Diagnostic Imaging Exam 1
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
133 Terms
Why should PTs learn about radiology
-Pt will bring x-rays with them to their PT visits
-better understand anatomy and pathology
-helps PTs know what the joint looks like postoperatively
-helps PTs to communicate with referring provider
-allows PTs to set realistic goals and have a better idea of prognosis
-educate patients on the extent of the injury
True/False: Military PTs can not order imaging
False
True/False: The diagnostic accuracy by PTs is equal to that of an orthopedic surgeon when comparing exams to MRI
True
what states clearly allow PTs to order imaging?
-Wisconsin
-DC
-Colorado
-Maryland
-New Jersey
-Utah
what states clearly prohibit PTs to order imaging?
-South Carolina
-New York
-Mississippi
define radiology
a branch of medicine concerned with radiant energy in radioactive substance, such as x-rays, isotope, and ionizing radiation, and the application of this information to prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of disease
define radiologists
physicians specializing in radiology
define radiographers
professional technicians who produce the images
types of diagnostic imaging
-plain radiograph
-MRI/MRA/fMRI/dMRI
-CT Scan
-Bone Scan
-PET Scan
-Ultrasound
-Arthrograms
-Myelograms
what is interventional radiology
the use of radiological modalities for the treatment of disease
what is an example of interventional radiology
radiation therapy used for cancer
what are the 3 requirements for a radiograph
-x-ray beam source
-patient
-x-ray film or other image receptor
what is x-ray film/plate
the physical material on which the image is exposed
what are x-rays?
a form of radiant energy with shorter wavelengths of visible light
how do radiolucent objects appear?
less dense and appear darker
how do radiopaque objects appear?
denser and appear lighter
what does radiodensity refer to?
how many x-rays are absorbed, with more x-rays being absorbed will result in a whiter structure
what determines the rate at which material will absorb the x-ray?
-atomic number/density of tissue
-tissue thickness
what is a conventional radiograph
-also called a plain film
-radiograph made without contrast enhancement or other modifications
what is a projection
the path of the x ray beam
what is the view
processed x-ray film/image
what are the advantages of conventional radiographs
-inexpensive relative to other imaging methods
-rapid evaluation
-demonstrates fine detail bone
what are the disadvantages of conventional radiographs
-ionizing source of radiation
-does not demonstrate soft tissue well
-low sensitivity changes in bone mineral density
what is needed to create an xray?
-source of electrons
-a force to move them rapidly
-something to stop them
what are the two ways a patient is exposed to ionizing radiation in imaging?
-ionizing radiation transmitted through tissue
-ionizing radiation emitted after injection or ingestion
what types of imaging transmit ionizing radiation through tissue?
-conventional radiographs
-fluoroscopy
-conventional tomography
-mammography
-contrast studies
-arthrograms
-myelograms
-computerized axial tomography
what types of imaging emit ionizing radiation after injection/ingestion?
-scintigraphy/bone scan
-positive emission tomography
what are the non-ionizing methods of imaging
-MRI
-Diagnostic US
how is radiation dosage measured?
effective dose which is measured in a millisievert
what is the effective does for a CT of the abdomen and pelvis?
10 mSv
a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis is comparable to how much natural background radiation?
3 years
a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis repeated with and without contrast material has what approximate effective dose?
20 mSv
a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis repeated with and without contrast material is comparable to natural background radiation for how long?
7 years
what is the approximate effective dose of a spine x-ray?
1.5 mSv
a spine x-ray is comparable to natural background radiation of how long?
6 months
what is the approximate effective dose of an extremity x ray
0.001 mSv
an extremity x-ray is comparable to the background radiation of how long?
3 hours
what is the approximate effective dose of a dental x ray
0.005 mSv
a dental x ray is comparable to what natural background radiation timeframe?
1 day
what is the approximate effective dose of a bone densitometry (DEXA)
0.001 mSv
what is the approximate effective dose of a mammography
0.4 mSv
what is the comparable natural background radiation to mammography
7 weeks
what does ALARA mean
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
what population is the MOST sensitive to the effects of radiation?
unborn children of a pregnant person
what types of cancer are females at greater risk for when exposed to radiation?
-Thyroid
-Breast
-Lung
Which of the following lists materials in order to radiopaque to radiolucent?
a. Air-Fat-Water-Bone-Metal
b. Air-Water-Fat-Bone-Metal
c. Metal-Bone-Water-Fat-Air
d. Metal-Bone-Fat-Water-Air
Metal-Bone-Water-Fat-Air
what is an example of a contrast media?
barium sulfate
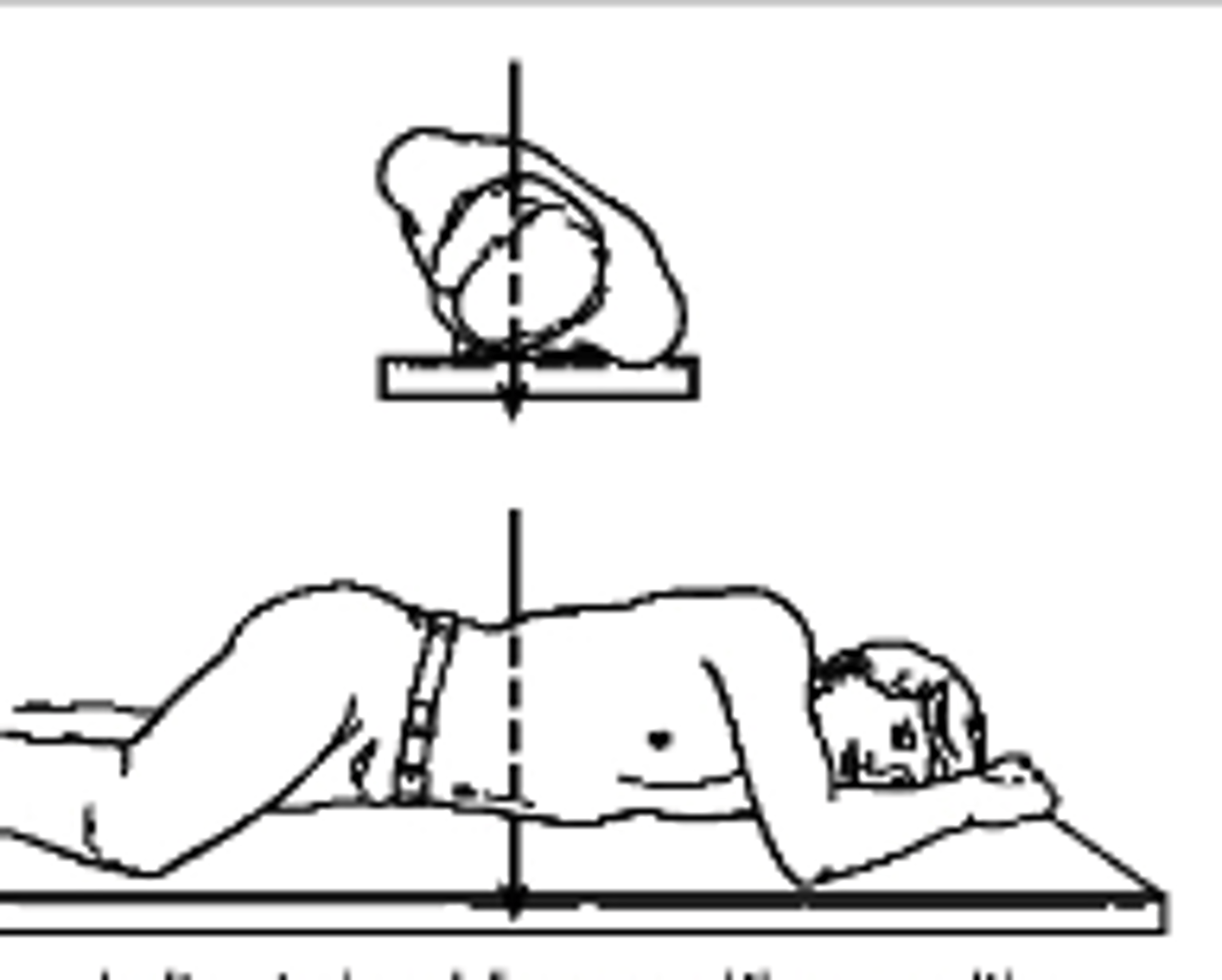
Anteroposterior
What type of projection is this?
a. Posteroanterior
b. Anteroposterior
c. Left Lateral
d. AP oblique
Posteroanterior
what type of projection is this?
a. Posteroanterior
b. Anteroposterior
c. Left Lateral
d. AP oblique
Left Lateral
what type of projection is this?
a. Left lateral
b. Right Lateral
c. Left AP Oblique
c. Right AP Oblique
Right Lateral
what type of projection is this?
