Chapter 12: Liquids, Solids, and Phase Changes
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
68 Terms
Solid
Rigid structure with definite shape and volume.

Liquid
Indefinite shape, fixed volume, particles glide.
Gas
No definite shape or volume, particles far apart.
Ordered Arrangement
Particles in solids are closely packed and organized.
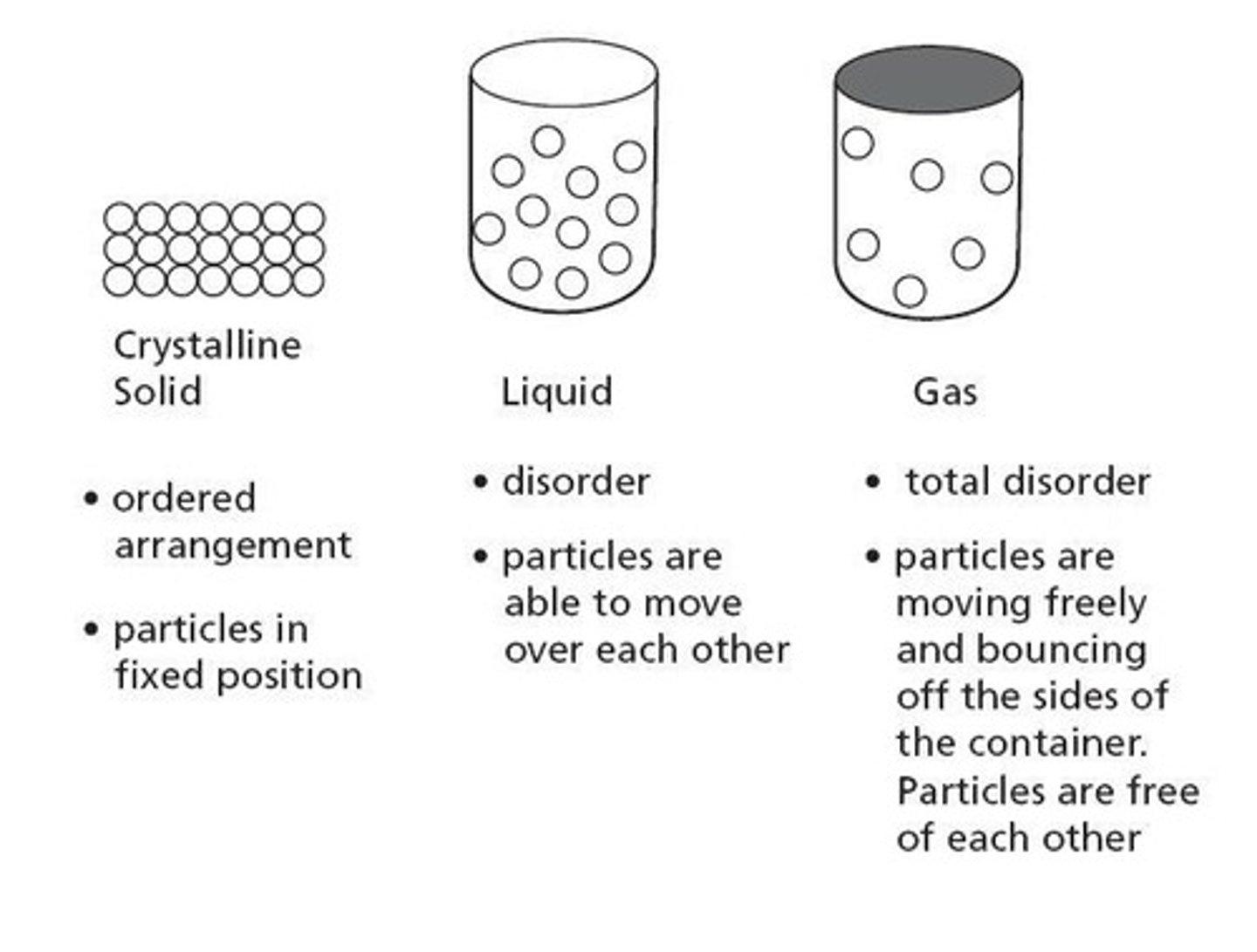
Total Disorder
Particles in gases have random arrangement.
Elastic Collisions
Particles do not lose speed upon collision.
