Mechanisms of neuroprotection
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
The skull
Viscerocramium = protecting the face
neurocranium = protecting the brain
Bones of the neurocranium
frontal bone
pareital bone
temporal bone
occipital bone
sephnoid bone
Viscerocranium bones
Zygomatic (cheekbone)
Maxilla (top teeth)
Mandible (bottom teeth)
Brain sutures
Lambdoid suture:
looks like lambda, in-between pareital and occipital bone.
Occipitomastoid suture:
between occipital and temporal bone.
Squameous suture:
beterrn temporal and pareital lobs.
Pterion - where all bones meet.
Coronal Suture
Saggital suture.
Fontanelles to sutures
Anterior = coronal
Posterios = lambdoid
posteriolateral = occipitomastoid
anterolateral = pterion
intro to the spine
24 vertebrae
7 cervical
12 thoracis
5 lumbar
1 saccrum (5 fused vertebrae)
1 coccys
General vertebral anatomy
form your hands into a diamond
hands = spine
forearms = lamina
elbows = transverse process
bedicle = arm
body = body!
additional vertebral anatomy
perpendicular to the tranverse proicess, there is the superior and articulate process.
Through the middle of spine = vertebral foramen.
Notches of the spine
Superior vertebral notch
Superior articular process
inferior vertabral notch
inferior articular facet
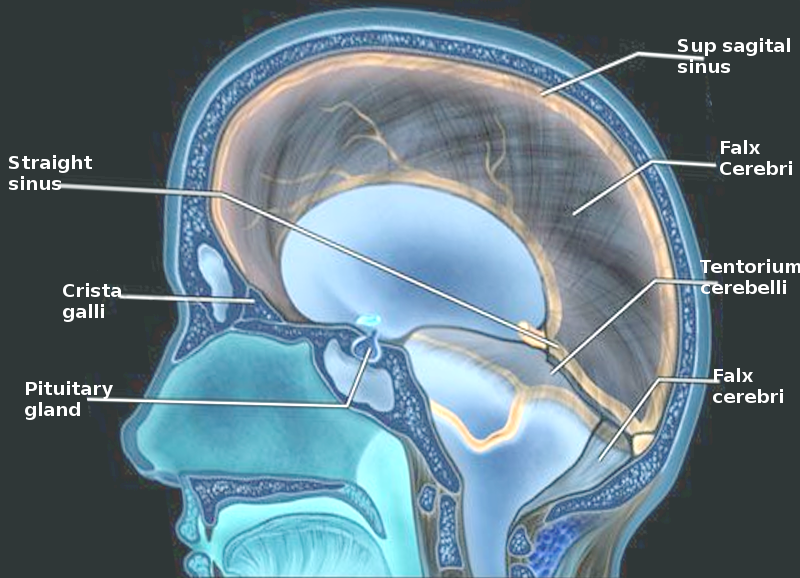
Brain & spinal chord meninges
Dura matter (skull)
Arachnoid matter (white & whispy)
pia mater (adhered to brain surface).
Spaces
Epidural space (dural artery)
Subdural space (sinuses)
sub arachnoid space - (CSF +CAC)
Dural sinuses
seperation between endosteal and meningial layers.
Dural folds / septa =
falx cerebri and falx cerebelli.
Tenrorium cerebelli
Diaphrama sellae
carotid + vertebral arteries
Common cartoited splits into internal and external at the caroited sinused
external = Superficial (face + meninges)
Internal = deep (brain)
Subclavian - vertebral
Travels in transverse foramen of cervical vertebrae.
Cerebral arterial circle
Prevents consequences of a stroke
anastomosis
only works before the circle
Name the arteries (in order of the circle of willis)
Vertebral arteries
Basilar artery
Posterior cerebral artery
Posterior communication
Internal caroid artery
middle cerebral artery
anterior communicating artery
Anterior cerebral artery
Distribution of blood supply
Middle cerebral artery: Temporal lobe
Anterior cerebral artery: Mohawk bart of the brain
posterior = bottom of brain
Stroke
ischemic stroke = blockage
hemmoragic stroke = bleed
symptoms occur on opposite side
Sinus blood flow - top to bottom
Superior saggital sinus, inferior saggital sinus, straight sinus, cofluence of sinuses, L/R transverse sinus, L/R sigmoid sinus, internal jugular vein.