a. Left lateral
b. Right Lateral
c. Left AP Oblique
c. Right AP Oblique
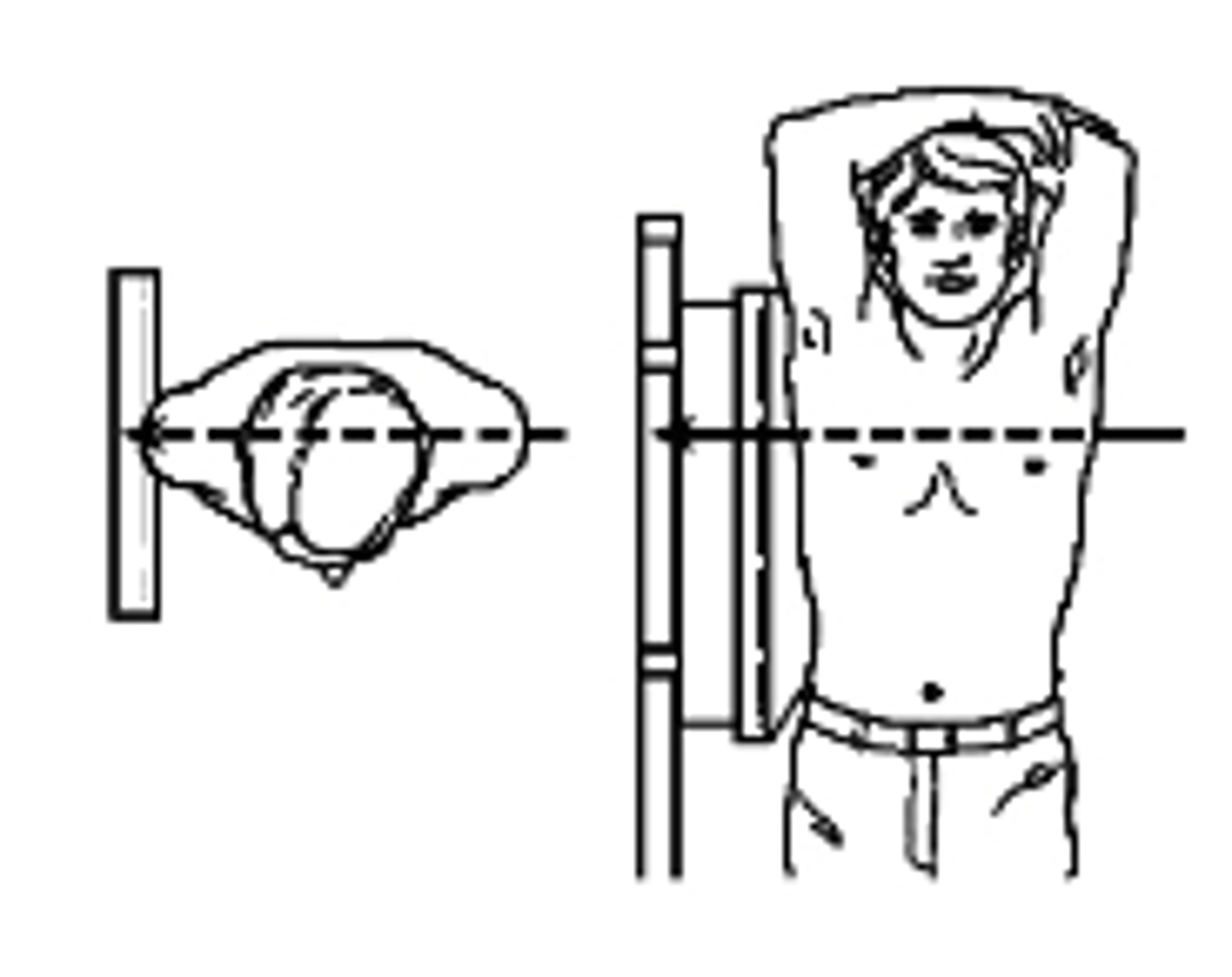
Left AP Oblique
what type of projection is this?
a. Left lateral
b. Right Lateral
c. Left AP Oblique
c. Right AP Oblique
Right AP Oblique
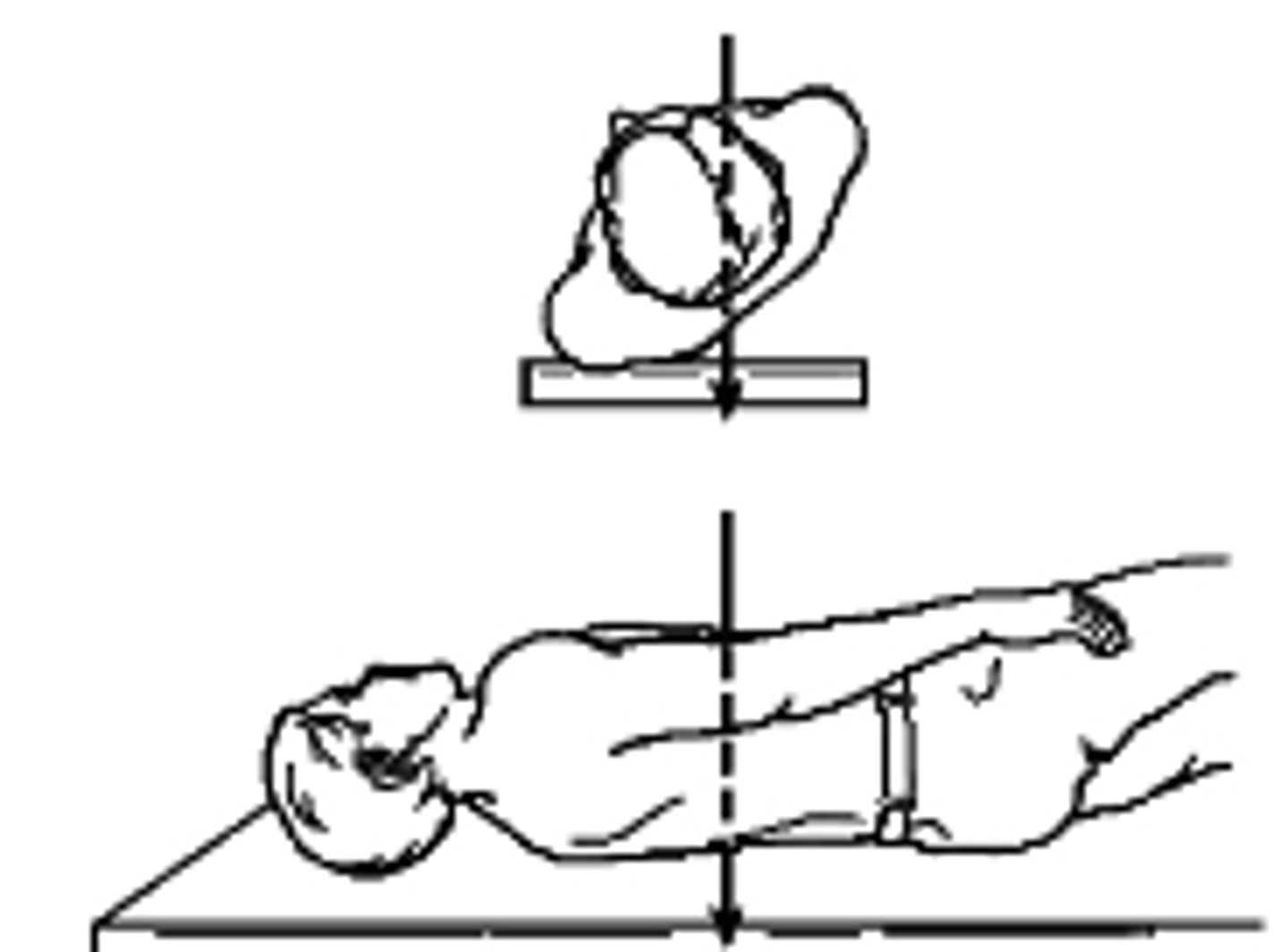
what type of projection is this?
a. Left lateral
b. Right Lateral
c. Left AP Oblique
c. Right AP Oblique
Right PA Oblique
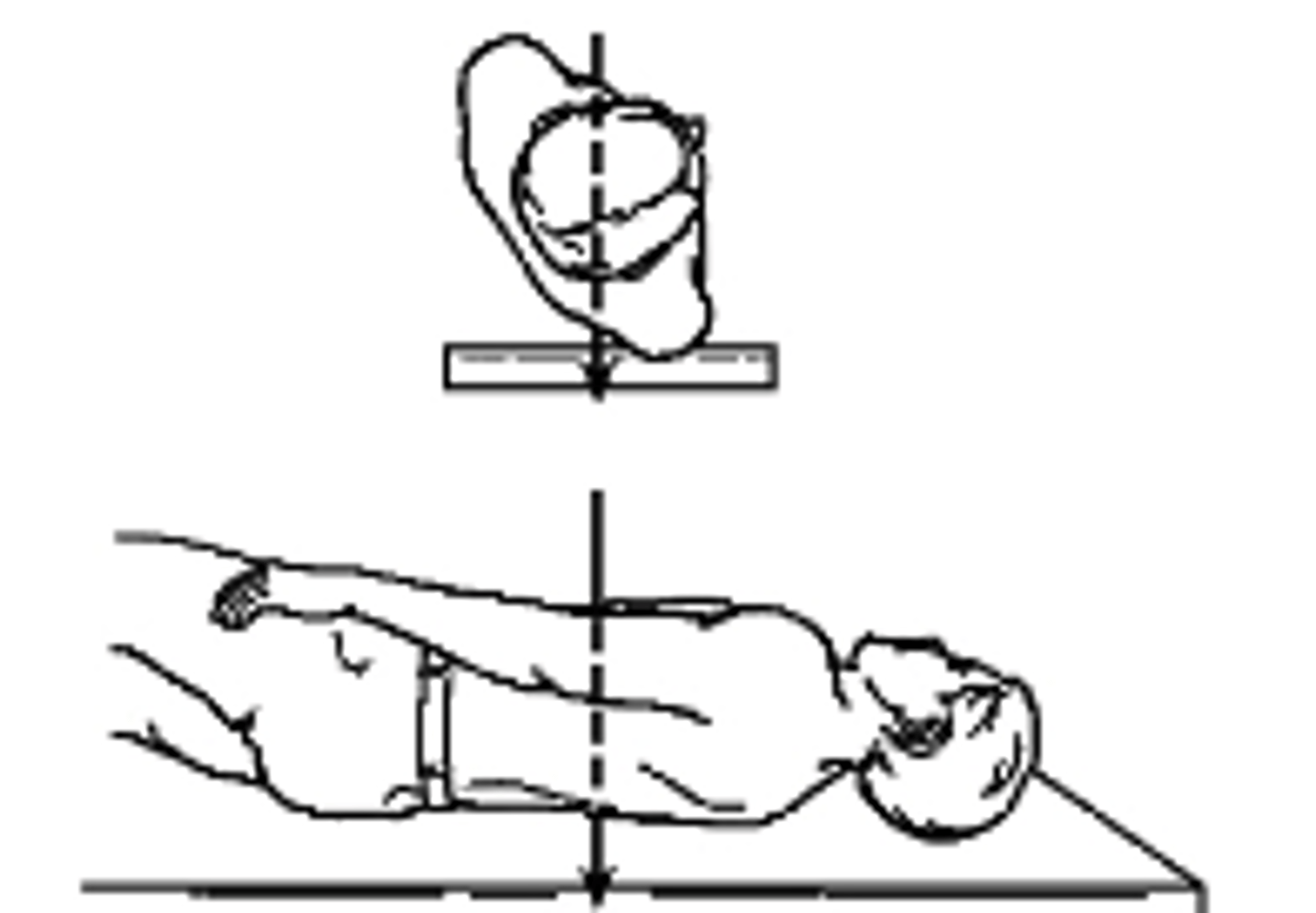
What type of projection is this?