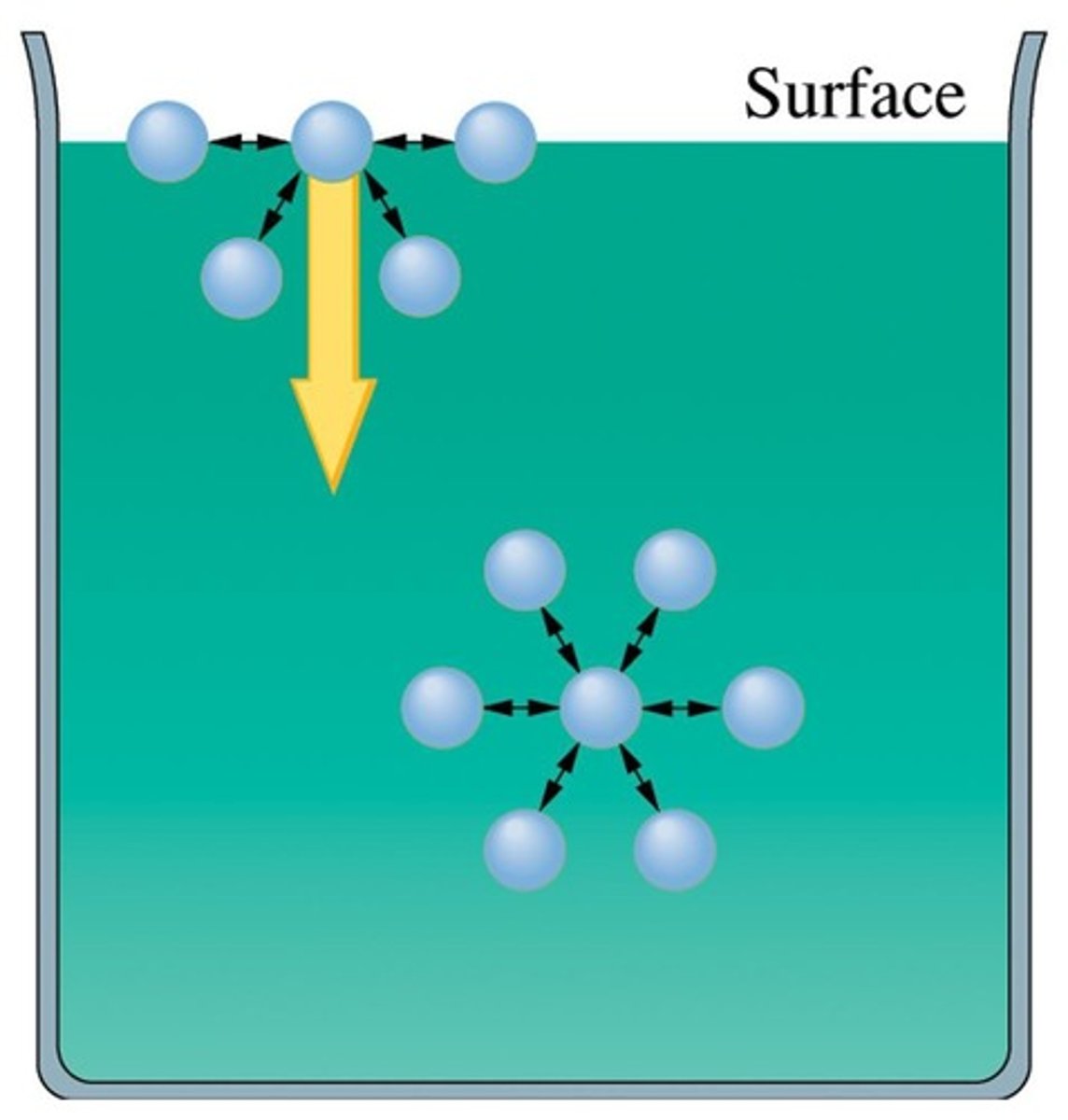
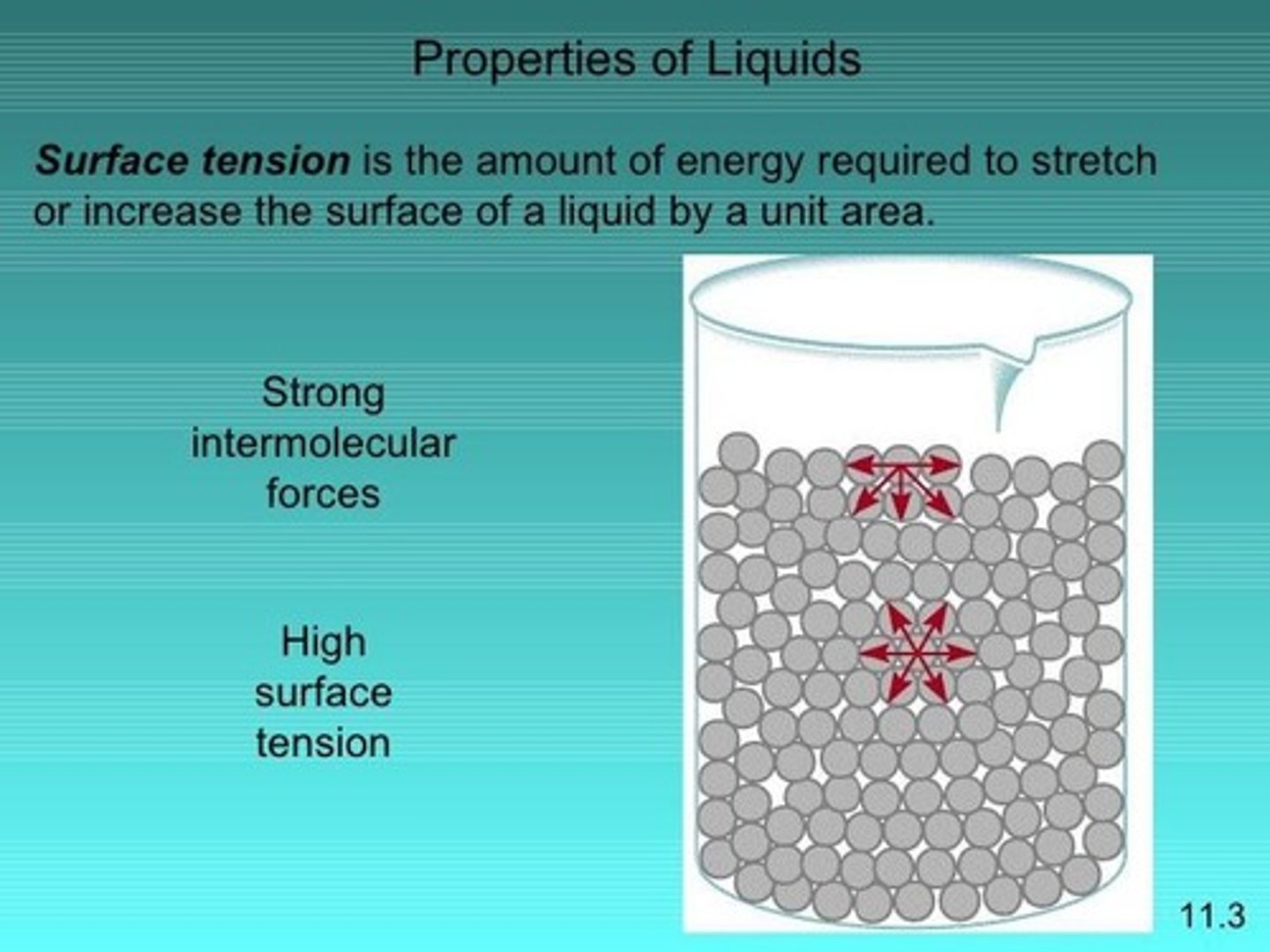
Surface Tension
Energy needed to increase liquid's surface area.
Viscosity
Resistance of a liquid to flow.
Cohesion
Attraction between like molecules within a substance.
