Carbohydrates
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Biopolymers
Large biological molecules: carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins
Monomer of carbohydrates
Monosaccharides (ex. glucose, fructose, galactose)
Condensation reaction
Connection of two monomers together, resulting in water leaving
Carbohydrate Condensation
2 monosaccharides → Disaccharide + H2O
Hydrolysis Reaction
Water is added to polymer, breaking it apart (consumes water instead of releasing)
Composition of Carbohydrates
C,H, and O; hydroxyl group and carbonyl group (ketone or aldehyde)
Formula for monosaccharides
Cx(H2O)x
Primary function of carbohydrates
Provide energy to organisms
2 types of carbs (sugars):
Simple - mono and disaccharides
Complex - polysaccharides
What is a carbohydrate with a ketone called?
Ketose (-ROR)
What is a carbohydrate with an aldehyde called?
Aldose (-ROH); glucose is an aldose
Ways of drawing carbohydrates:
Fischer projection (straight-chain)
Cyclic (how they are found in nature)
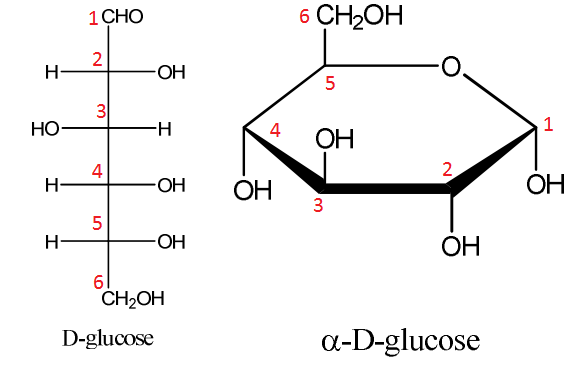
Stereoisomers of carbohydrates
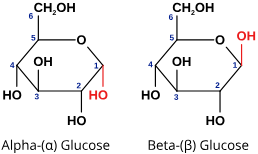
Alpha - hydroxyl next to oxygen faces DOWN
Beta - hydroxyl next to oxygen faces UP
Common name for glucose
Hexose/dextrose
Photosynthesis
Sunlight is used by plants to produce glucose
6CO2 + 6H2O + Sunlight → Glucose + 6O2
ATP Synthesis (Cellular Respiration)
Used by animals to convert glucose into ATP (energy)
Glucose + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
Glucose
6-carbon sugar with alpha hydroxyl
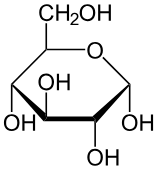
Fructose
Isomer of glucose stored and metabolized into glucose in liver (STORED)
Stored form of glucose
Fructose; converted by liver into glucose
What foods contain fructose?
Fruit, honey, and syrup
Galactose
Isomer of glucose that ISN’T common in nature
Which monosaccharide can pass through the bloodstream?
ONLY glucose, all carbohydrates MUST be converted to glucose
Which organ converts fructose and galactose into glucose?
The liver
All monosaccharides:
Glucose
Fructose
Galactose
Ribose
Deoxyribose
Ribose
5-carbon sugar that forms RNA (rRNA); gain little in diet
Deoxyribose
5-carbon structure used for DNA formation; we CAN make this
All disaccharides:
Maltose
Sucrose
Lactose
Maltose
2 glucose molecules to form alpha bond; fermentation reaction
Sucrose
1 glucose and 1 fructose form alpha bond
Lactose
1 glucose and 1 galactose form beta bond
Why do people have a lactose intolerance?
Lactose has a beta bond needing to be broken by enzyme lactase, which some people don’t produce
Methods to start hydrolysis:
Heat - would kill humans
Acid - take too long
Enzymes (-ase)
Ex. Lactase, maltase, sucrase (AKA invertase)
What is the other name for sucrase?
Invertase
Primary lactose maldigestion
Inherited inability to produce lactase
Production stops after 3-5 years old
The majority of people have this
Mutation allows for production after loss
Secondary lactose maldigestion
Temporary decrease in lactose production that increases with age
Can lactose intolerant eat yogurt?
Yes, low amount of lactose because bacteria converts lactose into lactic acid
Cheese and lactose intolerance
Lactose is in whey (water + lactose + protein) due to bacteria
Hard cheese - less lactose
Soft cheese - more lactose
Sugar beet/cane Preparation
Wash and cut
Extract juice
Evaporate and concentrate its syrup
Crystals fall from syrup, leaving molasses
Brown sugar composition
Sucrose + maltose
Honey
Contains mostly sugar (fructose and glucose) and phytochemicals
Functions of sugars in food preparation:
Sweeten foods
Preserve foods
Crystallization Agents (candies)
Caramelizing Agents
Fermentation (bread-making)
Which sugar is the most sweet?
Fructose
Which sugar is the least sweet?
Lactose
How do sugars preserve foods?
60% of sugar kills bacteria by osmosis (loss of water from cell)
How can you make milk sweeter?
Add lactase enzyme to break lactose into glucose and galactose
Sugar alcohols
Instead of carbonyl, a sugar has an extra hydroxyl group (making it an alcohol)
-ol ending
Ex. Sorbitol
Benefits of sugar alcohols
Not metabolized by bacteria, preventing tooth decay
Cooling sensation due to endothermic reaction (heat-absorbing)
Xylitol
Less calories
Side effects of sugar alcohols
Bloating, diarrhea, flatulence (laxative effect)
Not absorbed by small intestine
Oligosaccharides
3-10 monosaccharides (raffinose and stachyose)
What foods contain oligosaccharides?
