C1- Thermal physics in domestic and industrial applications
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
how do you convert kW to watts?
times 1000
How do you convert watts to megawatts?
times by 106
How do you convert watts to gigawatts?
times by 109
How do you convert kelvin to Celsius?
-273
How to convert celcius to kelvin?
+273
What is absolute zero?
the lowest temperature an object can be cooled to, where all thermal energy has been removed.
What is the unit for pressure?
pascal (p)
What is work done?
the energy done in a process is the amount of mechanical energy transferred
What unit is used to measure work?
joules (j)
What is the equation to calculate work done?
work done= force x distance moved in direction of the force
How do you calculate work done by a gas expanding?
work done= pressure x change in volume
What is the conservation of energy?
energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred
What is thermal equilibrium?
when 2 systems are in thermal contact, but no there is no net transfer of heat because their temperature in the same
How do you calculate energy efficiency?
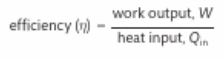
What idea does an ideal gas fit?
collisions are elastic
small molecular size, compared to the volume of the gas
molecules are mostly far apart, unless they collide
What is the equation for ideal gas equations?
pV= NkT
What does P sstand for?
pressure (pascals)
What doe V mean in the ideal gas equation?
volume
What does N stand for?
number of moles
What does K stand for?
boltzmann constant
What does T stand for?
temperature
What happens during condensation?
forces from the gases are suficient enough to form bind the molecules into a packed liquid structure
What is the meaning of vapourisation?
When a liquid is heated and it it’s molecules gain enough kinetic energy to break from the liquid surface and become a gas
What is the latent heat?
the energy transferred that has the effect of changing the physical state of a substance without changing the temperature
What the change of a liquid to a solid?
freezing
What is fusion?
the state change of a solid to a liquid
What is the triple point of water?
when the temperature and pressure of the three phases exist in equilibrium
Critical point?
The temperature and pressure of the density of the liquid and vapour phases become identical
What is the first law of thermodynamics?
internal energy is equal to the difference of the heat transfer into a system and the work done by the system
What is the formula for the first law of thermodynamics?
change in internal energy = Q-W
What is the second law of thermodynamics?
total disorder (entropy) of an isolated system always increases over time.
What does isothermal mean?
occurs at a fixed temperature
What is the meaning of adiabatic?
zero theral transfer
What is the purpose of a heat engine?
convert heat from a high temperature into work
What are the stages of the carnot cycle?
1-2
2-3
3-4
4-1
What is stage 1-2?
adiabatic compression- 0 heat transfer
What is stage 2-3??
isothermal expansion- heat absorbed by system (Qin)
What is stage 3-4?
adiabatic expansion- 0 heat transfer
What is stage 4-1?
isothermal compression- heat absorbed by system (Qout)
What does entropy mean?
a system’s disorder or randomness
What is heat capacity?
the number of heat units eeded to raise the temperature of a body by one degree.
What is the formula for theoretical efficiency?
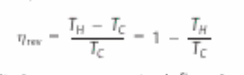
What occurs in a steam turbine engine?
water is heated in a boiler, to produce steam and the steam is expanded through a turbine, with the low pressure steam being cooled and condensed back into water.
What is the name of the engine cycle of a steam turbine engine?
The Rankine cycle
Why does diesel engines give the higher efficiencies?
the air can be more highly compressed, so higher initial temperature, at which fuel is injected and ignites immediately.
What is a reverse cycle?
It is a machine for moving heat from a colder body to a hotter body
What is the first stage of vapour compression?
compression, the refrigerant vapor enters the compressor, where it is squeezed into a superheated vapor.
What is the second stage of vapor compression?
the high pressure vapor flows through the condenser and it releases the heat the the surrounding environment, it cools and becomes a high pressure liquid.
What is the third stage of the vapor compression?
the refrigerant enters the evaporator where it absorbs heat from the space or environment to be cooled.
What is the goal of heat pumps?
release heat into an enclosed space by absorbing heat from a cooler source.