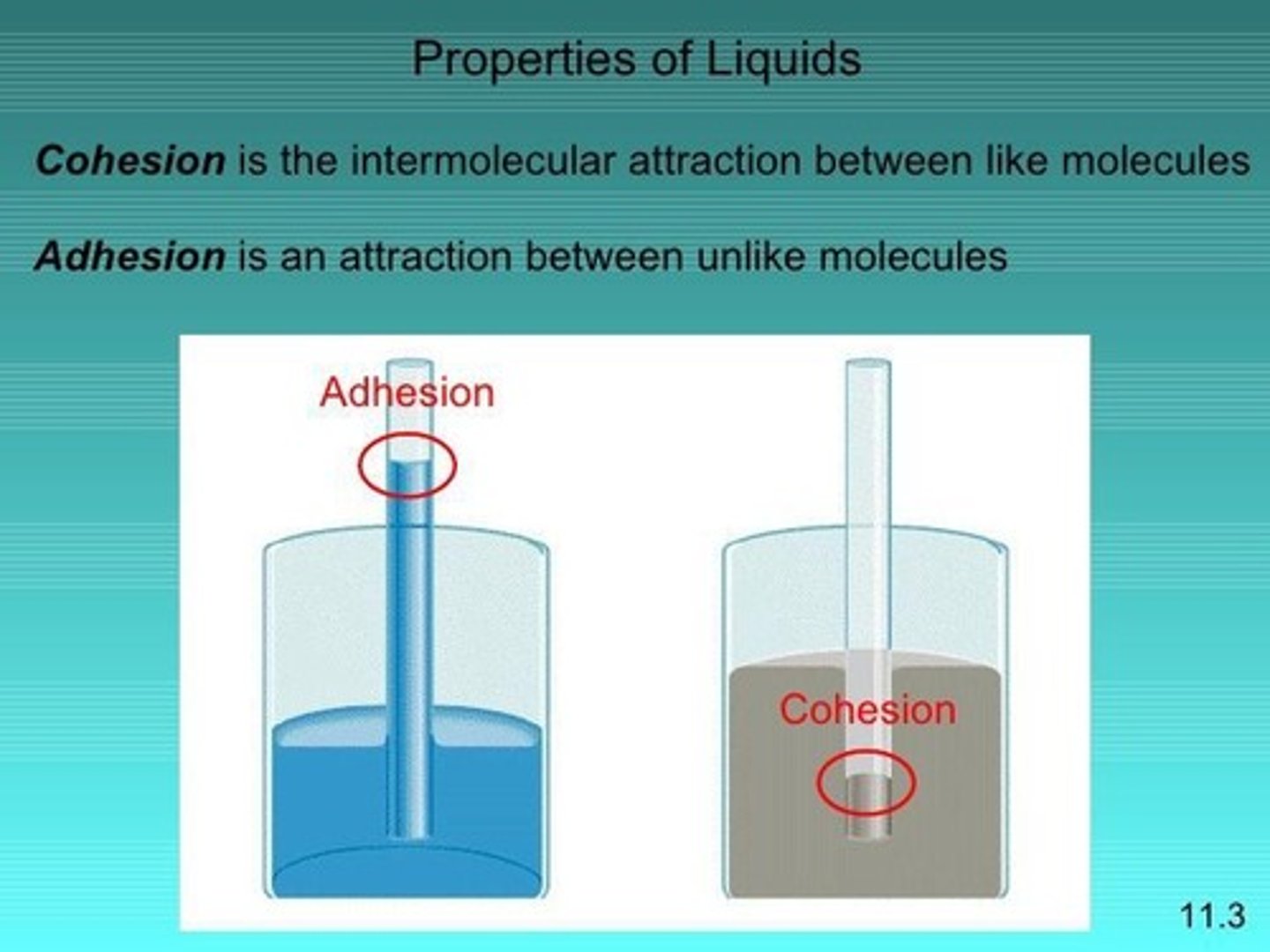
Adhesion
Attraction between different substances' molecules.
Meniscus
Curved surface of liquid in a container.
Capillary Action
Liquid rises in a narrow tube due to adhesion.
Evaporation
Liquid transitions to gas at the surface.
