A&P Urinary system
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
urinary system functions
filtration
excretion
homeostasis
filtration
removal of metabolic waste products from the blood
excretion
release of waste products via urine
creatine (produced muscle contractions)
urea (produced during the break down of proteins)
homeostasis
maintain electrolyte balance, pH, blood pressure, and RBC count
how is blood volume and pressure regulated?
by adjusting the water content of urine and producing the erythropoietin hormone
erythropoietin
stimulates RBC production
how are blood electrolytes regulated?
through the absorption or elimination of K+, Na+, and Cl-
how is blood pH maintained?
by excreting bicarbonate ions and uric acid
kidney location
against the deep muscles of the back and the floating ribs
high in abdominal cavity
against the dorsal body wall
one on each side of the spine
retroperitoneal
left kidney→ extends from T12 to L3
right kidney → under liver, slightly lower
size of kidney
fist
external anatomy of kidney
convex laterally (a)
medial indentation is the renal hilus (b)
enclosed by fibrous renal capsule
adrenal gland sits on superior surface (c)
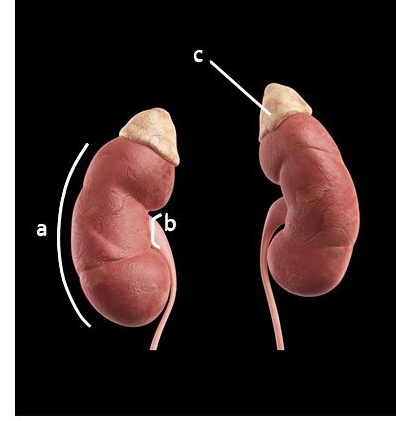
Where does unfiltered blood enter through?
renal artery
where does filtered blood leave through?
renal vein
what is the kidney protected by?
renal capsule
Renal capsule
made of dense connective tissue
protects/surrounds the kidney
renal medulla
inner portion of the kidney, made of cone-shaped renal pyramids
deep to the cortex, darker in color
contains 6-18 renal pyramids
renal pyramid
have a stripped appearance due to bundles of urine-collecting tubes
renal cortex
the outermost tissue, with columns that dip between the pyramids
most superficial region
renal pelvis
funnel-shaped sac that collects secreted urine
leads to the ureter
renal calyxes
branches of the renal pelvis
cup shaped area that collects urine from the base of the pyramids
several calyces drain into the renal pelvis
renal hilum is also called
medial indentation
ureter
tubes of smooth muscle that propel/drains urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder
extend from the renal pelvis → posterior bladder
~ 25 - 30 cm long & 3-4 mm in diameter
each ureter empties into the bladder at an opening called the ureteral orifice
nephrons
the functional unit of the kidney
Where does filtration take place? which two structures?
glomerulus
glomerular capsule
filtration
pushes fluids and solutes smaller than proteins out of blood and into the glomerular capsule
no-selective, passive process
what are the two main structures of a nephron?
glomerulus
renal tubule
glomerulus
cluster of capillaries that receives pressurized blood
glomerular capsule
a cup-like sac which receives filtrate from glomerulus
renal tubule
cup-shaped capsule that surrounds the glomerulus on one end, then twists and coils for about 3 cm before leading to a collecting duct
what is the capsule surrounding the glomerulus also called?
bowman’s capsule
urine production (2)
filtration
reabsorption
secretion
reabsorption
mostly in the proximal tubule, but also along the length of the renal tubule and collecting duct
water, glucose, amino acids, and needed ions from filtrate to re-enter capillary blood
diffusion and active transport
secretions
peritubular capillaries into the renal tubule → urine
urea, creatine, drugs, and certain ions are secreted
what are the capillaries and glomerular capsule are lined with?
simple squamous epithelium that is selectively permeable
what does filtrate contain?
water
urea
creatine
ammonia
electrolytes
tubular reabsorption
prevents the release of too much water or electrolytes
active transport
pulls salts out of the nephron into the renal medulla, creating a hypertonic environment
osmosis
moves water into the hypertonic medulla
peristalsis
smooth muscle contractions
where is urine stored?
urinary bladder
urethra
thin-walled tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body by peristalsis
internal urethral sphincter
hypothalamus
detects low blood pressure and low blood volume stimulates the posterior pituitary to release ADH
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
causes the kidneys to conserve more water and produce more concentrated urine
released in response to high solute concentration in the blood plasma
inhibited by alcohol
produced by the hypothalamus → posterior pituitary
what is urine color an indication of?
hydration status
pH of urine
slightly acidic, pH around 6
turbidity of urine
should be clear or transparent
specific gravity of urine
slightly higher than pure water; indicates concentration
urinalysis
often preformed with test strips which can detect the presence of drugs, proteins, glucose, blood cells, and other substances
what does dark urine suggest?