a. Right AP Oblique
b. Right PA Oblique
c. Left AP Oblique
d. Left PA Oblique
Left PA Oblique
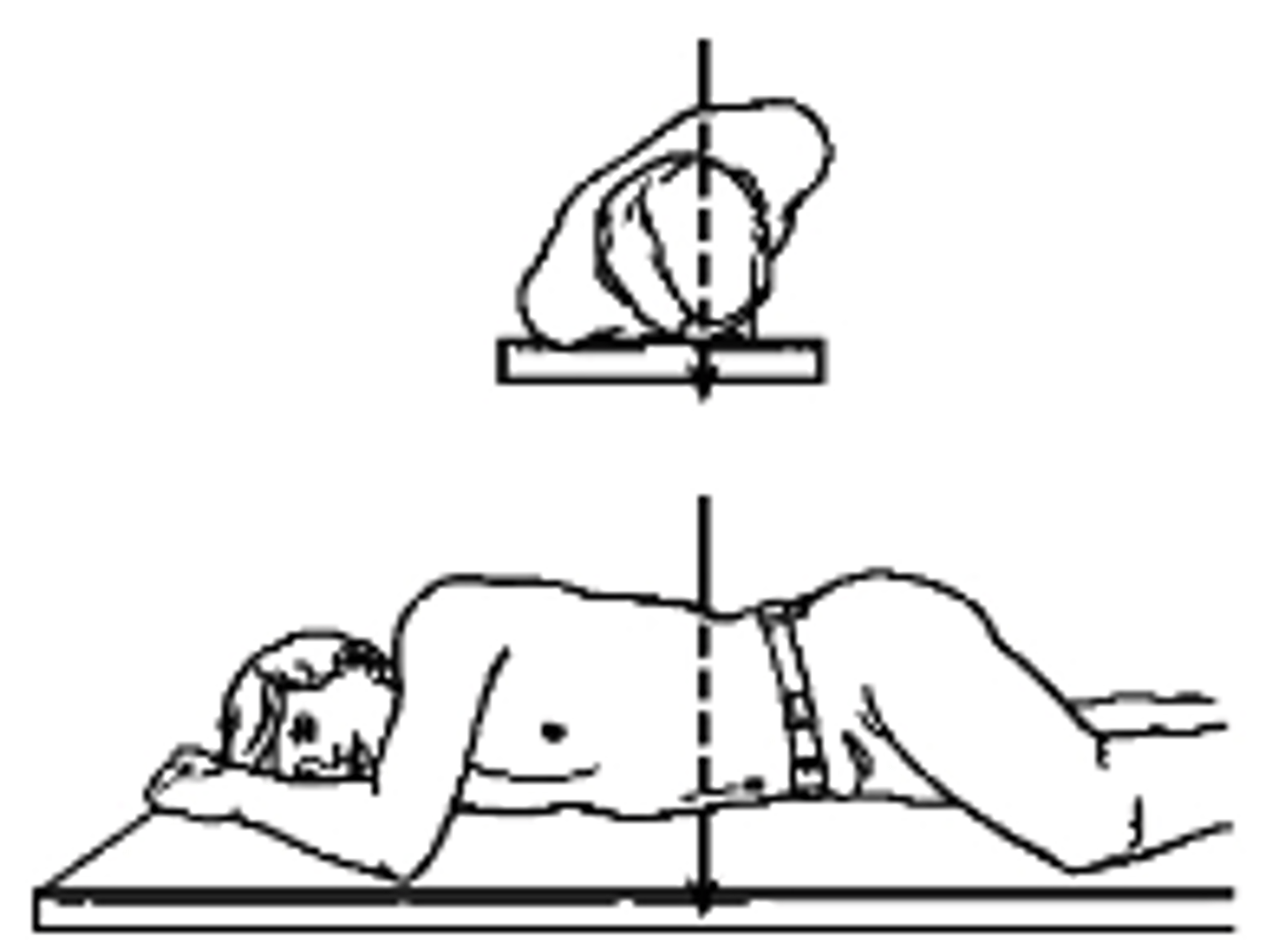
What type of projection is this?
a. Right AP Oblique
b. Right PA Oblique
c. Left AP Oblique
d. Left PA Oblique
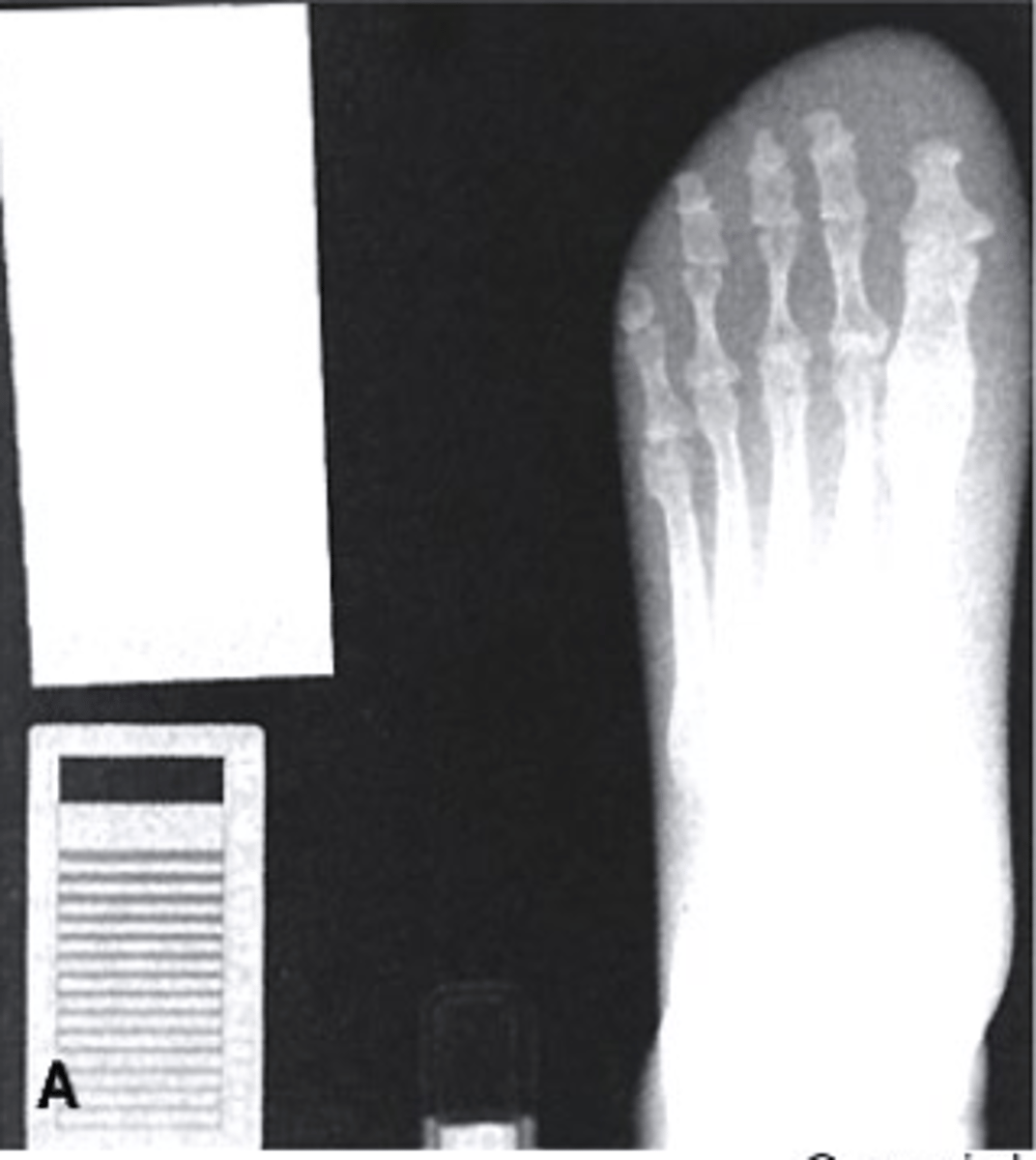
underexposed
Which of the following would be used to describe this radiograph?
a. Underexposed
b. Correctly Exposed
c. Overexposed
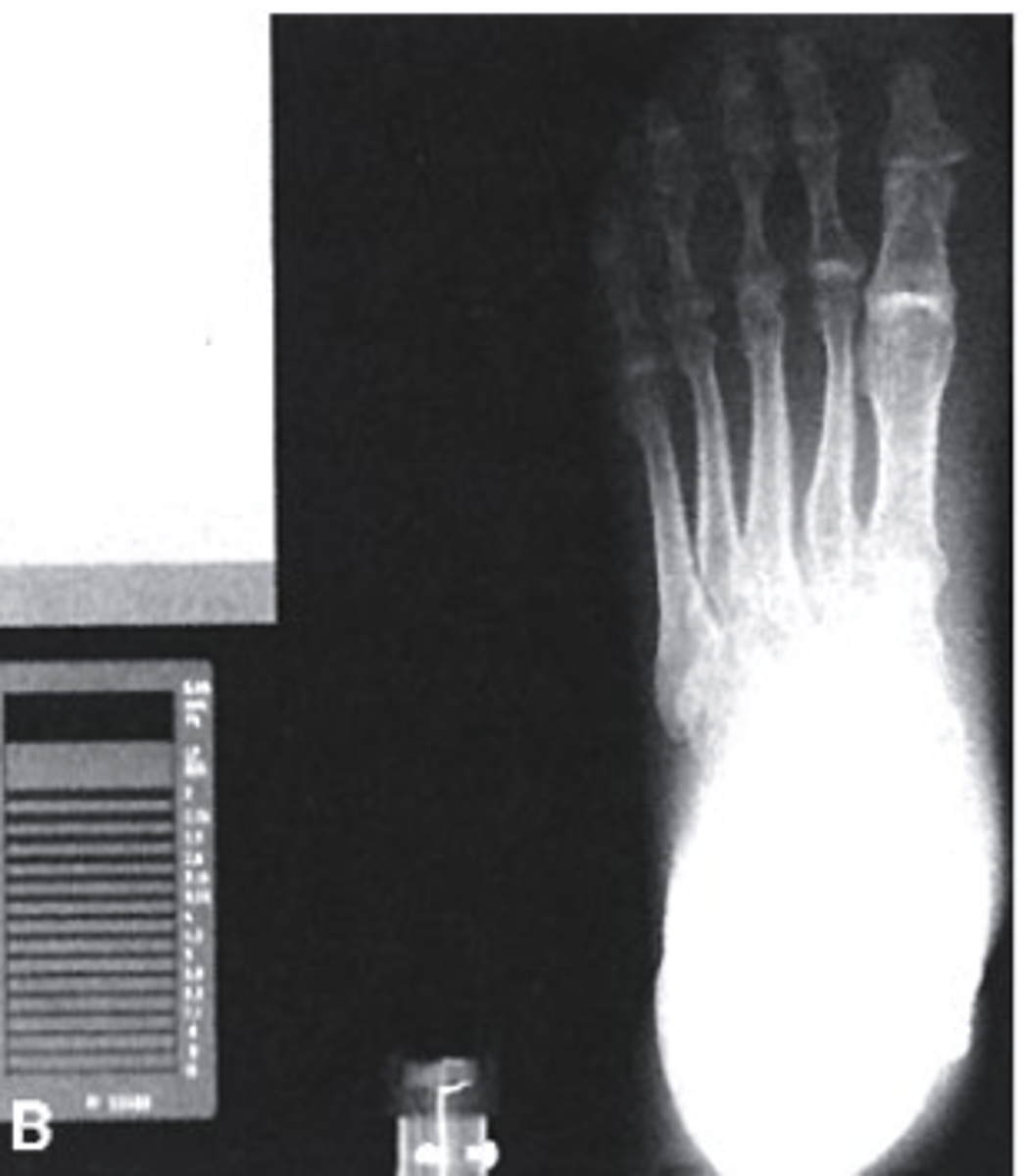
correctly exposed
Which of the following would be used to describe this radiograph?