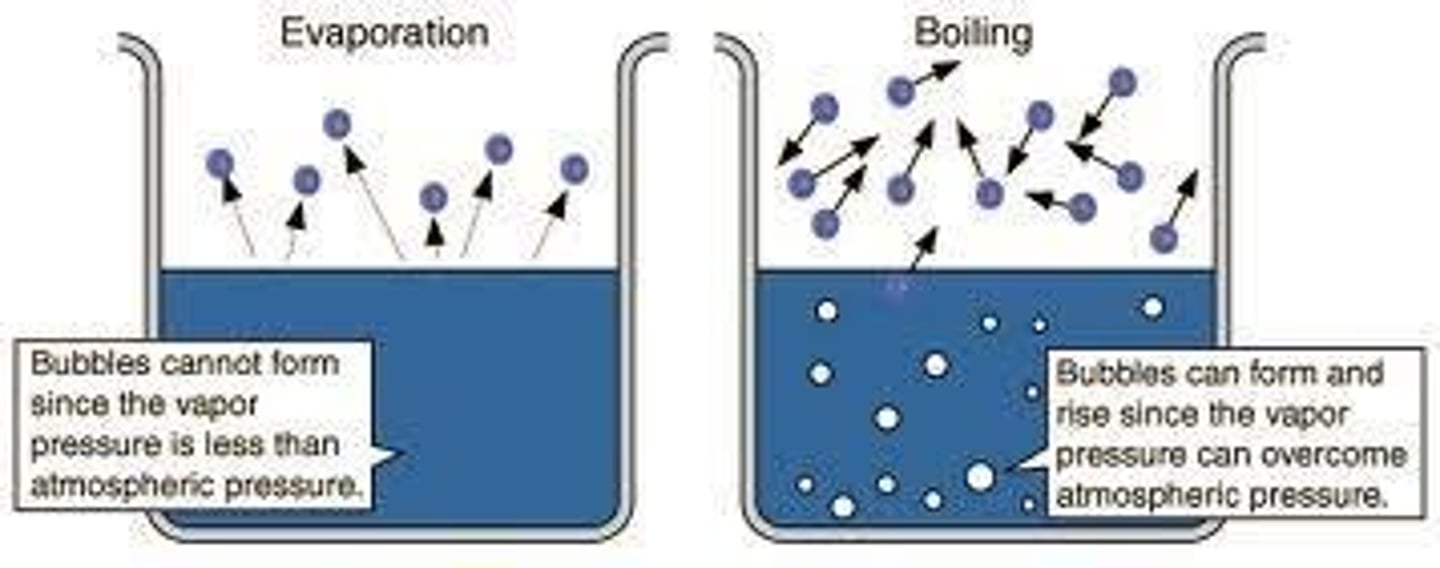
Boiling
Liquid transitions to gas throughout when vapor pressure equals atmospheric pressure.
Vapor Pressure
Pressure of vapor at equilibrium in a closed container.
Dynamic Equilibrium
Rate of condensation equals rate of evaporation.
Intermolecular Forces
Attractions between molecules that hold them together.
Volatile Liquids
Liquids that evaporate quickly due to high vapor pressure.
Temperature Effect on Viscosity
Viscosity decreases as temperature increases.
Pressure Effect on Vapor Pressure
Higher temperature increases vapor pressure.
Fixed Volume
Volume remains constant regardless of shape.
Particle Diagram
Visual representation of particle arrangement in states.
Kinetic Model of Gases
Particles move straight until colliding with walls.
Ion-dipole force
Attraction between an ion and polar molecule.
Dipole-dipole force
Attraction between positive and negative ends of polar molecules.
London dispersion forces