dehydration and/or elevated ADH levels
kidney stones
form when solutes in urine forms large, solid crystals that get stuck in a calyx, ureter, or urethra
hard mineral/salt deposits that form in the kidneys
lithotripsy
calcium stones
forms due to dehydration
uric acid stones
form due to excessive animal protein intake
urinary tract infections (UTI)
caused by bacteria growing in the urinary tract
more common in women due to a wider, shorter urethra
treated with antibiotics
kidney failure
occurs when the kidneys are no longer able to filter wastes from blood normally
causes: high bp and diabetes
dialysis
uses a machine to remove wastes/filters from blood in place of the kidneys
typically takes 3-5 hours, 3 days a week
average life expectancy is 5-10 years
kidney transplants
surgically insert a donor kidney into the lower abdomen at the iliac artery and vein
Final composition of urine
0,2% creatine, ammonia, uric acid
2.8% electrolytes
2.0% urea
95% water
Are leukocytes normally in urine?
no
What does the presence of leukocytes indicate?
indicates urinary tract infection
what do the presence of erythrocytes indicate?
can enter urine if the ureters, bladder, or kidneys are damaged
bilirubin
made from the breakdown of hemoglobin and is what makes urine yellow
What do high levels of bilirubin indicate?
sign of liver disease
what do the presence of proteins indicate?
excessive exercise
What foods lower pH of urine?
fish, meat, cheese
what foods raise pH of urine?
fruits and veggies
what does the presence of glucose indicate?
may be diabetic
ketones
byproducts of lipid metabolism
what can elevated levels of ketones mean?
lipid metabolism is happening very quickly
keto diets cause this
can lower blood pH
specific gravity
measures the salinity/electrolyte level of pH
what do elevated levels of specific gravity suggest?
severe dehydration
urea
a component of urine
waste product produced by the breakdown pf proteins in food
How much percent of total blood volume passes through the kidneys each minute?
20-25&
how many liters of urine do the kidneys produce each day?
1-2 L
urinary bladder
hollow muscular sac that stores urine before it’s eliminated
size & shape varies depending on the amount of urine it’s holding
located posterior to the pubic symphysis
internal urethral sphincter
INVOLUNTARY muscle that keeps urethra closed most of the time
smooth muscle
female urethra
3-4 cm long
external opening lies anterior to the vagina
male urethra
~ 20 cm long
passes through the penis
micturition (voiding/urination)
flow of urine is controlled by two sphincters
urine is forced past the internal sphincter
what triggers bladder contractions?
stretch receptors in the bladder wall
external sphincter
VOLUNTARY skeletal muscle
what type of waste do the kidneys excrete?
nitrogenous waste
where is majority of the water in the body found?
intracellular fluid (in cell)
extracellular fluid (outside cell)
interstitial fluid
blood plasma
water output
urine
sweat
lungs & skin
feces
water intake
ingestion of food and beverages
metabolism
osmolarity
water concentration in blood plasma
how do the kidneys control osmolarity
by controlling how much water is reabsorbed in the nephron/ released from the body in urine
electrolytes
substances that form ions in solution
kidneys control the excretion of several ions
important to proper body functions
water balance
nerve signals
muscle contractions
normal blood pH
7.35-7.45
how do the kidneys change blood pH?
by excreting H+ ions/conserving HCO3- ions to regulate acid-base balance
renin
triggers a series of reactions that constrict blood vessels and raise blood pressure
produced by kidney
aldosterone
steroid hormone produced by the adrenal cortex
function: regulate salt & water balance
presence of aldosterone increases the reabsorption of sodium which increases blood volume, and blood pressure
polycystic kidneys
inherited congenital defect in which the kidneys develop clusters of cysts
kidneys lose function over-time and kidney failure may result
lithotripsy
a procedure using sound waves to break up kidney stones
incontinence
inability to hold urine in the bladder
common causes: pressure on bladder from coughing, laughing, or lifting something heavy, urge incontinence
urge incontinence
sudden intense urge to urinate followed by an involuntary loss of urine
urinary retention
inability to completly empty the bladder
can be acute/chronic
most common cause in men: enlarged prostate gland
embryonic development
fetal kidneys begin excreting urine by the 10th week of pregnancy
the urine is released into the amniotic fluid
infants
filtration rate increases quickly during the first two weeks of life
newborn babies have limited ability remove excess sodium and to concentrate & dilute urine
toddlers
toddlers are eventually able to control the voluntary urethral sphincter and are ready for toilet training
the kidneys are fully mature and functioning by age 2
elderly
kidney mass and function begins to decline with age
urinary tract infections and other diseases that affect the kidneys are more common in people over 60