a. Underexposed
b. Correctly Exposed
c. Overexposed
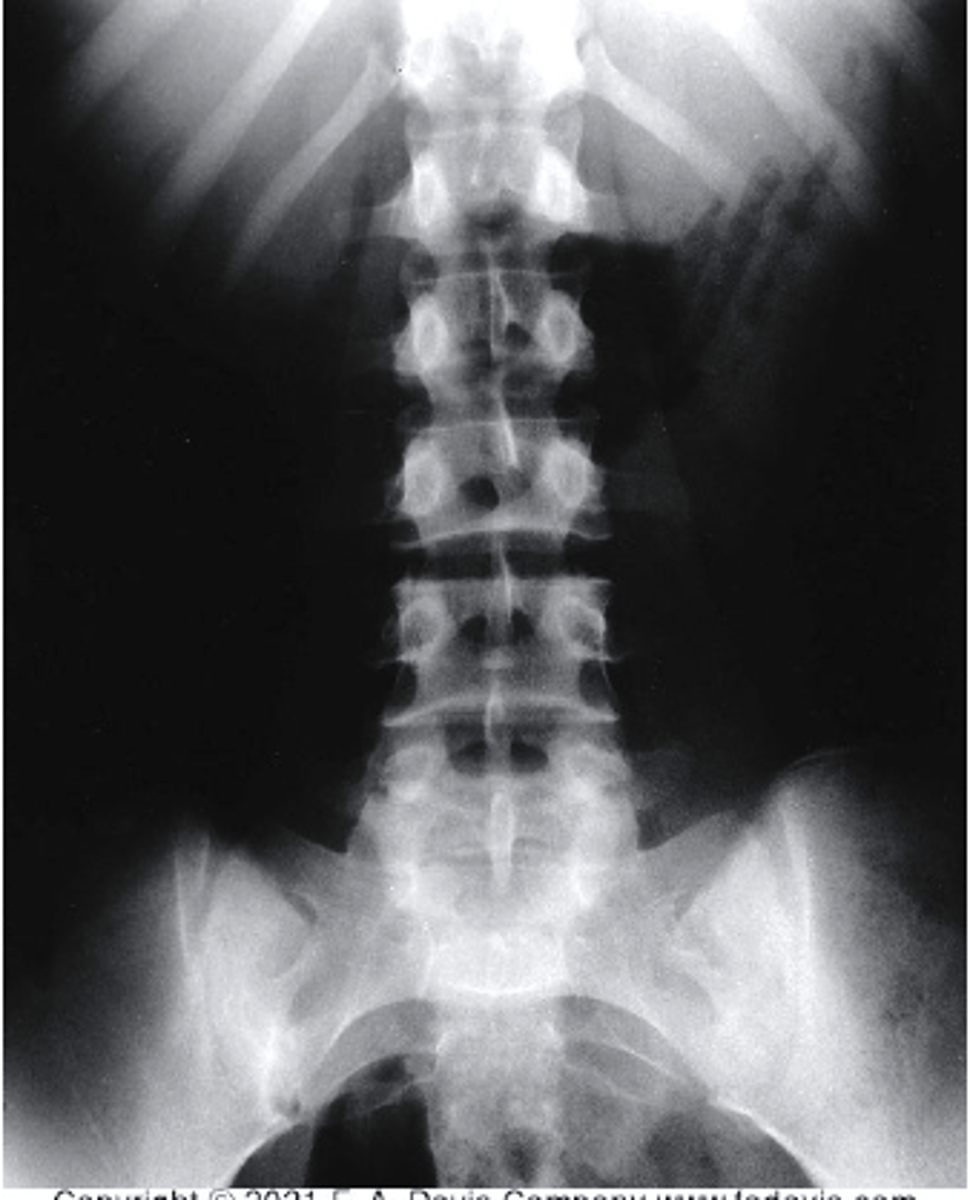
overexposed
Which of the following would be used to describe this radiograph?
a. Underexposed
b. Correctly Exposed
c. Overexposed

when performing a chest x-ray, would you prefer a low or high contrast radiograph?
low contrast
what is recorded detail
geometric sharpness or accuracy of the structural lines on the radiograph
what is recorded distortion
difference between the object being evaluated and its recorded image
radiolucent objects are ______________, and will appear ____________ on imaging
a. more dense, darker
b. more dense, lighter
c. less dense, darker
d. less dense, lighter
less dense, darker
view
This is an example of a _______.
a. view
b. projection
c. conventional MRI
d. none of these
recorded detail
Motion was discussed to affect the ______ of an image
a. recorded distortion
b. radiographic density
c. recorded detail
d. radiographic contrast
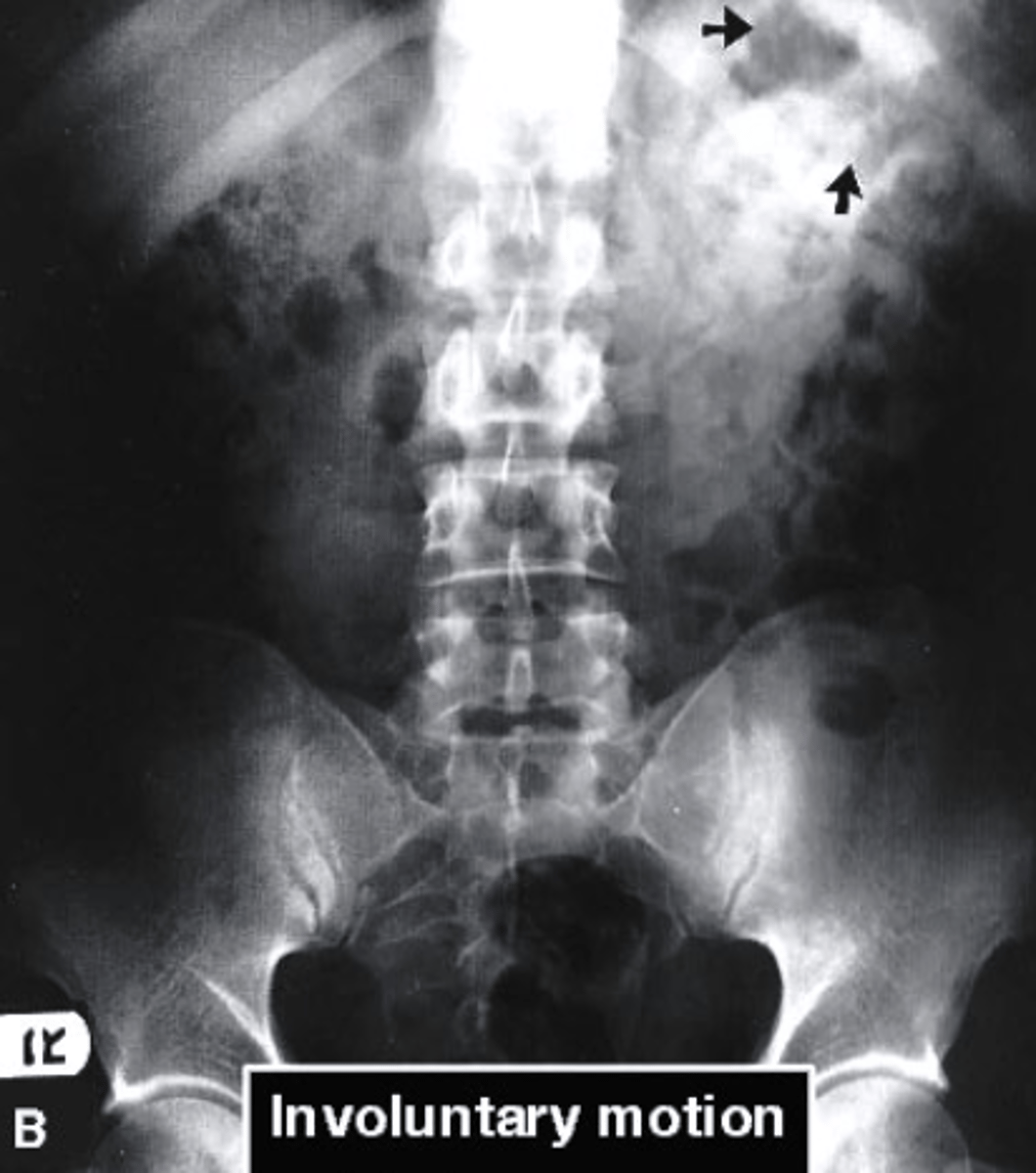
what are the two pitfalls of image interpretation
-errors of observation
-errors of interpretation
what is an error of observation
incomplete or faulty search patterns
what is an error of interpretation
practitioners failure to link abnormal radiologic signs to relevant clinical date
what does ABCs stand for with radiologic analysis
-alignment
-bone density
-cartilage spaces
-soft tissues
what should you be looking at with alignment?