Interactions from temporary dipoles in molecules.
Vapor pressure
Pressure exerted by vapor in equilibrium with liquid.
Boiling point
Temperature where liquid turns to gas.
Intermolecular forces
Forces holding molecules together in a substance.
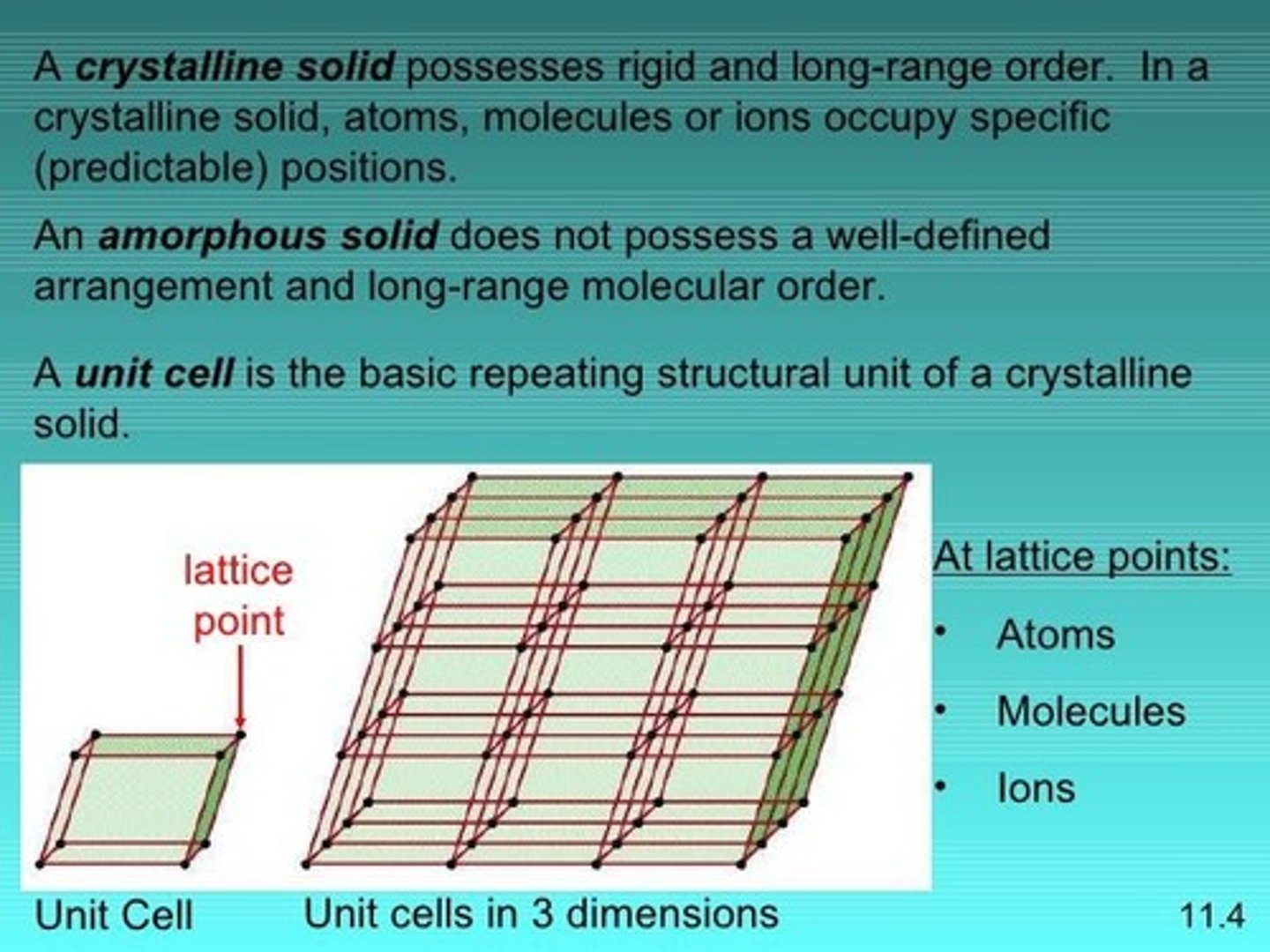
Crystal lattice
Regular, repeating 3-D arrangement of particles.
Crystalline solid
Solid with a defined atomic arrangement.
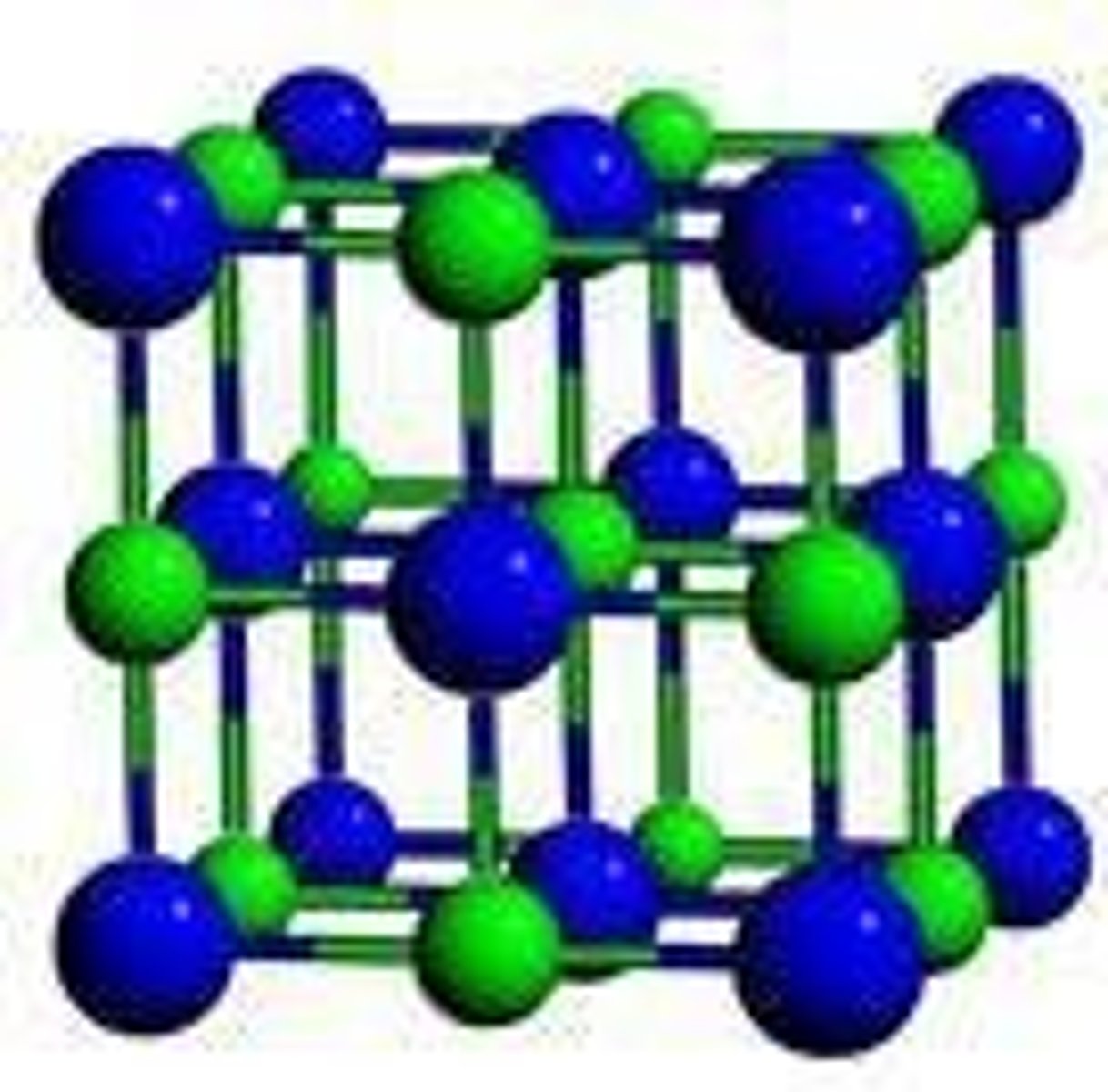
Ionic solid
Solid held together by ionic bonds.
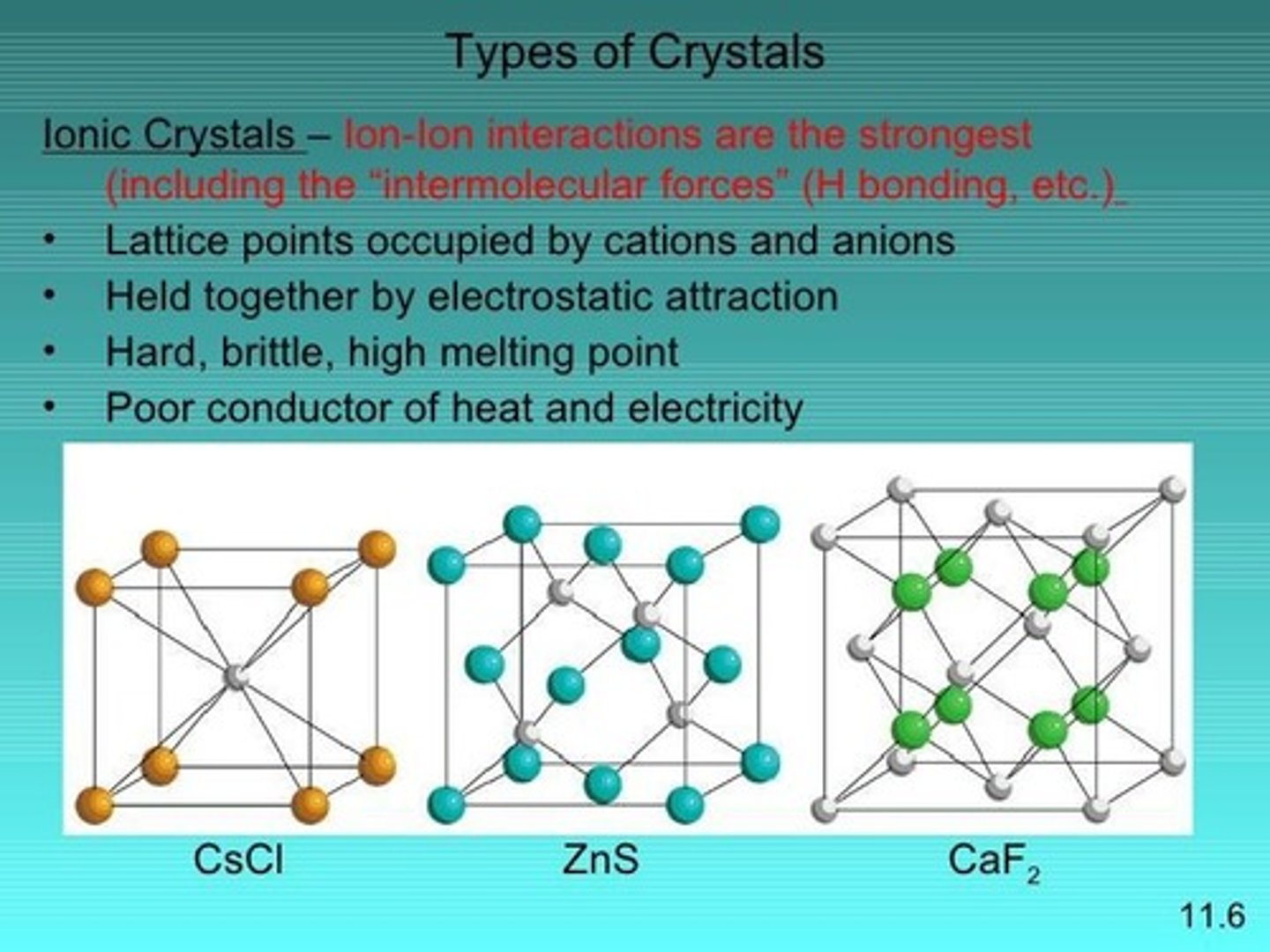
Molecular solid
Solid held by intermolecular forces, like ice.
Covalent network solid
Solid with atoms in large covalent networks.
Metallic solid
Solid with metallic bonds, high conductivity.
Amorphous solid
Solid with randomly arranged atoms, no order.
Phase change
Reversible change from one state of matter to another.
Heating curve
Graph showing temperature changes during phase transitions.
Heat of fusion (Hfus)