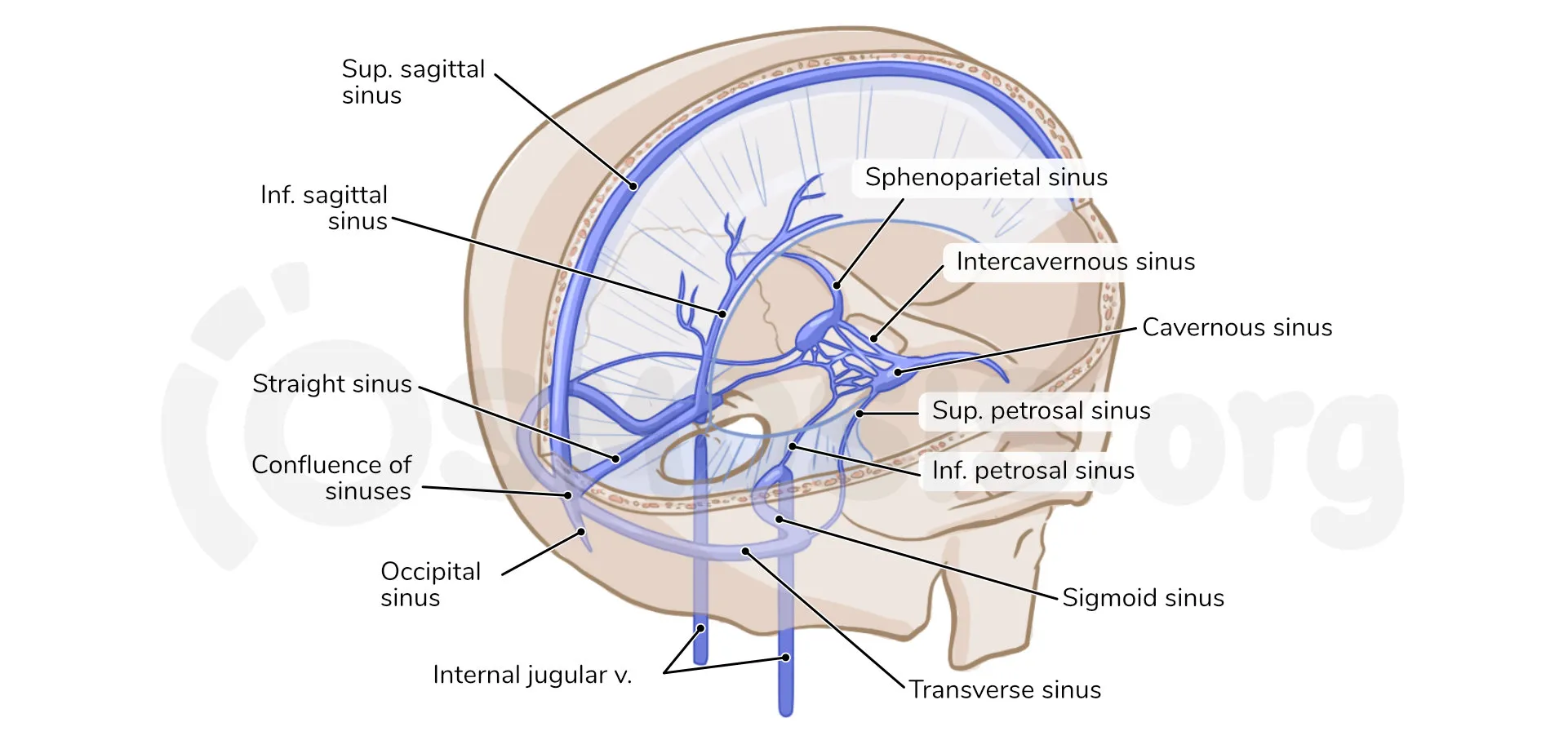
sinus function
drain deox. blood from the brain.
formed by split between endosteal and menengial layer of the brain.
Middle menengial artery
between skull and dura mater.
supplies dura and skull
branch of external carotid
deep to pterion
Where are the things
Menengial artery = Epidural
Venous sinus = Subdural
Carebral A = Subarachnoid
Cerebrospinal fluid
Roles:
Protection (buoyancy of CNS)
Homeostasis of interstitial fluid of the brain.
waste removal
Produced in the choroid plexus.
SUBARACHNOID SPACE
name parts of the ventricles in order
lateral ventricle
interventricular foramen
third ventricle
cerebral aqueduct
4th ventricle
central canal.
Circulation of CSF
CSF made by choroid plexus - ventricles (lat, 3rd, 4th), med/lat fenestations + central canal, sub-arachnoid space - goes into subarachnoid space, arachnoid granulations, venous sinus.
Middle cerebral artery
supplies the lateral surface of the front parietal and temporal lobes
Internal capsule
Contra lateral weakness and sensory loss more in face and arm
Aphasia
Anterior cerebral artery
supplies: médial surface of pariétal lobed (leg area of motor / sensory cortex)
Stroke = weakness In legs and urinary incontinence
Posterior cerebral artery
occipital lobe (visual)
Inferior temporal lobe
Thalamus
Visual field loss (contalateral)
Can read but can write and thalamus syndrome
Basilar safety
Cranial nerve defective (diplopie, facial weakness, dysarthria, dysphasia)
Contralateral motor and sensory loss.
Vertebral artery
medulla and inferior cerebellum
Ipsalateral face sensory loss (pan/temp)
Contralateral body sensory loss (pain/temp)
The type of circular blood supply to the brain is called
Anastomosis
Motor functions in the basal ganglia vs cerebellum
Cerebellum integrates vision and vestibular info while the basal ganglia was not
What is CSF produced from?
Arterial blood in cerebral circulation