-general skeletal architecture
-general contour of bone
-alignment of bones to adjacent bone
what should you be looking at with bone?
-general bone density
-textural abnormalities
-local bone density changes
what should you be looking for with cartilage?
-joint space width
-subchondral bone
-epiphyseal plates
what should you be looking for with soft tissue?
-muscles
-fat pads and fat lines
-joint capsules
-periosteum
-misc soft-tissue findings
what are the components of a radiology report
-heading/type of exam
-technique/protocol
-clinical information
-findings/main report
-conclusions/impressions
-signature of radiologist
what are the possible complications of a spinal fracture?
neurological injury
what are the possible complication of a pelvic/femur fracture ?
hemorrhage
what is a possible for multiple or crushing type fractures
fat embolism
what is a possible complication for elbow fracture?
brachial artery injury
what is a possible complication for proximal humeral fracture?
axillary nerve injury
what are possible complications for shoulder dislocation?
-axillary artery injury
-brachial plexus injury
-axillary nerve injury
what are the possible complications for elbow dislocation
-brachial artery injury
-median nerve injury
-ulnar nerve injury
what are the possible complications of a hip dislocation
-femoral artery injury
-femoral nerve injury
what are the possible complications for knee dislocation
-popliteal artery injury
-peroneal nerve injury
define fracture
a break in the structural continuity of bone or cartilage
what is key factor for closed fracture
skin and overlying soft tissue is intact
what are the 7 elements of fracture description
-anatomic site and extent of fracture
-complete vs incomplete
-alignment of fracture fragments
-direction of fracture line
-presence of special features
-associated abnormalities like dislocation
-special types of fractures as a result of abnormal stress
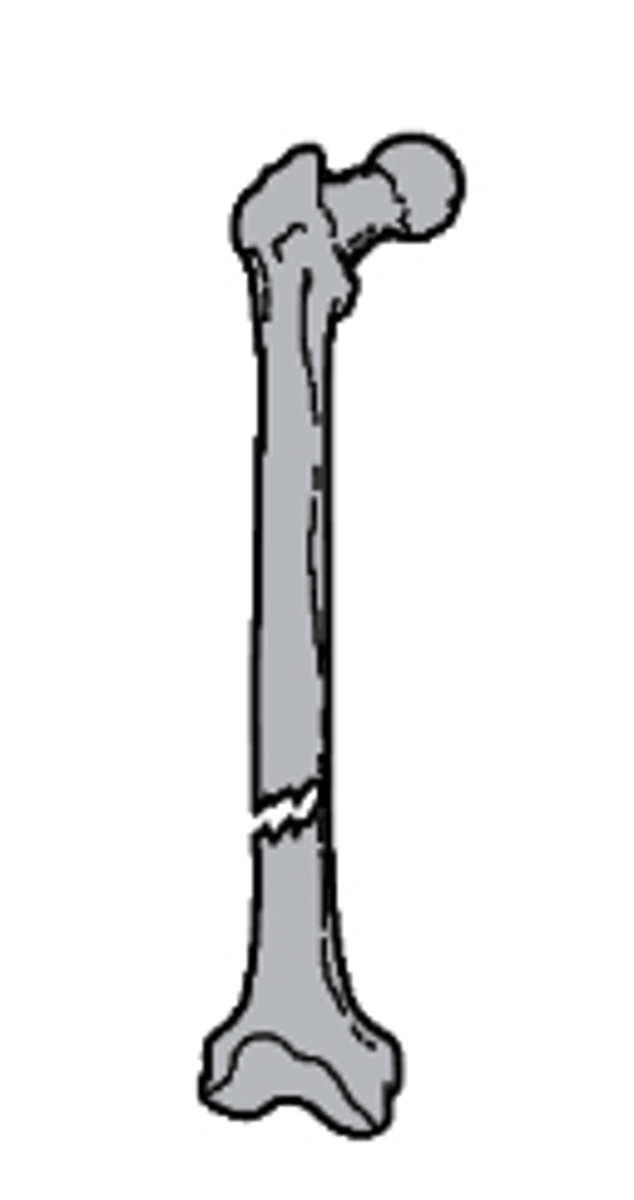
nondisplaced
what type of alignment is seen with this fracture?
a. nondisplaced
b. medial displacement
c. lateral displacement
d. distracted
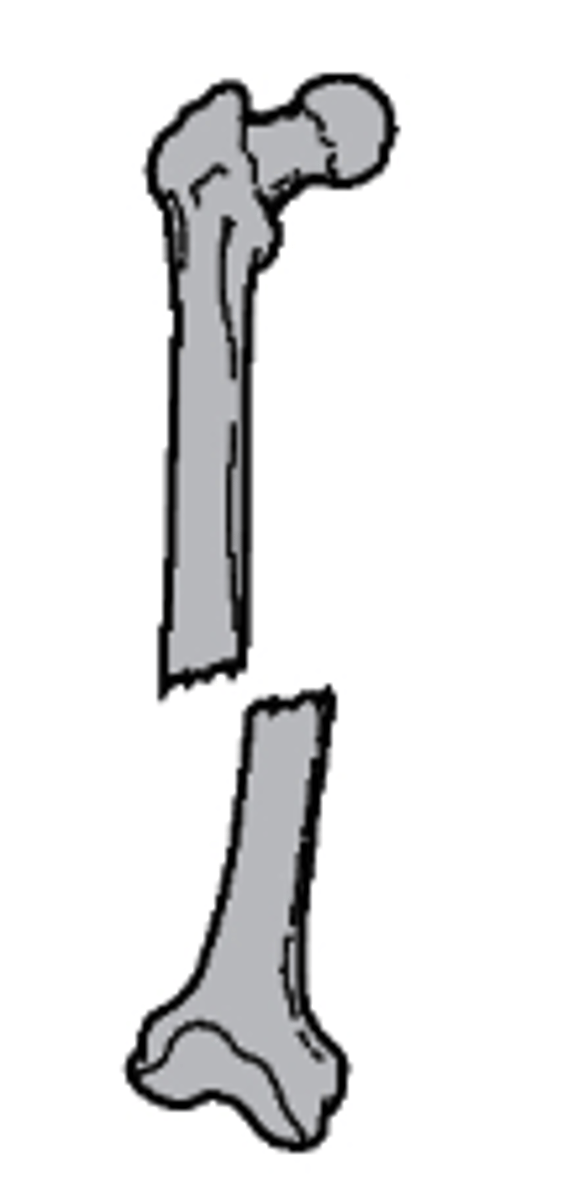
medial displacement
what type of alignment is seen with this fracture?
a. nondisplaced
b. medial displacement
c. lateral displacement
d. distracted
lateral displacement
what type of alignment is seen with this fracture?
a. nondisplaced
b. medial displacement
c. lateral displacement
d. distracted
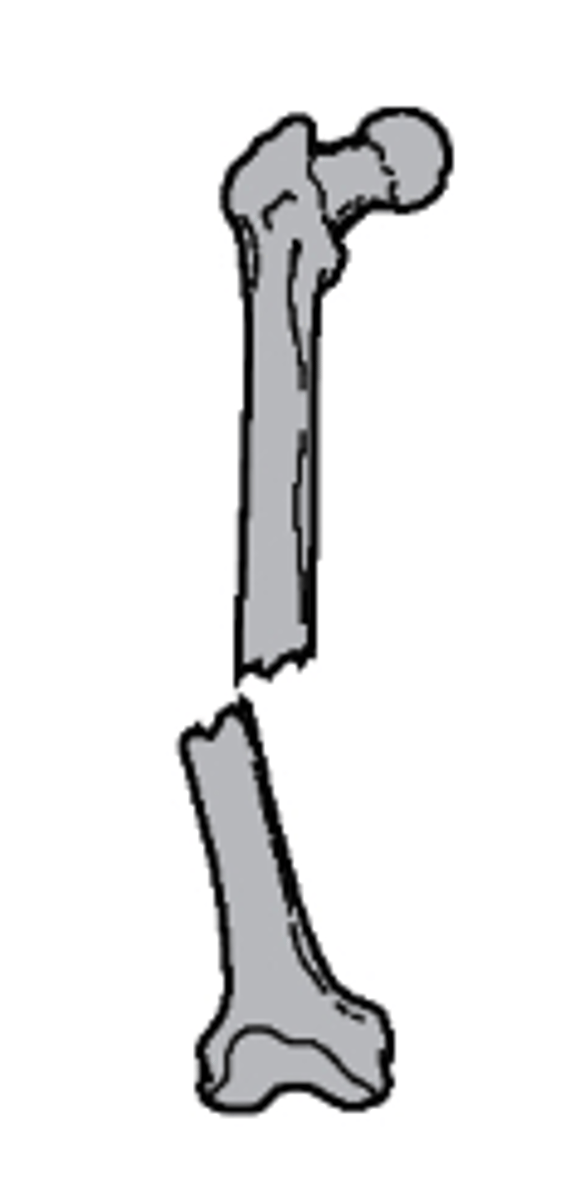
distracted
what type of alignment is seen with this fracture?