Energy needed to melt 1 gram of solid.
Melting point
Temperature where solid begins to melt.
Freezing point
Temperature where liquid turns into solid.
Heat of vaporization (Hvap)
Energy required to vaporize liquid at constant temperature.
Sublimation
Solid turns directly into gas without becoming liquid.
Condensation
Gas particles form a liquid by losing energy.
Deposition
Gas turns directly into solid under pressure.
Water Vapor
Gaseous state of water at same temperature as boiling.
Kinetic Energy
Energy of motion; increases causes gas formation.
Joule (J)
SI unit of energy; lifts 1 kg by 1 meter.
Heat of Fusion
Energy needed to melt ice; 334 J/g.
Heat of Vaporization
Energy needed to convert water to steam; 2260 J/g.
Molar Heat of Fusion
Energy to melt 1 mole of ice; 6.01 kJ/mol.
Molar Heat of Vaporization
Energy to vaporize 1 mole of water; 40.7 kJ/mol.
Specific Heat Capacity (Cp)
Heat needed to raise temperature of 1 g by 1°C.
Cp of Water
1.00 cal/g·K; heat capacity of liquid water.
Cp of Ice
0.493 cal/g·K; heat capacity of ice.
Cp of Steam
0.447 cal/g·K; heat capacity of steam.
Heat Energy Calculation
Sum of heat absorbed in multiple stages.
Phase Change Stages
Five stages: heating, melting, heating, vaporizing, heating.
Heat Absorption Stages
Ice heating, melting, water heating, vaporizing, steam heating.
Triple Point
Condition where solid, liquid, and vapor coexist.
Critical Point
Temperature/pressure where only vapor exists.
Volatility
Tendency of a substance to vaporize; diethyl ether most volatile.
Energy to Melt Ice
Energy needed to convert ice at 0°C to water.
Energy to Vaporize Water
Energy needed to convert water at 100°C to steam.
Energy to Raise Temperature
Energy needed to increase water temperature to boiling.
Energy to Convert Ice to Water
Energy needed to raise ice from -6°C to 25°C.
Heat Equation
q = m ∆T Cp; calculates heat transfer.
Heat of Fusion Calculation
q = m ∆Hf; calculates melting energy.