5 x 10 -5
11.54
Sample problem: pH
A sodium hydroxide solution has [OH- ] = 3.50 x 10-3 M. What is its pH?
10.87
Sample problem: pH
What is the pH of 0.032 M ammonia solution with Kb of 1.71 x10 -5
Buffer
Solutions that resists pH change even if a small amount of strong acid or strong base is added
It protects the formulation from a sudden change in pH
Carbonic acid
Bicarbonate
Primary buffer in blood
Acid buffer
Basic buffer
Types of Buffer
Weak acid + Conjugate base
Acid buffer
Weak base + Conjugate acid
Basic buffer
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
Buffer equation is also known as?
Used to calculate the pH of a buffer solution
p.s.: take note of its spelling! 🙂
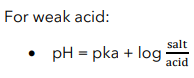
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation for Weak acid
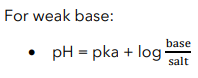
Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation for Weak base
4.56
Sample problem: pH
Calculate the pH of the buffer if the molar concentration of acetic acid is 0.03 M and that of sodium acetate is 0.02 M. The pKa for acetic acid 4.74
9.33
Sample problem: pH
What is the pH of a buffer solution that contains 0.24 M NH3 and 0.20 M NH4Cl?
Given: ka= 5.6 x10-10
Buffer capacity
Effectiveness of buffer in minimizing pH changes
The magnitude of resistance of a buffer to pH changes
The amount in gram equivalents per liter (Normality) of strong acid or strong base required to be added to a solution to change its pH unit by 1
Buffer effect
Buffer efficiency
Buffer index
Buffer value
Buffer capacity is also known as?
Van Slykes Equation
Buffer capacity equation

Van Slykes Equation
pH = pKa
Maximum Buffer Capacity
Bmax = 0.756 x C
Bmax = ?
0.092
Sample problem: pH
What is the maximum buffer capacity of a buffer solution containing 0.1 M of weak base and 0.06 M of its conjugate acid?