a. nondisplaced
b. medial displacement
c. lateral displacement
d. distracted
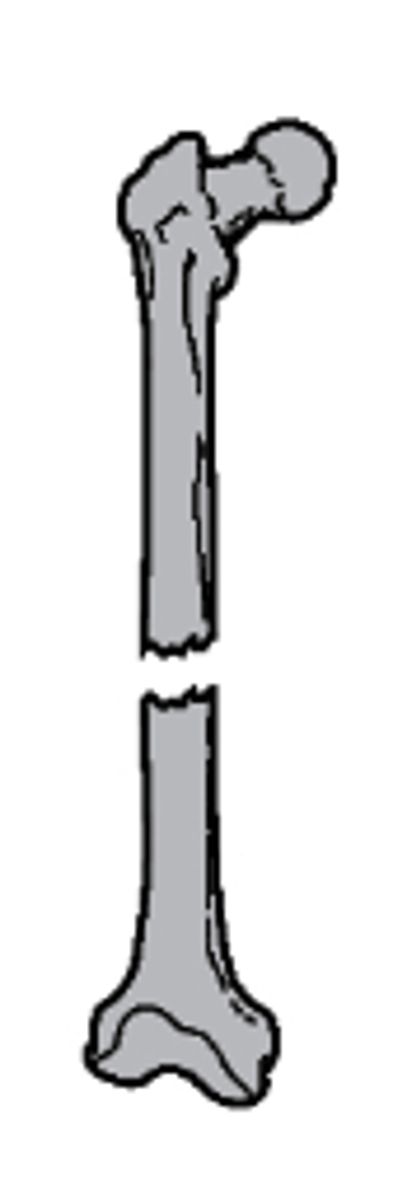
overriding with posterior and superior displacement
what type of fracture is this
a. overriding with posterior and superior displacement
b. distracted
c. lateral displacement
d. distracted and rotated laterally
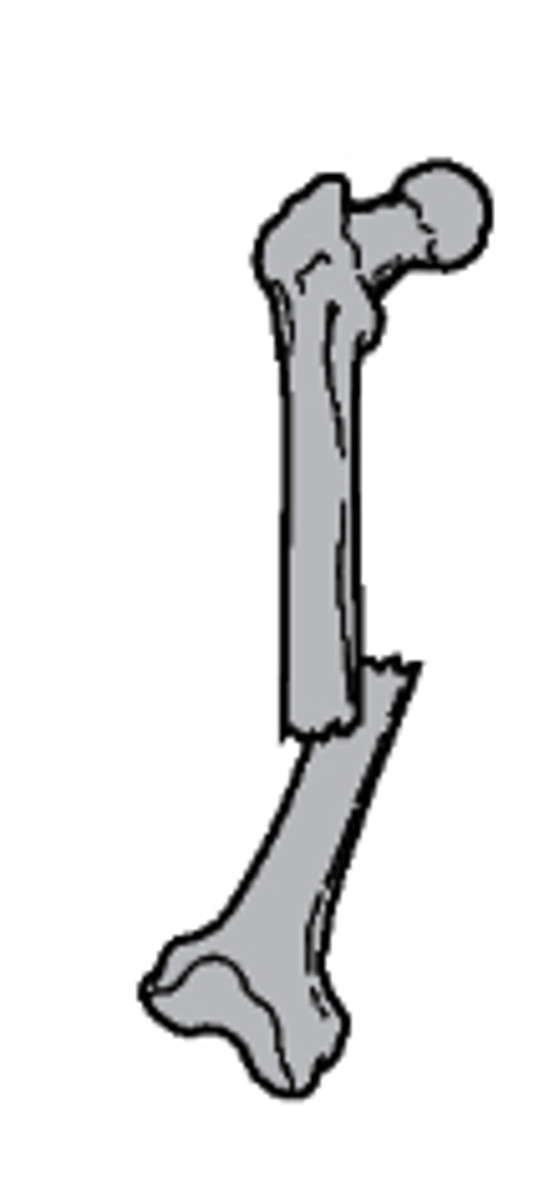
distracted and rotated laterally
what type of fracture is this
a. overriding with posterior and superior displacement
b. distracted
c. lateral displacement
d. distracted and rotated laterally
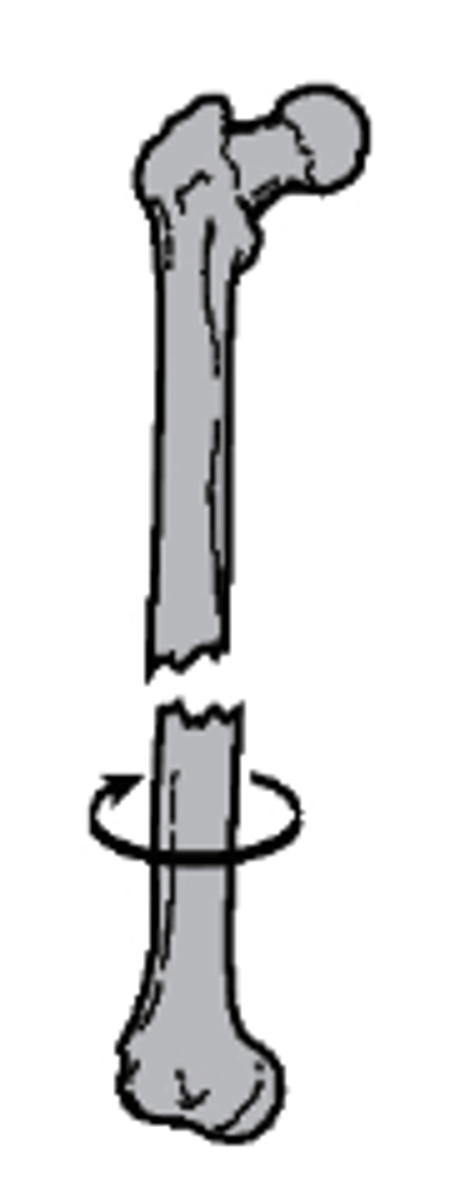
transverse
what is the direction of this fracture line?
a. transverse
b. longitudinal
c. oblique
d. spiral
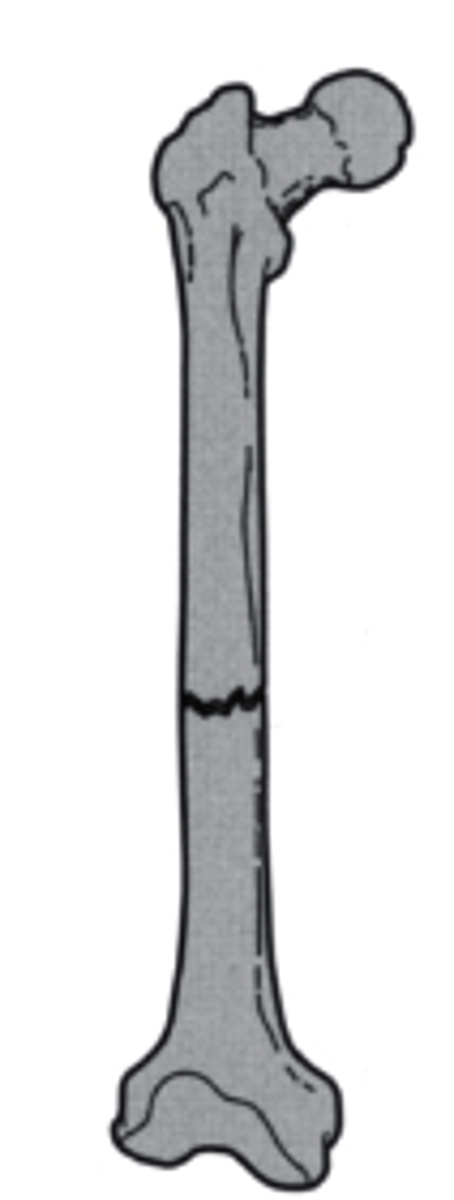
longitudinal
what is the direction of this fracture line?
a. transverse
b. longitudinal
c. oblique
d. spiral
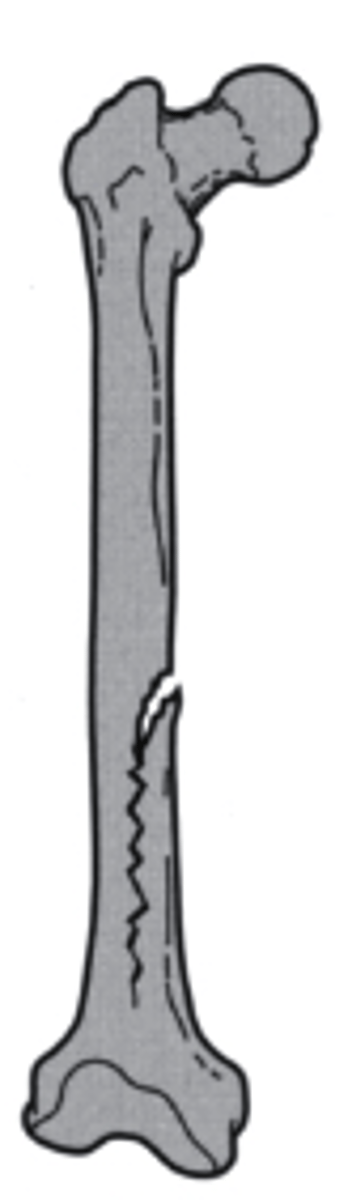
oblique
what is the direction of this fracture line?
a. transverse
b. longitudinal
c. oblique
d. spiral
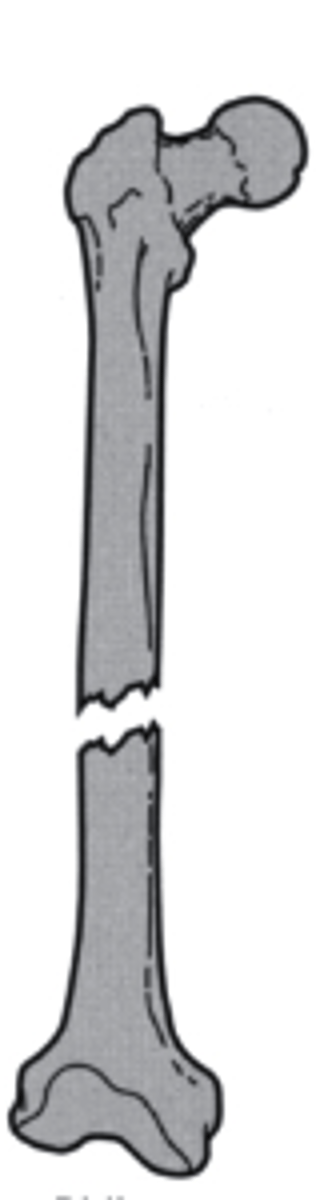
spiral
what is the direction of this fracture line?