Beans and legumes (high in fiber foods)
Digestion of oligosaccharides
CAN’T be digested, no enzyme
Fibers
Metabolized by bacteria, resulting in gas in large intestine
Polysaccharides
10+ monosaccharides that can be digestible or non-digestible
Digestible polysaccharides
Starch from plants
Glycogen from animals
Non-digestible polysaccharides
Fibers (soluble and insoluble) - definition is non-digestible polysaccharides
Starch
(Glucose)x, many glucose molecules connected by alpha bonds
2 types of starch:
Amylose (straight chain)
Amylopectin (branched)
Glycogen
Highly branched stored form of glucose in liver and muscles; holds more water
Why don’t we want to store so much glycogen?
It has more water, which would make us fat and give us less energy
Cellulose
Polysaccharide found only in plant cell wall, not digestible by humans (fiber)
Pectins
Polysaccharide in cell walls of fruits called “sugar acids”; fibers to humans
Use of pectins in food:
Used to make jams because they form strong gels in sugar due to dehydration
What makes fibers indigestible?
They all contain beta bonds which we don’t have enzymes for
Insoluble Fibers
Not fermented (Cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin)
Soluble Fibers
Can be fermented, giving calories (Gums and pectins)
Carbohydrate gums
Soluble polysaccharides from plants that thicken and stabilize food
Traps color and flavor
Used as additives
Salad dressing, candies, agar
Uses of complex polysaccharides in food:
Structure
Binding (bringing 2 things together that usually wouldn’t)
Thickening (gelatinization)
Carageenan
Carbohydrate for binding casein to cocoa powder
Gelatinization
Thickening a liquid with starch (amylose)
The more amylose, the thicker
Increasing temperature swells the granules
Gelatinization Point
Temperature when maximum granule swelling occurs (most water is held)
Jam-making
Use pectins (at least 60% to preserve), fresh fruit or juice, and lower pH with lemon juice’s citric acid
Which carbohydrates have to be digested?
Disaccharides and starches (polysaccharides)
What carbohydrates can be absorbed without being digested?
Monosaccharides, they can be converted to glucose in liver
Path of Carbohydrate Digestion
Amylase in saliva converts starches into smaller sugars via hydrolysis
Stomach acid inhibits amylase, no digestion
Pancreatic juice breaks down oligosaccharides
Intestinal cells release maltase, lactase, sucrase
Carbohydrate Absorption
Monosaccharides go to liver through the portal vein, where they are converted to glucose or store as glycogen
How much energy do carbohydrates give?
4 kcal/g
Protein Sparing
Consuming carbs saves proteins for other functions instead of making glucose with protein
Normal Blood Glucose
70-100 mg/dL
Pancreatic Enzymes for Glucose Regulation
Insulin and glucagon
Insulin
Secreted by beta cells during high blood sugar to begin uptake of glucose into cells from blood
Glucagon
Released by alpha cells during low blood sugar to start glycogenolysis
Glycogenolysis
Breaking down glycogen in the liver into glucose
Fight or Flight Response
Sympathetic response = cortisol and adrenaline released
Liver release glucose for muscles
More energy (glucose) needed
Increased blood sugar
Dietary Fiber Functions
Regular stools, no constipation
Reduce hemorrhoids, diverticulitis, colon cancer
Less pressure on inflammation
Weight control, feeling of fullness
Reduce cholesterol
Slow glucose absorption (good for T2 Diabetes)
Recommended Intake of Carbohydrates
Majority of kcal (45-65%); fiber requirement is lower for women than men
Where do most carbs come from in the US?
Bread, soda, baked goods; too much lipid intake
When is insulin mostly secreted?
Between meals
Type 1 Diabetes
Sudden onset usually when younger
Not as prevalent as Type 2
Result of autoimmunity to beta cells, no insulin production
Ketoacidosis is common
Type 2 Diabetes
Gradual onset from lifestyle choices, often in the obese
Insulin resistance, can produce but need more than normal
More prevalent than Type 1
Side Effects of High Sugar Intake
Empty calories
Dental caries from bacteria on enamel decaying tooth
Glycemic Index
Blood glucose response to certain foods
Lower index is healthier (less increase in blood sugar)
Uses glucose as standard
Glycemic Load
Amount of carbohydrate in food times index divided by 100
Better because it compensates for serving size
GI x grams of carb/100
High Glycemic Load Foods
Stimulates insulin, resulting in resistance and feeling hungry quicker
High LDL, more fat/triglycerides
Diabetes, and risk of cardiovascular disease
Why should diabetics have many small meals?
Small meals cause less insulin secretion, preventing resistance
Symptoms of diabetes
Fatigue, hunger, impotence, infection, frequent urination, poor wound healing, poor vision
Peripheral nerve dysfunction (amputation is common)
Cardiac arrest and death if uncontrolled
Managing Diabetes
Diet to decrease calories, fats, salt intake, and weight loss
Exercise to increase energy consumption
Stop smoking
Sugar and Cancer
Sugar (not fibers) linked to breast cancer
Polyphenols in coffee/tea can fight cancer
Antioxidants and without creamer/sugar
Issue with high fiber intake
Need more fluid intake
Fibers bind vitamins and minerals (can’t be used)
Lack of nutrients for young children (makes them feel full)
Nutritive Sweeteners
Give calories; sugars and sugar alcohols
Alternative Sweeteners
Saccharin
Aspartame
Neotame
Sucralose
Acesulfame-K
Stevia
Polydextrose
Saccharin
Sweeter but with an aftertaste; cancer in rats, but safe