a. transverse
b. longitudinal
c. oblique
d. spiral
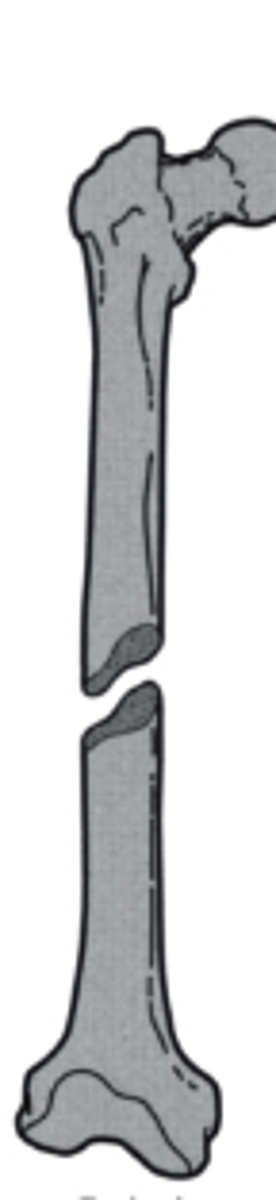
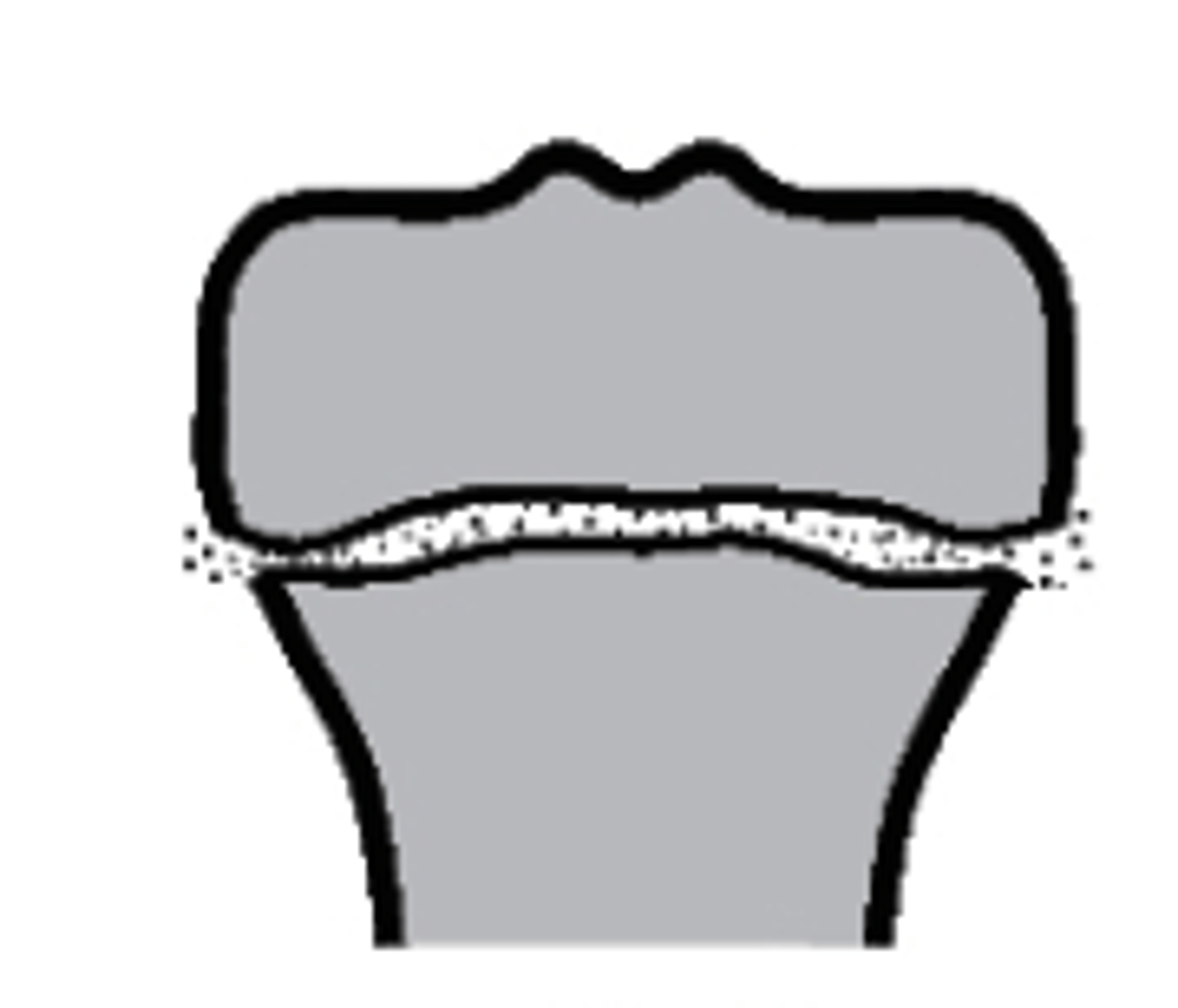
Type I
what type of Salter-Harris fracture is this?
a. Type I
b. Type III
c. Type IV
d. Type II
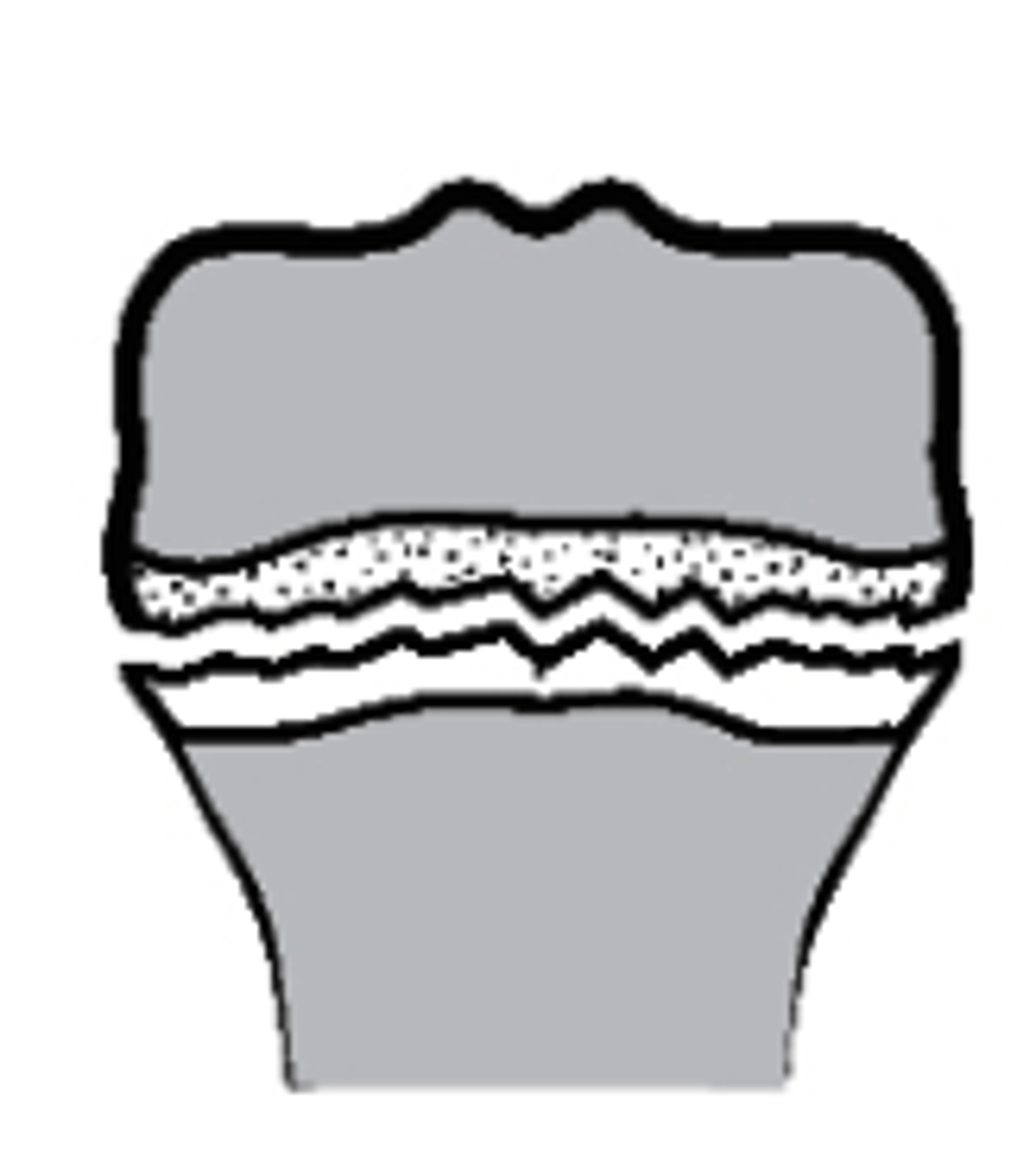
Type II
what type of Salter-Harris fracture is this?
a. Type I
b. Type III
c. Type IV
d. Type II
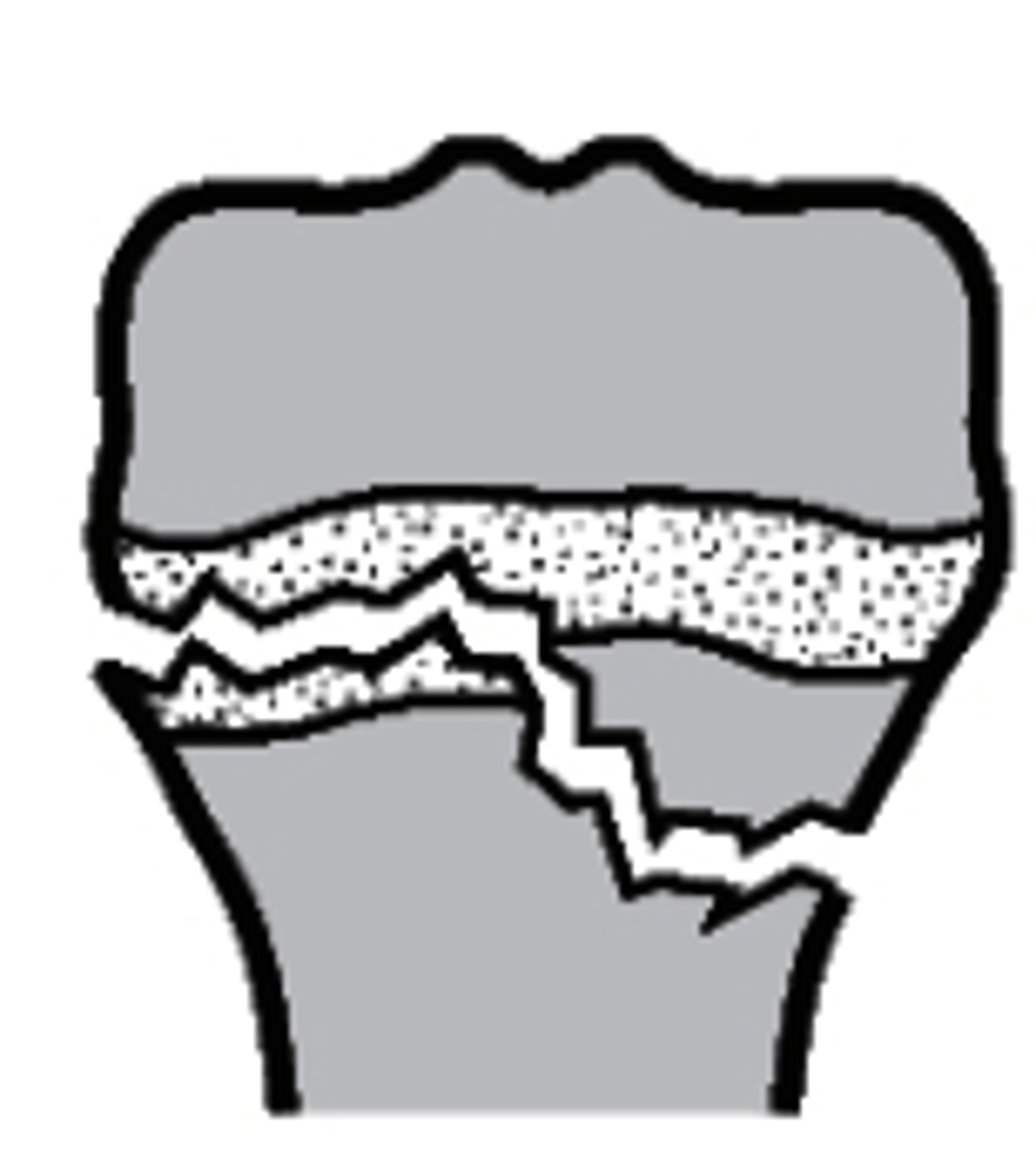
Type III
what type of Salter-Harris fracture is this?
a. Type I
b. Type III
c. Type IV
d. Type II
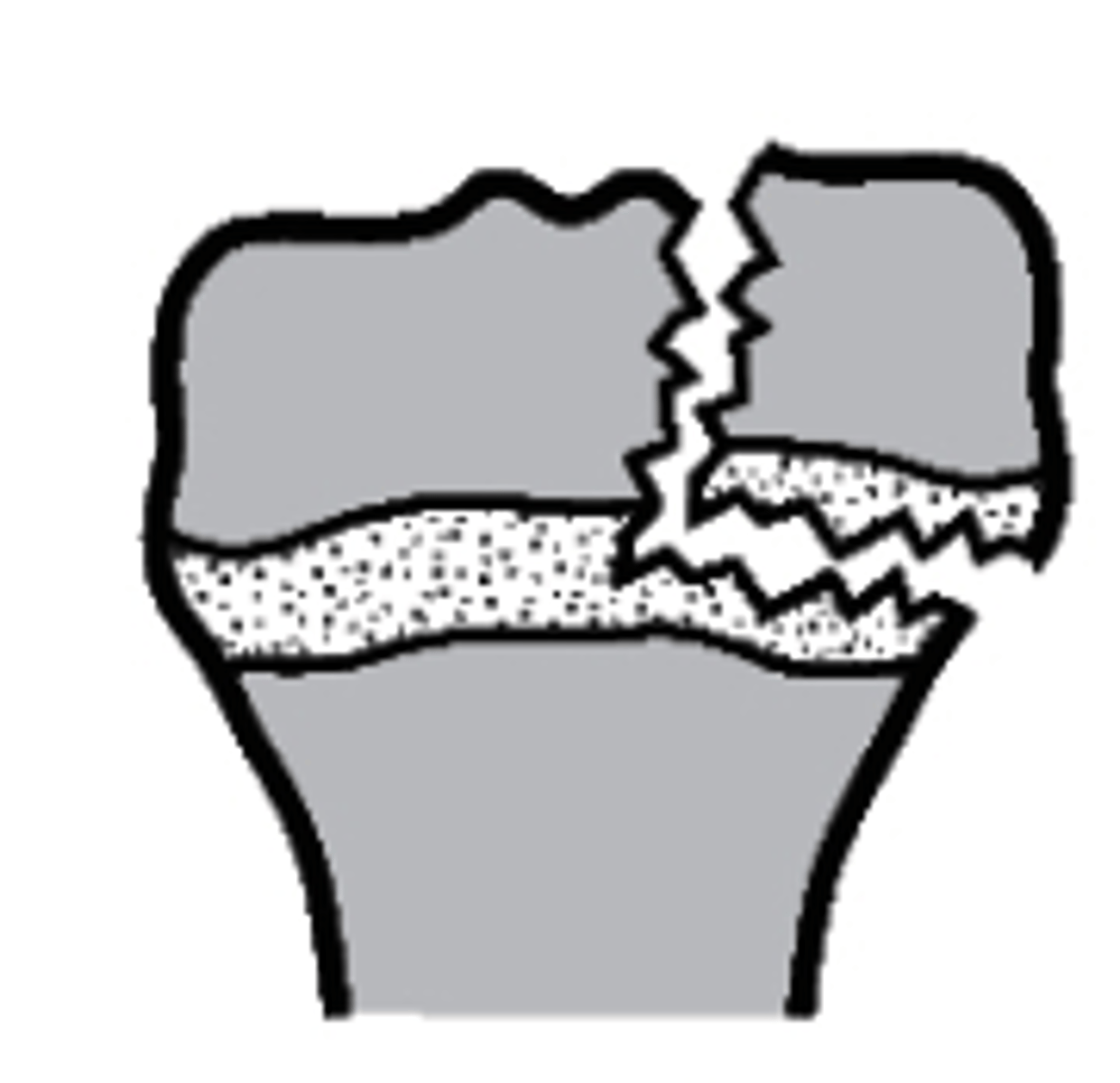
Type IV
what type of Salter-Harris fracture is this?
a. Type I
b. Type III
c. Type IV
d. Type II
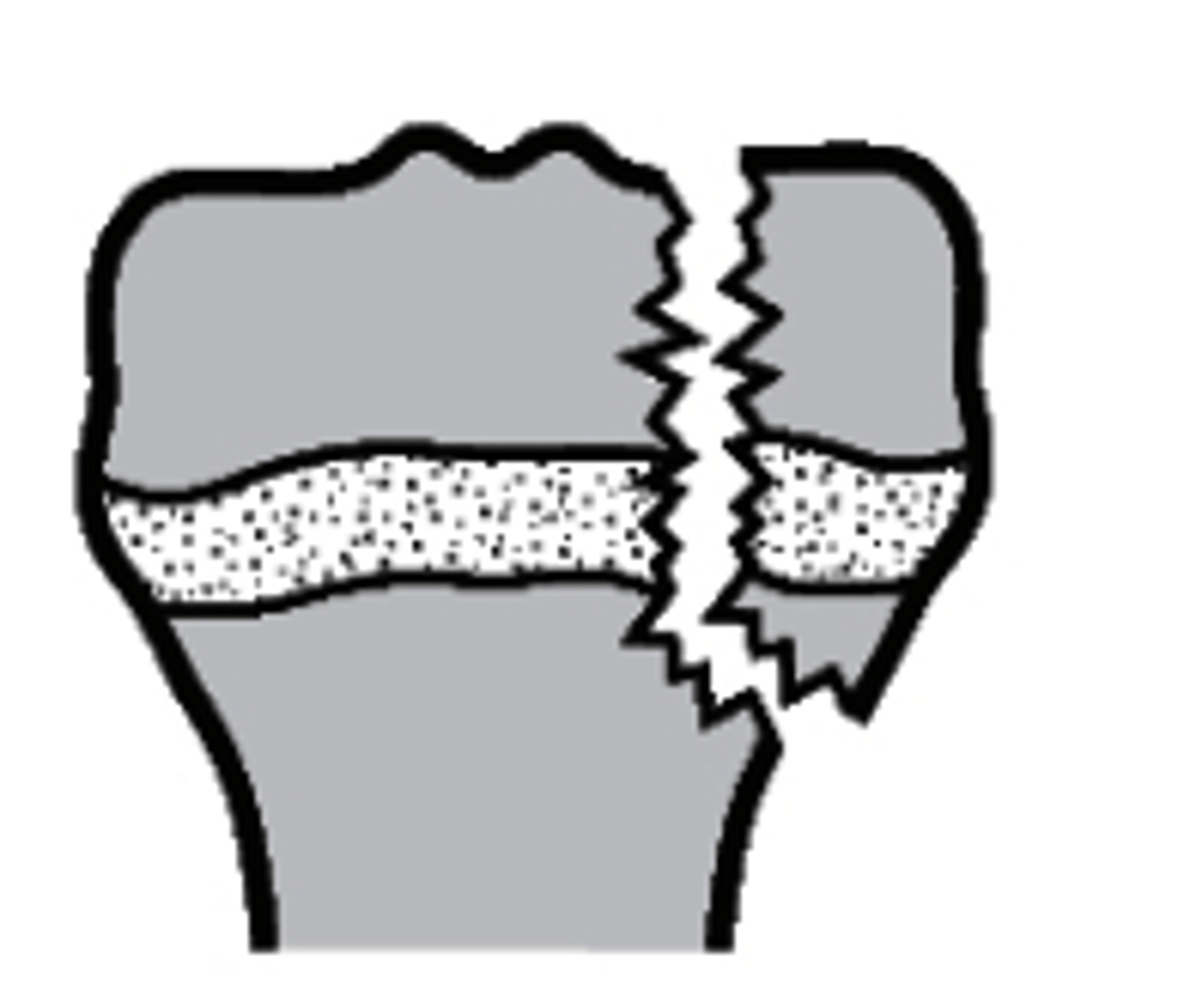
Type V
what type of Salter-Harris fracture is this?
a. Type I
b. Type IV
c. Type V
d. Type II